f76a40b5f8702ab47db1b4b745e6ee8e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 66
 Supervisor Drug / Alcohol Training for University of Idaho February 11, 2015
Supervisor Drug / Alcohol Training for University of Idaho February 11, 2015
 Agenda § Cost of Substance Abuse in the Workplace § Impact of alcohol and drug abuse § Signs and Symptoms of Substance Abuse § Stages of Addiction in the Workplace – alcohol and other drugs § Supervisor Responsibilities § Reasonable Suspicion Testing © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 2 2
Agenda § Cost of Substance Abuse in the Workplace § Impact of alcohol and drug abuse § Signs and Symptoms of Substance Abuse § Stages of Addiction in the Workplace – alcohol and other drugs § Supervisor Responsibilities § Reasonable Suspicion Testing © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 2 2
 Substance Abuse and the Workplace i Economic cost of alcohol and drug abuse is estimated at $366 b/year - cancer $171 b; diabetes $131 b (NIDA) i 77% of illegal drug users hold either full-time or parttime jobs i Studies have shown that employees who are substance abusers are more likely to: i. Frequently change jobs i. Show up late or are absent from work i. Be less productive i. Become involved in a workplace accident i. File a workers compensation claim (Source: US Department of Health & Human Services, (2009); The Center for SA Prevention at the US Dept. of HHS) © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 3 3
Substance Abuse and the Workplace i Economic cost of alcohol and drug abuse is estimated at $366 b/year - cancer $171 b; diabetes $131 b (NIDA) i 77% of illegal drug users hold either full-time or parttime jobs i Studies have shown that employees who are substance abusers are more likely to: i. Frequently change jobs i. Show up late or are absent from work i. Be less productive i. Become involved in a workplace accident i. File a workers compensation claim (Source: US Department of Health & Human Services, (2009); The Center for SA Prevention at the US Dept. of HHS) © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 3 3
 Impact of Alcohol and Drug Abuse · $12 billion lost annually to accidents and lost time · Employees who test positive: · Incur 300%+ more health costs · Are 1/3 less productive · Are absent from work three times as often · File twice as many worker’s compensation claims · Use twice as many medical benefits · Are 60% more likely to be responsible for accidents · Each employee pays about $640 per year to cover the cost incurred by substance users © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 4 4
Impact of Alcohol and Drug Abuse · $12 billion lost annually to accidents and lost time · Employees who test positive: · Incur 300%+ more health costs · Are 1/3 less productive · Are absent from work three times as often · File twice as many worker’s compensation claims · Use twice as many medical benefits · Are 60% more likely to be responsible for accidents · Each employee pays about $640 per year to cover the cost incurred by substance users © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 4 4
 Effects of Drugs and Alcohol on Individuals § § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Depression Low self esteem Outbursts Anger Mood swings Weight gain or loss Unkempt appearances Smell of alcohol Slow reaction time Impaired coordination Slowed or slurred speech Irritability Excessive talking Poor motivation or lack of energy § § § § Accidents or injuries Blackouts, sweating, chills Legal problems Poor job performance Family problems Sexual behavior that increases the risk of HIV infection Aggression Burnout Anxiety Paranoia Denial Inability to sit still Limited attention span 5
Effects of Drugs and Alcohol on Individuals § § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Depression Low self esteem Outbursts Anger Mood swings Weight gain or loss Unkempt appearances Smell of alcohol Slow reaction time Impaired coordination Slowed or slurred speech Irritability Excessive talking Poor motivation or lack of energy § § § § Accidents or injuries Blackouts, sweating, chills Legal problems Poor job performance Family problems Sexual behavior that increases the risk of HIV infection Aggression Burnout Anxiety Paranoia Denial Inability to sit still Limited attention span 5
 Effects of Drugs and Alcohol on the Workplace § Performance deterioration § Increased absences § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Productivity decreased Decision making impaired Risk to employee and public safety Decline in employee morale Security risks Employee health issues § § § Tardiness Inaccuracy Missed deadlines Increased accidents Organizational image and community relation issues Risk to overall company profits 6
Effects of Drugs and Alcohol on the Workplace § Performance deterioration § Increased absences § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Productivity decreased Decision making impaired Risk to employee and public safety Decline in employee morale Security risks Employee health issues § § § Tardiness Inaccuracy Missed deadlines Increased accidents Organizational image and community relation issues Risk to overall company profits 6
 Effects of Drugs and Alcohol on Home § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Strained relationship with spouse/ significant other and children DUI’s Deflecting responsibilities Missed events of children – e. g. school plays, games. Isolating behaviors Health problems – medical bills § § § § Legal problems Job loss Financial stressors Borrowing money from others Credit collectors Decreased intimacy Secrets Blaming others 7
Effects of Drugs and Alcohol on Home § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Strained relationship with spouse/ significant other and children DUI’s Deflecting responsibilities Missed events of children – e. g. school plays, games. Isolating behaviors Health problems – medical bills § § § § Legal problems Job loss Financial stressors Borrowing money from others Credit collectors Decreased intimacy Secrets Blaming others 7
 Medical Problems • Cirrhosis of the liver • AIDS • Hepatitis • Tuberculosis • Lung Problems • Certain types of cancer • Higher risk for all cancer • High blood pressure • Heart problems • Diabetes • Pancreatitis • Mental Illness (60% to 75% co-occurring) A sound drug policy and educated workforce helps reduce all these effects © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 8
