fcfc783ca7c544117419ddaa4bd5355b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 Surfing Technology Curves Steve Kleiman CTO Network Appliance Inc. 1
Surfing Technology Curves Steve Kleiman CTO Network Appliance Inc. 1
 Book Plug The Innovator’s Dilemma - When New Technologies Cause Great Firms to Fail · Clayton M. Christensen 2
Book Plug The Innovator’s Dilemma - When New Technologies Cause Great Firms to Fail · Clayton M. Christensen 2
 About Net. App Two product lines: · Network Attached File Servers (a. k. a. filers) · Web proxy caches: Net. Cache Founded in 1992 >$1 B revenue run rate >70% CAGR since founding >120% last year 3
About Net. App Two product lines: · Network Attached File Servers (a. k. a. filers) · Web proxy caches: Net. Cache Founded in 1992 >$1 B revenue run rate >70% CAGR since founding >120% last year 3
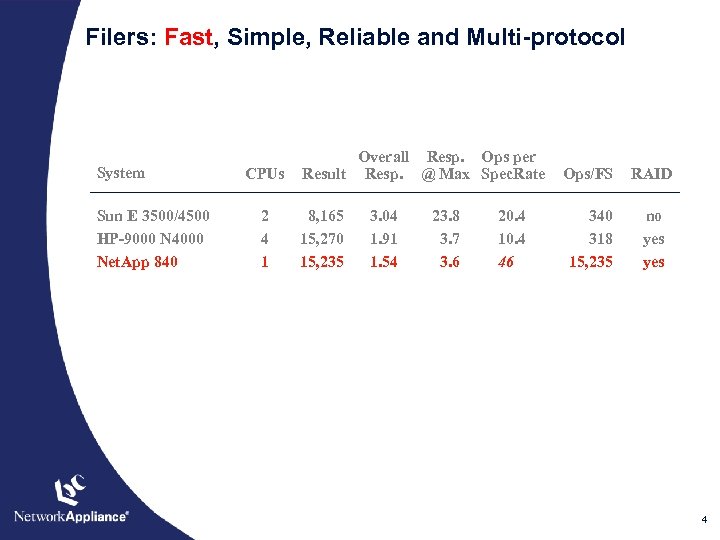 Filers: Fast, Simple, Reliable and Multi-protocol System Sun E 3500/4500 HP-9000 N 4000 Net. App 840 CPUs 2 4 1 Overall Resp. Ops per Result Resp. @ Max Spec. Rate 8, 165 15, 270 15, 235 3. 04 1. 91 1. 54 23. 8 3. 7 3. 6 20. 4 10. 4 46 Ops/FS RAID 340 318 15, 235 no yes 4
Filers: Fast, Simple, Reliable and Multi-protocol System Sun E 3500/4500 HP-9000 N 4000 Net. App 840 CPUs 2 4 1 Overall Resp. Ops per Result Resp. @ Max Spec. Rate 8, 165 15, 270 15, 235 3. 04 1. 91 1. 54 23. 8 3. 7 3. 6 20. 4 10. 4 46 Ops/FS RAID 340 318 15, 235 no yes 4
 Filers: Fast, Simple, Reliable and Multi-protocol Disk management · Filer finds disks and organizes into RAID groups and spares automatically · Simple addition of storage · Automatic RAID reconstruction Data management · Snapshots · Snap. Restore · Snap. Mirror Simple upgrade Small command set 5
Filers: Fast, Simple, Reliable and Multi-protocol Disk management · Filer finds disks and organizes into RAID groups and spares automatically · Simple addition of storage · Automatic RAID reconstruction Data management · Snapshots · Snap. Restore · Snap. Mirror Simple upgrade Small command set 5
 Filers: Fast, Simple, Reliable and Multi-protocol Built-in RAID Easy hardware maintenance · Hot plug disk, power, fans · Low MTTR Cluster Failover Autosupport >99. 995% measured field availability 6
Filers: Fast, Simple, Reliable and Multi-protocol Built-in RAID Easy hardware maintenance · Hot plug disk, power, fans · Low MTTR Cluster Failover Autosupport >99. 995% measured field availability 6
