65a7dd1506a1a80bfe1f12d6bcea08d2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
Super. Triplets: a triplet-based supertree approach to phylogenomics Vincent Ranwez, Alexis Criscuolo and Emmanuel J. P. Douzery
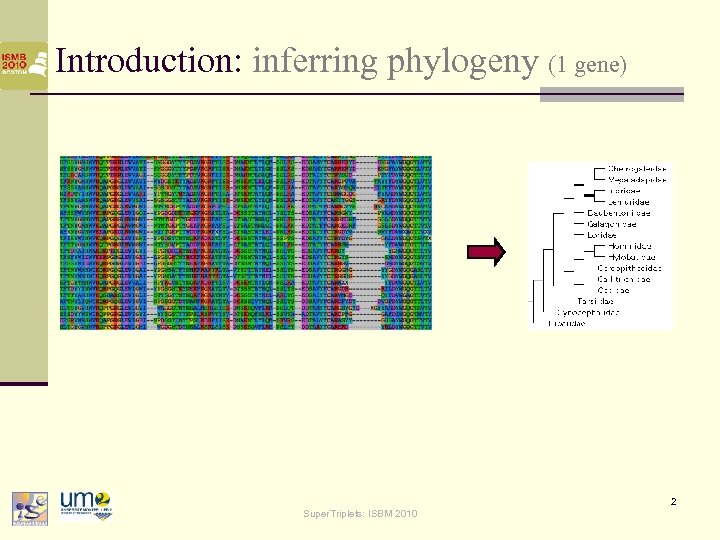
Introduction: inferring phylogeny (1 gene) 2 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
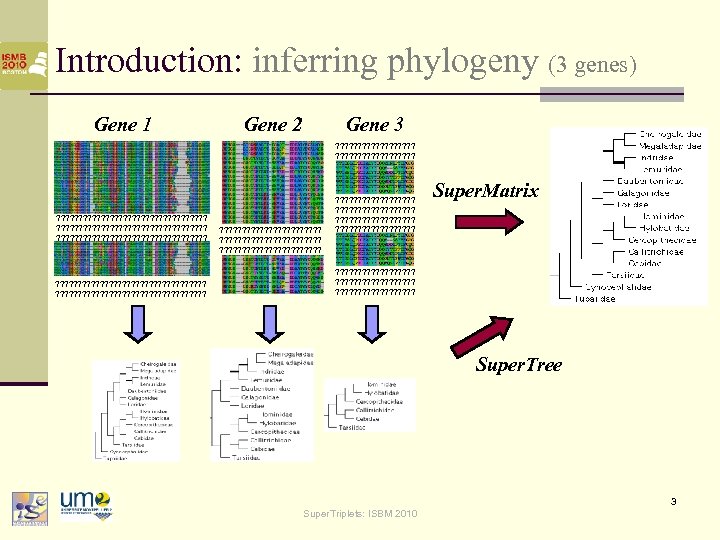
Introduction: inferring phylogeny (3 genes) Gene 1 Gene 2 Gene 3 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Super. Matrix ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Super. Tree 3 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
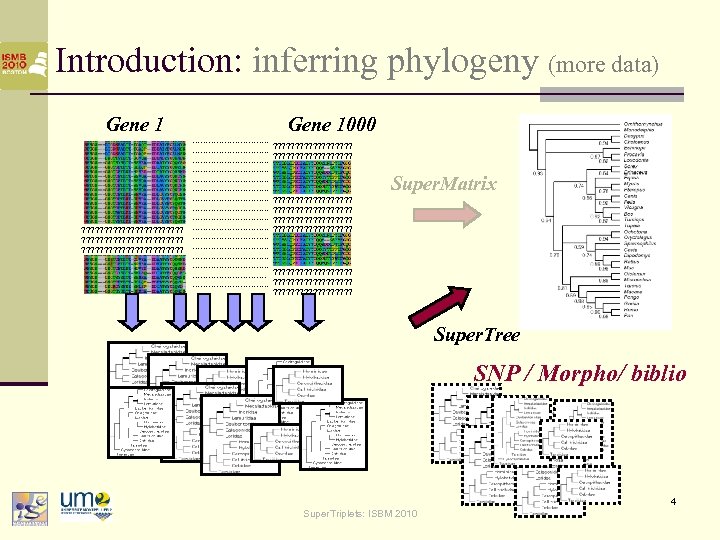
Introduction: inferring phylogeny (more data) Gene 1 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Gene 1000 ………………………. . ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Super. Matrix ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Super. Tree SNP / Morpho/ biblio 4 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
