2b8b6b0a48d67e45640fe8f734d3043e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Supplier Evaluation and Selection 1
Supplier Evaluation and Selection 1
 Outline è supplier evaluation & selection (Chapter 7) è industrial practices è effect of operations and culture on supply management 2
Outline è supplier evaluation & selection (Chapter 7) è industrial practices è effect of operations and culture on supply management 2
 Relation Between Chapters Well before … Supplier Evaluation & Selection (Chapter 7) Supplier Management & Development (Chapter 9) Specifications and Operations Standards Supplier Quality Management (Chapter 8)) 3
Relation Between Chapters Well before … Supplier Evaluation & Selection (Chapter 7) Supplier Management & Development (Chapter 9) Specifications and Operations Standards Supplier Quality Management (Chapter 8)) 3
 Chapter 7 Overview è supplier è key evaluation and selection process supplier evaluation criteria è developing a supplier evaluation and selection survey è critical supplier selection issues è reducing supplier evaluation and selection cycle time 4
Chapter 7 Overview è supplier è key evaluation and selection process supplier evaluation criteria è developing a supplier evaluation and selection survey è critical supplier selection issues è reducing supplier evaluation and selection cycle time 4
 Evaluation and Selection Process è no best way, at least no known best way è overall objective: best trade off in maximizing value and minimizing risk è long-term relationship with suppliers 5
Evaluation and Selection Process è no best way, at least no known best way è overall objective: best trade off in maximizing value and minimizing risk è long-term relationship with suppliers 5
 Supplier Selection and Evaluation Recognize the need for supplier selection Identify key sourcing requirements Determine sourcing strategy Identify potential supply sources Limit suppliers in selection pool Determine method of supplier evaluation and selection Select supplier and reach agreement Supplier Evaluation and Selection Process 6
Supplier Selection and Evaluation Recognize the need for supplier selection Identify key sourcing requirements Determine sourcing strategy Identify potential supply sources Limit suppliers in selection pool Determine method of supplier evaluation and selection Select supplier and reach agreement Supplier Evaluation and Selection Process 6
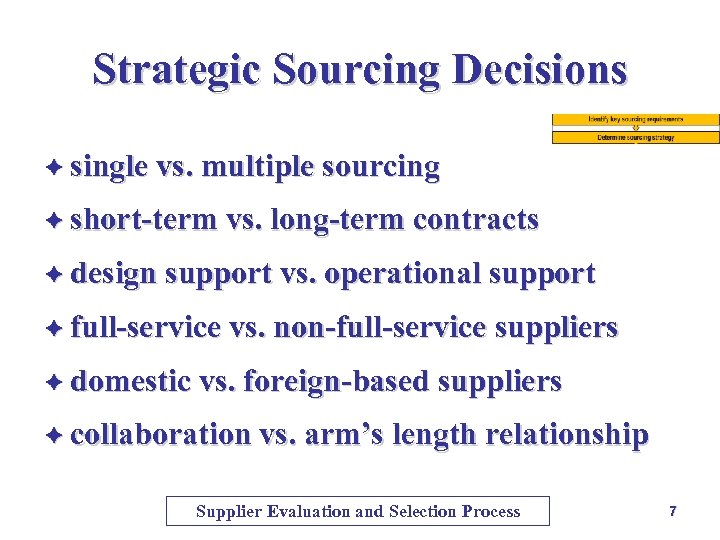 Strategic Sourcing Decisions è single vs. multiple sourcing è short-term vs. long-term contracts è design support vs. operational support è full-service vs. non-full-service suppliers è domestic vs. foreign-based suppliers è collaboration vs. arm’s length relationship Supplier Evaluation and Selection Process 7