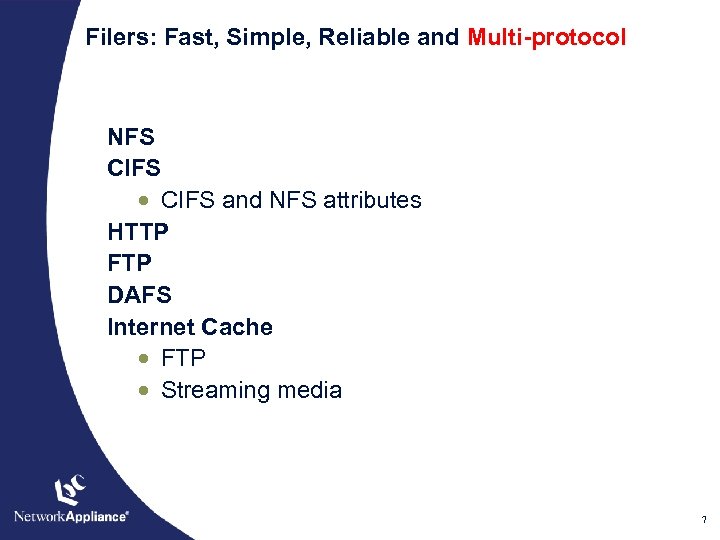 Filers: Fast, Simple, Reliable and Multi-protocol NFS CIFS · CIFS and NFS attributes HTTP FTP DAFS Internet Cache · FTP · Streaming media 7
Filers: Fast, Simple, Reliable and Multi-protocol NFS CIFS · CIFS and NFS attributes HTTP FTP DAFS Internet Cache · FTP · Streaming media 7
 Wave 1: Networks, Appliances and Software 8
Wave 1: Networks, Appliances and Software 8
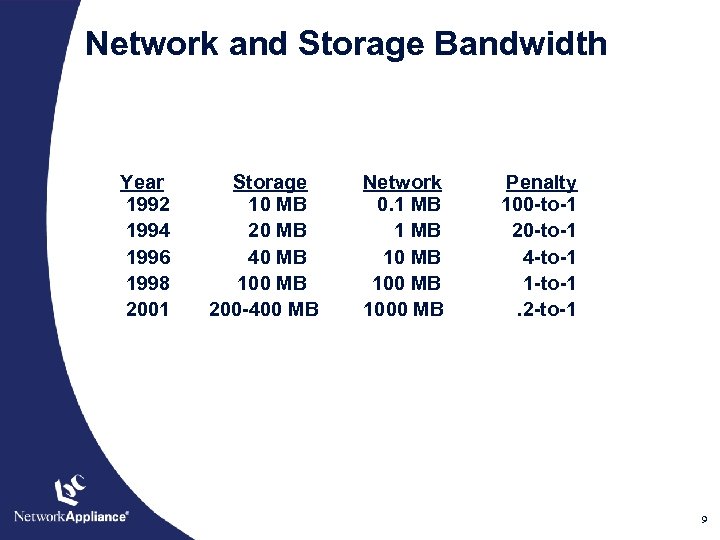 Network and Storage Bandwidth Year 1992 1994 1996 1998 2001 Storage 10 MB 20 MB 40 MB 100 MB 200 -400 MB Network 0. 1 MB 1000 MB Penalty 100 -to-1 20 -to-1 4 -to-1 1 -to-1. 2 -to-1 9
Network and Storage Bandwidth Year 1992 1994 1996 1998 2001 Storage 10 MB 20 MB 40 MB 100 MB 200 -400 MB Network 0. 1 MB 1000 MB Penalty 100 -to-1 20 -to-1 4 -to-1 1 -to-1. 2 -to-1 9
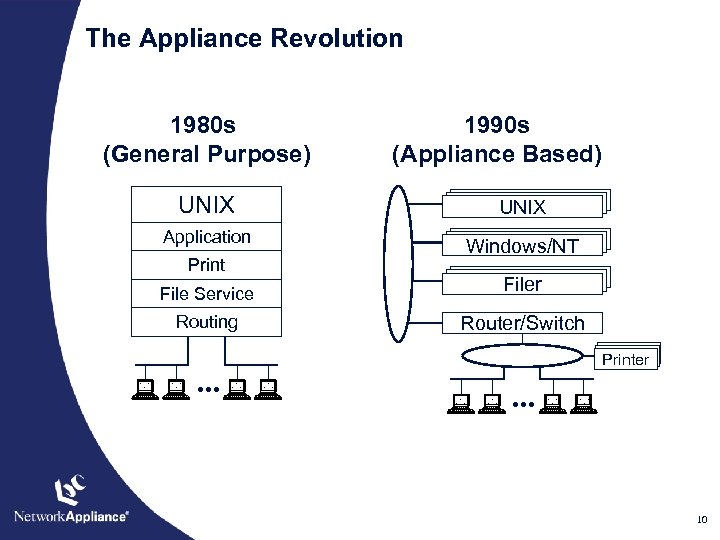 The Appliance Revolution 1980 s (General Purpose) 1990 s (Appliance Based) UNIX Application Windows/NT Print File Service Filer Routing Router/Switch . . . Printer . . . 10
The Appliance Revolution 1980 s (General Purpose) 1990 s (Appliance Based) UNIX Application Windows/NT Print File Service Filer Routing Router/Switch . . . Printer . . . 10
 Appliance philosophy breeds focus · External simplicity internal simplicity · RISC argument Don’t have to be all things to all people · Limited compatibility constraints - Interfaces are bits on wire · Think different! Can innovate with both software and hardware 11
Appliance philosophy breeds focus · External simplicity internal simplicity · RISC argument Don’t have to be all things to all people · Limited compatibility constraints - Interfaces are bits on wire · Think different! Can innovate with both software and hardware 11
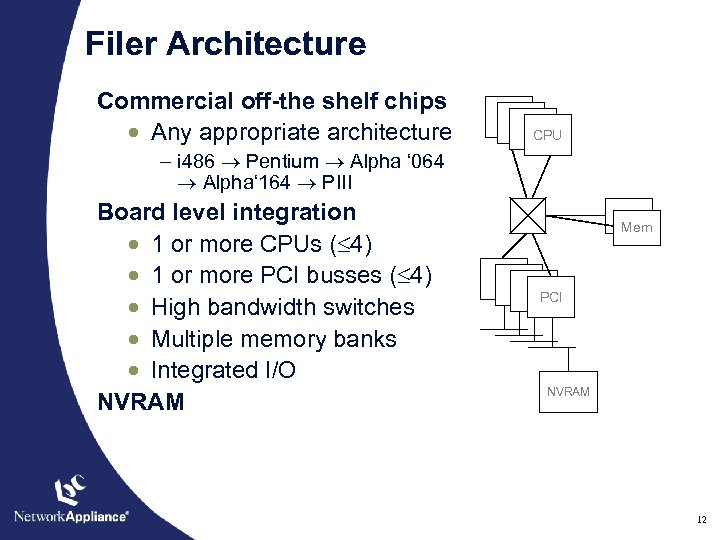 Filer Architecture Commercial off-the shelf chips · Any appropriate architecture CPU - i 486 Pentium Alpha ‘ 064 Alpha‘ 164 PIII Board level integration · 1 or more CPUs ( 4) · 1 or more PCI busses ( 4) · High bandwidth switches · Multiple memory banks · Integrated I/O NVRAM Mem PCI NVRAM 12
Filer Architecture Commercial off-the shelf chips · Any appropriate architecture CPU - i 486 Pentium Alpha ‘ 064 Alpha‘ 164 PIII Board level integration · 1 or more CPUs ( 4) · 1 or more PCI busses ( 4) · High bandwidth switches · Multiple memory banks · Integrated I/O NVRAM Mem PCI NVRAM 12
