ecd676e42d28166b49e9d7131639a1d6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 67
 Summing up Remarks May 27, 2008
Summing up Remarks May 27, 2008
 Final Presentation and Paper For Thurs, May 29, 2008 • Final Presentation to class. These should take approximately 20 minutes (~15 ppt slides) plus 5 minutes discussion – Include one slide on your team experience (pros and cons) By midnight Sunday evening June 1, 2008 • Final Report due. The Final report should be maximum 1520 pages double-spaced. – Added Appendix OK – Include references! Internet OK, private conversations but reference
Final Presentation and Paper For Thurs, May 29, 2008 • Final Presentation to class. These should take approximately 20 minutes (~15 ppt slides) plus 5 minutes discussion – Include one slide on your team experience (pros and cons) By midnight Sunday evening June 1, 2008 • Final Report due. The Final report should be maximum 1520 pages double-spaced. – Added Appendix OK – Include references! Internet OK, private conversations but reference
 Today • Ethics • Cases and Lectures- Key Takeaways • • • Class Discussion Core Competencies Seven Key Elements for Outstanding Development projects Risk and Risk Management Organization Project Management Rapid Prototyping
Today • Ethics • Cases and Lectures- Key Takeaways • • • Class Discussion Core Competencies Seven Key Elements for Outstanding Development projects Risk and Risk Management Organization Project Management Rapid Prototyping
 Ethics Discussion Ken Pickar E 103 5/27/08
Ethics Discussion Ken Pickar E 103 5/27/08
 Agenda • 4 questions • Cases • Supplement IEEE Code of Ethics
Agenda • 4 questions • Cases • Supplement IEEE Code of Ethics
 4 Questions • What is bothering you? – – Could not live up to expectations (yours, and clients) Long range not a good profit Worried about immediate appearance Huge cost to clients • What is the ethical issue involved? – Honesty – Willful negligence • Who are the people involved? – Customer, Everyone at company, Group in particular, Employee families, investors, future loss of business • Are you being true to yourself? • Who to talk to? – Boss’ boss, ombudsman, talk to others in group, come out with a patch
4 Questions • What is bothering you? – – Could not live up to expectations (yours, and clients) Long range not a good profit Worried about immediate appearance Huge cost to clients • What is the ethical issue involved? – Honesty – Willful negligence • Who are the people involved? – Customer, Everyone at company, Group in particular, Employee families, investors, future loss of business • Are you being true to yourself? • Who to talk to? – Boss’ boss, ombudsman, talk to others in group, come out with a patch
 Basic Question Are those ethical principles that are appropriate in a business context different than those used in one’s daily personal life? Yes No Why or Why Not?
Basic Question Are those ethical principles that are appropriate in a business context different than those used in one’s daily personal life? Yes No Why or Why Not?
 Hidden defects • I was heading a software development project team for a research laboratory client. It was about adding new features to existing software. The project had some revenue incentive to us if we delivered ahead of time. • My manager was very insistent that we should ship it at least 4 days before the scheduled date, and did not allow us to do the entire quality assurance phase. Just about after we had shipped it, we realized that we had shipped quite a defective product, something that could compromise the security of the client’s network. • I wanted to at least inform the client about this and ask them not to install it on their systems. However my manager put a complete stop to that and said that we would wait until they discovered it, and got back to us. Also, he suggested that I should cover it up by saying that it is not our fault and this defect had been there in the original software. • As this was my first assignment as a team lead, I was not sure what the expectations of the company itself would have been. From what I had seen and heard, I was almost sure that this is not the norm in the company. However I was not sure if I could just ignore my manager’s suggestions and tell the client anyway. This could lead to serious problems for the company’s image and future projects from the client.
