dee9c90878e1af0c782556f217affa62.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Supply Chain Management (2 nd Edition) Chapter 3 Supply Chain Drivers and Obstacles © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 3 -1
Supply Chain Management (2 nd Edition) Chapter 3 Supply Chain Drivers and Obstacles © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 3 -1
 Outline u Drivers of supply chain performance u A framework for structuring drivers u Facilities u Inventory u Transportation u Information u Obstacles to achieving fit © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 2
Outline u Drivers of supply chain performance u A framework for structuring drivers u Facilities u Inventory u Transportation u Information u Obstacles to achieving fit © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 2
 Drivers of Supply Chain Performance u Facilities – places where inventory is stored, assembled, or fabricated – production sites and storage sites u Inventory – raw materials, WIP, finished goods within a supply chain – inventory policies u Transportation – moving inventory from point to point in a supply chain – combinations of transportation modes and routes u Information – data and analysis regarding inventory, transportation, facilities throughout the supply chain – potentially the biggest driver of supply chain performance © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 3
Drivers of Supply Chain Performance u Facilities – places where inventory is stored, assembled, or fabricated – production sites and storage sites u Inventory – raw materials, WIP, finished goods within a supply chain – inventory policies u Transportation – moving inventory from point to point in a supply chain – combinations of transportation modes and routes u Information – data and analysis regarding inventory, transportation, facilities throughout the supply chain – potentially the biggest driver of supply chain performance © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 3
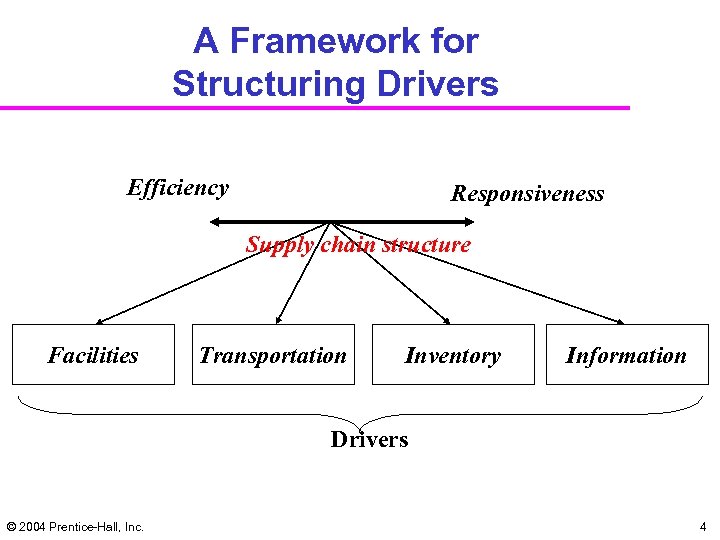 A Framework for Structuring Drivers Efficiency Responsiveness Supply chain structure Facilities Transportation Inventory Information Drivers © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 4
A Framework for Structuring Drivers Efficiency Responsiveness Supply chain structure Facilities Transportation Inventory Information Drivers © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 4
 Supply Chain Decisions: Structuring Drivers Strategy (Design) Planning Operation © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 5
Supply Chain Decisions: Structuring Drivers Strategy (Design) Planning Operation © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 5
 Facilities u Role in the supply chain – the “where” of the supply chain – manufacturing or storage (warehouses) u Role in the competitive strategy – economies of scale (efficiency priority) – larger number of smaller facilities (responsiveness priority) u Example 3. 1: Toyota and Honda u Components of facilities decisions © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 6
Facilities u Role in the supply chain – the “where” of the supply chain – manufacturing or storage (warehouses) u Role in the competitive strategy – economies of scale (efficiency priority) – larger number of smaller facilities (responsiveness priority) u Example 3. 1: Toyota and Honda u Components of facilities decisions © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 6
 Components of Facilities Decisions u Location – centralization (efficiency) vs. decentralization (responsiveness) – other factors to consider (e. g. , proximity to customers) u Capacity (flexibility versus efficiency) u Manufacturing methodology (product focused versus process focused) u Warehousing methodology (SKU storage, job lot storage, cross-docking) u Overall trade-off: Responsiveness versus efficiency © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 7
Components of Facilities Decisions u Location – centralization (efficiency) vs. decentralization (responsiveness) – other factors to consider (e. g. , proximity to customers) u Capacity (flexibility versus efficiency) u Manufacturing methodology (product focused versus process focused) u Warehousing methodology (SKU storage, job lot storage, cross-docking) u Overall trade-off: Responsiveness versus efficiency © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 7
 Inventory u Role in the supply chain u Role in the competitive strategy u Components of inventory decisions © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 8
Inventory u Role in the supply chain u Role in the competitive strategy u Components of inventory decisions © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 8
 Inventory: Role in the Supply Chain u Inventory exists because of a mismatch between supply and demand u Source of cost and influence on responsiveness u Impact on – material flow time: time elapsed between when material enters the supply chain to when it exits the supply chain – throughput » » » rate at which sales to end consumers occur I = RT (Little’s Law) I = inventory; R = throughput; T = flow time Example Inventory and throughput are “synonymous” in a supply chain © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 9