 Roads Not Taken No “unobtainium” · Minimalist infrastructure · No special purpose busses · No big MPs - Motherboards only: no cache coherent backplanes No functionally distributed computers No special purpose networks (e. g. HIPPI) No block access protocols 13
Roads Not Taken No “unobtainium” · Minimalist infrastructure · No special purpose busses · No big MPs - Motherboards only: no cache coherent backplanes No functionally distributed computers No special purpose networks (e. g. HIPPI) No block access protocols 13
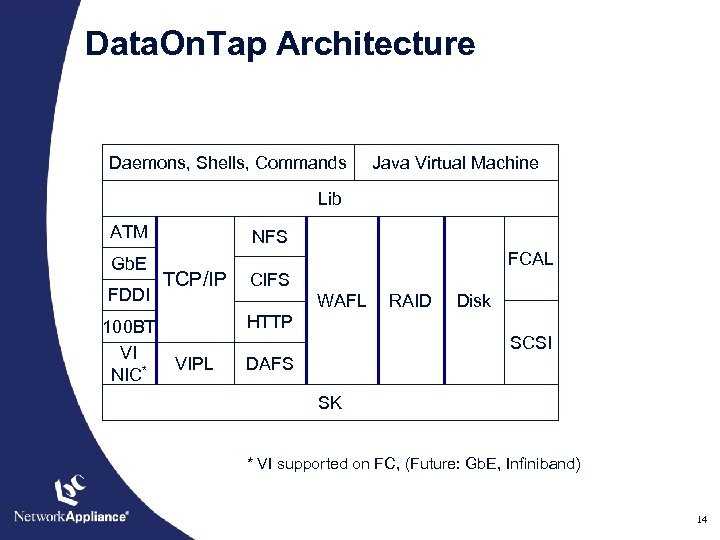 Data. On. Tap Architecture Daemons, Shells, Commands Java Virtual Machine Lib ATM Gb. E FDDI 100 BT VI NIC* NFS TCP/IP FCAL CIFS WAFL RAID Disk HTTP SCSI VIPL DAFS SK * VI supported on FC, (Future: Gb. E, Infiniband) 14
Data. On. Tap Architecture Daemons, Shells, Commands Java Virtual Machine Lib ATM Gb. E FDDI 100 BT VI NIC* NFS TCP/IP FCAL CIFS WAFL RAID Disk HTTP SCSI VIPL DAFS SK * VI supported on FC, (Future: Gb. E, Infiniband) 14
 Data. On. Tap Simple Kernel · Message passing · Non-preemptive Sample optimizations · Checksum caching · Suspend/Resume · Cache hit pass through 15
Data. On. Tap Simple Kernel · Message passing · Non-preemptive Sample optimizations · Checksum caching · Suspend/Resume · Cache hit pass through 15
 WAFL: Write Anywhere File Layout Log-like write throughput · No segment cleaning (LFS) · Write data allocated to optimize RAID performance - Delayed write allocation Active data is never overwritten (shadow paging) · On-disk data is always consistent · File system state is changed atomically - Every 10 sec, by default Client modification requests are logged to NVRAM · NVRAM log is replayed only on reboot 16
WAFL: Write Anywhere File Layout Log-like write throughput · No segment cleaning (LFS) · Write data allocated to optimize RAID performance - Delayed write allocation Active data is never overwritten (shadow paging) · On-disk data is always consistent · File system state is changed atomically - Every 10 sec, by default Client modification requests are logged to NVRAM · NVRAM log is replayed only on reboot 16
 Wave 2: Memory-to-Memory Interconnects (a. k. a NUMA, NORMA) 17
Wave 2: Memory-to-Memory Interconnects (a. k. a NUMA, NORMA) 17
 Problem: Remove single points of failure · Without doubling hardware · Minimizing performance overhead · Without decreasing reliability 18