Medical Problems • Cirrhosis of the liver • AIDS • Hepatitis • Tuberculosis • Lung Problems • Certain types of cancer • Higher risk for all cancer • High blood pressure • Heart problems • Diabetes • Pancreatitis • Mental Illness (60% to 75% co-occurring) A sound drug policy and educated workforce helps reduce all these effects © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 8
 Abuse Using a substance to modify or control mood or state of mind in a manner that is illegal or harmful to oneself or others Potential consequences of abuse include: − − − Accidents or injuries Blackouts Legal problems Poor job performance Family problems Risk-taking behaviors © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 9
Abuse Using a substance to modify or control mood or state of mind in a manner that is illegal or harmful to oneself or others Potential consequences of abuse include: − − − Accidents or injuries Blackouts Legal problems Poor job performance Family problems Risk-taking behaviors © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 9
 How to Recognize Substance Abuse § Observe behaviors, look for changes in behavior, personality and mood § Identify physiological changes—hyperactivity, coordination problems § Remember, it is not your role to diagnose anyone with suspected substance abuse; these are signs and symptoms to respond to cautiously and immediately, but they do not necessarily mean that a person is a substance abuser. © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 10
How to Recognize Substance Abuse § Observe behaviors, look for changes in behavior, personality and mood § Identify physiological changes—hyperactivity, coordination problems § Remember, it is not your role to diagnose anyone with suspected substance abuse; these are signs and symptoms to respond to cautiously and immediately, but they do not necessarily mean that a person is a substance abuser. © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 10
 Work Signs of Substance Abuse • Being careless, repeatedly making mistakes • Damaging equipment or property • Accidents, regardless of whether that individual is the one who is injured • Being unreliable/being a slacker—not carrying one’s load • Showing a lack of detail in performing routine job duties • Being unwilling to follow directions • Being argumentative • Giving elaborate, increasingly unbelievable excuses • Being unresponsive to usual cajoling • Taking unnecessary risks • Disregarding safety for self and others © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 11
Work Signs of Substance Abuse • Being careless, repeatedly making mistakes • Damaging equipment or property • Accidents, regardless of whether that individual is the one who is injured • Being unreliable/being a slacker—not carrying one’s load • Showing a lack of detail in performing routine job duties • Being unwilling to follow directions • Being argumentative • Giving elaborate, increasingly unbelievable excuses • Being unresponsive to usual cajoling • Taking unnecessary risks • Disregarding safety for self and others © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 11
 Addiction • The irresistible compulsion to use alcohol and other drugs despite adverse consequences • Characterized by repeated failures to control use, increased tolerance and increased disruption in the family © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 12
Addiction • The irresistible compulsion to use alcohol and other drugs despite adverse consequences • Characterized by repeated failures to control use, increased tolerance and increased disruption in the family © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 12
 Stages of Chemical Dependency in the Workplace § Stage One § Stage Two – On the job “absenteeism” – Signs of difficulty in personal life – Difficulty concentrating – Complaints of not feeling well – Decreased efficiency – Avoids supervisor – Occasional shortened days • In late • Long lunches • Out early © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. – Increased absenteeism – Difficulty with co-workers (unreasonable resentment) – Borrows money from coworkers with increasing frequency – Excess of excuses/alibis – Reduced performance – Increased minor accidents – Outward signs of abuse • Hangovers • Physical signs 13
Stages of Chemical Dependency in the Workplace § Stage One § Stage Two – On the job “absenteeism” – Signs of difficulty in personal life – Difficulty concentrating – Complaints of not feeling well – Decreased efficiency – Avoids supervisor – Occasional shortened days • In late • Long lunches • Out early © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. – Increased absenteeism – Difficulty with co-workers (unreasonable resentment) – Borrows money from coworkers with increasing frequency – Excess of excuses/alibis – Reduced performance – Increased minor accidents – Outward signs of abuse • Hangovers • Physical signs 13
 Stages of Chemical Dependency in the Workplace § Stage Four § Stage Three – – – – Significant personal losses Decreased self-respect Totally undependable Increased substance abuse Visible physical deterioration Generally incompetent Threat of job loss or actual job loss – Illness, death, imprisonment – Repeated absences of several days (sometimes, without notification) – Broken promises to supervisor – Problems with courts/spouse – Apparent money problems – Extreme fluctuations in personality or mood – Refuses to discuss problems – Underperforming © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 14
Stages of Chemical Dependency in the Workplace § Stage Four § Stage Three – – – – Significant personal losses Decreased self-respect Totally undependable Increased substance abuse Visible physical deterioration Generally incompetent Threat of job loss or actual job loss – Illness, death, imprisonment – Repeated absences of several days (sometimes, without notification) – Broken promises to supervisor – Problems with courts/spouse – Apparent money problems – Extreme fluctuations in personality or mood – Refuses to discuss problems – Underperforming © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 14
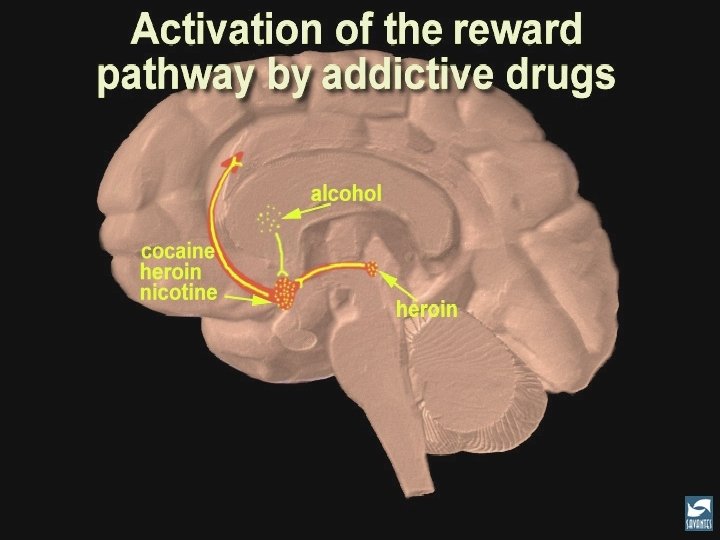 15
15
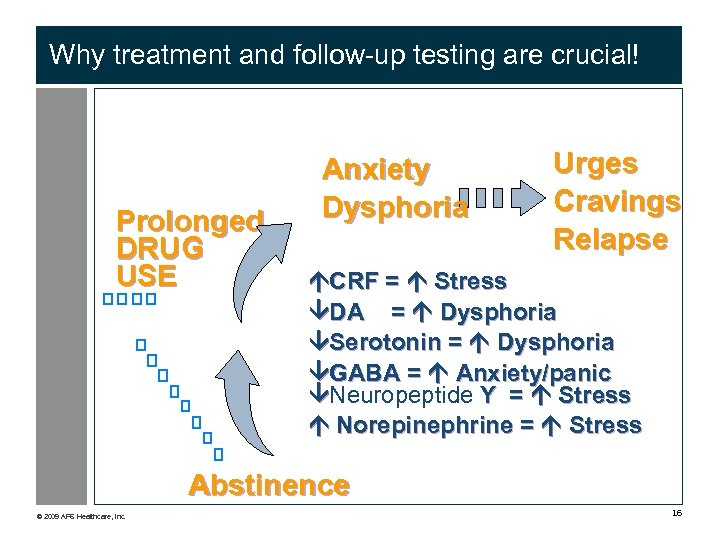 Why treatment and follow-up testing are crucial! Prolonged DRUG USE Anxiety Dysphoria Urges Cravings Relapse CRF = Stress DA = Dysphoria Serotonin = Dysphoria GABA = Anxiety/panic Neuropeptide Y = Stress Norepinephrine = Stress Abstinence © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 16
Why treatment and follow-up testing are crucial! Prolonged DRUG USE Anxiety Dysphoria Urges Cravings Relapse CRF = Stress DA = Dysphoria Serotonin = Dysphoria GABA = Anxiety/panic Neuropeptide Y = Stress Norepinephrine = Stress Abstinence © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 16
