4_asp_SCM.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 41
 SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Maria Tsenzharik, Ph. D
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Maria Tsenzharik, Ph. D
 Structure • Distribution systems • New trends in distribution • Supply chain management: cases
Structure • Distribution systems • New trends in distribution • Supply chain management: cases
 Supply chain • encompasses the steps to get a good or service from the supplier to the customer • includes every company that comes into contact with a particular product: üvendors that supply raw material, üproducers converting material into products, üwarehouses storing products, üdistribution centers delivering them to retailers, üretailers bringing the product to the final
Supply chain • encompasses the steps to get a good or service from the supplier to the customer • includes every company that comes into contact with a particular product: üvendors that supply raw material, üproducers converting material into products, üwarehouses storing products, üdistribution centers delivering them to retailers, üretailers bringing the product to the final
 Supply chain management • Management of material and information flows in the supply chain to provide the highest degree of customer satisfaction at the lowest possible cost • Requires commitment of supply chain partners to work closely to coordinate order generation, order taking, and order fulfillment • They thereby create an extended enterprise spreading far beyond the producer’s location
Supply chain management • Management of material and information flows in the supply chain to provide the highest degree of customer satisfaction at the lowest possible cost • Requires commitment of supply chain partners to work closely to coordinate order generation, order taking, and order fulfillment • They thereby create an extended enterprise spreading far beyond the producer’s location
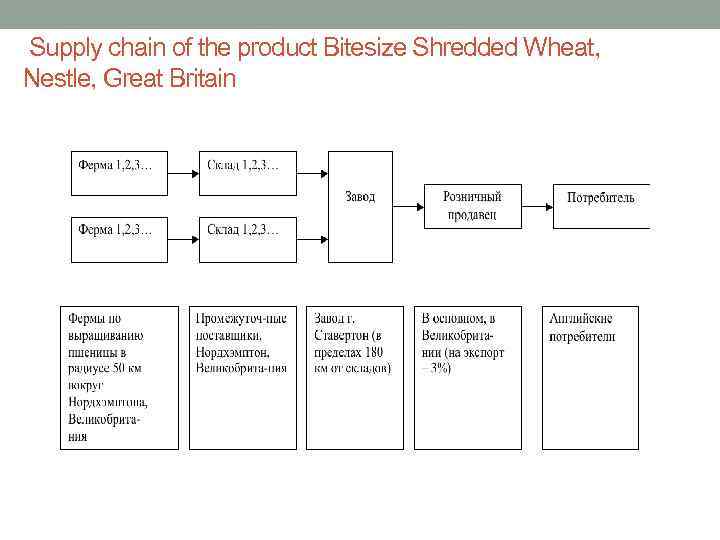 Supply chain of the product Bitesize Shredded Wheat, Nestle, Great Britain
Supply chain of the product Bitesize Shredded Wheat, Nestle, Great Britain
 Distribution • is the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption by a consumer or business user
Distribution • is the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption by a consumer or business user
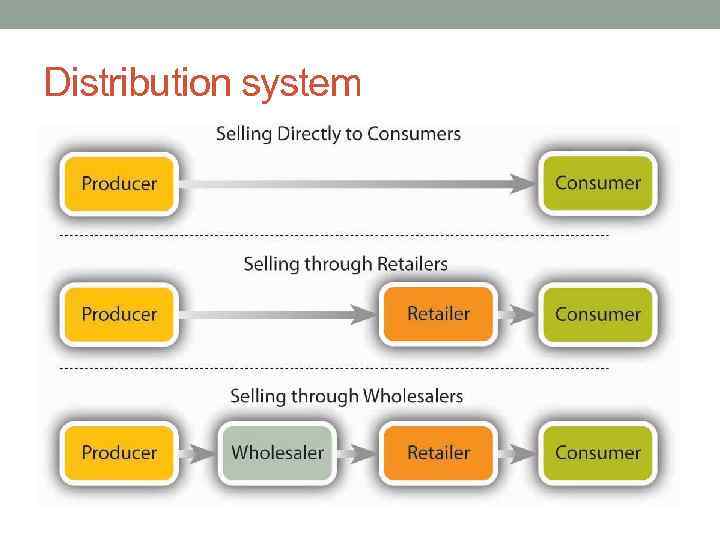 Distribution system
Distribution system
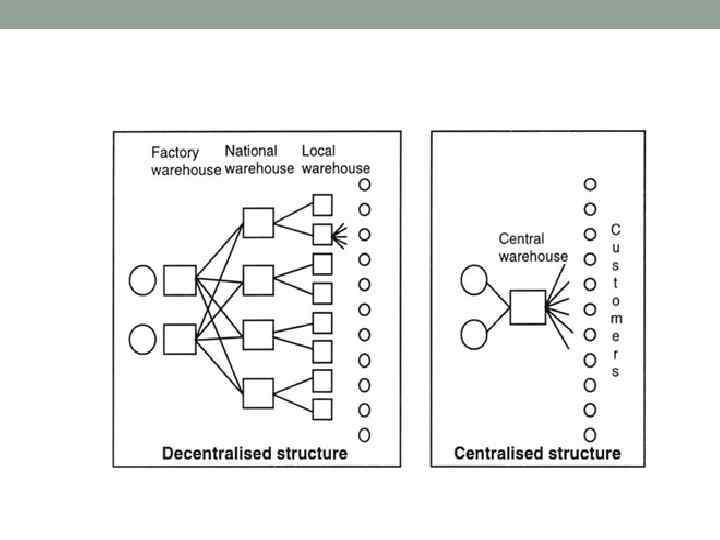