Strategic Sourcing Decisions è single vs. multiple sourcing è short-term vs. long-term contracts è design support vs. operational support è full-service vs. non-full-service suppliers è domestic vs. foreign-based suppliers è collaboration vs. arm’s length relationship Supplier Evaluation and Selection Process 7
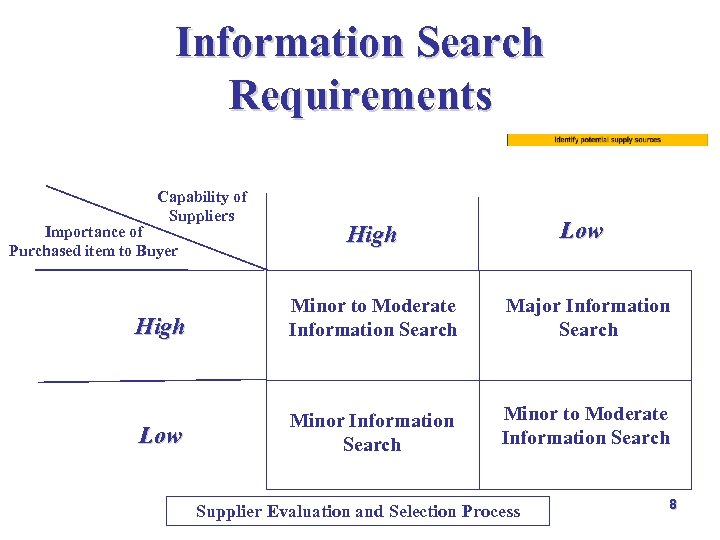 Information Search Requirements Capability of Suppliers Importance of Purchased item to Buyer Low High Minor to Moderate Information Search Major Information Search Low Minor Information Search Minor to Moderate Information Search Supplier Evaluation and Selection Process 8
Information Search Requirements Capability of Suppliers Importance of Purchased item to Buyer Low High Minor to Moderate Information Search Major Information Search Low Minor Information Search Minor to Moderate Information Search Supplier Evaluation and Selection Process 8
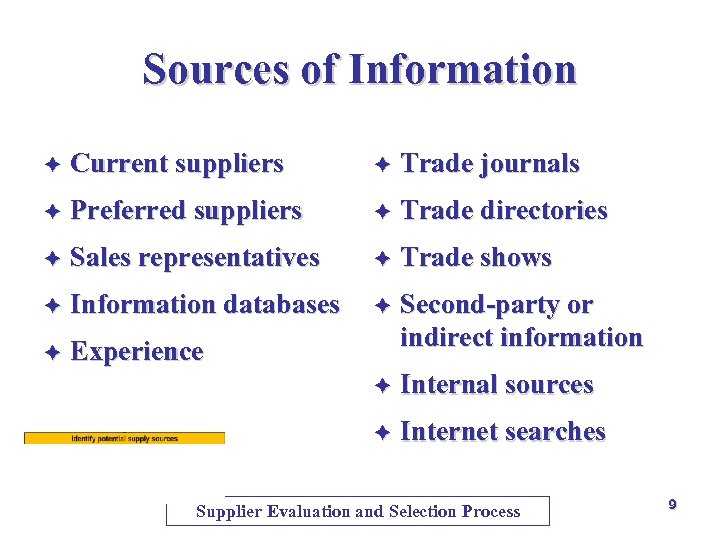 Sources of Information è Current suppliers è Trade journals è Preferred suppliers è Trade directories è Sales representatives è Trade shows è Information databases è è Experience Second-party or indirect information è Internal sources è Internet searches Supplier Evaluation and Selection Process 9
Sources of Information è Current suppliers è Trade journals è Preferred suppliers è Trade directories è Sales representatives è Trade shows è Information databases è è Experience Second-party or indirect information è Internal sources è Internet searches Supplier Evaluation and Selection Process 9
 Sourcing Alternatives è multiple vs. single sourcing è large vs. small suppliers è manufacturer vs. distributor è local, national, or international suppliers Supplier Evaluation and Selection Process 10
Sourcing Alternatives è multiple vs. single sourcing è large vs. small suppliers è manufacturer vs. distributor è local, national, or international suppliers Supplier Evaluation and Selection Process 10
 Limit Suppliers in Selection Pool è removing obviously inappropriate suppliers, by, e. g. , è financial risk analysis è Ex. Dun and Bradstreet reports è evaluation of supplier performance è for existing suppliers è evaluation of supplier-provided information è preliminary surveys (entry qualifiers) Supplier Evaluation and Selection Process 11
Limit Suppliers in Selection Pool è removing obviously inappropriate suppliers, by, e. g. , è financial risk analysis è Ex. Dun and Bradstreet reports è evaluation of supplier performance è for existing suppliers è evaluation of supplier-provided information è preliminary surveys (entry qualifiers) Supplier Evaluation and Selection Process 11
 Methods of Evaluation and Selection è evaluation from supplier-provided information è supplier visits è use of preferred suppliers è external or third-party information Supplier Evaluation and Selection Process 12
Methods of Evaluation and Selection è evaluation from supplier-provided information è supplier visits è use of preferred suppliers è external or third-party information Supplier Evaluation and Selection Process 12