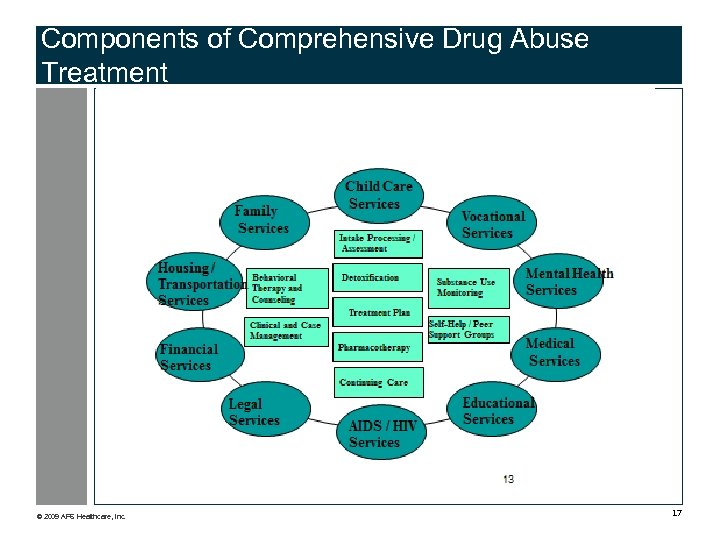 Components of Comprehensive Drug Abuse Treatment © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 17
Components of Comprehensive Drug Abuse Treatment © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 17
 Alcohol and other Drugs § Sedatives § Marijuana § Cocaine § Amphetamines and methamphetamines § Opiates/narcotics § Hallucinogens, psychedelics and PCP © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 18
Alcohol and other Drugs § Sedatives § Marijuana § Cocaine § Amphetamines and methamphetamines § Opiates/narcotics § Hallucinogens, psychedelics and PCP © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 18
 Immediate Effects of Alcohol § § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Odor on breath Initial stimulation, followed by depressed nervous system Flushed skin Glazed appearance of the eyes Slowed reaction time Impaired motor skills Difficulty focusing 19
Immediate Effects of Alcohol § § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Odor on breath Initial stimulation, followed by depressed nervous system Flushed skin Glazed appearance of the eyes Slowed reaction time Impaired motor skills Difficulty focusing 19
 Alcohol § Stays in the body for up to 24 hours § Effects – Body processes. 015 BAC per hour – BAC = 0. 10: Simple reactions, such as braking are 11% slower – BAC = 0. 05 Complex reactions, such as braking, steering and shifting are 41% slower – BAC 0. 5 Usually fatal © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 20
Alcohol § Stays in the body for up to 24 hours § Effects – Body processes. 015 BAC per hour – BAC = 0. 10: Simple reactions, such as braking are 11% slower – BAC = 0. 05 Complex reactions, such as braking, steering and shifting are 41% slower – BAC 0. 5 Usually fatal © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 20
 Blood Alcohol Levels. 02 Mellow feeling, less inhibited, body warmth. 05 Noticeable relaxation, impaired coordination. 08 Limit for DUI, impaired judgment. 10 Noisy, embarrassing behavior, mood swings. 15 Impaired balance, clearly drunk. 30 Many pass out. 40 Most pass out, some die. 50 Breathing stops, many die © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 21
Blood Alcohol Levels. 02 Mellow feeling, less inhibited, body warmth. 05 Noticeable relaxation, impaired coordination. 08 Limit for DUI, impaired judgment. 10 Noisy, embarrassing behavior, mood swings. 15 Impaired balance, clearly drunk. 30 Many pass out. 40 Most pass out, some die. 50 Breathing stops, many die © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 21
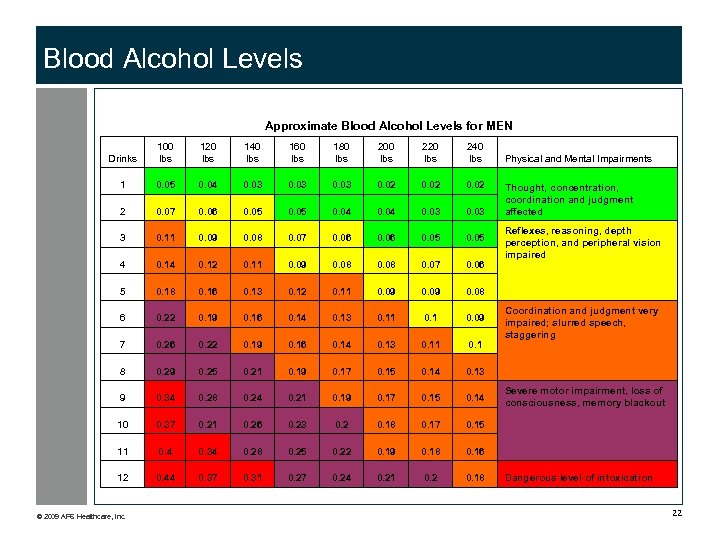 Blood Alcohol Levels Approximate Blood Alcohol Levels for MEN Drinks 100 lbs 120 lbs 140 lbs 160 lbs 180 lbs 200 lbs 220 lbs 240 lbs 1 0. 05 0. 04 0. 03 0. 02 2 0. 07 0. 06 0. 05 0. 04 0. 03 3 0. 11 0. 09 0. 08 0. 07 0. 06 0. 05 4 0. 12 0. 11 0. 09 0. 08 0. 07 0. 06 5 0. 18 0. 16 0. 13 0. 12 0. 11 0. 09 0. 08 6 0. 22 0. 19 0. 16 0. 14 0. 13 0. 11 0. 09 7 0. 26 0. 22 0. 19 0. 16 0. 14 0. 13 0. 11 0. 1 8 0. 29 0. 25 0. 21 0. 19 0. 17 0. 15 0. 14 0. 13 9 0. 34 0. 28 0. 24 0. 21 0. 19 0. 17 0. 15 0. 14 10 0. 37 0. 21 0. 26 0. 23 0. 2 0. 18 0. 17 0. 15 11 0. 4 0. 34 0. 28 0. 25 0. 22 0. 19 0. 18 0. 16 12 0. 44 0. 37 0. 31 0. 27 0. 24 0. 21 0. 2 0. 18 © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Physical and Mental Impairments Thought, concentration, coordination and judgment affected Reflexes, reasoning, depth perception, and peripheral vision impaired Coordination and judgment very impaired; slurred speech, staggering Severe motor impairment, loss of consciousness, memory blackout Dangerous level of intoxication 22
Blood Alcohol Levels Approximate Blood Alcohol Levels for MEN Drinks 100 lbs 120 lbs 140 lbs 160 lbs 180 lbs 200 lbs 220 lbs 240 lbs 1 0. 05 0. 04 0. 03 0. 02 2 0. 07 0. 06 0. 05 0. 04 0. 03 3 0. 11 0. 09 0. 08 0. 07 0. 06 0. 05 4 0. 12 0. 11 0. 09 0. 08 0. 07 0. 06 5 0. 18 0. 16 0. 13 0. 12 0. 11 0. 09 0. 08 6 0. 22 0. 19 0. 16 0. 14 0. 13 0. 11 0. 09 7 0. 26 0. 22 0. 19 0. 16 0. 14 0. 13 0. 11 0. 1 8 0. 29 0. 25 0. 21 0. 19 0. 17 0. 15 0. 14 0. 13 9 0. 34 0. 28 0. 24 0. 21 0. 19 0. 17 0. 15 0. 14 10 0. 37 0. 21 0. 26 0. 23 0. 2 0. 18 0. 17 0. 15 11 0. 4 0. 34 0. 28 0. 25 0. 22 0. 19 0. 18 0. 16 12 0. 44 0. 37 0. 31 0. 27 0. 24 0. 21 0. 2 0. 18 © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Physical and Mental Impairments Thought, concentration, coordination and judgment affected Reflexes, reasoning, depth perception, and peripheral vision impaired Coordination and judgment very impaired; slurred speech, staggering Severe motor impairment, loss of consciousness, memory blackout Dangerous level of intoxication 22
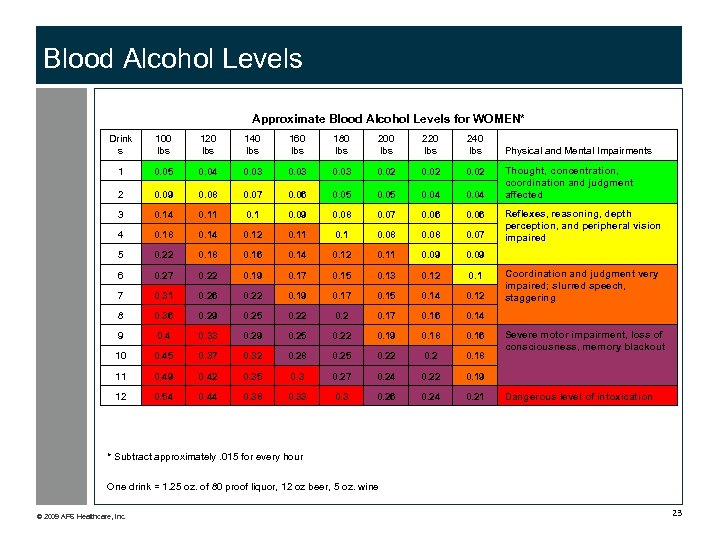 Blood Alcohol Levels Approximate Blood Alcohol Levels for WOMEN* Drink s 100 lbs 120 lbs 140 lbs 160 lbs 180 lbs 200 lbs 220 lbs 240 lbs 1 0. 05 0. 04 0. 03 0. 02 2 0. 09 0. 08 0. 07 0. 06 0. 05 0. 04 3 0. 14 0. 11 0. 09 0. 08 0. 07 0. 06 4 0. 18 0. 14 0. 12 0. 11 0. 08 0. 07 5 0. 22 0. 18 0. 16 0. 14 0. 12 0. 11 0. 09 6 0. 27 0. 22 0. 19 0. 17 0. 15 0. 13 0. 12 0. 1 7 0. 31 0. 26 0. 22 0. 19 0. 17 0. 15 0. 14 0. 12 8 0. 36 0. 29 0. 25 0. 22 0. 17 0. 16 0. 14 9 0. 4 0. 33 0. 29 0. 25 0. 22 0. 19 0. 18 0. 16 10 0. 45 0. 37 0. 32 0. 28 0. 25 0. 22 0. 18 11 0. 49 0. 42 0. 35 0. 3 0. 27 0. 24 0. 22 0. 19 12 0. 54 0. 44 0. 38 0. 33 0. 26 0. 24 0. 21 Physical and Mental Impairments Thought, concentration, coordination and judgment affected Reflexes, reasoning, depth perception, and peripheral vision impaired Coordination and judgment very impaired; slurred speech, staggering Severe motor impairment, loss of consciousness, memory blackout Dangerous level of intoxication * Subtract approximately. 015 for every hour One drink = 1. 25 oz. of 80 proof liquor, 12 oz beer, 5 oz. wine © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 23
