da8a23cd983097932c9bf0393330adf0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Supply Chain Execution Systems Warehouse Management Systems Lecture Resource Adapted with permission from presentations by John Hill, © 2002, 2003 John M. Hill, ESYNC
Supply Chain Execution Systems Warehouse Management Systems Lecture Resource Adapted with permission from presentations by John Hill, © 2002, 2003 John M. Hill, ESYNC
 Supply Chain Execution Systems (SCES) o o Manage inventory, space, material handling equipment, labor, and transportation resources in real time to assure timely, error-free fulfillment, delivery, and visibility of order status throughout the supply chain Matching material and information flow
Supply Chain Execution Systems (SCES) o o Manage inventory, space, material handling equipment, labor, and transportation resources in real time to assure timely, error-free fulfillment, delivery, and visibility of order status throughout the supply chain Matching material and information flow
 SCES Impact Areas o o Fulfillment Delivery Visibility Responsiveness
SCES Impact Areas o o Fulfillment Delivery Visibility Responsiveness
 Fulfillment and Delivery o o Material handling and controls n Right condition Auto. ID and data collection n Right material Supply chain execution systems n Right time People n Necessary for all of the above
Fulfillment and Delivery o o Material handling and controls n Right condition Auto. ID and data collection n Right material Supply chain execution systems n Right time People n Necessary for all of the above
 Responsiveness o o The best decision making is executed on the basis of events as or before, not after, they occur Responsive logistics systems provide discipline and control that is based not only upon plans and performance goals, but also upon the dynamics of actual operations
Responsiveness o o The best decision making is executed on the basis of events as or before, not after, they occur Responsive logistics systems provide discipline and control that is based not only upon plans and performance goals, but also upon the dynamics of actual operations
 SCES Components o o o Warehouse and Labor Management Transportation Management Yard Management International Trade Logistics Supply Chain Visibility and Event Management
SCES Components o o o Warehouse and Labor Management Transportation Management Yard Management International Trade Logistics Supply Chain Visibility and Event Management
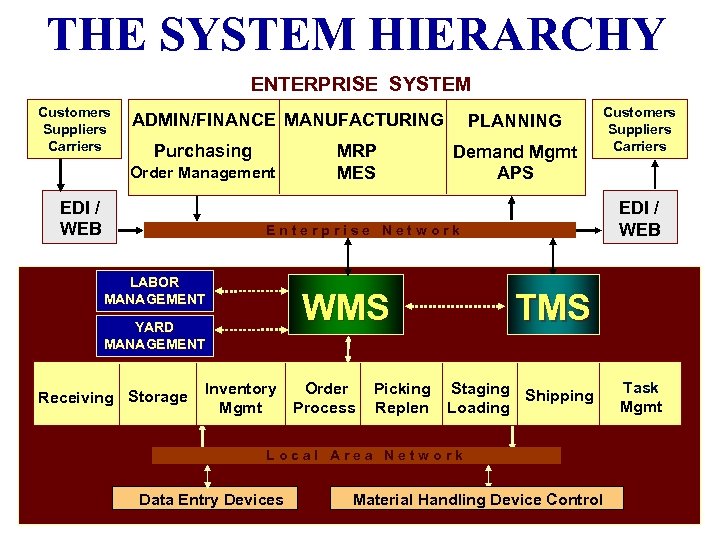 THE SYSTEM HIERARCHY ENTERPRISE SYSTEM Customers Suppliers Carriers ADMIN/FINANCE MANUFACTURING Purchasing Order Management EDI / WEB MRP MES PLANNING Demand Mgmt APS Customers Suppliers Carriers EDI / WEB Enterprise Network LABOR MANAGEMENT WMS YARD MANAGEMENT Receiving Storage Inventory Mgmt Order Process Picking Replen TMS Staging Shipping Loading Local Area Network Data Entry Devices Material Handling Device Control Task Mgmt
THE SYSTEM HIERARCHY ENTERPRISE SYSTEM Customers Suppliers Carriers ADMIN/FINANCE MANUFACTURING Purchasing Order Management EDI / WEB MRP MES PLANNING Demand Mgmt APS Customers Suppliers Carriers EDI / WEB Enterprise Network LABOR MANAGEMENT WMS YARD MANAGEMENT Receiving Storage Inventory Mgmt Order Process Picking Replen TMS Staging Shipping Loading Local Area Network Data Entry Devices Material Handling Device Control Task Mgmt
 Warehouse Management Systems o Manages warehouse inventory, space, equipment, and labor resources to direct the flow of materials and information from receiving and putaway to light assembly, order picking, value-added processing and shipment
Warehouse Management Systems o Manages warehouse inventory, space, equipment, and labor resources to direct the flow of materials and information from receiving and putaway to light assembly, order picking, value-added processing and shipment
 WMS History o o o o 1975: First WMS installed at J. C. Penney. 1986: First WMS installation in “C” on a UNIX platform. 1990’s: Hundreds of new stock locator & WMS systems; Windows NT platform emerges. 1995: MHIA WMS product section formed. 1999: First WMS company reaches annual revenues of $100 million. 2000: Expanded suites with TMS & SCV. Today: User-configurability & scalability remain key differentiators.