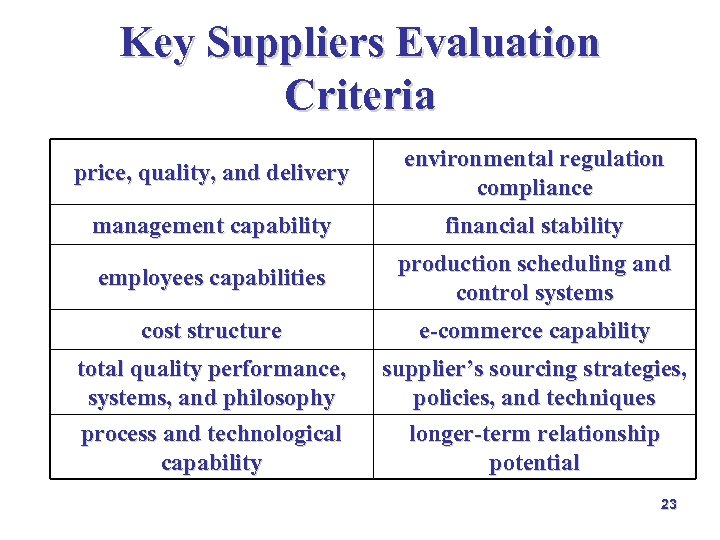
 Key Suppliers Evaluation Criteria è price, quality, and delivery è management capability è employees capabilities è cost structure è total quality performance, systems, and philosophy è process and technological capability Key Supplier Evaluation Criteria 13
Key Suppliers Evaluation Criteria è price, quality, and delivery è management capability è employees capabilities è cost structure è total quality performance, systems, and philosophy è process and technological capability Key Supplier Evaluation Criteria 13
 Key Suppliers Evaluation Criteria è environmental regulation compliance è financial stability è production scheduling and control systems è e-commerce capability è supplier’s sourcing strategies, policies, and techniques è longer-term relationship potential Key Supplier Evaluation Criteria 14
Key Suppliers Evaluation Criteria è environmental regulation compliance è financial stability è production scheduling and control systems è e-commerce capability è supplier’s sourcing strategies, policies, and techniques è longer-term relationship potential Key Supplier Evaluation Criteria 14
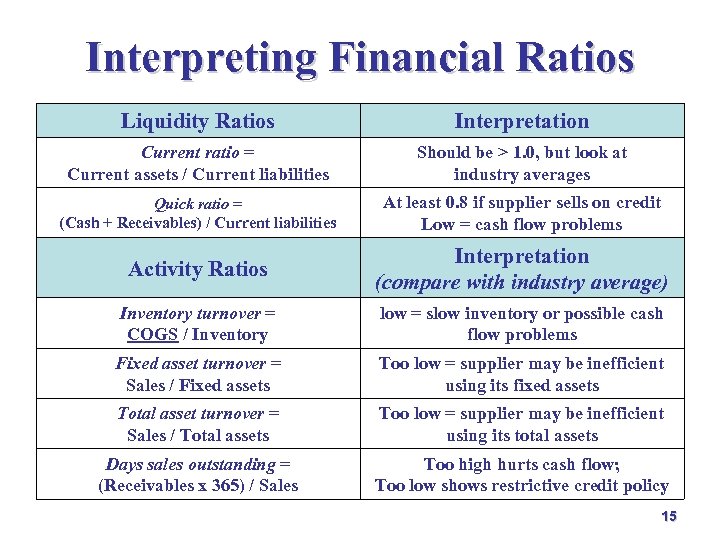 Interpreting Financial Ratios Liquidity Ratios Interpretation Current ratio = Current assets / Current liabilities Should be > 1. 0, but look at industry averages Quick ratio = (Cash + Receivables) / Current liabilities At least 0. 8 if supplier sells on credit Low = cash flow problems Activity Ratios Interpretation (compare with industry average) Inventory turnover = COGS / Inventory low = slow inventory or possible cash flow problems Fixed asset turnover = Sales / Fixed assets Too low = supplier may be inefficient using its fixed assets Total asset turnover = Sales / Total assets Too low = supplier may be inefficient using its total assets Days sales outstanding = (Receivables x 365) / Sales Too high hurts cash flow; Too low shows restrictive credit policy 15
Interpreting Financial Ratios Liquidity Ratios Interpretation Current ratio = Current assets / Current liabilities Should be > 1. 0, but look at industry averages Quick ratio = (Cash + Receivables) / Current liabilities At least 0. 8 if supplier sells on credit Low = cash flow problems Activity Ratios Interpretation (compare with industry average) Inventory turnover = COGS / Inventory low = slow inventory or possible cash flow problems Fixed asset turnover = Sales / Fixed assets Too low = supplier may be inefficient using its fixed assets Total asset turnover = Sales / Total assets Too low = supplier may be inefficient using its total assets Days sales outstanding = (Receivables x 365) / Sales Too high hurts cash flow; Too low shows restrictive credit policy 15