Problem: Remove single points of failure · Without doubling hardware · Minimizing performance overhead · Without decreasing reliability 18
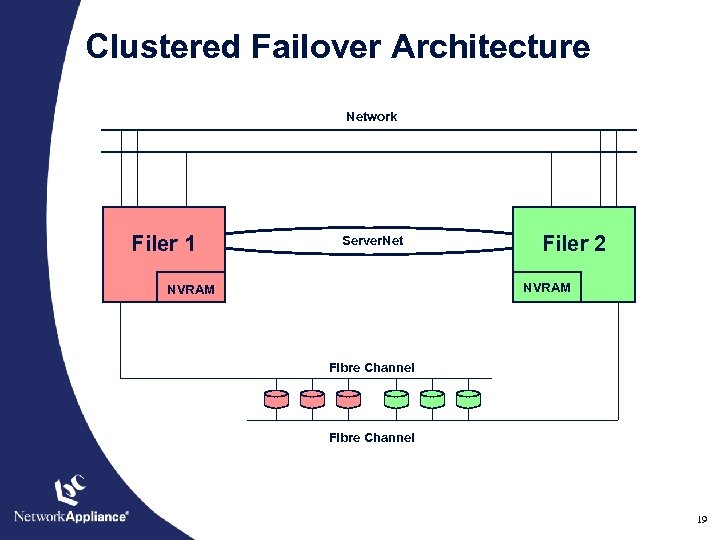 Clustered Failover Architecture Network Filer 1 Server. Net Filer 2 NVRAM Fibre Channel 19
Clustered Failover Architecture Network Filer 1 Server. Net Filer 2 NVRAM Fibre Channel 19
 Memory-to-Memory Interconnects Efficient transfer model · Allows minimal overhead on receiver Scaleable Bandwidth · High speed ASIC based switching · Gigabit technology Open architecture · PCI, not coherent bus interface · Incorporate multiple technologies Relatively inexpensive 20
Memory-to-Memory Interconnects Efficient transfer model · Allows minimal overhead on receiver Scaleable Bandwidth · High speed ASIC based switching · Gigabit technology Open architecture · PCI, not coherent bus interface · Incorporate multiple technologies Relatively inexpensive 20
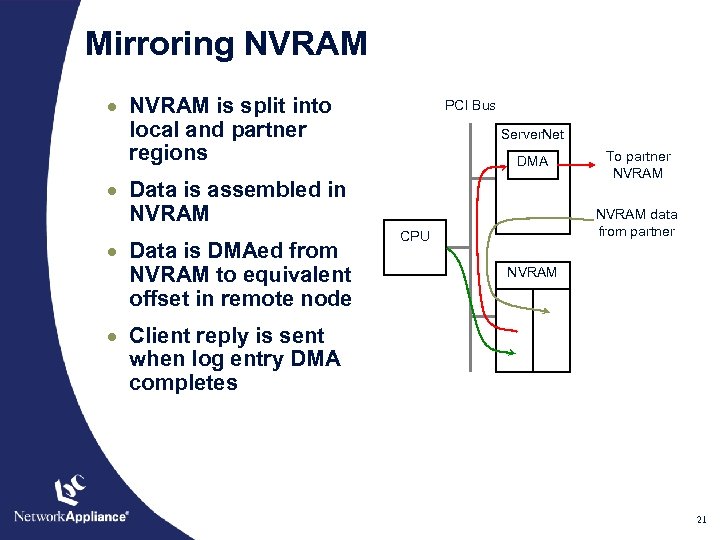 Mirroring NVRAM · NVRAM is split into local and partner regions PCI Bus Server. Net DMA · Data is assembled in NVRAM · Data is DMAed from NVRAM to equivalent offset in remote node To partner NVRAM data from partner CPU NVRAM · Client reply is sent when log entry DMA completes 21
Mirroring NVRAM · NVRAM is split into local and partner regions PCI Bus Server. Net DMA · Data is assembled in NVRAM · Data is DMAed from NVRAM to equivalent offset in remote node To partner NVRAM data from partner CPU NVRAM · Client reply is sent when log entry DMA completes 21
 Leveraged Components Memory-to-Memory interconnects · Low overhead, high-bandwidth, cheap WAFL · Always consistent file system · Built-in NVRAM logging/replay Fibre Channel disks · Two independent ports Single function appliance software Þ Simple, low-overhead failover 22
Leveraged Components Memory-to-Memory interconnects · Low overhead, high-bandwidth, cheap WAFL · Always consistent file system · Built-in NVRAM logging/replay Fibre Channel disks · Two independent ports Single function appliance software Þ Simple, low-overhead failover 22
 Wave 3: The Internet 23
Wave 3: The Internet 23
 The Consequences of Higher-speed Internet Access 200 K-400 K home cable head-end · Requires 1. 5 -3 Gbps access capability - 30% subscription rate, 20% online - Minimum 128 Kbps BW Enterprise · Remote sites still connected by slow links · Require high-quality access to content · Overloaded web servers ISP · Require distribution and caching of large media files 24