Hidden defects • I was heading a software development project team for a research laboratory client. It was about adding new features to existing software. The project had some revenue incentive to us if we delivered ahead of time. • My manager was very insistent that we should ship it at least 4 days before the scheduled date, and did not allow us to do the entire quality assurance phase. Just about after we had shipped it, we realized that we had shipped quite a defective product, something that could compromise the security of the client’s network. • I wanted to at least inform the client about this and ask them not to install it on their systems. However my manager put a complete stop to that and said that we would wait until they discovered it, and got back to us. Also, he suggested that I should cover it up by saying that it is not our fault and this defect had been there in the original software. • As this was my first assignment as a team lead, I was not sure what the expectations of the company itself would have been. From what I had seen and heard, I was almost sure that this is not the norm in the company. However I was not sure if I could just ignore my manager’s suggestions and tell the client anyway. This could lead to serious problems for the company’s image and future projects from the client.
 Case 2 The bag man • Case: After a few months of effort, we finally had a client (a reputed cooperative bank in India) who was ready to implement our software. The client had long and exhaustive discussions in the executive room with the CEO of my company during the closure of the call, and sometimes I was requested to be excluded from the meetings though it was my account. Finally, the day came when I was called upon by the client to pick up the purchase order and I was extremely delighted. Just before going to meet the client, I was called upon by the CEO to congratulate and hand over a bag which was to be given to the Director (decision maker) of the bank. I was naive enough to ask about the contents of the bag, and was shocked to know the answer. Finally, I roamed around with the bag in my hand for a few hours before handing it over to the Director. I will never forget those hours as they have left a lasting impression on me.
Case 2 The bag man • Case: After a few months of effort, we finally had a client (a reputed cooperative bank in India) who was ready to implement our software. The client had long and exhaustive discussions in the executive room with the CEO of my company during the closure of the call, and sometimes I was requested to be excluded from the meetings though it was my account. Finally, the day came when I was called upon by the client to pick up the purchase order and I was extremely delighted. Just before going to meet the client, I was called upon by the CEO to congratulate and hand over a bag which was to be given to the Director (decision maker) of the bank. I was naive enough to ask about the contents of the bag, and was shocked to know the answer. Finally, I roamed around with the bag in my hand for a few hours before handing it over to the Director. I will never forget those hours as they have left a lasting impression on me.
 • • Case 3 The helpful consultant John Weng I have a consulting assignment one time that required me to be at the client site for 4 months. The company is a major airline in the US and I was brought in to head an airport ticket project that was already six months late. My main tasks are to define scope, develop a reasonable project timeline, put together a programming team and pick a client project manager to finish the project according to the scope. I have befriended the IT director and we talked a lot about their business and their goals. Because of my experience in the client's industry, I came up with an idea to streamline their back-office operations that would cut a major chunk of back-office operational cost. The IT director was quite excited by it and proposed that I meet with the CIO to discuss the idea. However, as I did more research on the back-office operations and discuss it with colleagues both from the client and my company, I discovered that my idea of consolidating the back-office operations would have a severe negative impact on an important revenue stream for my company. I thought that I should approach my managers to explain the situation and ask for their opinions. However, the IT director has already briefed the CIO about the idea and is working on putting together a budget for her review. I am not due back to my office for another two weeks but the CIO meeting is three days away and cannot be delayed because of the CIO’s schedule. I wonder whether I should just put the proposal together and present it or I should still get my manager’s opinion before I proceed.
• • Case 3 The helpful consultant John Weng I have a consulting assignment one time that required me to be at the client site for 4 months. The company is a major airline in the US and I was brought in to head an airport ticket project that was already six months late. My main tasks are to define scope, develop a reasonable project timeline, put together a programming team and pick a client project manager to finish the project according to the scope. I have befriended the IT director and we talked a lot about their business and their goals. Because of my experience in the client's industry, I came up with an idea to streamline their back-office operations that would cut a major chunk of back-office operational cost. The IT director was quite excited by it and proposed that I meet with the CIO to discuss the idea. However, as I did more research on the back-office operations and discuss it with colleagues both from the client and my company, I discovered that my idea of consolidating the back-office operations would have a severe negative impact on an important revenue stream for my company. I thought that I should approach my managers to explain the situation and ask for their opinions. However, the IT director has already briefed the CIO about the idea and is working on putting together a budget for her review. I am not due back to my office for another two weeks but the CIO meeting is three days away and cannot be delayed because of the CIO’s schedule. I wonder whether I should just put the proposal together and present it or I should still get my manager’s opinion before I proceed.