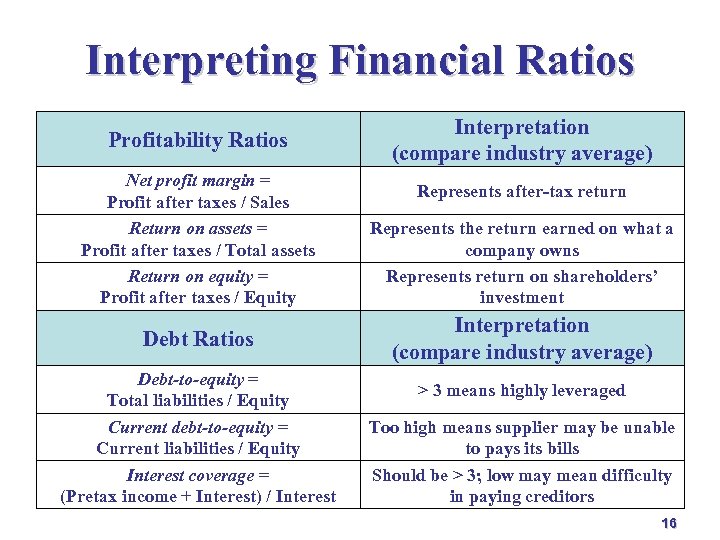 Interpreting Financial Ratios Profitability Ratios Net profit margin = Profit after taxes / Sales Return on assets = Profit after taxes / Total assets Return on equity = Profit after taxes / Equity Debt Ratios Debt-to-equity = Total liabilities / Equity Current debt-to-equity = Current liabilities / Equity Interest coverage = (Pretax income + Interest) / Interest Interpretation (compare industry average) Represents after-tax return Represents the return earned on what a company owns Represents return on shareholders’ investment Interpretation (compare industry average) > 3 means highly leveraged Too high means supplier may be unable to pays its bills Should be > 3; low may mean difficulty in paying creditors 16
Interpreting Financial Ratios Profitability Ratios Net profit margin = Profit after taxes / Sales Return on assets = Profit after taxes / Total assets Return on equity = Profit after taxes / Equity Debt Ratios Debt-to-equity = Total liabilities / Equity Current debt-to-equity = Current liabilities / Equity Interest coverage = (Pretax income + Interest) / Interest Interpretation (compare industry average) Represents after-tax return Represents the return earned on what a company owns Represents return on shareholders’ investment Interpretation (compare industry average) > 3 means highly leveraged Too high means supplier may be unable to pays its bills Should be > 3; low may mean difficulty in paying creditors 16
 Evaluation and Selection Surveys è identify supplier evaluation categories è assign a weight to each category è identify and weight subcategories è define a scoring system for categories and subcategories è evaluate supplier directly è review results and make decision developing a supplier evaluation and selection survey 17
Evaluation and Selection Surveys è identify supplier evaluation categories è assign a weight to each category è identify and weight subcategories è define a scoring system for categories and subcategories è evaluate supplier directly è review results and make decision developing a supplier evaluation and selection survey 17
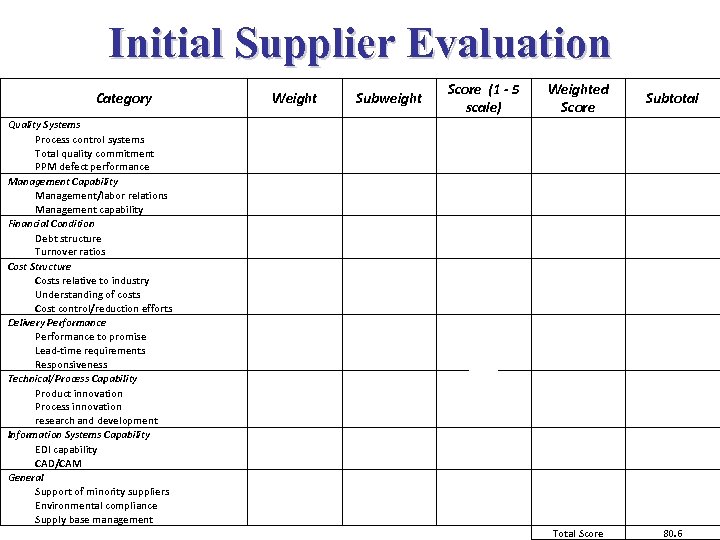 Initial Supplier Evaluation Category Quality Systems Process control systems Total quality commitment PPM defect performance Management Capability Management/labor relations Management capability Financial Condition Debt structure Turnover ratios Cost Structure Costs relative to industry Understanding of costs Cost control/reduction efforts Delivery Performance to promise Lead-time requirements Responsiveness Technical/Process Capability Product innovation Process innovation research and development Information Systems Capability EDI capability CAD/CAM General Support of minority suppliers Environmental compliance Supply base management Weight Subweight Score (1 - 5 scale) Weighted Score Subtotal 20 10 10 15 15 5 10 5 8 7 5 5 5 5 5 5 3 2 2 3 5 4 4 3 4 5 4 5 3 3 3 4 5 5 5 0 3 5 4 4. 0 6. 4 7. 0 4. 0 3. 0 4. 0 5. 0 4. 0 5. 0 3. 0 4. 0 5. 0 3. 0 0. 0 1. 2 3. 0 4. 0 Total Score 17. 4 8. 0 7. 0 14. 0 9. 0 14. 0 3. 0 8. 2 80. 6