 Old distribution system (before mid 80 s) in Europe • Factors: • Crossing borders (customs control etc) • National transportation systems (poor transport connections) • Weak information exchange • Results: • Large amount of elements of supply chain • High delivery costs • Long delivery time • Higher delivery risks
Old distribution system (before mid 80 s) in Europe • Factors: • Crossing borders (customs control etc) • National transportation systems (poor transport connections) • Weak information exchange • Results: • Large amount of elements of supply chain • High delivery costs • Long delivery time • Higher delivery risks
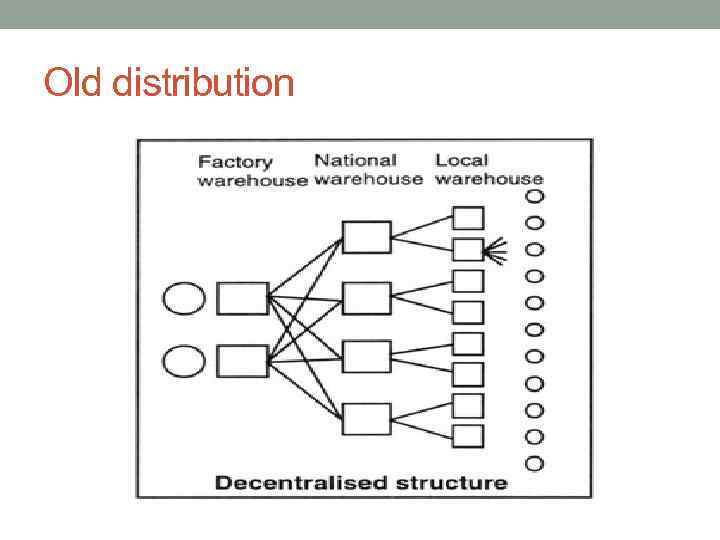 Old distribution
Old distribution
 New distribution: factors of influence • Liberalization of trade (EC expansion) • Standardization of transportation • ICT • Logistics operators • Results:
New distribution: factors of influence • Liberalization of trade (EC expansion) • Standardization of transportation • ICT • Logistics operators • Results:
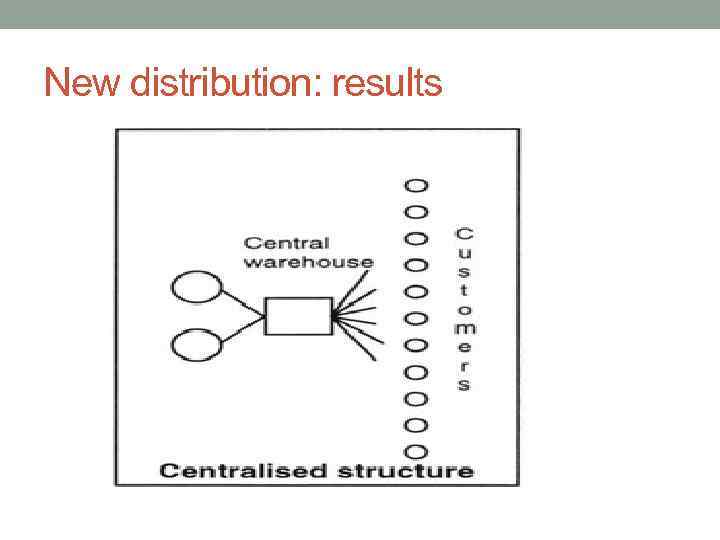 New distribution: results
New distribution: results
 New distribution: results • Decreasing number of elements • Reducing delivery costs • Diminishing delivery tome • Reducing risks • Time based delivery • Centralization of physical flows • New functions of warehouses
New distribution: results • Decreasing number of elements • Reducing delivery costs • Diminishing delivery tome • Reducing risks • Time based delivery • Centralization of physical flows • New functions of warehouses
 Functions of modern warehouse • Storing • Container processing • Transportation • Customs control • Inventory management • Information processing • Services
Functions of modern warehouse • Storing • Container processing • Transportation • Customs control • Inventory management • Information processing • Services
 Distribution/Logistics center • Thus, with new functions, warehouses started to cover all logistics operations and have been transformed into distribution centers (or logistics centers)
Distribution/Logistics center • Thus, with new functions, warehouses started to cover all logistics operations and have been transformed into distribution centers (or logistics centers)
 Clothing and accesories retail company which sells worldwide. • Founded in 1975 in a small town of Galicia (Spain). • belongs to the Inditex group • headquarters are in Galicia • Nowadays: -Revenue: 7000 Billion € -Employees: >82. 000 -1283 stores in 73 countries -10000 new designs each year