 IEEE code of Ethics • • • We, the members of the IEEE, in recognition of the importance of our technologies in affecting the quality of life throughout the world, and in accepting a personal obligation to our profession, its members and the communities we serve, do hereby commit ourselves to the highest ethical and professional conduct and agree: 1. to accept responsibility in making engineering decisions consistent with the safety, health and welfare of the public, and to disclose promptly factors that might endanger the public or the environment; 2. to avoid real or perceived conflicts of interest whenever possible, and to disclose them to affected parties when they do exist; 3. to be honest and realistic in stating claims or estimates based on available data; 4. to reject bribery in all its forms; 5. to improve the understanding of technology, its appropriate application, and potential consequences; 6. to maintain and improve our technical competence and to undertake technological tasks for others only if qualified by training or experience, or after full disclosure of pertinent limitations; 7. to seek, accept, and offer honest criticism of technical work, to acknowledge and correct errors, and to credit properly the contributions of others; 8. to treat fairly all persons regardless of such factors as race, religion, gender, disability, age, or national origin; 9. to avoid injuring others, their property, reputation, or employment by false or malicious action; 10. to assist colleagues and co-workers in their professional development and to support them in following this code of ethics. Approved by the IEEE Board of Directors August 1990
IEEE code of Ethics • • • We, the members of the IEEE, in recognition of the importance of our technologies in affecting the quality of life throughout the world, and in accepting a personal obligation to our profession, its members and the communities we serve, do hereby commit ourselves to the highest ethical and professional conduct and agree: 1. to accept responsibility in making engineering decisions consistent with the safety, health and welfare of the public, and to disclose promptly factors that might endanger the public or the environment; 2. to avoid real or perceived conflicts of interest whenever possible, and to disclose them to affected parties when they do exist; 3. to be honest and realistic in stating claims or estimates based on available data; 4. to reject bribery in all its forms; 5. to improve the understanding of technology, its appropriate application, and potential consequences; 6. to maintain and improve our technical competence and to undertake technological tasks for others only if qualified by training or experience, or after full disclosure of pertinent limitations; 7. to seek, accept, and offer honest criticism of technical work, to acknowledge and correct errors, and to credit properly the contributions of others; 8. to treat fairly all persons regardless of such factors as race, religion, gender, disability, age, or national origin; 9. to avoid injuring others, their property, reputation, or employment by false or malicious action; 10. to assist colleagues and co-workers in their professional development and to support them in following this code of ethics. Approved by the IEEE Board of Directors August 1990
 Basic Question Are those ethical principles that are appropriate in a business context different than those used in one’s daily personal life? Yes No Why or Why Not?
Basic Question Are those ethical principles that are appropriate in a business context different than those used in one’s daily personal life? Yes No Why or Why Not?