Initial Supplier Evaluation Category Quality Systems Process control systems Total quality commitment PPM defect performance Management Capability Management/labor relations Management capability Financial Condition Debt structure Turnover ratios Cost Structure Costs relative to industry Understanding of costs Cost control/reduction efforts Delivery Performance to promise Lead-time requirements Responsiveness Technical/Process Capability Product innovation Process innovation research and development Information Systems Capability EDI capability CAD/CAM General Support of minority suppliers Environmental compliance Supply base management Weight Subweight Score (1 - 5 scale) Weighted Score Subtotal 20 10 10 15 15 5 10 5 8 7 5 5 5 5 5 5 3 2 2 3 5 4 4 3 4 5 4 5 3 3 3 4 5 5 5 0 3 5 4 4. 0 6. 4 7. 0 4. 0 3. 0 4. 0 5. 0 4. 0 5. 0 3. 0 4. 0 5. 0 3. 0 0. 0 1. 2 3. 0 4. 0 Total Score 17. 4 8. 0 7. 0 14. 0 9. 0 14. 0 3. 0 8. 2 80. 6
 Dell Make or Buy 19
Dell Make or Buy 19
 Make or Buy a Technology è merits in either way è general è buy strategy if there are many developers in the market è follow and invest on the winners 20
Make or Buy a Technology è merits in either way è general è buy strategy if there are many developers in the market è follow and invest on the winners 20
 Dell Selecting Suppliers 21
Dell Selecting Suppliers 21
 Selecting an ODM of Notebooks for Dell è 1991, Aug, three potential suppliers Compal (仁寶), Inventec Corporation (英業達), and Quanta (廣達) è è è Compal: most promising Quanta: relatively immature by then result: Inventec Corporation, because of site visits è GM of Compal answered all questions, even cutting answers of subordinates è è insufficient respect for professional, insufficient delegation of power, reliability of answers Inventec Corporation showed division of labor during interview, and provided detailed test in reliability 22
Selecting an ODM of Notebooks for Dell è 1991, Aug, three potential suppliers Compal (仁寶), Inventec Corporation (英業達), and Quanta (廣達) è è è Compal: most promising Quanta: relatively immature by then result: Inventec Corporation, because of site visits è GM of Compal answered all questions, even cutting answers of subordinates è è insufficient respect for professional, insufficient delegation of power, reliability of answers Inventec Corporation showed division of labor during interview, and provided detailed test in reliability 22
 Key Suppliers Evaluation Criteria price, quality, and delivery environmental regulation compliance management capability financial stability employees capabilities production scheduling and control systems cost structure e-commerce capability total quality performance, systems, and philosophy process and technological capability supplier’s sourcing strategies, policies, and techniques longer-term relationship potential 23