WMS History o o o o 1975: First WMS installed at J. C. Penney. 1986: First WMS installation in “C” on a UNIX platform. 1990’s: Hundreds of new stock locator & WMS systems; Windows NT platform emerges. 1995: MHIA WMS product section formed. 1999: First WMS company reaches annual revenues of $100 million. 2000: Expanded suites with TMS & SCV. Today: User-configurability & scalability remain key differentiators.
 WMS Functions o Receiving n n n o Putaway n n n o Blind ASN/EDI Conventional or Automatic Dedicated, Random or Hybrid Location Selection: System or Operator Put Confirmation Picking and Shipping n n Pick by Order, Batch, Wave Pick Confirmation Shipping Check Lists Manifests, Bills of Lading
WMS Functions o Receiving n n n o Putaway n n n o Blind ASN/EDI Conventional or Automatic Dedicated, Random or Hybrid Location Selection: System or Operator Put Confirmation Picking and Shipping n n Pick by Order, Batch, Wave Pick Confirmation Shipping Check Lists Manifests, Bills of Lading
 WMS Differentiators o o o Order Planning & Scheduling Unit of Measure Conversion Location Management / Slotting Inventory Allocation Shelf Life Monitoring Lot & Serial Number Tracking o o o o Cartonization Cycle Counting Replenishment & Consolidation Task Assignment & Monitoring Reverse Logistics Scalability & Configurability Upgrade Support
WMS Differentiators o o o Order Planning & Scheduling Unit of Measure Conversion Location Management / Slotting Inventory Allocation Shelf Life Monitoring Lot & Serial Number Tracking o o o o Cartonization Cycle Counting Replenishment & Consolidation Task Assignment & Monitoring Reverse Logistics Scalability & Configurability Upgrade Support