Blood Alcohol Levels Approximate Blood Alcohol Levels for WOMEN* Drink s 100 lbs 120 lbs 140 lbs 160 lbs 180 lbs 200 lbs 220 lbs 240 lbs 1 0. 05 0. 04 0. 03 0. 02 2 0. 09 0. 08 0. 07 0. 06 0. 05 0. 04 3 0. 14 0. 11 0. 09 0. 08 0. 07 0. 06 4 0. 18 0. 14 0. 12 0. 11 0. 08 0. 07 5 0. 22 0. 18 0. 16 0. 14 0. 12 0. 11 0. 09 6 0. 27 0. 22 0. 19 0. 17 0. 15 0. 13 0. 12 0. 1 7 0. 31 0. 26 0. 22 0. 19 0. 17 0. 15 0. 14 0. 12 8 0. 36 0. 29 0. 25 0. 22 0. 17 0. 16 0. 14 9 0. 4 0. 33 0. 29 0. 25 0. 22 0. 19 0. 18 0. 16 10 0. 45 0. 37 0. 32 0. 28 0. 25 0. 22 0. 18 11 0. 49 0. 42 0. 35 0. 3 0. 27 0. 24 0. 22 0. 19 12 0. 54 0. 44 0. 38 0. 33 0. 26 0. 24 0. 21 Physical and Mental Impairments Thought, concentration, coordination and judgment affected Reflexes, reasoning, depth perception, and peripheral vision impaired Coordination and judgment very impaired; slurred speech, staggering Severe motor impairment, loss of consciousness, memory blackout Dangerous level of intoxication * Subtract approximately. 015 for every hour One drink = 1. 25 oz. of 80 proof liquor, 12 oz beer, 5 oz. wine © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 23
 So what if I went out last night! § § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 2: 00 AM - Go to bed with BAC of. 19 4: 00 AM - Sleeping with BAC of. 16 6: 00 AM - Get up for work with BAC of. 13 7: 00 AM- Leaving home with BAC of. 115 8: 00 AM- At work with BAC of. 10 9: 00 AM - Spills coffee with BAC of. 085 10: 00 AM - Still impaired at. 07 12: 00 Noon - Still impaired at. 055 24
So what if I went out last night! § § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 2: 00 AM - Go to bed with BAC of. 19 4: 00 AM - Sleeping with BAC of. 16 6: 00 AM - Get up for work with BAC of. 13 7: 00 AM- Leaving home with BAC of. 115 8: 00 AM- At work with BAC of. 10 9: 00 AM - Spills coffee with BAC of. 085 10: 00 AM - Still impaired at. 07 12: 00 Noon - Still impaired at. 055 24
 Sedatives § Sedatives are depressants, typically prescribed for anxiety management or as a sleep aid § They have similar effects to alcohol § High potential for overdose with all sedatives, particularly when combined with alcohol § Look for these signs and symptoms of abuse: – – – © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Eyes react slowly to light Slurred speech Drowsiness Disorientation May mimic alcohol abuse symptoms, but without odor 25
Sedatives § Sedatives are depressants, typically prescribed for anxiety management or as a sleep aid § They have similar effects to alcohol § High potential for overdose with all sedatives, particularly when combined with alcohol § Look for these signs and symptoms of abuse: – – – © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Eyes react slowly to light Slurred speech Drowsiness Disorientation May mimic alcohol abuse symptoms, but without odor 25
 Opiates/Narcotics § Opiates are narcotics, derived from the poppy plant § They are injected into a vein, swallowed, smoked or snorted § In small doses as painkillers, narcotics cause an initial feeling of euphoria § This is followed by drowsiness, nausea and vomiting. § Intoxication cause the pupils of the eyes to constrict, confusion, mental dullness or slurred speech § Heroin is highly addictive; withdrawal symptoms begin within four to six hours after the last injection © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 26
Opiates/Narcotics § Opiates are narcotics, derived from the poppy plant § They are injected into a vein, swallowed, smoked or snorted § In small doses as painkillers, narcotics cause an initial feeling of euphoria § This is followed by drowsiness, nausea and vomiting. § Intoxication cause the pupils of the eyes to constrict, confusion, mental dullness or slurred speech § Heroin is highly addictive; withdrawal symptoms begin within four to six hours after the last injection © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 26
 Opiates § Heroine and prescription drugs – Oxycodone, Oxycontin (up 4 x) (Percodan/Percocet) – Codeine – Methadone – Delaudid – Ultram – Vicodin (Hydrocodone -Lortab) Surge of euphoria ("rush") Warm flushing of the skin Dry mouth, constipation Constricted pupils “On the nod, " an alternately wakeful and drowsy state § Mental functioning becomes clouded § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 27
Opiates § Heroine and prescription drugs – Oxycodone, Oxycontin (up 4 x) (Percodan/Percocet) – Codeine – Methadone – Delaudid – Ultram – Vicodin (Hydrocodone -Lortab) Surge of euphoria ("rush") Warm flushing of the skin Dry mouth, constipation Constricted pupils “On the nod, " an alternately wakeful and drowsy state § Mental functioning becomes clouded § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 27
 Depressants Effects When Operating Machinery § § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Impaired reaction time Visual distortion/pinpoint pupils Lowered concentration Less inhibited, more risk taking React in anger to other motorists High followed by stupor Difficulty focusing 28
Depressants Effects When Operating Machinery § § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Impaired reaction time Visual distortion/pinpoint pupils Lowered concentration Less inhibited, more risk taking React in anger to other motorists High followed by stupor Difficulty focusing 28
 Stimulants § Cocaine (snorted) Crack (smoked) § Amphetamines – Crank, Ice, Crystal, Speed – Methamphetamine • Ecstasy (MDMA) up 2% (stim + halluc) – Prescription Drugs • Ritalin, Concerta, Adderall © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 29
Stimulants § Cocaine (snorted) Crack (smoked) § Amphetamines – Crank, Ice, Crystal, Speed – Methamphetamine • Ecstasy (MDMA) up 2% (stim + halluc) – Prescription Drugs • Ritalin, Concerta, Adderall © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 29
 Immediate Effects § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Euphoria Mind races Dilated pupils Increased blood pressure, heart rate, respiration rate and body temperature 30
Immediate Effects § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Euphoria Mind races Dilated pupils Increased blood pressure, heart rate, respiration rate and body temperature 30
 Stimulants – Signs and Symptoms of Abuse § § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Restlessness and depression Lapses in attention and concentration Aggressive behavior, grandiosity Overreaction, suspiciousness, paranoia Restlessness, talkative but changes subject Sweating/tremulous Blurred vision Dry mouth frequent lip licking; nose bleeds 31
Stimulants – Signs and Symptoms of Abuse § § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Restlessness and depression Lapses in attention and concentration Aggressive behavior, grandiosity Overreaction, suspiciousness, paranoia Restlessness, talkative but changes subject Sweating/tremulous Blurred vision Dry mouth frequent lip licking; nose bleeds 31
 Stimulants - Effects When Operating Machinery § § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Impaired coordination Lapses in attention and concentration Tendency to overreact/overcompensate Impaired judgment Distorted vision and difficulty in seeing False sense of alertness and security Anxiety, irritability, accident prone 32
