Intonation 1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9

Suprasegmental Phonetics Prosody and Intonation 1. Basic concepts. 2. Prosodic Bases of English and Russian. 3. Sentence Stress. Prosody and Intonation. 4. Functions of Intonation.

Prosody and intonation: basic concepts Prosodic features are variations in pitch, loudness, tempo, rhythm (including the pause), and voice quality. Crystal 1980: “Prosody is a term used in suprasegmental phonetics and phonology to refer collectively to variations in pitch, loudness, tempo and rhythm”. P. Poach, 2001: + voice quality

: Narrow approach to intonation (the British school) Intonation is “a term used in the study of suprasegmental phonology referring to the distinctive use of patterns of pitch, or melody” (Crystal 1980); “Intonation is the use of pitch variation to convey meaning” (Poach, 2001).

: Broad approach to intonation (the Russian school): Intonation = speech melody + stress + tempo + rhythm + timbre (voice quality). “Intonation is a complex unity formed by communicatively relevant variations in: 1. voice pitch, or speech melody; 2. the prominence of words, or their accent; 3. the tempo, rhythm and pausation of the utterance, and 4. voice timber…. ” (Vassilyev, 1970)

Prosodic features: Most linguistic → Least linguistic (D. Crystal) Pitch change Pitch range Loudness Tempo Pause Rhythm Voice quality

Principles of defining intonation components (by N. D. Svetozarova and J. B. Vereninova) 1. To be a component of intonation a phonetic feature should have a correlate on the acoustic level, this correlate being of homogeneous nature. 2. A component of intonation should be linguistically relevant, i. e. be able to distinguish meaning. Prosodic features that meet this requirement are pitch, loudness, tempo, pause and voice quality.

Functions of Prosody Structural function e. g. 1 newsreading: pitch changes shape paragraphs of information e. g. 2 Sports commentary: prosodic changes reflect the progress of the action Social function e. g. to indicate social status, social role, dominance/submissiveness

Functions of Intonation 1. Syntactic function (phrasing) E. g. Those who sold quickly /made profit. // Those who sold /quickly made profit. // 2. Accentual function. E. g. This is Mark Darcy. He’s a top ↓barrister. 3. Attitudinal function. E. g. ↓John’s come. ↓↓John’s come! 4. Semantic function. E. g. She doesn’t lend her books to anybody. (low fall) – не дает книги никому. She doesn’t lend her books to anybody. (fall-rise) – не дает книги случайным людям. 5. Discourse function: shared knowledge, focusing attention, turn-taking 6. Stylistic function
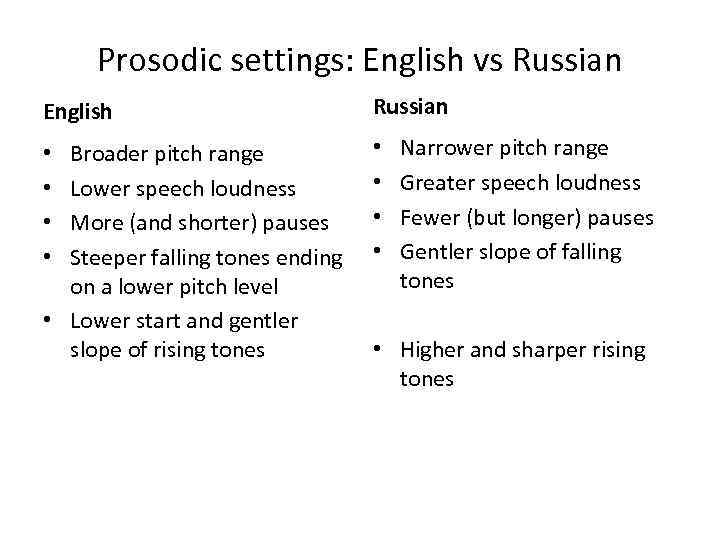
Prosodic settings: English vs Russian English Russian Broader pitch range Lower speech loudness More (and shorter) pauses Steeper falling tones ending on a lower pitch level • Lower start and gentler slope of rising tones • • Narrower pitch range Greater speech loudness Fewer (but longer) pauses Gentler slope of falling tones • Higher and sharper rising tones
Intonation 1.ppt