 WMS Setup o Product Files n n n o Location Files n n o o Descriptions Dimensions Units of Measure Bills of Material Substitutions Numbering / Sequencing Dimensions / Capacity Equipment Files Employee Files
WMS Setup o Product Files n n n o Location Files n n o o Descriptions Dimensions Units of Measure Bills of Material Substitutions Numbering / Sequencing Dimensions / Capacity Equipment Files Employee Files
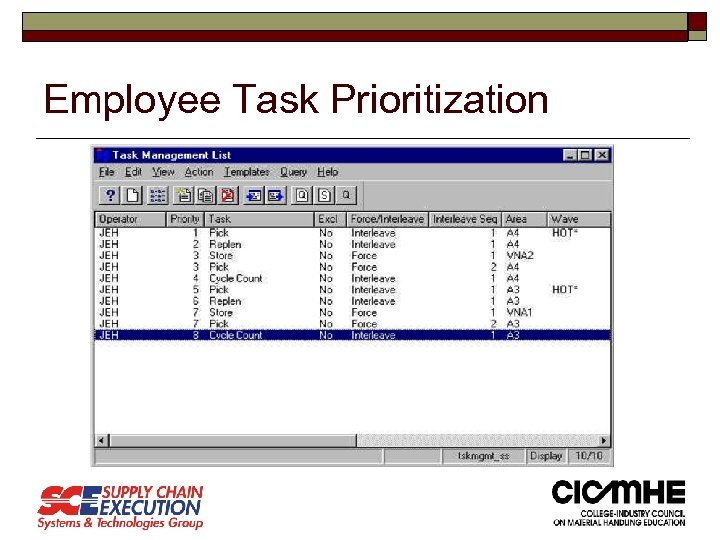 Employee Task Prioritization
Employee Task Prioritization
 Workload Management o Equipment Profiles o Material Profiles o Location Profiles o Operator / Equipment Matrices o Operator / Task Priorities o Labor Standards
Workload Management o Equipment Profiles o Material Profiles o Location Profiles o Operator / Equipment Matrices o Operator / Task Priorities o Labor Standards
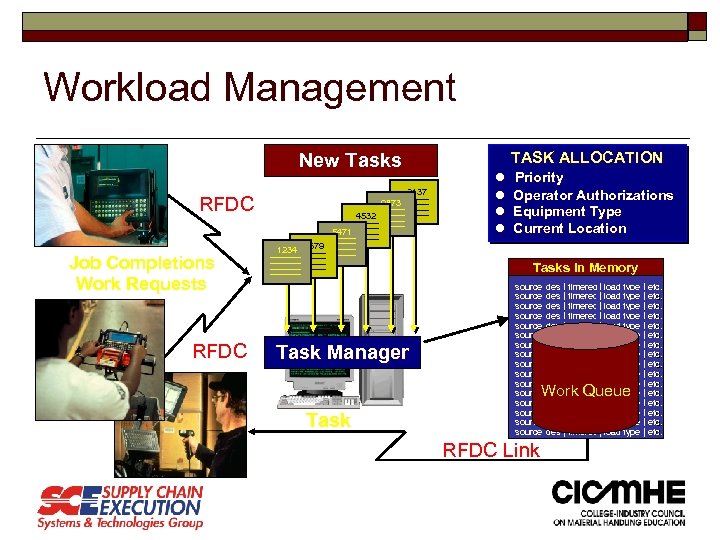 Workload Management TASK ALLOCATION New Tasks 2137 RFDC 9873 4532 5471 Job Completions Work Requests RFDC Priority Operator Authorizations Equipment Type Current Location 1234 3679 Tasks in Memory Task Manager source |dest | time- eq | load type | etc. req r source |dest | time- eq | load type | etc. req r Work Queue Task RFDC Link
Workload Management TASK ALLOCATION New Tasks 2137 RFDC 9873 4532 5471 Job Completions Work Requests RFDC Priority Operator Authorizations Equipment Type Current Location 1234 3679 Tasks in Memory Task Manager source |dest | time- eq | load type | etc. req r source |dest | time- eq | load type | etc. req r Work Queue Task RFDC Link
 Material Handling Interfaces o o o o Conveyor Sortation Palletizer AGVs Pick (Pack)-To-Light Carousel AS/RS
Material Handling Interfaces o o o o Conveyor Sortation Palletizer AGVs Pick (Pack)-To-Light Carousel AS/RS