![Supertree overview: MRP n MRP [Baum 1992, Ragan 1992] n n 1 binary sequence Supertree overview: MRP n MRP [Baum 1992, Ragan 1992] n n 1 binary sequence](https://present5.com/presentation/65a7dd1506a1a80bfe1f12d6bcea08d2/image-5.jpg)
Supertree overview: MRP n MRP [Baum 1992, Ragan 1992] n n 1 binary sequence per taxon 1 site per clade (1=in the clade; 0 outside; ? missing) MR 01001? 11? 0100 01? ? 0? 011? 0? ? ? 0010 P ? ? 0011010? ? 001? ? 0100010? ? 001? 0 111? ? 0101000? ? 01 n [Goloboff and Pol, 2002] n A B C D E F Relation contradicted by all source trees C D E A B F MRP C D E F B A 5 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
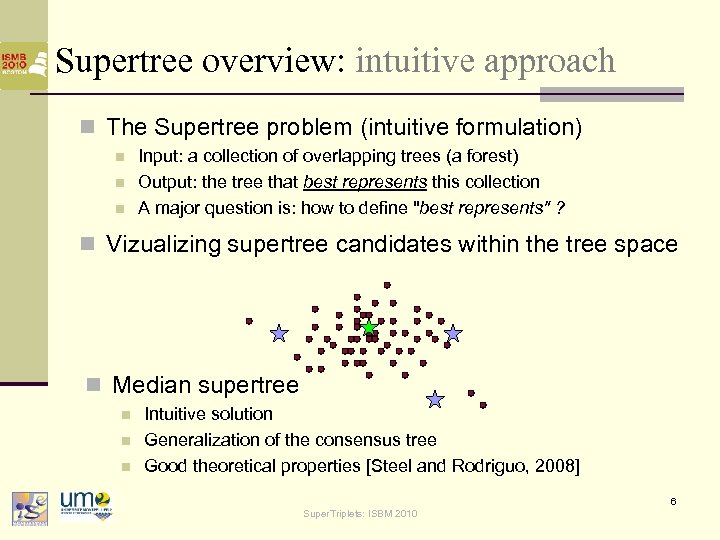
Supertree overview: intuitive approach n The Supertree problem (intuitive formulation) n n n Input: a collection of overlapping trees (a forest) Output: the tree that best represents this collection A major question is: how to define "best represents" ? n Vizualizing supertree candidates within the tree space n Median supertree n n n Intuitive solution Generalization of the consensus tree Good theoretical properties [Steel and Rodriguo, 2008] 6 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
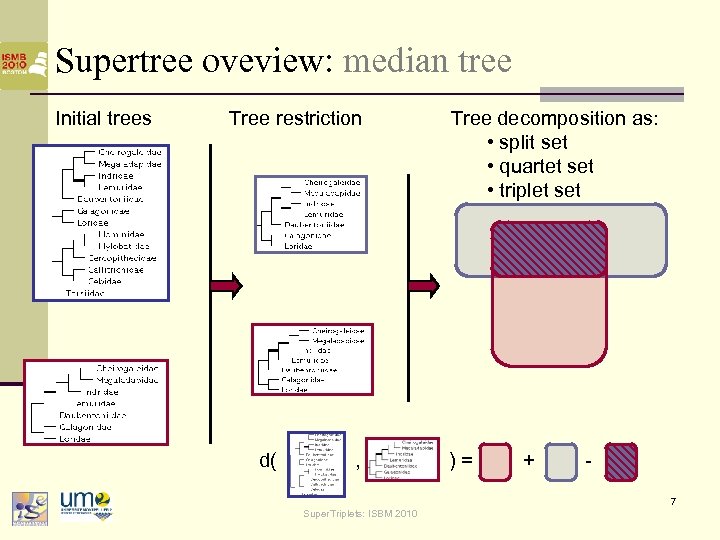