Clothing and accesories retail company which sells worldwide. • Founded in 1975 in a small town of Galicia (Spain). • belongs to the Inditex group • headquarters are in Galicia • Nowadays: -Revenue: 7000 Billion € -Employees: >82. 000 -1283 stores in 73 countries -10000 new designs each year
 Key factor of Zara • Logistics system. • They follow the Just In Time system (JIT) by Toyota. Time to develop new product and send to stores: 6 months for its competitors in average. Time for Zara: 2 weeks worldwide.
Key factor of Zara • Logistics system. • They follow the Just In Time system (JIT) by Toyota. Time to develop new product and send to stores: 6 months for its competitors in average. Time for Zara: 2 weeks worldwide.
 Design 300 designers work in Galicia and send the templates to the factories Production facilities 49% Spain and Portugal. 35% Asia 14% Europe and North Africa 2% Other countries
Design 300 designers work in Galicia and send the templates to the factories Production facilities 49% Spain and Portugal. 35% Asia 14% Europe and North Africa 2% Other countries
 Process After the product is made, it is send to Galicia, the logistic center of Inditex for Zara. After they send all the products to the stores in the world. Time If the distribution takes less than 24 hours by truck, it is delivered by truck. If takes more time, by plane. Internet In september 2010, Zara launched “Zara Online”, customers can buy Zara products from Internet. They can pick them up from the store they choose in 2 -3 days or can receive them at home in 5 days.
Process After the product is made, it is send to Galicia, the logistic center of Inditex for Zara. After they send all the products to the stores in the world. Time If the distribution takes less than 24 hours by truck, it is delivered by truck. If takes more time, by plane. Internet In september 2010, Zara launched “Zara Online”, customers can buy Zara products from Internet. They can pick them up from the store they choose in 2 -3 days or can receive them at home in 5 days.
 The Coca-Cola Company • World’s largest beverage company, headquartered in Atlanta, USA. • Operate in more than 200 countries and offers more than 3500 beverage products • Markets more than 500 brands • more than 1. 9 billion servings a day (57 billion servings of all beverages worldwide) • 129’ 200 employees worldwide.
The Coca-Cola Company • World’s largest beverage company, headquartered in Atlanta, USA. • Operate in more than 200 countries and offers more than 3500 beverage products • Markets more than 500 brands • more than 1. 9 billion servings a day (57 billion servings of all beverages worldwide) • 129’ 200 employees worldwide.