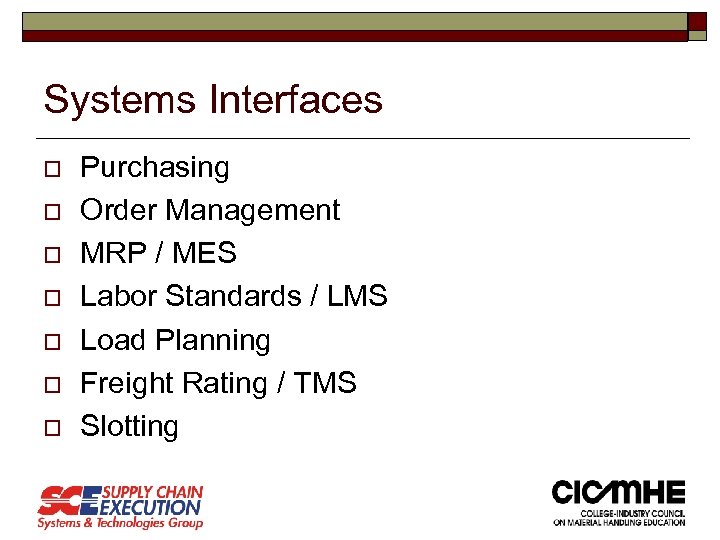 Systems Interfaces o o o o Purchasing Order Management MRP / MES Labor Standards / LMS Load Planning Freight Rating / TMS Slotting
Systems Interfaces o o o o Purchasing Order Management MRP / MES Labor Standards / LMS Load Planning Freight Rating / TMS Slotting
 Receiving o o o o ASNs / Purchase Order Receiving Carrier Appointment Scheduling Pre-Tagged Receipts Blind (Unanticipated) Receipts Load Tagging/Labeling Quality Assurance Returns
Receiving o o o o ASNs / Purchase Order Receiving Carrier Appointment Scheduling Pre-Tagged Receipts Blind (Unanticipated) Receipts Load Tagging/Labeling Quality Assurance Returns
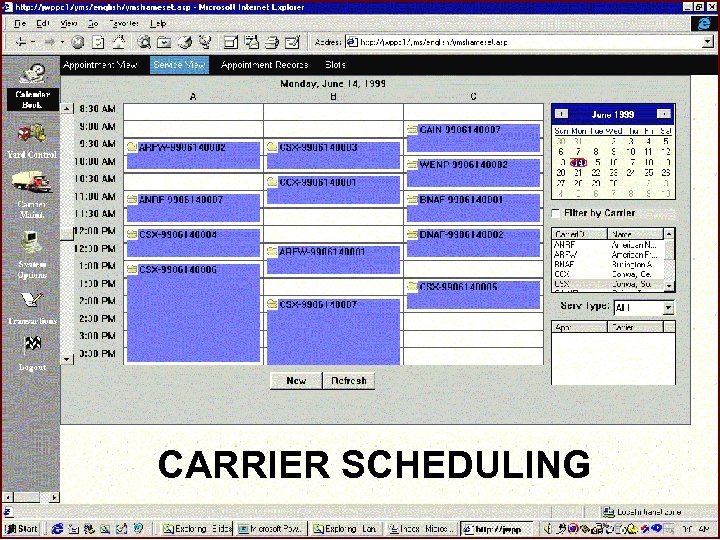 CARRIER SCHEDULING
CARRIER SCHEDULING
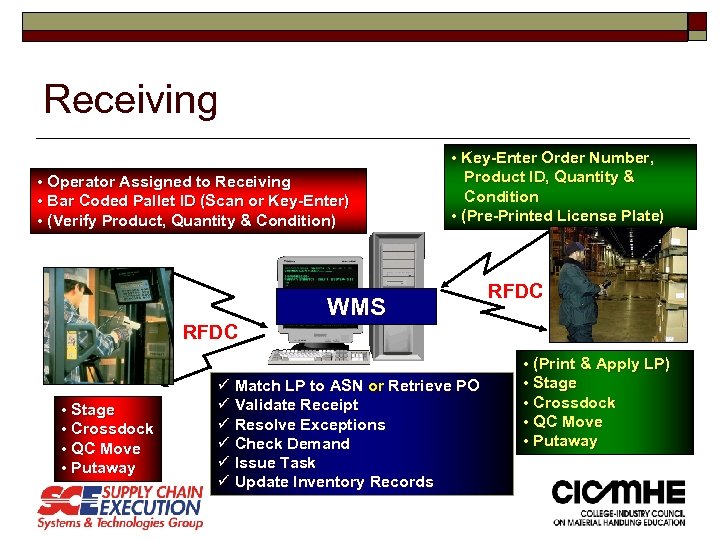 Receiving • Operator Assigned to Receiving • Bar Coded Pallet ID (Scan or Key-Enter) • (Verify Product, Quantity & Condition) RFDC • Stage • Crossdock • QC Move • Putaway • Key-Enter Order Number, Product ID, Quantity & Condition • (Pre-Printed License Plate) WMS ü Match LP to ASN or Retrieve PO ü Validate Receipt ü Resolve Exceptions ü Check Demand ü Issue Task ü Update Inventory Records RFDC • (Print & Apply LP) • Stage • Crossdock • QC Move • Putaway
Receiving • Operator Assigned to Receiving • Bar Coded Pallet ID (Scan or Key-Enter) • (Verify Product, Quantity & Condition) RFDC • Stage • Crossdock • QC Move • Putaway • Key-Enter Order Number, Product ID, Quantity & Condition • (Pre-Printed License Plate) WMS ü Match LP to ASN or Retrieve PO ü Validate Receipt ü Resolve Exceptions ü Check Demand ü Issue Task ü Update Inventory Records RFDC • (Print & Apply LP) • Stage • Crossdock • QC Move • Putaway
 Reverse Logistics HOLIDAYS 2000 e. Sales: $6 Billion Returns: $900 Million Source: Biz. Rate. com Warehouse Wasteland or Competitive Edge?