Supertree oveview: median tree Initial trees Tree restriction Tree decomposition as: • split set • quartet set • triplet set d( , ) = + - 7 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
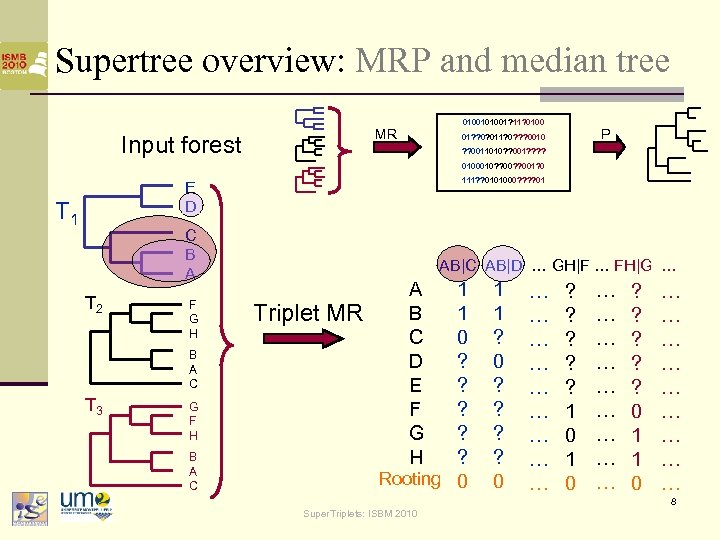
Supertree overview: MRP and median tree 01001? 11? 0100 MR Input forest P 01? ? 0? 011? 0? ? ? 0010 ? ? 0011010? ? 001? ? 0100010? ? 001? 0 111? ? 0101000? ? 01 E D T 1 C B A T 2 F G H B A C T 3 G F H B A C AB|D … GH|F … FH|G … Triplet MR A B C D E F G H 1 1 0 ? ? ? Rooting 0 1 1 ? 0 ? ? 0 … … … … … ? ? ? 1 0 … … … … … ? ? ? 0 1 1 0 … … … … … 8 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
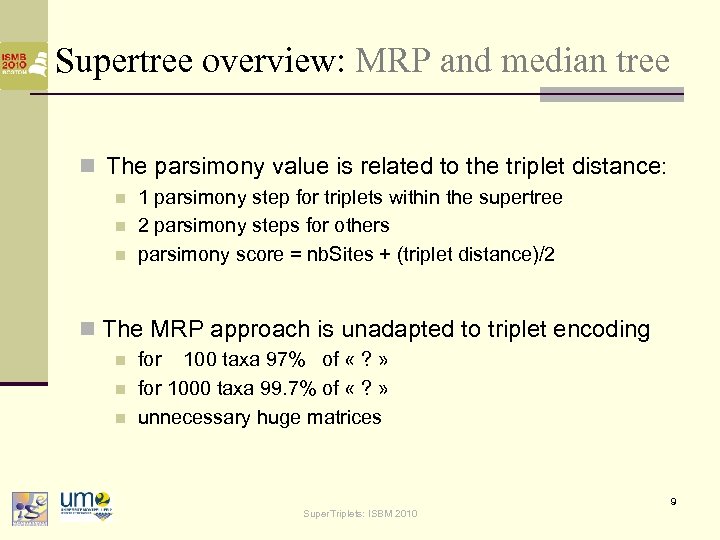
Supertree overview: MRP and median tree n The parsimony value is related to the triplet distance: n n n 1 parsimony step for triplets within the supertree 2 parsimony steps for others parsimony score = nb. Sites + (triplet distance)/2 n The MRP approach is unadapted to triplet encoding n for 100 taxa 97% of « ? » n for 1000 taxa 99. 7% of « ? » n unnecessary huge matrices 9 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
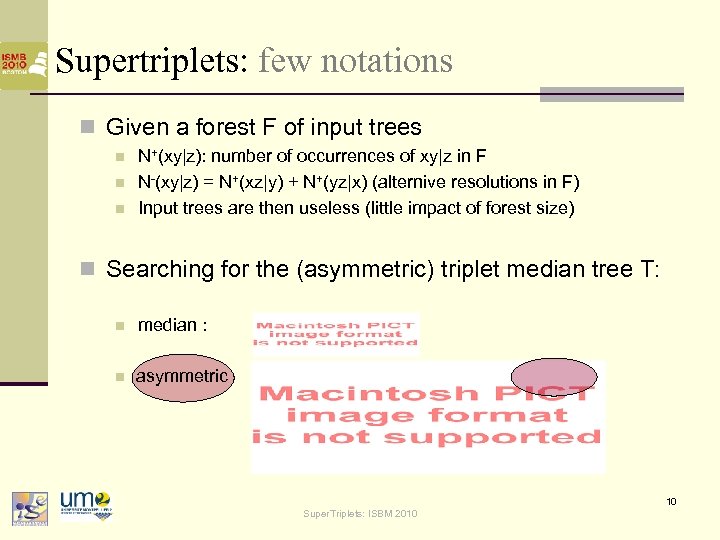