The Consequences of Higher-speed Internet Access 200 K-400 K home cable head-end · Requires 1. 5 -3 Gbps access capability - 30% subscription rate, 20% online - Minimum 128 Kbps BW Enterprise · Remote sites still connected by slow links · Require high-quality access to content · Overloaded web servers ISP · Require distribution and caching of large media files 24
 Yet Another Appliance Cisco Net. App 25
Yet Another Appliance Cisco Net. App 25
 Net. Cache HTTP/FTP proxy cache appliance · Highly deployable · Forward and reverse proxy Transparency Filtering i. CAP · Enables value added services - Virus scanning, transcoding, ad insertion, … Stream splitting Stream caching Content distribution 26
Net. Cache HTTP/FTP proxy cache appliance · Highly deployable · Forward and reverse proxy Transparency Filtering i. CAP · Enables value added services - Virus scanning, transcoding, ad insertion, … Stream splitting Stream caching Content distribution 26
 Cacheable Content Time Static Content Dynamic Content Streaming Media 27
Cacheable Content Time Static Content Dynamic Content Streaming Media 27
 Wave 4: The Death of Tapes 28
Wave 4: The Death of Tapes 28
 Using Tapes for Disaster Recovery 29
Using Tapes for Disaster Recovery 29
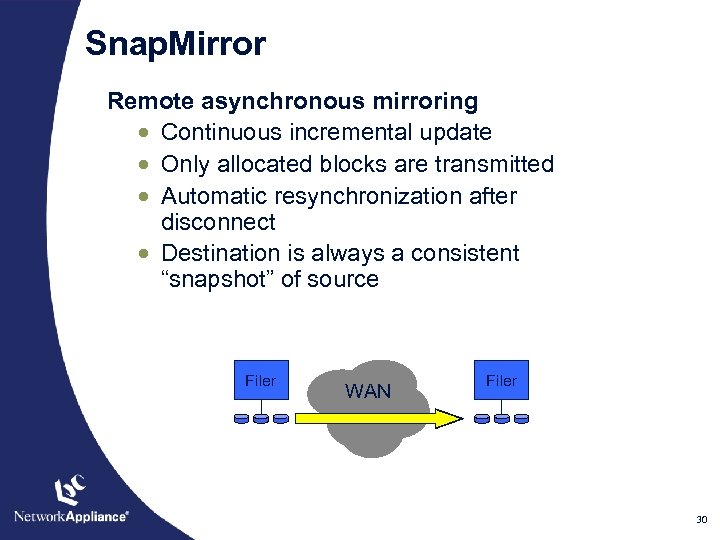 Snap. Mirror Remote asynchronous mirroring · Continuous incremental update · Only allocated blocks are transmitted · Automatic resynchronization after disconnect · Destination is always a consistent “snapshot” of source Filer WAN Filer 30
Snap. Mirror Remote asynchronous mirroring · Continuous incremental update · Only allocated blocks are transmitted · Automatic resynchronization after disconnect · Destination is always a consistent “snapshot” of source Filer WAN Filer 30
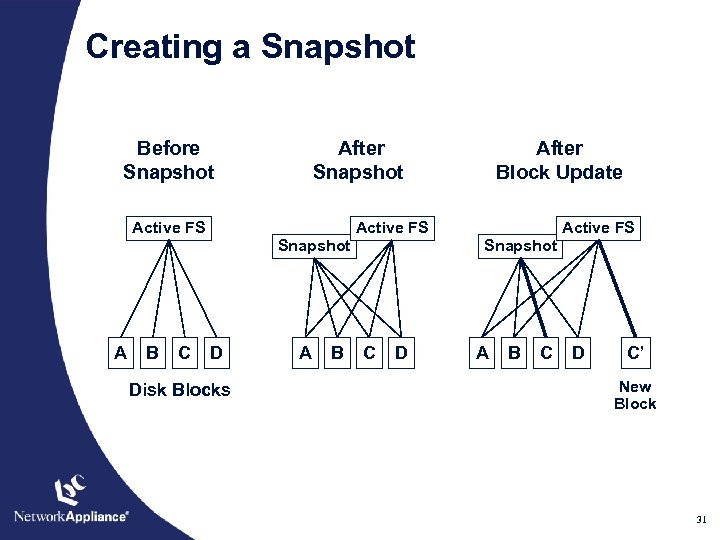 Creating a Snapshot Before Snapshot After Snapshot Active FS Snapshot A B C After Block Update D Disk Blocks A B Active FS Snapshot C D A B C D C’ New Block 31
Creating a Snapshot Before Snapshot After Snapshot Active FS Snapshot A B C After Block Update D Disk Blocks A B Active FS Snapshot C D A B C D C’ New Block 31
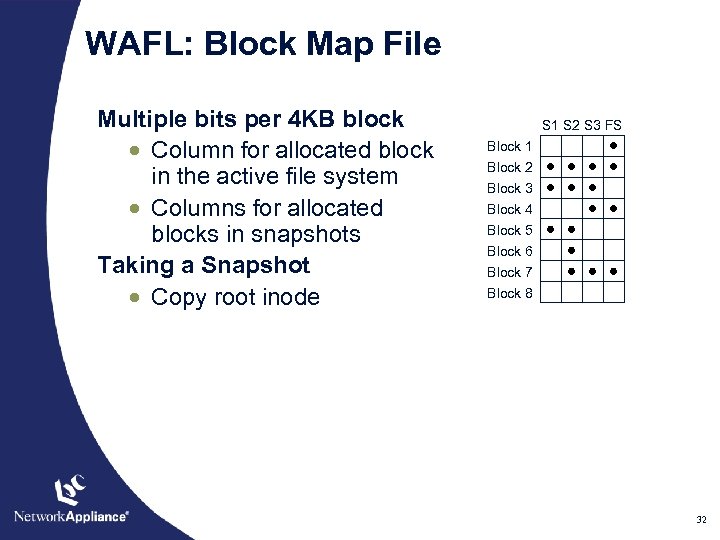 WAFL: Block Map File Multiple bits per 4 KB block · Column for allocated block in the active file system · Columns for allocated blocks in snapshots Taking a Snapshot · Copy root inode S 1 S 2 S 3 FS Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Block 4 Block 5 Block 6 Block 7 Block 8 32