Reverse Logistics HOLIDAYS 2000 e. Sales: $6 Billion Returns: $900 Million Source: Biz. Rate. com Warehouse Wasteland or Competitive Edge?
 Storage and Putaway o o o Location Selection Override Location Confirmation Crossdocking Relocation Consolidation
Storage and Putaway o o o Location Selection Override Location Confirmation Crossdocking Relocation Consolidation
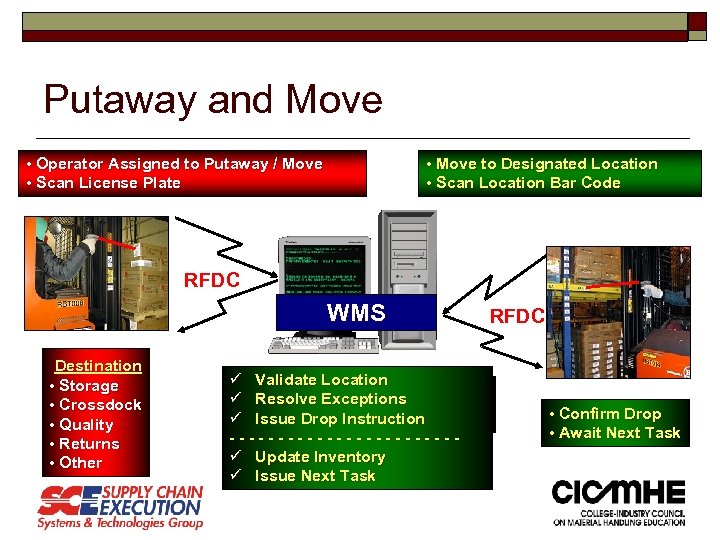 Putaway and Move • Operator Assigned to Putaway / Move • Scan License Plate • Move to Designated Location • Scan Location Bar Code RFDC WMS Destination • Storage • Crossdock • Quality • Returns • Other ü Validate Location ü Resolve Exceptions ü Check Demand for Product ü Issue Drop Instruction -ü -Issue -Move - - - - - Task ü Update Inventory ü Issue Next Task RFDC • Confirm Drop • Await Next Task
Putaway and Move • Operator Assigned to Putaway / Move • Scan License Plate • Move to Designated Location • Scan Location Bar Code RFDC WMS Destination • Storage • Crossdock • Quality • Returns • Other ü Validate Location ü Resolve Exceptions ü Check Demand for Product ü Issue Drop Instruction -ü -Issue -Move - - - - - Task ü Update Inventory ü Issue Next Task RFDC • Confirm Drop • Await Next Task
 Inventory Management o Lot, Date Code, and Serial Number Tracking o Shelf-Life Monitoring and Rotation o Catch Weighing o Routine and Exception Cycle Counting o Full Physicals
Inventory Management o Lot, Date Code, and Serial Number Tracking o Shelf-Life Monitoring and Rotation o Catch Weighing o Routine and Exception Cycle Counting o Full Physicals
 Replenishment o o o Forward Pick Locations Floating Forward Pick Replenishment Trigger Controls Demand Replenishment Batch Replenishment Reslotting
Replenishment o o o Forward Pick Locations Floating Forward Pick Replenishment Trigger Controls Demand Replenishment Batch Replenishment Reslotting
 Pick Planning o o o Host Download Format and Frequency Wave and Batch Planning Material Allocation Order / Shipment Release Changes and Cancellations
Pick Planning o o o Host Download Format and Frequency Wave and Batch Planning Material Allocation Order / Shipment Release Changes and Cancellations
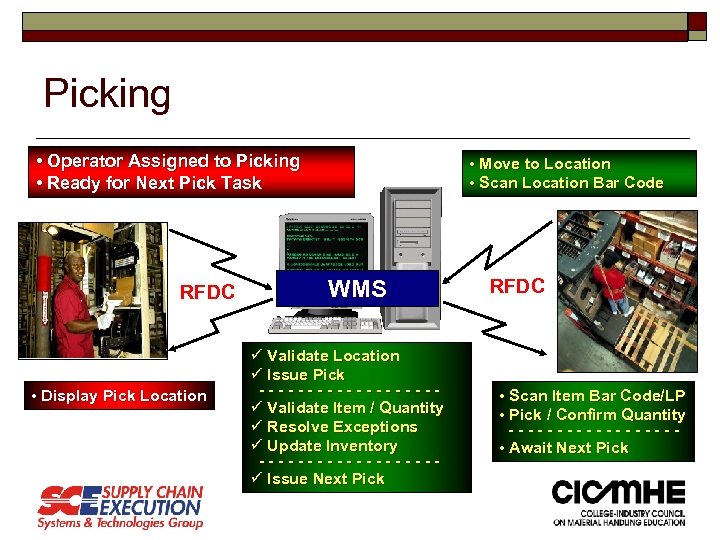 Picking • Operator Assigned to Picking • Ready for Next Pick Task RFDC • Display Pick Location • Move to Location • Scan Location Bar Code WMS ü Validate Location ü Issue Pick ---------ü Validate Item / Quantity ü Resolve Exceptions ü Update Inventory ---------ü Issue Next Pick RFDC • Scan Item Bar Code/LP • Pick / Confirm Quantity --------- • Await Next Pick
Picking • Operator Assigned to Picking • Ready for Next Pick Task RFDC • Display Pick Location • Move to Location • Scan Location Bar Code WMS ü Validate Location ü Issue Pick ---------ü Validate Item / Quantity ü Resolve Exceptions ü Update Inventory ---------ü Issue Next Pick RFDC • Scan Item Bar Code/LP • Pick / Confirm Quantity --------- • Await Next Pick