Supertriplets: few notations n Given a forest F of input trees n n n N+(xy|z): number of occurrences of xy|z in F N-(xy|z) = N+(xz|y) + N+(yz|x) (alternive resolutions in F) Input trees are then useless (little impact of forest size) n Searching for the (asymmetric) triplet median tree T: n median : n asymmetric 10 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
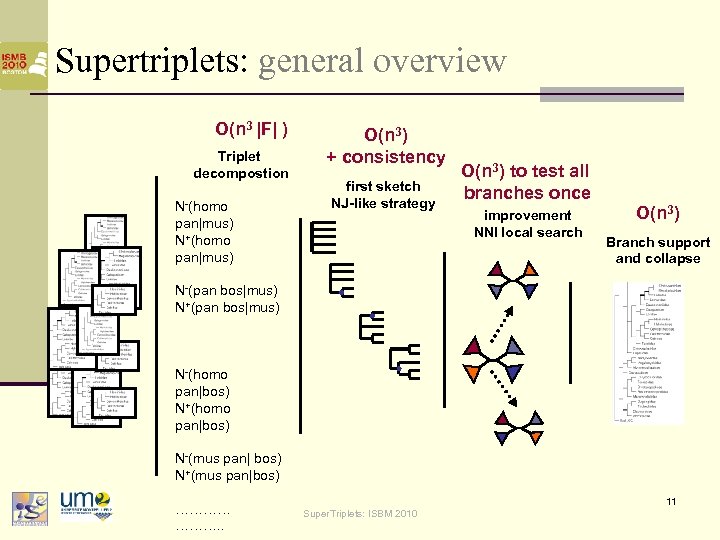
Supertriplets: general overview O(n 3 |F| ) Triplet decompostion N-(homo pan|mus) N+(homo pan|mus) O(n 3) + consistency first sketch NJ-like strategy O(n 3) to test all branches once improvement NNI local search O(n 3) Branch support and collapse N-(pan bos|mus) N+(pan bos|mus) N-(homo pan|bos) N+(homo pan|bos) N-(mus pan| bos) N+(mus pan|bos) ………… ………. . 11 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
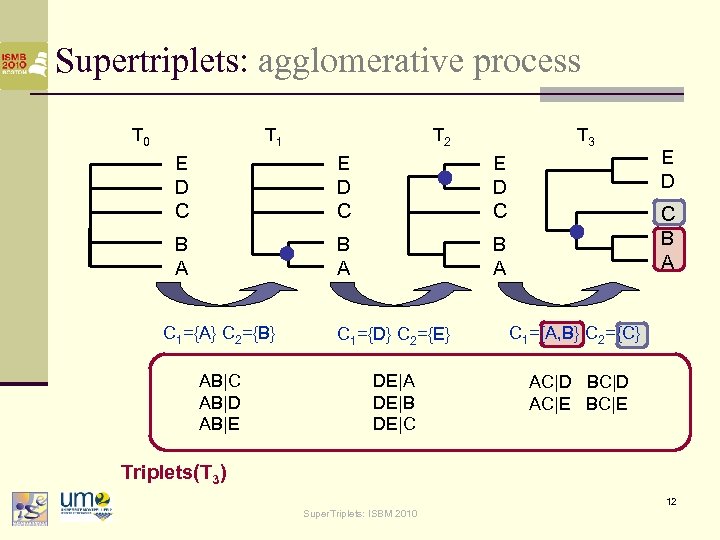
Supertriplets: agglomerative process T 0 T 1 T 2 T 3 E D C B A B A E D C B A C 1={A} C 2={B} C 1={D} C 2={E} C 1={A, B} C 2={C} AB|C AB|D AB|E DE|A DE|B DE|C AC|D BC|D AC|E BC|E Triplets(T 3) 12 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
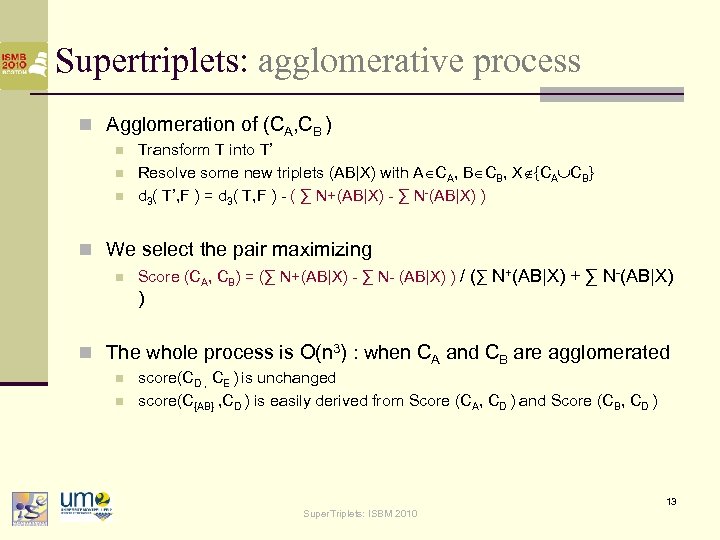