WAFL: Block Map File Multiple bits per 4 KB block · Column for allocated block in the active file system · Columns for allocated blocks in snapshots Taking a Snapshot · Copy root inode S 1 S 2 S 3 FS Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Block 4 Block 5 Block 6 Block 7 Block 8 32
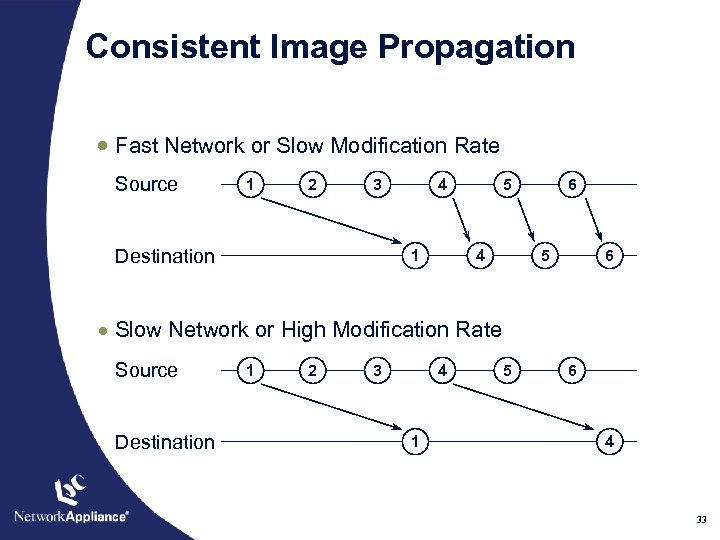 Consistent Image Propagation · Fast Network or Slow Modification Rate Source 1 2 3 Destination 4 1 5 4 6 5 6 · Slow Network or High Modification Rate Source Destination 1 2 3 4 1 5 6 4 33
Consistent Image Propagation · Fast Network or Slow Modification Rate Source 1 2 3 Destination 4 1 5 4 6 5 6 · Slow Network or High Modification Rate Source Destination 1 2 3 4 1 5 6 4 33
 Wave 5: Local File Sharing and Virtual Interface Architecture 34
Wave 5: Local File Sharing and Virtual Interface Architecture 34
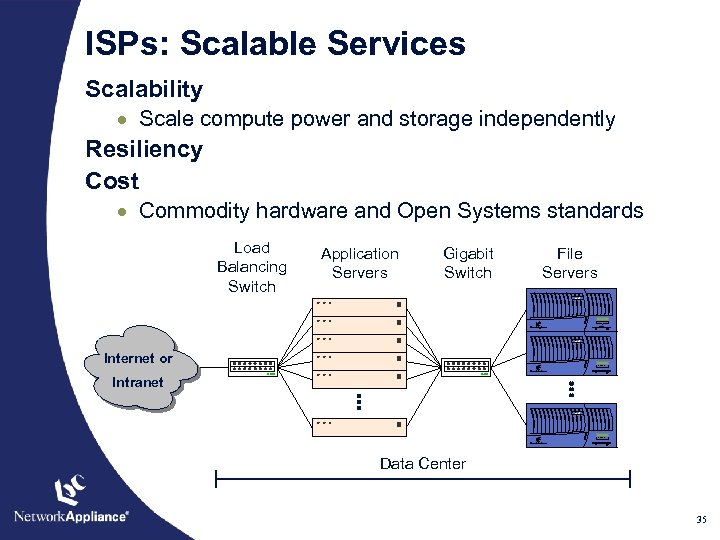 ISPs: Scalable Services Scalability · Scale compute power and storage independently Resiliency Cost · Commodity hardware and Open Systems standards Load Balancing Switch Application Servers Gigabit Switch File Servers F 760 Internet or Intranet F 760 Data Center 35
ISPs: Scalable Services Scalability · Scale compute power and storage independently Resiliency Cost · Commodity hardware and Open Systems standards Load Balancing Switch Application Servers Gigabit Switch File Servers F 760 Internet or Intranet F 760 Data Center 35
 Database Better Manageability · Offline backup with snapshots · Replication · Recovery from snapshots · Easy storage management Equal or better performance · Less retuning F 760 36
Database Better Manageability · Offline backup with snapshots · Replication · Recovery from snapshots · Easy storage management Equal or better performance · Less retuning F 760 36
 Local File Sharing Geographically constrained · 1 or 2 machine rooms Mostly homogeneous clients · Can be large or small · 1 - 100 machines Single administrative control High performance applications · Web service, Cache · Email, News · Database, GIS 37
Local File Sharing Geographically constrained · 1 or 2 machine rooms Mostly homogeneous clients · Can be large or small · 1 - 100 machines Single administrative control High performance applications · Web service, Cache · Email, News · Database, GIS 37