Stimulants - Effects When Operating Machinery § § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Impaired coordination Lapses in attention and concentration Tendency to overreact/overcompensate Impaired judgment Distorted vision and difficulty in seeing False sense of alertness and security Anxiety, irritability, accident prone 32
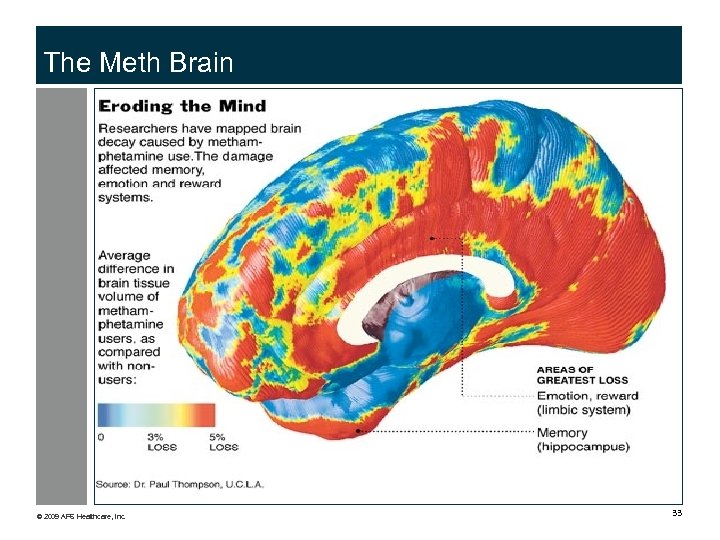 The Meth Brain © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 33
The Meth Brain © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 33
 Faces of Meth © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. (Multnomah County) 34
Faces of Meth © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. (Multnomah County) 34
 Marijuana § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. THC (Pot, grass, joint, reefer. Pot, grass, sinsemilla, blunts, mota, yerba, grifa , Aunt Mary, Boom, Chronic (marijuana alone or marijuana with crack), Dope ganja, Gangster, Hash, Herb, Kif, Mary Jane, Pot, Reefer, Sinsemilla, Skunk, Weed) Hash, hashish Tranquilizes, alters mood; perception Can impact memory, immune function, motivation, anxiety, mood, and cause psychosis (COMT gene). 35
Marijuana § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. THC (Pot, grass, joint, reefer. Pot, grass, sinsemilla, blunts, mota, yerba, grifa , Aunt Mary, Boom, Chronic (marijuana alone or marijuana with crack), Dope ganja, Gangster, Hash, Herb, Kif, Mary Jane, Pot, Reefer, Sinsemilla, Skunk, Weed) Hash, hashish Tranquilizes, alters mood; perception Can impact memory, immune function, motivation, anxiety, mood, and cause psychosis (COMT gene). 35
 Facts On Marijuana § § § Reddened eyes Giddiness Moodiness Slowed reflexes Reduced concentration Problem-solving difficulties § Anxiety/panic © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. § Trance-like state § Short-term memory loss § Slowed speech § Lackadaisical “I don’t care” attitude § Distorted sense of time 36
Facts On Marijuana § § § Reddened eyes Giddiness Moodiness Slowed reflexes Reduced concentration Problem-solving difficulties § Anxiety/panic © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. § Trance-like state § Short-term memory loss § Slowed speech § Lackadaisical “I don’t care” attitude § Distorted sense of time 36
 Signs and Symptoms of Abuse § § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Rapid, loud talking Excessive laughter Sensory distortion Increased appetite Odor similar to burnt rope/sweet grass Paraphernalia Suspiciousness, paranoia 37
Signs and Symptoms of Abuse § § § § © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Rapid, loud talking Excessive laughter Sensory distortion Increased appetite Odor similar to burnt rope/sweet grass Paraphernalia Suspiciousness, paranoia 37
 Facts on Marijuana (cont. ) § Workplace Issues: – – – – © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Delayed decision-making Time distortions Diminished concentration Impaired short-term memory Impaired visual tracking Erratic ability to understand learn Interpersonal conflict/suspiciousness 38
Facts on Marijuana (cont. ) § Workplace Issues: – – – – © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Delayed decision-making Time distortions Diminished concentration Impaired short-term memory Impaired visual tracking Erratic ability to understand learn Interpersonal conflict/suspiciousness 38
 Medical Marijuana Card § Card is protection for owner from getting citation for possession and growing. § Not a prescription or an authorization for DOT or workplace § Does come in prescription forms: Marinol, Cesamet, and Sativex (UK, Canada) used for nausea and pain in patients with CA and MS pain § Rx is safer and can be covered by some insurances and allowed by some employers © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 39
Medical Marijuana Card § Card is protection for owner from getting citation for possession and growing. § Not a prescription or an authorization for DOT or workplace § Does come in prescription forms: Marinol, Cesamet, and Sativex (UK, Canada) used for nausea and pain in patients with CA and MS pain § Rx is safer and can be covered by some insurances and allowed by some employers © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 39
 Hallucinogens Phencyclidine (PCP) § Acts like hallucinogen, depressant/stimulant § Signs and symptoms: – Dilated pupils – Rigid muscles, strange gait – Impaired coordination – Severe confusion – Unpredictable moods (passive to violent) – Jerky eye movements, dilated pupils – Delusions, anxiety, panic, terror – Increased blood pressure – Seizures; convulsions © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 40
Hallucinogens Phencyclidine (PCP) § Acts like hallucinogen, depressant/stimulant § Signs and symptoms: – Dilated pupils – Rigid muscles, strange gait – Impaired coordination – Severe confusion – Unpredictable moods (passive to violent) – Jerky eye movements, dilated pupils – Delusions, anxiety, panic, terror – Increased blood pressure – Seizures; convulsions © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 40
 Phencyclidine: Effects When Operating Machinery § Impaired coordination § Risk-taking behaviors § Reduced concentration § Severe disorientation © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 41
Phencyclidine: Effects When Operating Machinery § Impaired coordination § Risk-taking behaviors § Reduced concentration § Severe disorientation © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 41
 Other Drugs of Concern § Salvia Divnorum (Sal, Magic Mint, Mystic Sage) – – Herb found in Sierra Mazatec Region in Mexico Used as psychedelic and smoked Stimulates opioid receptors Analgesia, hallucinations, changes in visual perception, mood, and external reality, difficulty interacting with self/surroundings, Dizziness – People like it for the “trip, ” happiness, hallucinations – Dislike it for short duration, fatigue, heaviness, dizziness – Oral use from liquid extract, leaves, tea, pills, seeds © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 42
Other Drugs of Concern § Salvia Divnorum (Sal, Magic Mint, Mystic Sage) – – Herb found in Sierra Mazatec Region in Mexico Used as psychedelic and smoked Stimulates opioid receptors Analgesia, hallucinations, changes in visual perception, mood, and external reality, difficulty interacting with self/surroundings, Dizziness – People like it for the “trip, ” happiness, hallucinations – Dislike it for short duration, fatigue, heaviness, dizziness – Oral use from liquid extract, leaves, tea, pills, seeds © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 42