Supertriplets: agglomerative process n Agglomeration of (CA, CB ) n n n Transform T into T’ Resolve some new triplets (AB|X) with A CA, B CB, X {CA CB} d 3( T’, F ) = d 3( T, F ) - ( ∑ N+(AB|X) - ∑ N-(AB|X) ) n We select the pair maximizing n Score (CA, CB) = (∑ N+(AB|X) - ∑ N- (AB|X) ) / (∑ N+(AB|X) + ∑ N-(AB|X) ) n The whole process is O(n 3) : when CA and CB are agglomerated n n score(CD , CE ) is unchanged score(C{AB} , CD ) is easily derived from Score (CA, CD ) and Score (CB, CD ) 13 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
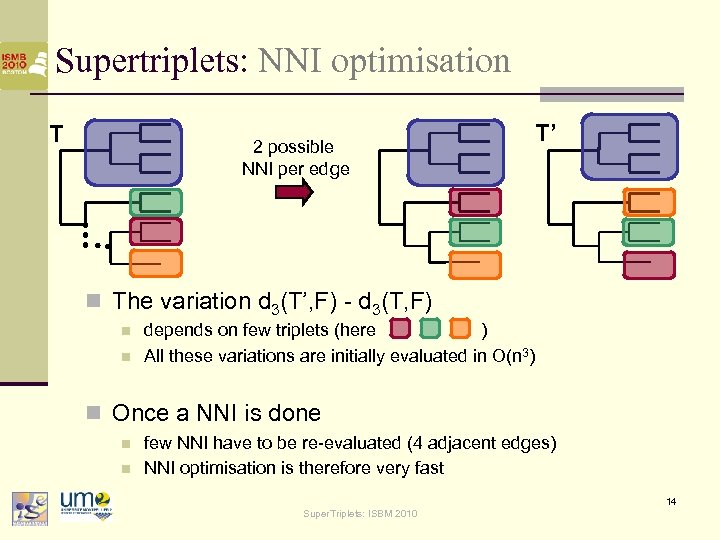
Supertriplets: NNI optimisation T 2 possible NNI per edge T’ n The variation d 3(T’, F) - d 3(T, F) n n depends on few triplets (here ) All these variations are initially evaluated in O(n 3) n Once a NNI is done n n few NNI have to be re-evaluated (4 adjacent edges) NNI optimisation is therefore very fast 14 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
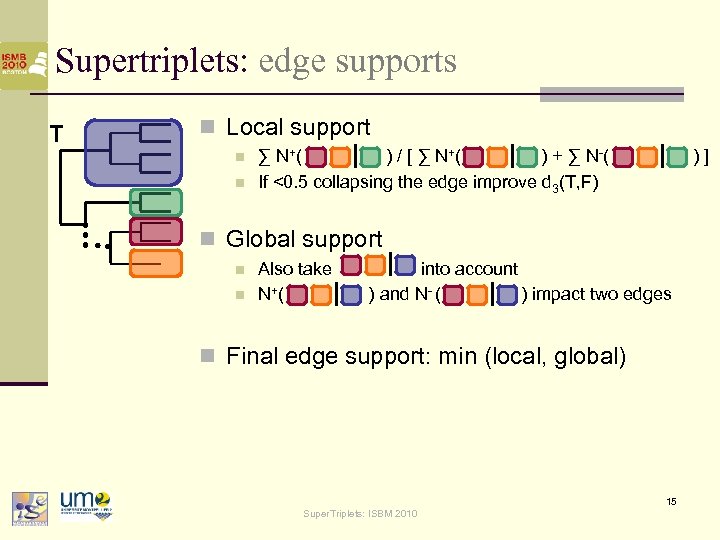