Inventory: Role in the Supply Chain u Inventory exists because of a mismatch between supply and demand u Source of cost and influence on responsiveness u Impact on – material flow time: time elapsed between when material enters the supply chain to when it exits the supply chain – throughput » » » rate at which sales to end consumers occur I = RT (Little’s Law) I = inventory; R = throughput; T = flow time Example Inventory and throughput are “synonymous” in a supply chain © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 9
 Inventory: Role in Competitive Strategy u If responsiveness is a strategic competitive priority, a firm can locate larger amounts of inventory closer to customers u If cost is more important, inventory can be reduced to make the firm more efficient u Trade-off u Example 3. 2 – Nordstrom © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 10
Inventory: Role in Competitive Strategy u If responsiveness is a strategic competitive priority, a firm can locate larger amounts of inventory closer to customers u If cost is more important, inventory can be reduced to make the firm more efficient u Trade-off u Example 3. 2 – Nordstrom © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 10
 Components of Inventory Decisions u Cycle inventory – Average amount of inventory used to satisfy demand between shipments – Depends on lot size u Safety inventory – inventory held in case demand exceeds expectations – costs of carrying too much inventory versus cost of losing sales u Seasonal inventory – inventory built up to counter predictable variability in demand – cost of carrying additional inventory versus cost of flexible production u Overall trade-off: Responsiveness versus efficiency – more inventory: greater responsiveness but greater cost – less inventory: lower cost but lower responsiveness © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 11
Components of Inventory Decisions u Cycle inventory – Average amount of inventory used to satisfy demand between shipments – Depends on lot size u Safety inventory – inventory held in case demand exceeds expectations – costs of carrying too much inventory versus cost of losing sales u Seasonal inventory – inventory built up to counter predictable variability in demand – cost of carrying additional inventory versus cost of flexible production u Overall trade-off: Responsiveness versus efficiency – more inventory: greater responsiveness but greater cost – less inventory: lower cost but lower responsiveness © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 11
 Transportation u Role in the supply chain u Role in the competitive strategy u Components of transportation decisions © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 12
Transportation u Role in the supply chain u Role in the competitive strategy u Components of transportation decisions © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 12
 Transportation: Role in the Supply Chain u Moves the product between stages in the supply chain u Impact on responsiveness and efficiency u Faster transportation allows greater responsiveness but lower efficiency u Also affects inventory and facilities © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 13
Transportation: Role in the Supply Chain u Moves the product between stages in the supply chain u Impact on responsiveness and efficiency u Faster transportation allows greater responsiveness but lower efficiency u Also affects inventory and facilities © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 13
 Transportation: Role in the Competitive Strategy u If responsiveness is a strategic competitive priority, then faster transportation modes can provide greater responsiveness to customers who are willing to pay for it u Can also use slower transportation modes for customers whose priority is price (cost) u Can also consider both inventory and transportation to find the right balance u Example 3. 3: Laura Ashley © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 14
Transportation: Role in the Competitive Strategy u If responsiveness is a strategic competitive priority, then faster transportation modes can provide greater responsiveness to customers who are willing to pay for it u Can also use slower transportation modes for customers whose priority is price (cost) u Can also consider both inventory and transportation to find the right balance u Example 3. 3: Laura Ashley © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 14
 Components of Transportation Decisions u Mode of transportation: – air, truck, rail, ship, pipeline, electronic transportation – vary in cost, speed, size of shipment, flexibility u Route and network selection – route: path along which a product is shipped – network: collection of locations and routes u In-house or outsource u Overall trade-off: Responsiveness versus efficiency © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 15