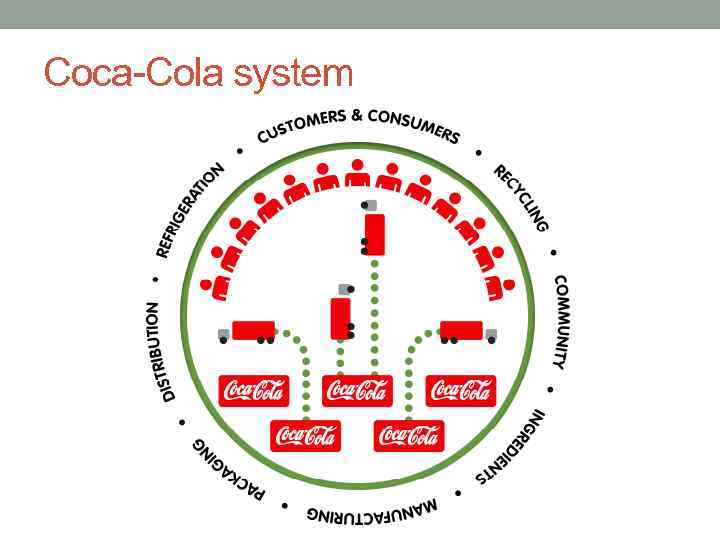 Coca-Cola system
Coca-Cola system
 Coca-Cola’s distribution system • 6 operating groups: Eurasia and Africa, Europe, Latin America, North America, Pacific and Bottling Investments. • Coca-Cola Company only produces the concentrates and syrups. They then sell them to bottling partners -> franchised distribution system • Not a single entity from a legal perspective. • More than 300 bottling partners worldwide. Majority of them are not owned or controlled by the Coca-Cola Company. • Bottling partners are responsible for manufacturing the beverages and distributing the final products to local grocery stores, restaurants and street vendors around the world
Coca-Cola’s distribution system • 6 operating groups: Eurasia and Africa, Europe, Latin America, North America, Pacific and Bottling Investments. • Coca-Cola Company only produces the concentrates and syrups. They then sell them to bottling partners -> franchised distribution system • Not a single entity from a legal perspective. • More than 300 bottling partners worldwide. Majority of them are not owned or controlled by the Coca-Cola Company. • Bottling partners are responsible for manufacturing the beverages and distributing the final products to local grocery stores, restaurants and street vendors around the world
 Пример: компания Cargill - основной поставщик сиропа для Coca-Cola • Coca-Cola не отслеживает качество сиропа, а поручает Cargill регулярно предоставлять данные по процессу его приготовления. • Cargill проводит мониторинг составляющих процесса производства сиропа, направляет данные Coca-Cola и поставляет сироп на производственные линии Соса-Соla. • Cargill доказала, что может поддерживать строгие стандарты качества с помощью контроля за составляющими процесса
Пример: компания Cargill - основной поставщик сиропа для Coca-Cola • Coca-Cola не отслеживает качество сиропа, а поручает Cargill регулярно предоставлять данные по процессу его приготовления. • Cargill проводит мониторинг составляющих процесса производства сиропа, направляет данные Coca-Cola и поставляет сироп на производственные линии Соса-Соla. • Cargill доказала, что может поддерживать строгие стандарты качества с помощью контроля за составляющими процесса
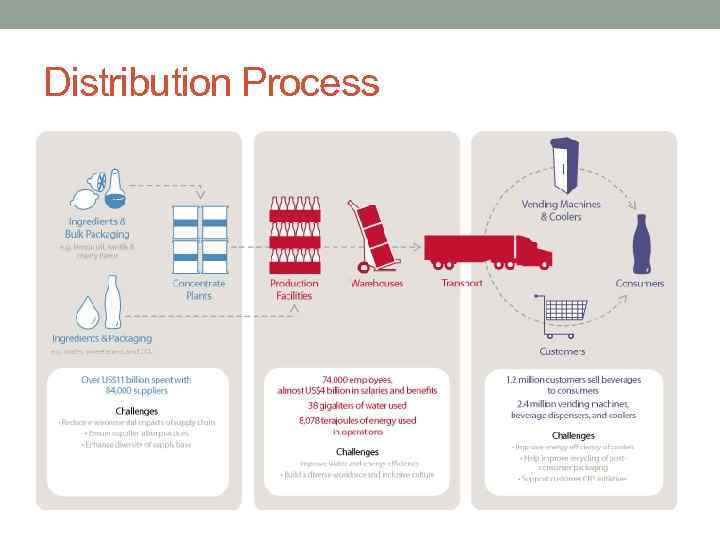 Distribution Process
Distribution Process

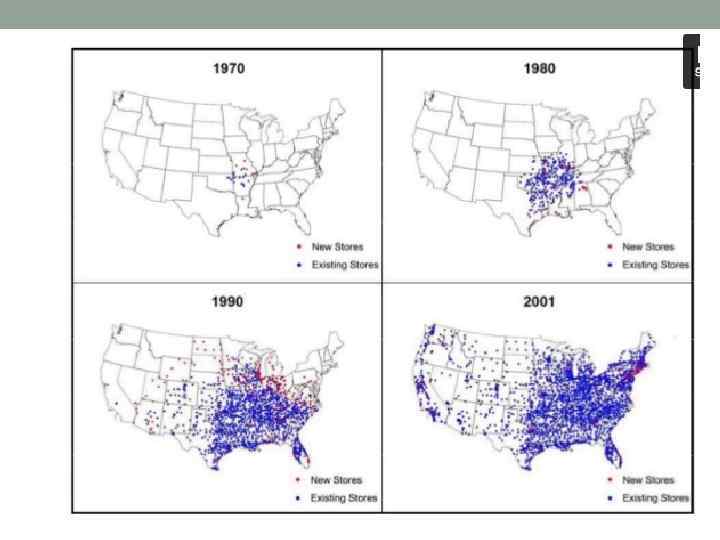