 Local File Sharing Architecture Characteristics Applications tend to avoid OS · e. g. No virtual memory Applications tend to have OS adaptation layer Different access protocol requirements · e. g. high-performance locking, recovery, streaming 38
Local File Sharing Architecture Characteristics Applications tend to avoid OS · e. g. No virtual memory Applications tend to have OS adaptation layer Different access protocol requirements · e. g. high-performance locking, recovery, streaming 38
 What is VI? Virtual Interface (VI) Architecture · VI architecture organization - Promoted by Intel, Compaq and Microsoft · VI Developer’s Forum Standard capabilities · Send/receive message, remote DMA read/write · Multiple channels with send/completion queues · Data transfer bypasses kernel - Memory pre-registration 39
What is VI? Virtual Interface (VI) Architecture · VI architecture organization - Promoted by Intel, Compaq and Microsoft · VI Developer’s Forum Standard capabilities · Send/receive message, remote DMA read/write · Multiple channels with send/completion queues · Data transfer bypasses kernel - Memory pre-registration 39
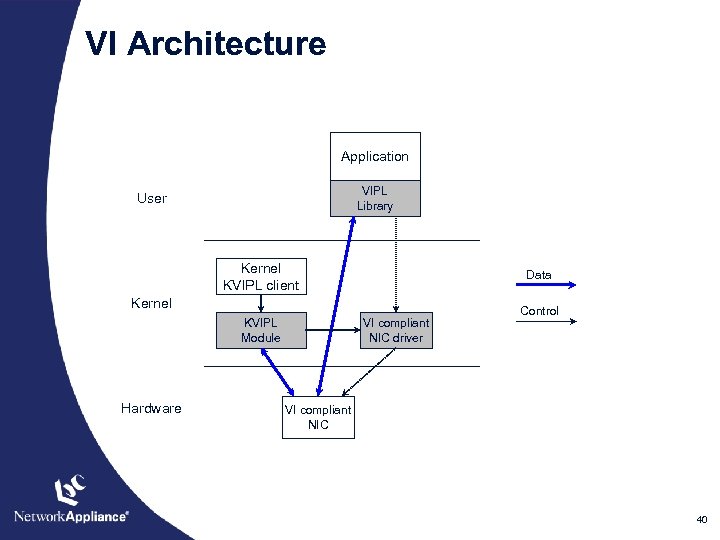 VI Architecture Application VIPL Library User Kernel KVIPL client Data Kernel KVIPL Module Hardware VI compliant NIC driver Control VI compliant NIC 40
VI Architecture Application VIPL Library User Kernel KVIPL client Data Kernel KVIPL Module Hardware VI compliant NIC driver Control VI compliant NIC 40
 VI-compliant implementations Fibre channel (FC-VI draft standard) · e. g. Troika, Emulex Giganet Servernet II Infiniband · Enables 1 U MP heads Future: VI over TCP/IP 41
VI-compliant implementations Fibre channel (FC-VI draft standard) · e. g. Troika, Emulex Giganet Servernet II Infiniband · Enables 1 U MP heads Future: VI over TCP/IP 41
 How VI Improves Data Transfer No fragmentation, reassembly and realignment data copies No user/kernel boundary crossing No user/kernel data copies · Data transfer direct to application buffers 42
How VI Improves Data Transfer No fragmentation, reassembly and realignment data copies No user/kernel boundary crossing No user/kernel data copies · Data transfer direct to application buffers 42
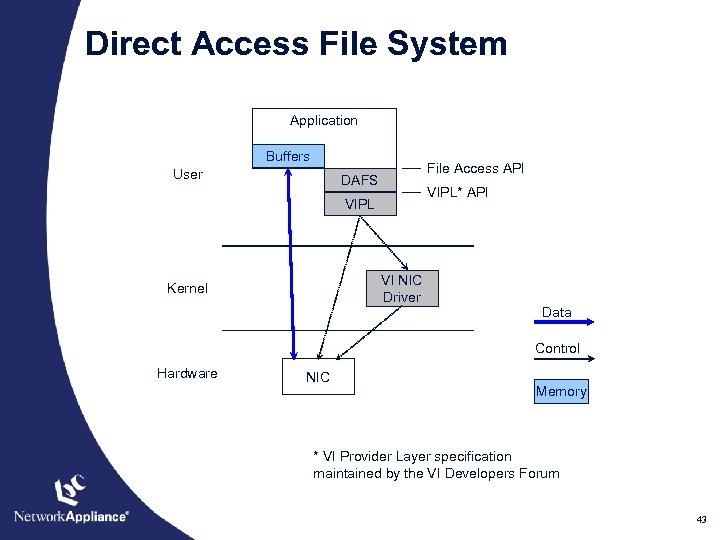 Direct Access File System Application Buffers User File Access API DAFS VIPL* API VIPL VI NIC Driver Kernel Data Control Hardware NIC Memory * VI Provider Layer specification maintained by the VI Developers Forum 43