 Staging and Shipping o o o o Trailer Scheduling / Processing Staging Location Management Staged Load Confirmation Door / Truck Verification Shipping Labels Manifests / Bills of Lading Shipment Confirmation
Staging and Shipping o o o o Trailer Scheduling / Processing Staging Location Management Staged Load Confirmation Door / Truck Verification Shipping Labels Manifests / Bills of Lading Shipment Confirmation
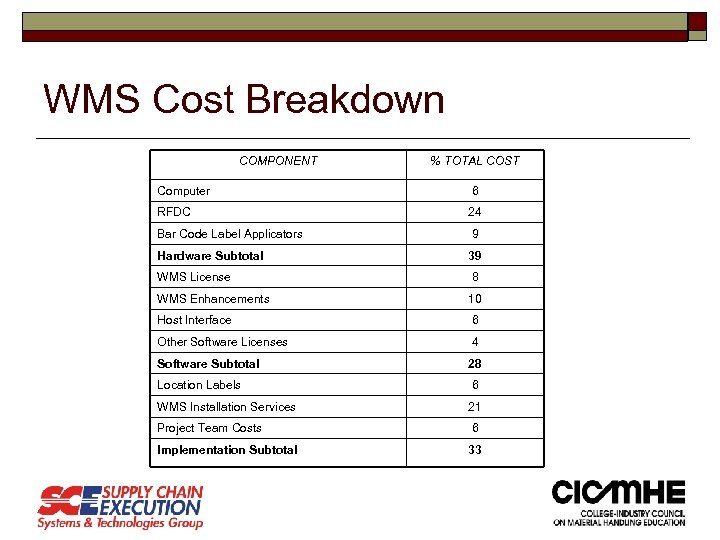 WMS Cost Breakdown COMPONENT % TOTAL COST Computer 6 RFDC 24 Bar Code Label Applicators 9 Hardware Subtotal 39 WMS License 8 WMS Enhancements 10 Host Interface 6 Other Software Licenses 4 Software Subtotal 28 Location Labels 6 WMS Installation Services 21 Project Team Costs 6 Implementation Subtotal 33
WMS Cost Breakdown COMPONENT % TOTAL COST Computer 6 RFDC 24 Bar Code Label Applicators 9 Hardware Subtotal 39 WMS License 8 WMS Enhancements 10 Host Interface 6 Other Software Licenses 4 Software Subtotal 28 Location Labels 6 WMS Installation Services 21 Project Team Costs 6 Implementation Subtotal 33
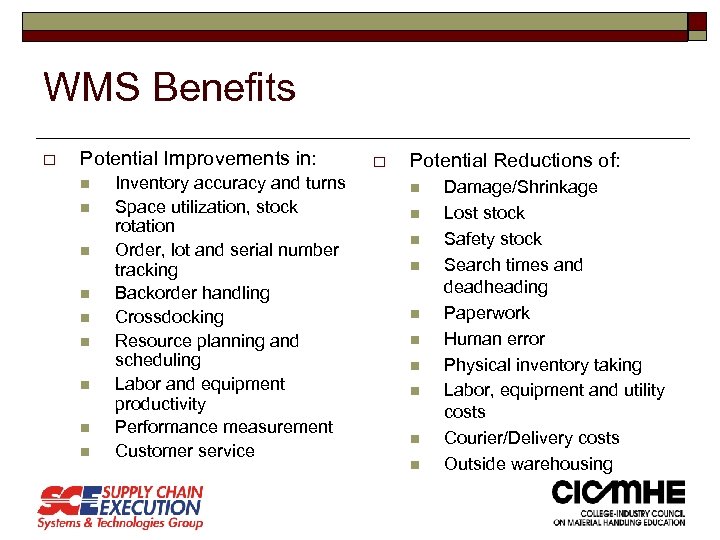 WMS Benefits o Potential Improvements in: n n n n n Inventory accuracy and turns Space utilization, stock rotation Order, lot and serial number tracking Backorder handling Crossdocking Resource planning and scheduling Labor and equipment productivity Performance measurement Customer service o Potential Reductions of: n n n n n Damage/Shrinkage Lost stock Safety stock Search times and deadheading Paperwork Human error Physical inventory taking Labor, equipment and utility costs Courier/Delivery costs Outside warehousing
WMS Benefits o Potential Improvements in: n n n n n Inventory accuracy and turns Space utilization, stock rotation Order, lot and serial number tracking Backorder handling Crossdocking Resource planning and scheduling Labor and equipment productivity Performance measurement Customer service o Potential Reductions of: n n n n n Damage/Shrinkage Lost stock Safety stock Search times and deadheading Paperwork Human error Physical inventory taking Labor, equipment and utility costs Courier/Delivery costs Outside warehousing
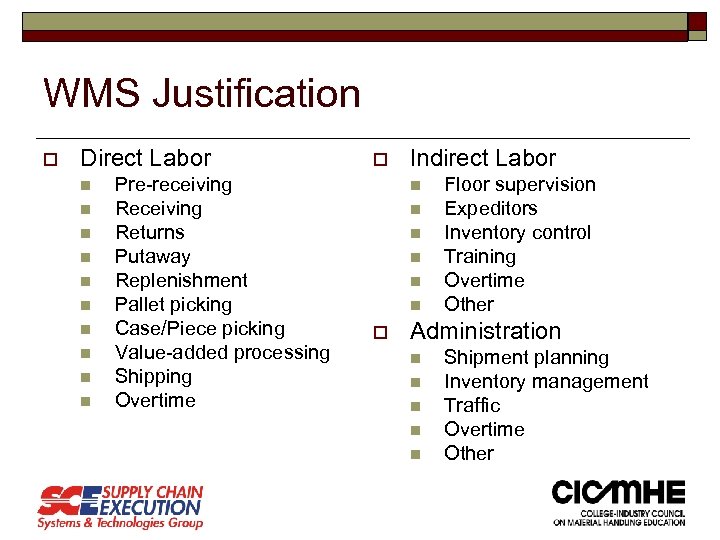 WMS Justification o Direct Labor n n n n n Pre-receiving Returns Putaway Replenishment Pallet picking Case/Piece picking Value-added processing Shipping Overtime o Indirect Labor n n n o Floor supervision Expeditors Inventory control Training Overtime Other Administration n n Shipment planning Inventory management Traffic Overtime Other
WMS Justification o Direct Labor n n n n n Pre-receiving Returns Putaway Replenishment Pallet picking Case/Piece picking Value-added processing Shipping Overtime o Indirect Labor n n n o Floor supervision Expeditors Inventory control Training Overtime Other Administration n n Shipment planning Inventory management Traffic Overtime Other