Supertriplets: edge supports T n Local support n n ∑ N+( ) / [ ∑ N+( ) + ∑ N-( ) ] If <0. 5 collapsing the edge improve d 3(T, F) n Global support n n Also take into account N+( ) and N- ( ) impact two edges n Final edge support: min (local, global) 15 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
![Supertriplets: simulation protocol [Eulenstein et al. 2004] [Criscuolo et al. 2006] Are they similar? Supertriplets: simulation protocol [Eulenstein et al. 2004] [Criscuolo et al. 2006] Are they similar?](https://present5.com/presentation/65a7dd1506a1a80bfe1f12d6bcea08d2/image-16.jpg)
Supertriplets: simulation protocol [Eulenstein et al. 2004] [Criscuolo et al. 2006] Are they similar? Triplet/split measure 16 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
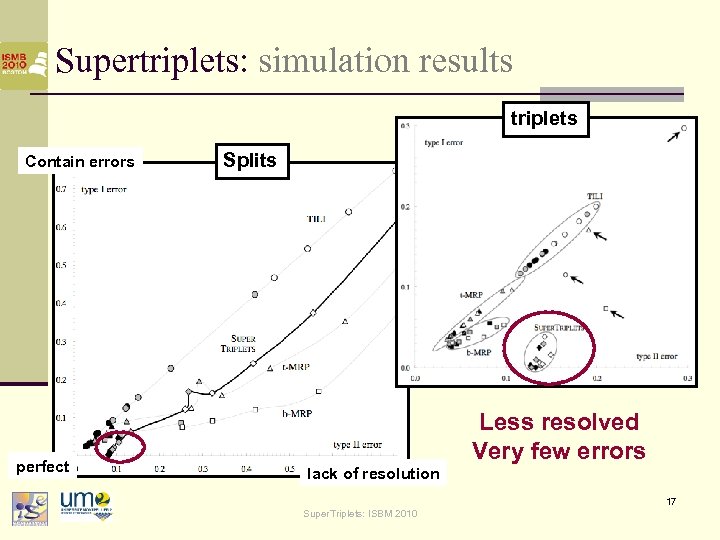
Supertriplets: simulation results triplets Contain errors perfect Splits Less resolved Very few errors lack of resolution 17 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
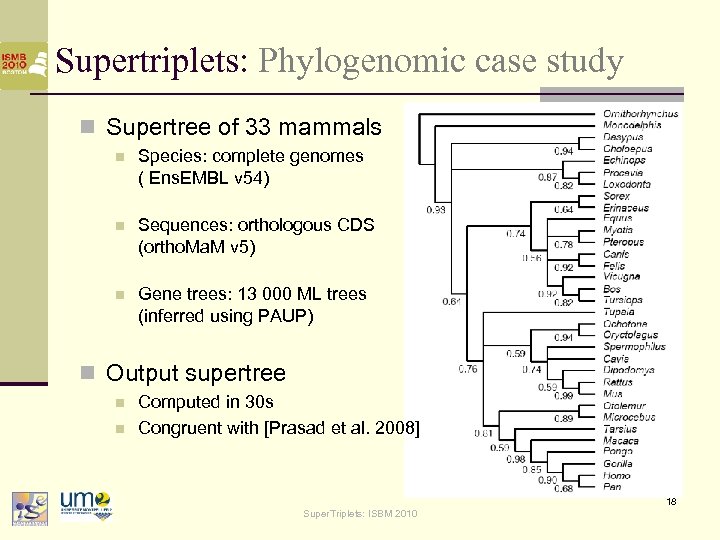
Supertriplets: Phylogenomic case study n Supertree of 33 mammals n Species: complete genomes ( Ens. EMBL v 54) n Sequences: orthologous CDS (ortho. Ma. M v 5) n Gene trees: 13 000 ML trees (inferred using PAUP) n Output supertree n n Computed in 30 s Congruent with [Prasad et al. 2008] 18 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