 Other Drugs of Concern § Synthetic Marijuana (K 2; Spice, Serenity, Genie, Hush, etc. ) – Ingredient (JWH) impacts canabinoid receptors – Dry mouth, Light headed, blurred vision, agitation, restlessness, normal pupils, perceptual changes, time distortion, mild anxiety/paranoia, sedation, exhaustion – Up to 4 times more powerful than marijuana – March 1 st 2011 DEA banned possession and distribution © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 43
Other Drugs of Concern § Synthetic Marijuana (K 2; Spice, Serenity, Genie, Hush, etc. ) – Ingredient (JWH) impacts canabinoid receptors – Dry mouth, Light headed, blurred vision, agitation, restlessness, normal pupils, perceptual changes, time distortion, mild anxiety/paranoia, sedation, exhaustion – Up to 4 times more powerful than marijuana – March 1 st 2011 DEA banned possession and distribution © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 43
 Other Drugs of Concern § Synthetic Stimulants (Bath Salts, Plant food, Ivory wave, Red Dove, Blue silk, Cloud Nine and, etc. ) – Active Ingredients vary: MPDV, Mephedrone, Pyrovalerone – Cocaine/Meth-like effects including, aggression, paranoia, suicide – Intense cravings, high risk for overdose – increased ER visits – deaths reported in US and Europe – White House has issued ER alerts -- Legislation to ban in HI, MI, LA, KY © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 44
Other Drugs of Concern § Synthetic Stimulants (Bath Salts, Plant food, Ivory wave, Red Dove, Blue silk, Cloud Nine and, etc. ) – Active Ingredients vary: MPDV, Mephedrone, Pyrovalerone – Cocaine/Meth-like effects including, aggression, paranoia, suicide – Intense cravings, high risk for overdose – increased ER visits – deaths reported in US and Europe – White House has issued ER alerts -- Legislation to ban in HI, MI, LA, KY © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 44
 Inhalants § Volatile Solvents – Thinners, removers, cleaning fluids, gas (benzene, toulene), glues, correction fluid, felt markers § Aerosols (propellants contain solvents) – Spray paints, deodorants, cooking sprays, fabric sprays § Gases (i. e. , medical gases) – Ether, chloroform, nitrous oxide (whipped cream can), butane lighters, refrigerants (Freon) § Nitrites (work by dilating blood vessels/relax muscles) – Cyclohexyl nitrite, isobutyl nitrite, amyl nitrite (video head cleaner, room deodorizer, leather cleaner, liquid aroma). – Used to enhance sexual experience © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 45
Inhalants § Volatile Solvents – Thinners, removers, cleaning fluids, gas (benzene, toulene), glues, correction fluid, felt markers § Aerosols (propellants contain solvents) – Spray paints, deodorants, cooking sprays, fabric sprays § Gases (i. e. , medical gases) – Ether, chloroform, nitrous oxide (whipped cream can), butane lighters, refrigerants (Freon) § Nitrites (work by dilating blood vessels/relax muscles) – Cyclohexyl nitrite, isobutyl nitrite, amyl nitrite (video head cleaner, room deodorizer, leather cleaner, liquid aroma). – Used to enhance sexual experience © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 45
 Inhalants § Signs – Chemical odors on breath/clothing – Paint/stains on face/hands/cloths – Hidden empty containers/soaked rags – Drunk/disoriented appearance – Slurred speech – Nausea or loss of appetite – Inattentiveness, lack of coordination, irritability, depression. © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 46
Inhalants § Signs – Chemical odors on breath/clothing – Paint/stains on face/hands/cloths – Hidden empty containers/soaked rags – Drunk/disoriented appearance – Slurred speech – Nausea or loss of appetite – Inattentiveness, lack of coordination, irritability, depression. © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 46
 Drug Abuse and Mental Illness § Signs of drug use similar to symptoms of mental illness… – Depression • Irritable, angry, sad, anergia, amotivation, anhedonia, problems concentrating, hopelessness – Mania • Racing mind/speech, irritable, euphoria, grandeur, many started projects, spending © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 47
Drug Abuse and Mental Illness § Signs of drug use similar to symptoms of mental illness… – Depression • Irritable, angry, sad, anergia, amotivation, anhedonia, problems concentrating, hopelessness – Mania • Racing mind/speech, irritable, euphoria, grandeur, many started projects, spending © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 47
 Drug Abuse and Mental Illness § Mental illnesses – Psychotic Disorder • Audio/visual hallucinations, flat affect, depression – Anxiety • Irritability, fearful, avoidance, panic symptoms, agoraphobia § Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) – Covers Chemical Dependency/Abuse – Does not cover if test positive © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 48
Drug Abuse and Mental Illness § Mental illnesses – Psychotic Disorder • Audio/visual hallucinations, flat affect, depression – Anxiety • Irritability, fearful, avoidance, panic symptoms, agoraphobia § Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) – Covers Chemical Dependency/Abuse – Does not cover if test positive © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 48
 Drug / Alcohol Testing § Types of testing – – – © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Pre-employment Post-accident Random Reasonable Suspicion Return to duty Follow-up 49
Drug / Alcohol Testing § Types of testing – – – © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. Pre-employment Post-accident Random Reasonable Suspicion Return to duty Follow-up 49
 Review of General Signs and Symptoms of Use DRUGS • Dilated pupils, red eyes • Slowed reactions • Dizziness • Impaired motor skills • Blush colored skin • Inability to concentrate • Dry mouth ALCOHOL • Odor- breath or body • Bloodshot or glazed eyes • Slowed reaction • Slurred speech • Impaired motor skills • Flushed skins • Loss of Balance http: //www. ncadd. org/index. php/learn-about-alcohol/signs-and-symptoms © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 50
Review of General Signs and Symptoms of Use DRUGS • Dilated pupils, red eyes • Slowed reactions • Dizziness • Impaired motor skills • Blush colored skin • Inability to concentrate • Dry mouth ALCOHOL • Odor- breath or body • Bloodshot or glazed eyes • Slowed reaction • Slurred speech • Impaired motor skills • Flushed skins • Loss of Balance http: //www. ncadd. org/index. php/learn-about-alcohol/signs-and-symptoms © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 50