 WMS Justification o Other Tangible Savings n n n n n Space utilization Transportation Expedited delivery Reduced paperwork Reduced operating costs Damage Shrinkage Perishable loss reduction Storage/picking/shipping errors Physical inventory costs o Intangible Savings n n n n Order cycle times Customer service Inventory turns Reduced obsolescence Lost orders ABC facilitation Performance measurement
WMS Justification o Other Tangible Savings n n n n n Space utilization Transportation Expedited delivery Reduced paperwork Reduced operating costs Damage Shrinkage Perishable loss reduction Storage/picking/shipping errors Physical inventory costs o Intangible Savings n n n n Order cycle times Customer service Inventory turns Reduced obsolescence Lost orders ABC facilitation Performance measurement
 WMS Benchmarking o o Order Fulfillment Inventory Management Warehouse Productivity Transportation Performance
WMS Benchmarking o o Order Fulfillment Inventory Management Warehouse Productivity Transportation Performance
 Order Fulfillment Measures o o o On-time Delivery Order Fill Rate Order Accuracy Line Accuracy Order Cycle Time Perfect Order Completion Percentage
Order Fulfillment Measures o o o On-time Delivery Order Fill Rate Order Accuracy Line Accuracy Order Cycle Time Perfect Order Completion Percentage
 Inventory Management Measures o o o Inventory Accuracy Damaged Inventory Days On Hand Storage Utilization Dock to Stock Time Inventory Visibility
Inventory Management Measures o o o Inventory Accuracy Damaged Inventory Days On Hand Storage Utilization Dock to Stock Time Inventory Visibility
 Warehouse Productivity Measures o o o Orders per Hour Lines per Hour Items per Hour Cost per Order Cost as % of Sales
Warehouse Productivity Measures o o o Orders per Hour Lines per Hour Items per Hour Cost per Order Cost as % of Sales
 Transportation Performance Measures o o o o On-time Deliveries Damage Demurrage Cost Percentage Assessorials Cost Percentage Missed Appointments Percentage Freight Bill Accuracy Cost per Order Cost as % of Sales
Transportation Performance Measures o o o o On-time Deliveries Damage Demurrage Cost Percentage Assessorials Cost Percentage Missed Appointments Percentage Freight Bill Accuracy Cost per Order Cost as % of Sales
 Creating a Responsive WMS o Use contemporary ADC technology and systems to assure n n n o Accurate execution of receiving, storage, and move tasks Error-free picking, replenishment, and shipping Traceability Provide seamless interfaces to other corporate systems to assure n Real-time visibility of inventory availability o n n o by SKU, quantity, lot number, serial number and shelf life by location Real-time order confirmation and status for customers Event-driven exception handling Facilitate a quick match of available resources to current and expected inbound, replenishment, and outbound workload n n Select the best operators and equipment for tasks based upon proximity, skill sets and priority Task operators to immediately store or cross-dock receipts