 Wal-Mart Stores an American multinational retail corporation that runs chains of large discount department stores and warehouse stores. the biggest private employer in the world with over two million employees the largest retailer in the world Sam Walton (1918– 1992) founded Walmart in 1962 in Rogers, Arkansas, based on a low-price/high-volume business model. Walmart has over 11, 000 stores in 27 countries, under 55 different names.
Wal-Mart Stores an American multinational retail corporation that runs chains of large discount department stores and warehouse stores. the biggest private employer in the world with over two million employees the largest retailer in the world Sam Walton (1918– 1992) founded Walmart in 1962 in Rogers, Arkansas, based on a low-price/high-volume business model. Walmart has over 11, 000 stores in 27 countries, under 55 different names.
 • AFRICA: Walmart acquired a majority stake in Massmart Holdings Limited, the leading African retailer of general merchandise, home mprovement equipment and supplies, that comprises nine wholesale and retail chains, and one buying group, operating in 13 countries in Sub. Saharan Africa. • Total retail units, 2012: 347 • GUATEMALA: Acquired 33 percent interest in Central American Retail Holding Company (CARHCO) from the Dutch retailer Royal Ahold NV. In March 2006, they increased the interest to 51 percent and the CARHCO name became Walmart Centroamérica. • Total Retail Units, 2012: 200 • MEXICO: Joint venture with Cifra to open a Sam’s Club in Mexico City. Then, acquired a majority of Cifra, and in February 2000, the Cifra name officially changed to Walmart de México (WALMEX). • Total Retail Units 2012: 2, 088
• AFRICA: Walmart acquired a majority stake in Massmart Holdings Limited, the leading African retailer of general merchandise, home mprovement equipment and supplies, that comprises nine wholesale and retail chains, and one buying group, operating in 13 countries in Sub. Saharan Africa. • Total retail units, 2012: 347 • GUATEMALA: Acquired 33 percent interest in Central American Retail Holding Company (CARHCO) from the Dutch retailer Royal Ahold NV. In March 2006, they increased the interest to 51 percent and the CARHCO name became Walmart Centroamérica. • Total Retail Units, 2012: 200 • MEXICO: Joint venture with Cifra to open a Sam’s Club in Mexico City. Then, acquired a majority of Cifra, and in February 2000, the Cifra name officially changed to Walmart de México (WALMEX). • Total Retail Units 2012: 2, 088