Key Suppliers Evaluation Criteria price, quality, and delivery environmental regulation compliance management capability financial stability employees capabilities production scheduling and control systems cost structure e-commerce capability total quality performance, systems, and philosophy process and technological capability supplier’s sourcing strategies, policies, and techniques longer-term relationship potential 23
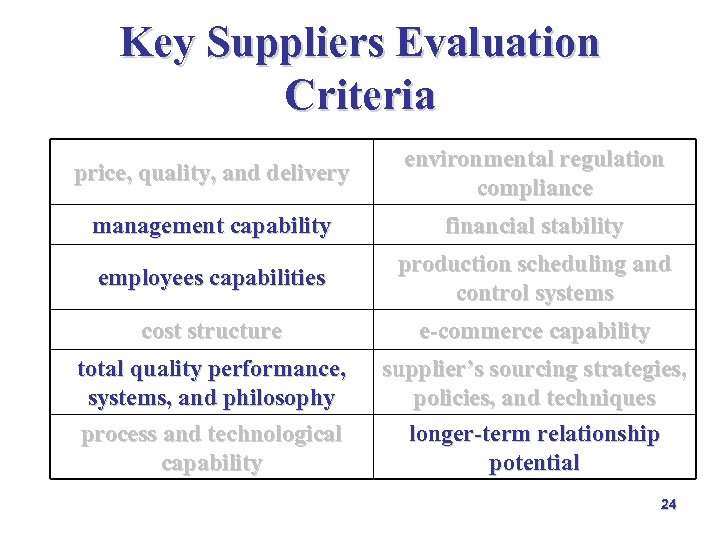 Key Suppliers Evaluation Criteria price, quality, and delivery environmental regulation compliance management capability financial stability employees capabilities production scheduling and control systems cost structure e-commerce capability total quality performance, systems, and philosophy process and technological capability supplier’s sourcing strategies, policies, and techniques longer-term relationship potential 24
Key Suppliers Evaluation Criteria price, quality, and delivery environmental regulation compliance management capability financial stability employees capabilities production scheduling and control systems cost structure e-commerce capability total quality performance, systems, and philosophy process and technological capability supplier’s sourcing strategies, policies, and techniques longer-term relationship potential 24
 Selecting a Supplier of Power Supply for Dell è early 1991, three qualified suppliers: Delta ( 台達)、Lite-On (光寶)、Vidar-SMSCO (三 光惟達) è Delta distant leader è result: Lite-On è Lite-On: proactive and responsive in quotation stage and in preparation of sample 25
Selecting a Supplier of Power Supply for Dell è early 1991, three qualified suppliers: Delta ( 台達)、Lite-On (光寶)、Vidar-SMSCO (三 光惟達) è Delta distant leader è result: Lite-On è Lite-On: proactive and responsive in quotation stage and in preparation of sample 25
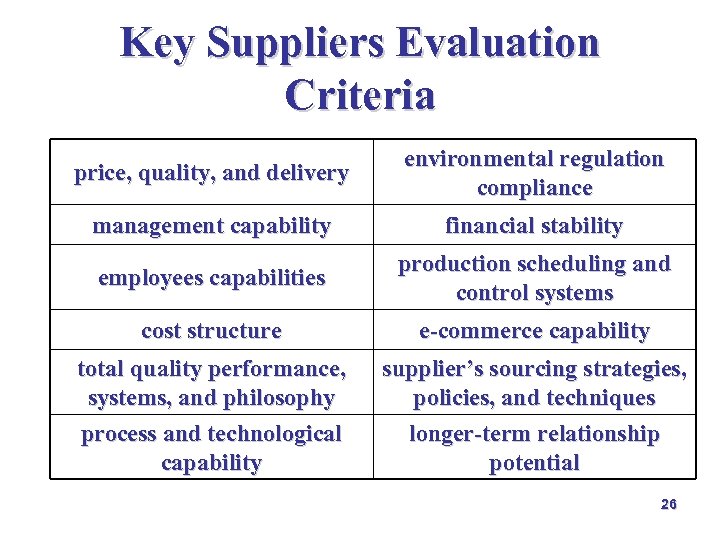 Key Suppliers Evaluation Criteria price, quality, and delivery environmental regulation compliance management capability financial stability employees capabilities production scheduling and control systems cost structure e-commerce capability total quality performance, systems, and philosophy process and technological capability supplier’s sourcing strategies, policies, and techniques longer-term relationship potential 26
Key Suppliers Evaluation Criteria price, quality, and delivery environmental regulation compliance management capability financial stability employees capabilities production scheduling and control systems cost structure e-commerce capability total quality performance, systems, and philosophy process and technological capability supplier’s sourcing strategies, policies, and techniques longer-term relationship potential 26
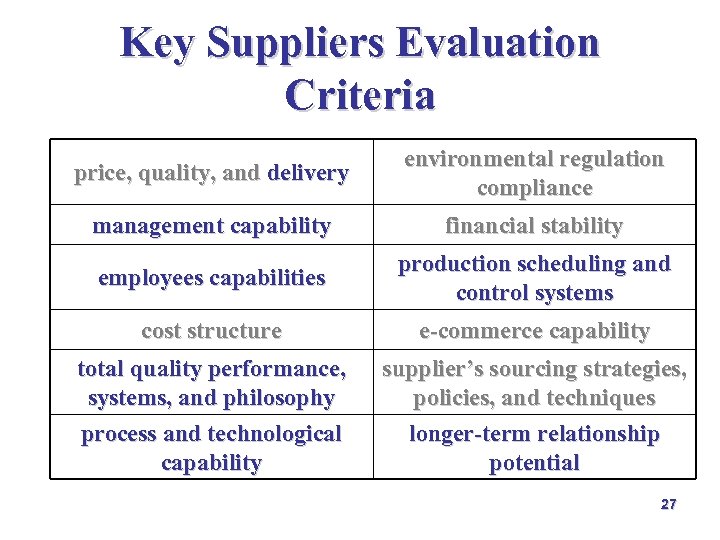 Key Suppliers Evaluation Criteria price, quality, and delivery environmental regulation compliance management capability financial stability employees capabilities production scheduling and control systems cost structure e-commerce capability total quality performance, systems, and philosophy process and technological capability supplier’s sourcing strategies, policies, and techniques longer-term relationship potential 27