Creating a Responsive WMS o Use contemporary ADC technology and systems to assure n n n o Accurate execution of receiving, storage, and move tasks Error-free picking, replenishment, and shipping Traceability Provide seamless interfaces to other corporate systems to assure n Real-time visibility of inventory availability o n n o by SKU, quantity, lot number, serial number and shelf life by location Real-time order confirmation and status for customers Event-driven exception handling Facilitate a quick match of available resources to current and expected inbound, replenishment, and outbound workload n n Select the best operators and equipment for tasks based upon proximity, skill sets and priority Task operators to immediately store or cross-dock receipts
 Creating a Responsive WMS o o o o o Support returns processing and reverse logistics Use task interleaving to minimize deadheading Improve order consolidation, wave planning, inventory allocation, and pick sequencing Identify consolidation opportunities to free space and reduce outside storage requirements Support bill of material, work order, and value-added processing Update inventory records as events occur Provide accuracy that allows replacement of full physicals with scheduled cycle counts Time stamp each transaction and identify the operator who performed it Provide feedback to the workforce and support performance measurement Measure supplier and carrier performance
Creating a Responsive WMS o o o o o Support returns processing and reverse logistics Use task interleaving to minimize deadheading Improve order consolidation, wave planning, inventory allocation, and pick sequencing Identify consolidation opportunities to free space and reduce outside storage requirements Support bill of material, work order, and value-added processing Update inventory records as events occur Provide accuracy that allows replacement of full physicals with scheduled cycle counts Time stamp each transaction and identify the operator who performed it Provide feedback to the workforce and support performance measurement Measure supplier and carrier performance
 WMS Trends o o Further industry consolidation as well as alliances with enterprise systems providers Activity based costing and management Embedded profiling tools for space use analysis to facilitate relayout and inventory slotting Object-oriented tool kits for requirements modeling and WMS development
WMS Trends o o Further industry consolidation as well as alliances with enterprise systems providers Activity based costing and management Embedded profiling tools for space use analysis to facilitate relayout and inventory slotting Object-oriented tool kits for requirements modeling and WMS development