Conclusion & prospects n (Asymmetric) median supertree n n Easy to understand Makes tree weighting natural n MRP, triplets and median supertree n n n Understanding the criteria optimized by MRP Design a dedicated algorithm to optimize it http: //www. supertriplets. univ-montp 2. fr/ n Supertrees & supermatrix are complementary n n 1 000 vertebrate genome project Divide and conquer approach i) trees based on multiple CDSs (supermatrix) ii) assembling those trees (supertree) 19 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
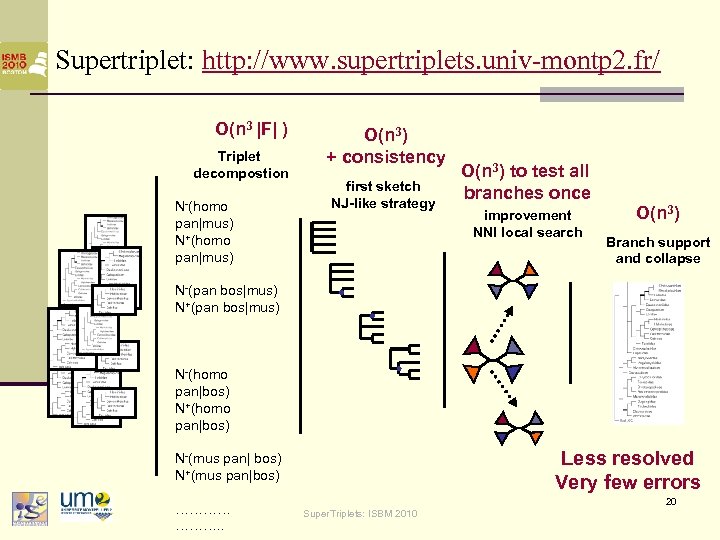
Supertriplet: http: //www. supertriplets. univ-montp 2. fr/ O(n 3 |F| ) Triplet decompostion N-(homo pan|mus) N+(homo pan|mus) O(n 3) + consistency first sketch NJ-like strategy O(n 3) to test all branches once improvement NNI local search O(n 3) Branch support and collapse N-(pan bos|mus) N+(pan bos|mus) N-(homo pan|bos) N+(homo pan|bos) Less resolved Very few errors N-(mus pan| bos) N+(mus pan|bos) ………… ………. . 20 Super. Triplets: ISBM 2010
65a7dd1506a1a80bfe1f12d6bcea08d2.ppt