 My take: Engineering (Business) Ethical behavior is integral to other ethical issues you confront in your life • • • in business in your profession in your communities in your state or country in your family In the University – Curriculum – Behaviors In my opinion, Engineering Ethics cannot legitimately be compartmentalized
My take: Engineering (Business) Ethical behavior is integral to other ethical issues you confront in your life • • • in business in your profession in your communities in your state or country in your family In the University – Curriculum – Behaviors In my opinion, Engineering Ethics cannot legitimately be compartmentalized
 David Baltimore
David Baltimore
 Kent Kresa, Northrop Grumman • • Strong vision Predict spending and allign company Shareholder Forging partnerships to enhance technical capabilities • Targeted acquisitions
Kent Kresa, Northrop Grumman • • Strong vision Predict spending and allign company Shareholder Forging partnerships to enhance technical capabilities • Targeted acquisitions
 Key take-aways • Rob Manning JPL – – – – Leadership How to inspire engineers Enthusiasm Cultural advantage Set by leader Diversity required age race etc. Learning from failures
Key take-aways • Rob Manning JPL – – – – Leadership How to inspire engineers Enthusiasm Cultural advantage Set by leader Diversity required age race etc. Learning from failures
 Henry Kressel, Warburg Pincus Diversify risks Too soon is OK Interesting Career path How useful knowledge recurred in life Don’t compete with big guys Don’t rely on others dong market research
Henry Kressel, Warburg Pincus Diversify risks Too soon is OK Interesting Career path How useful knowledge recurred in life Don’t compete with big guys Don’t rely on others dong market research
 Key takeaways Genzyme Money to be made in small markets Importance of legislation Lobbying Financial model Customer relations through ins co
Key takeaways Genzyme Money to be made in small markets Importance of legislation Lobbying Financial model Customer relations through ins co
 Satyam Cherukuri, David Sarnoff Labs • Take existing idea and market it someplace else • Ethical guidelines • International nature of technology • Importance of Quality
Satyam Cherukuri, David Sarnoff Labs • Take existing idea and market it someplace else • Ethical guidelines • International nature of technology • Importance of Quality
 Kitty Hawk • • • Focus on one product. Don’t try to do it all Difficulty in predicting mkts Difficulty in being too far ahead Can do lots of things right and still fail Difficult to change technologies and markets together • Hard for a big company to act like small company too deep pockets
Kitty Hawk • • • Focus on one product. Don’t try to do it all Difficulty in predicting mkts Difficulty in being too far ahead Can do lots of things right and still fail Difficult to change technologies and markets together • Hard for a big company to act like small company too deep pockets
 Case: Claire Mc. Cloud • Career opportunity- take it • Don’t let your background hold you back
Case: Claire Mc. Cloud • Career opportunity- take it • Don’t let your background hold you back
 Core Competency and Focus after Prahad and Hamel (Burgleman) • Necessity to rethink the corporation – Traditionally vertically integrated model was very successful, why? • Example Ford River Rouge, US Steel, General Electric, AT&T – What is the problem with that methodology today? • Too expensive • Too much to know – Companies need to focus on what they are good at and what the customer values. – What are Competencies?
Core Competency and Focus after Prahad and Hamel (Burgleman) • Necessity to rethink the corporation – Traditionally vertically integrated model was very successful, why? • Example Ford River Rouge, US Steel, General Electric, AT&T – What is the problem with that methodology today? • Too expensive • Too much to know – Companies need to focus on what they are good at and what the customer values. – What are Competencies?
 Core Competencies 1. Provides potential access to a wide variety of companies 2. A core competence is perceived by the customer as a significant benefit in dealing with you 3. Barriers to entry- difficult for actual or potential competitor to imitate
Core Competencies 1. Provides potential access to a wide variety of companies 2. A core competence is perceived by the customer as a significant benefit in dealing with you 3. Barriers to entry- difficult for actual or potential competitor to imitate
 Core Competencies? • The collective learnings of an organization – Organization of work and the delivery of value – Knowing what your customer values in you and what is a “don’t care. ” – Understanding what lies beneath your product stream – What do they do better than anyone else – For a new company- to understand what they can do, what they must do, and what can be done better by someone else
Core Competencies? • The collective learnings of an organization – Organization of work and the delivery of value – Knowing what your customer values in you and what is a “don’t care. ” – Understanding what lies beneath your product stream – What do they do better than anyone else – For a new company- to understand what they can do, what they must do, and what can be done better by someone else
 How many Core Competencies can a company have?
How many Core Competencies can a company have?