Components of Transportation Decisions u Mode of transportation: – air, truck, rail, ship, pipeline, electronic transportation – vary in cost, speed, size of shipment, flexibility u Route and network selection – route: path along which a product is shipped – network: collection of locations and routes u In-house or outsource u Overall trade-off: Responsiveness versus efficiency © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 15
 Information u Role in the supply chain u Role in the competitive strategy u Components of information decisions © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 16
Information u Role in the supply chain u Role in the competitive strategy u Components of information decisions © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 16
 Information: Role in the Supply Chain u The connection between the various stages in the supply chain – allows coordination between stages u Crucial to daily operation of each stage in a supply chain – e. g. , production scheduling, inventory levels © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 17
Information: Role in the Supply Chain u The connection between the various stages in the supply chain – allows coordination between stages u Crucial to daily operation of each stage in a supply chain – e. g. , production scheduling, inventory levels © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 17
 Information: Role in the Competitive Strategy u Allows supply chain to become more efficient and more responsive at the same time (reduces the need for a trade-off) u Information technology u What information is most valuable? u Example 3. 4: Andersen Windows u Example 3. 5: Dell © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 18
Information: Role in the Competitive Strategy u Allows supply chain to become more efficient and more responsive at the same time (reduces the need for a trade-off) u Information technology u What information is most valuable? u Example 3. 4: Andersen Windows u Example 3. 5: Dell © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 18
 Components of Information Decisions u Push (MRP) versus pull (demand information transmitted quickly throughout the supply chain) u Coordination and information sharing u Forecasting and aggregate planning u Enabling technologies – – EDI Internet ERP systems Supply Chain Management software u Overall © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. trade-off: Responsiveness versus efficiency 19
Components of Information Decisions u Push (MRP) versus pull (demand information transmitted quickly throughout the supply chain) u Coordination and information sharing u Forecasting and aggregate planning u Enabling technologies – – EDI Internet ERP systems Supply Chain Management software u Overall © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. trade-off: Responsiveness versus efficiency 19
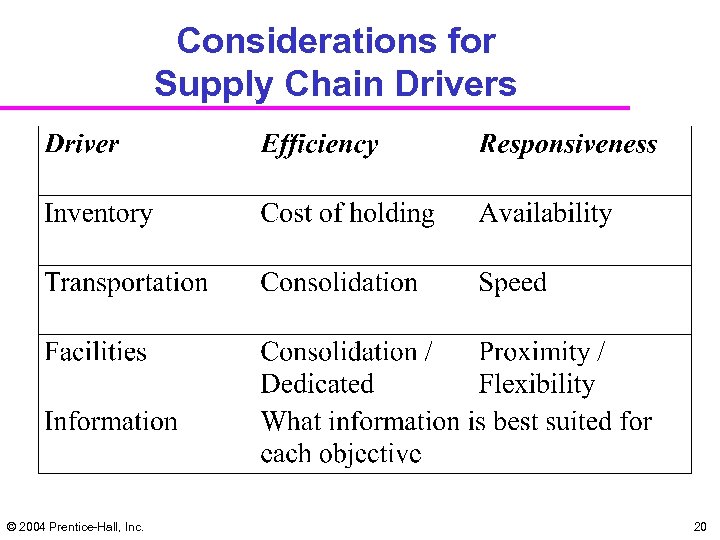 Considerations for Supply Chain Drivers © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 20
Considerations for Supply Chain Drivers © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 20
 Obstacles to Achieving Strategic Fit u Increasing variety of products u Decreasing product life cycles u Increasingly demanding customers u Fragmentation of supply chain ownership u Globalization u Difficulty executing new strategies © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 21
Obstacles to Achieving Strategic Fit u Increasing variety of products u Decreasing product life cycles u Increasingly demanding customers u Fragmentation of supply chain ownership u Globalization u Difficulty executing new strategies © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 21
 Major Obstacles to Achieving Fit u Multiple owners / incentives in a supply chain Local optimization and lack of global fit u Increasing product variety / shrinking life cycles / customer fragmentation Increasing implied uncertainty © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 22
Major Obstacles to Achieving Fit u Multiple owners / incentives in a supply chain Local optimization and lack of global fit u Increasing product variety / shrinking life cycles / customer fragmentation Increasing implied uncertainty © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 22
 Summary u What are the major drivers of supply chain performance? u What is the role of each driver in creating strategic fit between supply chain strategy and competitive strategy (or between implied demand uncertainty and supply chain responsiveness)? u What are the major obstacles to achieving strategic fit? u In the remainder of the course, we will learn how to make decisions with respect to these drivers in order to achieve strategic fit and surmount these obstacles © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 23
Summary u What are the major drivers of supply chain performance? u What is the role of each driver in creating strategic fit between supply chain strategy and competitive strategy (or between implied demand uncertainty and supply chain responsiveness)? u What are the major obstacles to achieving strategic fit? u In the remainder of the course, we will learn how to make decisions with respect to these drivers in order to achieve strategic fit and surmount these obstacles © 2004 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 23