 Detection Periods for Drugs / Alcohol DRUG DETECTION PERIOD Alcohol Amphetamine Cocaine Heroin PCP (Phencyclidine) 3 -10 Hours 1 -2 Days 5 Hours 1 -2 Days 2 -8 Hours © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 51
Detection Periods for Drugs / Alcohol DRUG DETECTION PERIOD Alcohol Amphetamine Cocaine Heroin PCP (Phencyclidine) 3 -10 Hours 1 -2 Days 5 Hours 1 -2 Days 2 -8 Hours © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 51
 Detection Periods for Drugs (continued) THC (Marijuana) 1 Joint -- 2 Days 3 Times/wk -- 2 Weeks Daily -- 3 -6 Weeks * Body fat has impact on duration © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 52
Detection Periods for Drugs (continued) THC (Marijuana) 1 Joint -- 2 Days 3 Times/wk -- 2 Weeks Daily -- 3 -6 Weeks * Body fat has impact on duration © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 52
 Reasonable Suspicion Drug and Alcohol Testing • Reasonable suspicion means– You have reason to believe an employee has used alcohol or drugs in the workplace, OR – An employee is unable to perform his/her job safely because of being under the influence of drugs and alcohol, regardless of when that use occurred. • Reasonable suspicion testing– Employee may be required to submit to drug/alcohol screening whenever the Institution has a reasonable suspicion that they are under the influence of drugs or alcohol while working. © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 53
Reasonable Suspicion Drug and Alcohol Testing • Reasonable suspicion means– You have reason to believe an employee has used alcohol or drugs in the workplace, OR – An employee is unable to perform his/her job safely because of being under the influence of drugs and alcohol, regardless of when that use occurred. • Reasonable suspicion testing– Employee may be required to submit to drug/alcohol screening whenever the Institution has a reasonable suspicion that they are under the influence of drugs or alcohol while working. © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 53
 Reasonable Suspicion Testing Process • Identifying – Observing specific, articulable work performance, behaviors, and/or appearance – During, just preceding, or just after shift/work period – Use University of Idaho Reasonable Suspicion Determination Checklist and Documentation Form • Example: Employee is extremely fatigued or sleeping on the job • Example: Employee falls down, slurs words, smells of alcohol – Have second trained supervisor confirm observation • Documenting – Record behavior or patterns of behavior, include witnesses, and • Example: On May 31, xxxx, at 2 pm, Team Lead Joan S. and I observed Employee X falling down to the ground and said employee’s breath smelled of alcohol, employee needed help to stand up. © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 54
Reasonable Suspicion Testing Process • Identifying – Observing specific, articulable work performance, behaviors, and/or appearance – During, just preceding, or just after shift/work period – Use University of Idaho Reasonable Suspicion Determination Checklist and Documentation Form • Example: Employee is extremely fatigued or sleeping on the job • Example: Employee falls down, slurs words, smells of alcohol – Have second trained supervisor confirm observation • Documenting – Record behavior or patterns of behavior, include witnesses, and • Example: On May 31, xxxx, at 2 pm, Team Lead Joan S. and I observed Employee X falling down to the ground and said employee’s breath smelled of alcohol, employee needed help to stand up. © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 54
 Supervisor Steps § Meet with employee (along with Human Resources/ Manager if appropriate) – – – – – As soon as possible Review observation document with employee Be specific, stick to the facts Focus on job performance only Show support and concern for all, sticking to performance Keep it private and confidential Have the employee sign the document Notify HR if the employee refuses testing Do not allow employee to drive to test site; arrange for transportation © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 55
Supervisor Steps § Meet with employee (along with Human Resources/ Manager if appropriate) – – – – – As soon as possible Review observation document with employee Be specific, stick to the facts Focus on job performance only Show support and concern for all, sticking to performance Keep it private and confidential Have the employee sign the document Notify HR if the employee refuses testing Do not allow employee to drive to test site; arrange for transportation © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 55
 When Speaking with Employees § Don’t − − − − − Be judgmental Humiliate Create win/lose situations Talk to other co-workers about your concern—rumors can be vicious Rescue the abuser from the consequences of substance abuse Take the abuser’s drug use personally; he or she is not abusing drugs because of you or something you may or may not have done Get angry Blame the other person Criticize © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 56
When Speaking with Employees § Don’t − − − − − Be judgmental Humiliate Create win/lose situations Talk to other co-workers about your concern—rumors can be vicious Rescue the abuser from the consequences of substance abuse Take the abuser’s drug use personally; he or she is not abusing drugs because of you or something you may or may not have done Get angry Blame the other person Criticize © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 56
 Question: What does a positive test mean? Saint? Sot? Sampler? Sufferer? -Common to make judgments and treat differently - Beneficial to view as a policy violation rendering them “technically incapacitated” to do certain work. © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 57
Question: What does a positive test mean? Saint? Sot? Sampler? Sufferer? -Common to make judgments and treat differently - Beneficial to view as a policy violation rendering them “technically incapacitated” to do certain work. © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 57
 EAP as Possible Resource § Employee tests positive/refuses test/self discloses substance problem § HR notifies EAP – Employee history, MRO results (including levels), safety concerns – Has Employee sign ROI to EAP § Face-to-face clinical evaluation with EAP – Clinical history – CD screen including – Referral to CD Treatment – Referral for other treatment as indicated – Levels of CD interventions • ADIS, Individual, Outpatient, Inpatient © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 58