 • UNITED KINGDOM: Walmart acquired the group retailer Asda and has grown into Britain’s second largest supermarket. • Total Retail Units, 2012: 541 JAPAN: acquired a majority interest in Seiyu, making Seiyu a Walmart subsidiary and continue increasing its ownership until being wholly owned. • Total Retail Units, 2012: 419 • U. S. A. : Walmart is associated with a wholesale club named “Sam’s Club”, which counts with more than 590 of these members-only warehouse clubs. From these wholesalers, products are send directly to retailers. Walmart International 5. 651 Walmart U. S. 4. 479
• UNITED KINGDOM: Walmart acquired the group retailer Asda and has grown into Britain’s second largest supermarket. • Total Retail Units, 2012: 541 JAPAN: acquired a majority interest in Seiyu, making Seiyu a Walmart subsidiary and continue increasing its ownership until being wholly owned. • Total Retail Units, 2012: 419 • U. S. A. : Walmart is associated with a wholesale club named “Sam’s Club”, which counts with more than 590 of these members-only warehouse clubs. From these wholesalers, products are send directly to retailers. Walmart International 5. 651 Walmart U. S. 4. 479
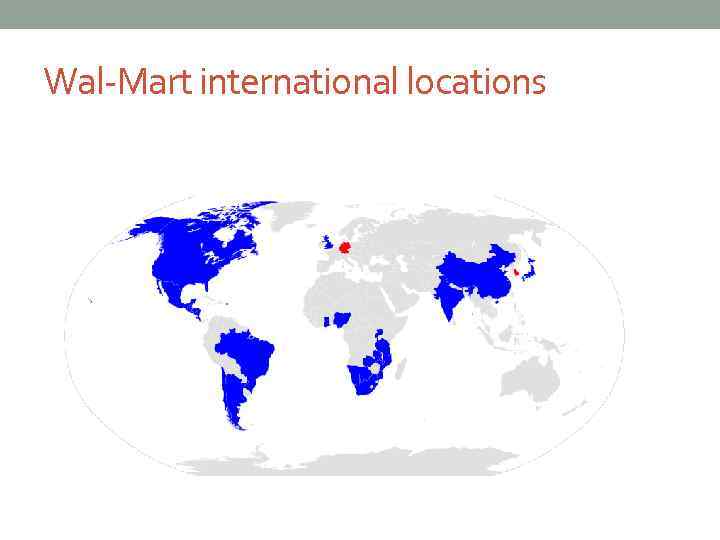 Wal-Mart international locations
Wal-Mart international locations
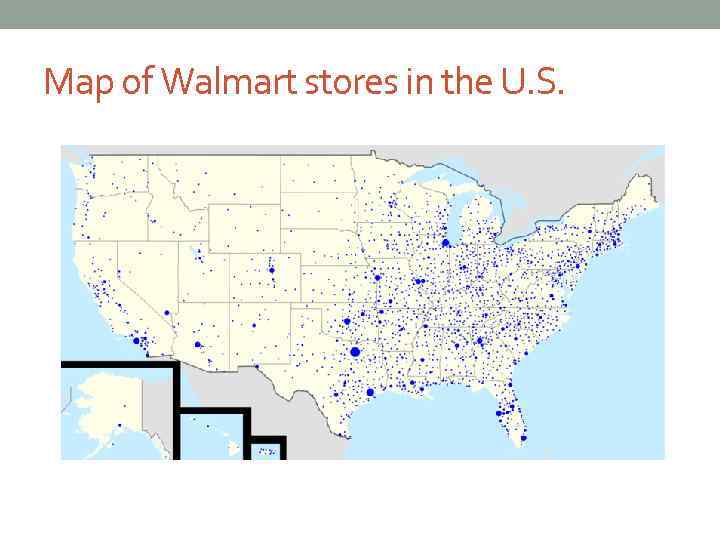 Map of Walmart stores in the U. S.
Map of Walmart stores in the U. S.
 Retail stores • discount stores sell variety goods; • supercenters sell variety goods plus food; • neighborhood markets sell only food; • "marketside" stores are being tested (as a version of the convenience store); • Sam’s Clubs operate as members’ only warehouses • Fully 60% of the entire U. S. population lives within 5 miles of a Wal-Mart location and 96% are within 20 miles.
Retail stores • discount stores sell variety goods; • supercenters sell variety goods plus food; • neighborhood markets sell only food; • "marketside" stores are being tested (as a version of the convenience store); • Sam’s Clubs operate as members’ only warehouses • Fully 60% of the entire U. S. population lives within 5 miles of a Wal-Mart location and 96% are within 20 miles.
 Retailers • The total area of these almost 4, 300 retail locations is over 675 million square feet, or about 15, 500 acres. (Manhattan, by comparison, encompasses 14, 694 acres. ) • Each individual store is modeled on one of a collection of company prototypes, which are then modified according to commercial considerations such as size, layout and program, and to local conditions such as building codes, zoning ordinances, traffic access, etc.