 Core Competencies in Technology • From a portfolio of companies to technologies a portfolio of • Harmonizing streams of technology • Example of Japanese companies exploiting computing/communications convergence in the 80 s and 90 s while IBM and AT&T failed • What are Satyam’s companies core competencies? • What is your core competency? What should it be?
Core Competencies in Technology • From a portfolio of companies to technologies a portfolio of • Harmonizing streams of technology • Example of Japanese companies exploiting computing/communications convergence in the 80 s and 90 s while IBM and AT&T failed • What are Satyam’s companies core competencies? • What is your core competency? What should it be?
 Core (Technical) Competencies? • Caltech – World class research – graduates • Intel – Reliable microp • Google – Search – Coupling of advertising to search • Walmart – logistics • Dell – Customer
Core (Technical) Competencies? • Caltech – World class research – graduates • Intel – Reliable microp • Google – Search – Coupling of advertising to search • Walmart – logistics • Dell – Customer
 Apply this to actually getting something done. . . Seven Key Elements for Outstanding Development projects – Bowen et al 1. 2. Core Capabilities Guiding Visions – – – 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Business Vision Project vision Product concept Pushing the Envelope Project Leadership and organization Ownership and Commitment Prototyping- Rapid Learning and early testing of product and, if possible, the market Integration within Development Project P(success)=P(1)P(2)P(3)P(4)P(5)P(6)P(7)
Apply this to actually getting something done. . . Seven Key Elements for Outstanding Development projects – Bowen et al 1. 2. Core Capabilities Guiding Visions – – – 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Business Vision Project vision Product concept Pushing the Envelope Project Leadership and organization Ownership and Commitment Prototyping- Rapid Learning and early testing of product and, if possible, the market Integration within Development Project P(success)=P(1)P(2)P(3)P(4)P(5)P(6)P(7)
 Creating Effective Visions • • Customer Specification Voice of the Current Customer Competitive Benchmarking Tire-kicking Voice of Lead Users Empathetic Design Market intuition Scenarios of the future Reactive Pro-active