Key Suppliers Evaluation Criteria price, quality, and delivery environmental regulation compliance management capability financial stability employees capabilities production scheduling and control systems cost structure e-commerce capability total quality performance, systems, and philosophy process and technological capability supplier’s sourcing strategies, policies, and techniques longer-term relationship potential 27
 Large or Small Suppliers? 28
Large or Small Suppliers? 28
 Which One to Choose from, Large or Small? è possible problems with small ones (first clip: 00: 25: 48 – 00: 28: 53) è unreliable 29
Which One to Choose from, Large or Small? è possible problems with small ones (first clip: 00: 25: 48 – 00: 28: 53) è unreliable 29
 Mc. Donald Selecting Suppliers 30
Mc. Donald Selecting Suppliers 30
 Mc. Donald è competition in the fast food industry è not advanced technology è helpful with resource in marketing and expansion, but not critical è keys è the lowest prices from suppliers è the lowest operations costs è the most appropriate technology è the highest morale in operations è the strongest desire to improve 31
Mc. Donald è competition in the fast food industry è not advanced technology è helpful with resource in marketing and expansion, but not critical è keys è the lowest prices from suppliers è the lowest operations costs è the most appropriate technology è the highest morale in operations è the strongest desire to improve 31
 Mc. Donald è large suppliers played no attention to the strict rules and standards of Mc. Donald è operations è risky standards of Mc. Donald with small ones è unsure technological and financial ability to expand in the pace of Mc. Donald è successfully to turn into organized, efficient, and motivated suppliers 32
Mc. Donald è large suppliers played no attention to the strict rules and standards of Mc. Donald è operations è risky standards of Mc. Donald with small ones è unsure technological and financial ability to expand in the pace of Mc. Donald è successfully to turn into organized, efficient, and motivated suppliers 32
 Effect of Operations and Culture on Supply Management Japanese Influences in Manufacturing Processes 33
Effect of Operations and Culture on Supply Management Japanese Influences in Manufacturing Processes 33
 Relation Between Chapters Well before … Supplier Evaluation & Selection (Chapter 7) Supplier Management & Development (Chapter 9) Specifications and Operations Standards Supplier Quality Management (Chapter 8)) 34
Relation Between Chapters Well before … Supplier Evaluation & Selection (Chapter 7) Supplier Management & Development (Chapter 9) Specifications and Operations Standards Supplier Quality Management (Chapter 8)) 34