Direct Access File System Application Buffers User File Access API DAFS VIPL* API VIPL VI NIC Driver Kernel Data Control Hardware NIC Memory * VI Provider Layer specification maintained by the VI Developers Forum 43
 DAFS Benefits 1. File access protocol with implicit data sharing 2. Direct application access · File data transfers directly to application buffers · Bypasses Operating System · File semantics 3. Optimized for high throughput and low latency 4. Consistent high speed locking 5. Graceful recovery/failover of clients and servers 6. Fencing 7. Enhanced data recovery 8. Leverages VI for transport independence 44
DAFS Benefits 1. File access protocol with implicit data sharing 2. Direct application access · File data transfers directly to application buffers · Bypasses Operating System · File semantics 3. Optimized for high throughput and low latency 4. Consistent high speed locking 5. Graceful recovery/failover of clients and servers 6. Fencing 7. Enhanced data recovery 8. Leverages VI for transport independence 44
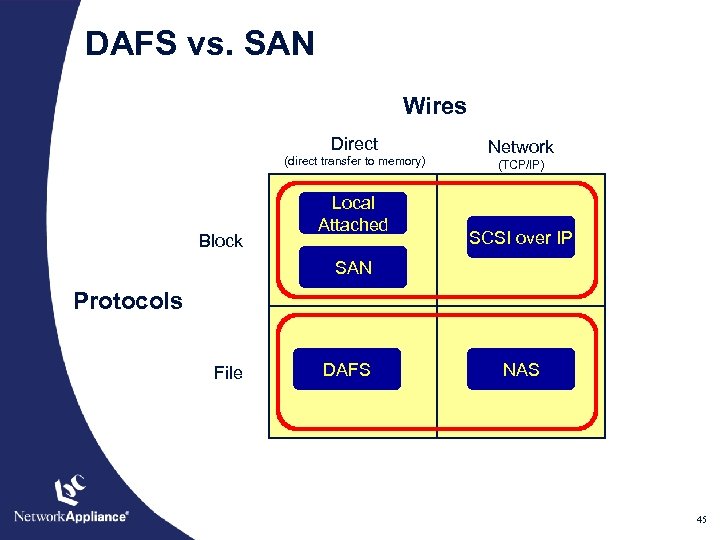 DAFS vs. SAN Wires Direct (direct transfer to memory) Block Local Attached Network (TCP/IP) SCSI over IP SAN Protocols File DAFS NAS 45
DAFS vs. SAN Wires Direct (direct transfer to memory) Block Local Attached Network (TCP/IP) SCSI over IP SAN Protocols File DAFS NAS 45
 Summary Wave 1: Filers · Technology: Fast networks, commodity servers · Environment: Appliance-ization Wave 2: Failover · Technology: Memory-to-memory interconnects, Dual ported FC disks · Environment: 24 x 7 requirements Wave 3: Net. Cache · Technology: Internet, HTTP · Environment: High BW requirements, POP deployability 46
Summary Wave 1: Filers · Technology: Fast networks, commodity servers · Environment: Appliance-ization Wave 2: Failover · Technology: Memory-to-memory interconnects, Dual ported FC disks · Environment: 24 x 7 requirements Wave 3: Net. Cache · Technology: Internet, HTTP · Environment: High BW requirements, POP deployability 46
 Summary Wave 4: Snap. Mirror · Technology: Disk areal density, Fibre Channel, fast networks · Environment: Cost of downtime for recovery Wave 5: DAFS · Technology: VI architecture · Environment: Local file sharing 47
Summary Wave 4: Snap. Mirror · Technology: Disk areal density, Fibre Channel, fast networks · Environment: Cost of downtime for recovery Wave 5: DAFS · Technology: VI architecture · Environment: Local file sharing 47