Retailers • The total area of these almost 4, 300 retail locations is over 675 million square feet, or about 15, 500 acres. (Manhattan, by comparison, encompasses 14, 694 acres. ) • Each individual store is modeled on one of a collection of company prototypes, which are then modified according to commercial considerations such as size, layout and program, and to local conditions such as building codes, zoning ordinances, traffic access, etc.
 Distribution centers • Each of our 42 regional U. S. distribution centers is over 1 million square feet • with more than 12 miles of conveyor belts to move 5. 5 billion cases of merchandise. • Some distribution centers operate 24/7 around the clock to keep the Walmart fleet rolling • It’s all designed to pass on savings to customers and communities.
Distribution centers • Each of our 42 regional U. S. distribution centers is over 1 million square feet • with more than 12 miles of conveyor belts to move 5. 5 billion cases of merchandise. • Some distribution centers operate 24/7 around the clock to keep the Walmart fleet rolling • It’s all designed to pass on savings to customers and communities.
 Walmart's distribution centers Are hybrid structures — part architecture, part infrastructure Walmart’s domestic distribution network consists of more than 100, 000 suppliers, 180 distribution centers, two data centers, the U. S. transportation infrastructure (mostly the publicly funded highway system), 7, 200 tractors, 53, 000 trailers, 7, 950 drivers, and more than 85, 000 employees. Every distribution center supports 90 to 100 stores in a 200 -mile radius
Walmart's distribution centers Are hybrid structures — part architecture, part infrastructure Walmart’s domestic distribution network consists of more than 100, 000 suppliers, 180 distribution centers, two data centers, the U. S. transportation infrastructure (mostly the publicly funded highway system), 7, 200 tractors, 53, 000 trailers, 7, 950 drivers, and more than 85, 000 employees. Every distribution center supports 90 to 100 stores in a 200 -mile radius
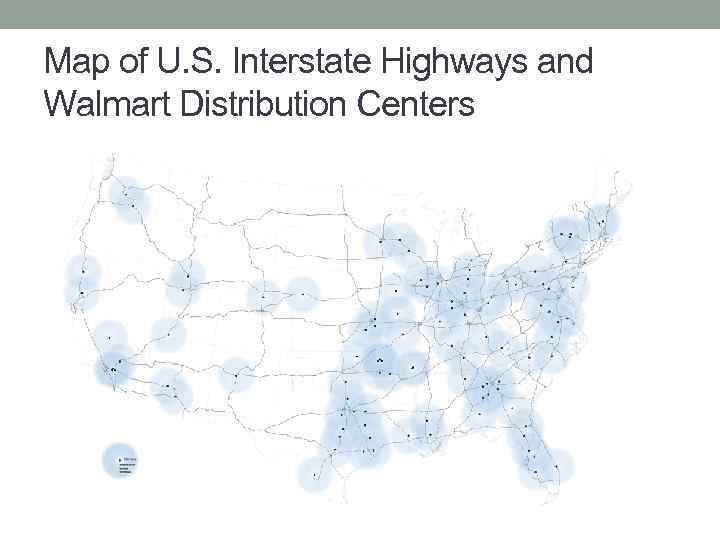 Map of U. S. Interstate Highways and Walmart Distribution Centers
Map of U. S. Interstate Highways and Walmart Distribution Centers
 Thus: The stores and distribution centers are strategically located to optimize the flow of goods; they form a dynamic and expanding network whose locations are calculated in miles and minutes. The stores are designed to function more as valves regulating flow than as reservoirs capturing it: they are containers, to be sure, but they are also conduits. Because the distribution system is so tightly coordinated, the store designs can minimize areas for stock and maximize floor space for retail.
Thus: The stores and distribution centers are strategically located to optimize the flow of goods; they form a dynamic and expanding network whose locations are calculated in miles and minutes. The stores are designed to function more as valves regulating flow than as reservoirs capturing it: they are containers, to be sure, but they are also conduits. Because the distribution system is so tightly coordinated, the store designs can minimize areas for stock and maximize floor space for retail.