EAP as Possible Resource § Employee tests positive/refuses test/self discloses substance problem § HR notifies EAP – Employee history, MRO results (including levels), safety concerns – Has Employee sign ROI to EAP § Face-to-face clinical evaluation with EAP – Clinical history – CD screen including – Referral to CD Treatment – Referral for other treatment as indicated – Levels of CD interventions • ADIS, Individual, Outpatient, Inpatient © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 58
 EAP Service Flow § EAP obtains release to CD agency § Employee begins treatment services § Employee returns to duty after RTD test § EAP supports employee with continued sessions, monitors progress and informs HR until treatment is completed © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 59
EAP Service Flow § EAP obtains release to CD agency § Employee begins treatment services § Employee returns to duty after RTD test § EAP supports employee with continued sessions, monitors progress and informs HR until treatment is completed © 2009 APS Healthcare, Inc. 59
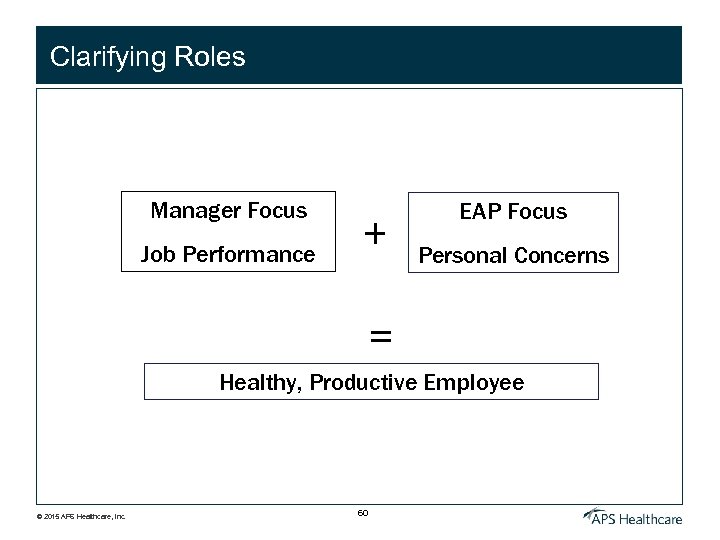 Clarifying Roles Manager Focus Job Performance + EAP Focus Personal Concerns = Healthy, Productive Employee © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 60
Clarifying Roles Manager Focus Job Performance + EAP Focus Personal Concerns = Healthy, Productive Employee © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 60
 General Guidelines When Recommending the EAP • Personal problems affect a person’s quality of life and negatively affect their ability to perform effectively on the job • Employees may frequently deny that they are having problems, be unaware of the problems or don’t know where to turn for help • Employees may be resistant or embarrassed about needing help • Managers are in a great position to motivate employees to get help by connecting them to the EAP © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 61
General Guidelines When Recommending the EAP • Personal problems affect a person’s quality of life and negatively affect their ability to perform effectively on the job • Employees may frequently deny that they are having problems, be unaware of the problems or don’t know where to turn for help • Employees may be resistant or embarrassed about needing help • Managers are in a great position to motivate employees to get help by connecting them to the EAP © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 61
 Tips on Referring Employees to EAP Mention EAP in general, but refrain from discussing specific services Suggested: “I want to be sure you are aware of our EAP. They can assist people with a really wide range of questions and issues. ” Avoid: “You can get psychological counseling through our EAP” © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 62
Tips on Referring Employees to EAP Mention EAP in general, but refrain from discussing specific services Suggested: “I want to be sure you are aware of our EAP. They can assist people with a really wide range of questions and issues. ” Avoid: “You can get psychological counseling through our EAP” © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 62
 Tips on Referring Employees to the EAP One of the concerns most managers have when dealing with employees is how to approach an employee when some problem is affecting his/her work performance. Some good rules of thumb include: • Address the workplace impact, not your theory of the underlying cause Suggested: "In the past month, I have noticed that you have become habitually late, coming in over 30 minutes tardy nearly every day" Avoid: “I think that your drinking has become a problem; you've been tardy nearly every day lately” © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 63
Tips on Referring Employees to the EAP One of the concerns most managers have when dealing with employees is how to approach an employee when some problem is affecting his/her work performance. Some good rules of thumb include: • Address the workplace impact, not your theory of the underlying cause Suggested: "In the past month, I have noticed that you have become habitually late, coming in over 30 minutes tardy nearly every day" Avoid: “I think that your drinking has become a problem; you've been tardy nearly every day lately” © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 63
 Resources § Employee Assistance Program – 800 -999 -1077 – Management Consultation Services – APSHelp. Link. com Company Code: Ul 1 § Office of Drug & Alcohol Policy and Compliance – 202 -366 -3784 § Alcoholics Anonymous – 212 -870 -3400 § Narcotics Anonymous – 818 -773 -9999 § Cocaine Anonymous – 800 -347 -8998 § SAMHSA Treatment Locator – http: //findtreatment. samhsa. gov © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 64
Resources § Employee Assistance Program – 800 -999 -1077 – Management Consultation Services – APSHelp. Link. com Company Code: Ul 1 § Office of Drug & Alcohol Policy and Compliance – 202 -366 -3784 § Alcoholics Anonymous – 212 -870 -3400 § Narcotics Anonymous – 818 -773 -9999 § Cocaine Anonymous – 800 -347 -8998 § SAMHSA Treatment Locator – http: //findtreatment. samhsa. gov © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 64
 Recommended Website • The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) maintains a website on commonly abused drugs – – Names of substances Examples How administered Effects www. nida. nih. gov/Drug. Pages/Drugsof. Abuse. html © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 65
Recommended Website • The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) maintains a website on commonly abused drugs – – Names of substances Examples How administered Effects www. nida. nih. gov/Drug. Pages/Drugsof. Abuse. html © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 65
 Employee Assistance Program For additional assistance on substance abuse or other concerns, please call your employee assistance program anytime. Simply Call: 1 -800 -999 -1077 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year It’s free and confidential! © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 66
Employee Assistance Program For additional assistance on substance abuse or other concerns, please call your employee assistance program anytime. Simply Call: 1 -800 -999 -1077 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year It’s free and confidential! © 2015 APS Healthcare, Inc. 66