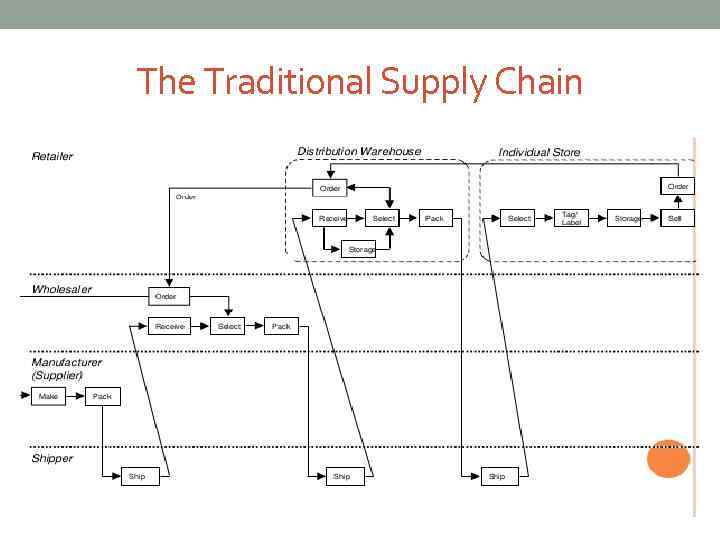 The Traditional Supply Chain
The Traditional Supply Chain
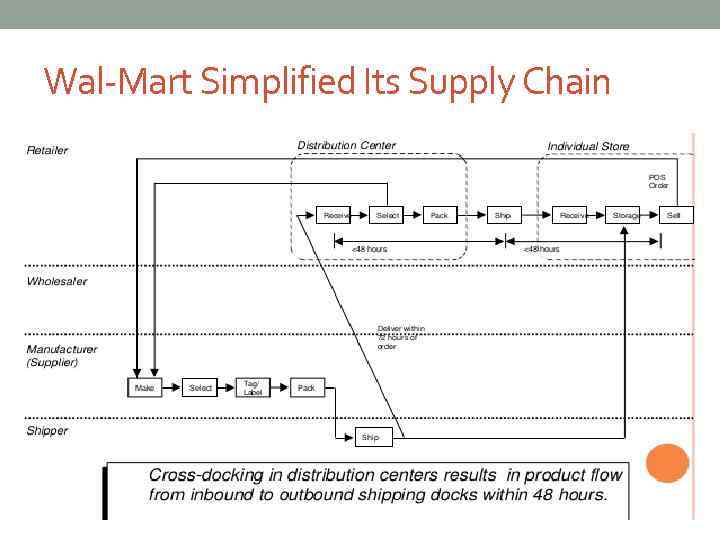 Wal-Mart Simplified Its Supply Chain
Wal-Mart Simplified Its Supply Chain
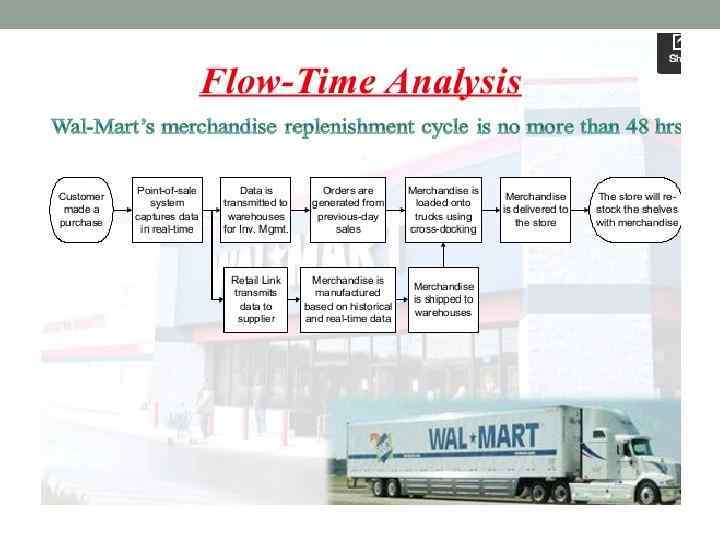
 Features of Wal-Mart logistics - “Cross-docking” - Investments in IT and communication system to effectively track sales and merchandise inventories. - Stores are allowed to manage their own stocks - RFID - Low transportation costs (3% against competitors’ 5%) - Faster delivery to stores(48 hours) and replenishment (4 times) - Strong relationship with suppliers
Features of Wal-Mart logistics - “Cross-docking” - Investments in IT and communication system to effectively track sales and merchandise inventories. - Stores are allowed to manage their own stocks - RFID - Low transportation costs (3% against competitors’ 5%) - Faster delivery to stores(48 hours) and replenishment (4 times) - Strong relationship with suppliers