Creating Effective Visions • • Customer Specification Voice of the Current Customer Competitive Benchmarking Tire-kicking Voice of Lead Users Empathetic Design Market intuition Scenarios of the future Reactive Pro-active
 Technical Assessment • Current Capabilities • Reverse Engineering • Product or process benchmarking (competitors) • Best-in-world benchmarking • Experience and Performance curves • Technological Breakthroughs Reactive Aggressive
Technical Assessment • Current Capabilities • Reverse Engineering • Product or process benchmarking (competitors) • Best-in-world benchmarking • Experience and Performance curves • Technological Breakthroughs Reactive Aggressive
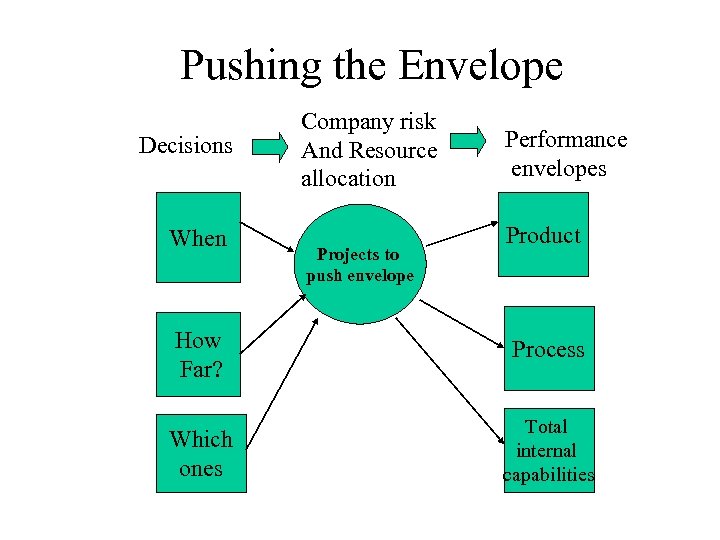 Pushing the Envelope Decisions When Company risk And Resource allocation Projects to push envelope Performance envelopes Product How Far? Process Which ones Total internal capabilities
Pushing the Envelope Decisions When Company risk And Resource allocation Projects to push envelope Performance envelopes Product How Far? Process Which ones Total internal capabilities
 Pushing the Envelope (cont. ) • Use Product Development Teams • Placing Manufacturing people in the field (or bring customers to the factory) • Doing R&D on the manufacturing line
Pushing the Envelope (cont. ) • Use Product Development Teams • Placing Manufacturing people in the field (or bring customers to the factory) • Doing R&D on the manufacturing line
 Managing and Controlling Risk • Technical Risk • Market Risk • Managerial Risk
Managing and Controlling Risk • Technical Risk • Market Risk • Managerial Risk

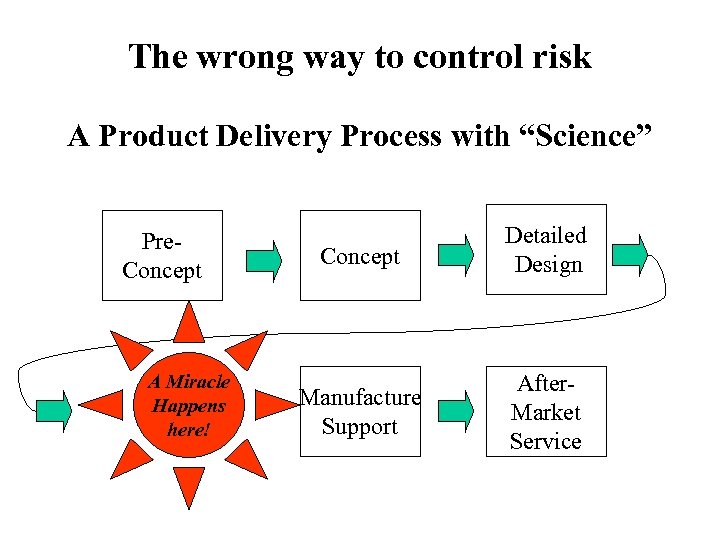 The wrong way to control risk A Product Delivery Process with “Science” Pre. Concept A Miracle Happens here! Concept Detailed Design Manufacture Support After. Market Service
The wrong way to control risk A Product Delivery Process with “Science” Pre. Concept A Miracle Happens here! Concept Detailed Design Manufacture Support After. Market Service
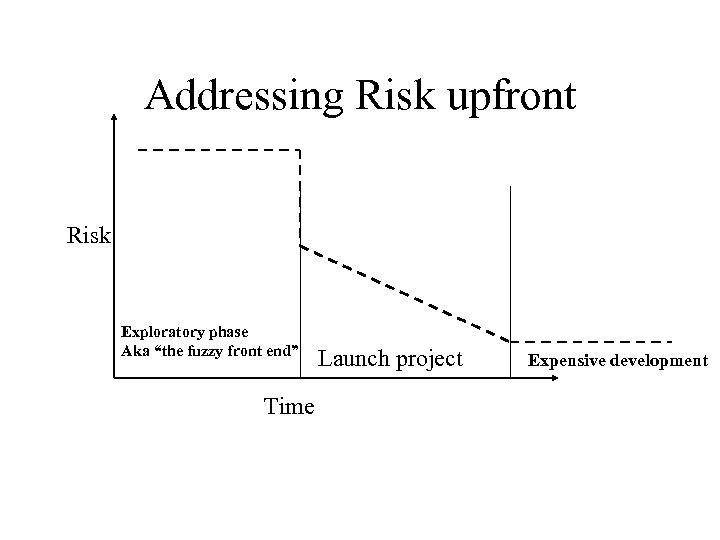 Addressing Risk upfront Risk Exploratory phase Aka “the fuzzy front end” Time Launch project Expensive development
Addressing Risk upfront Risk Exploratory phase Aka “the fuzzy front end” Time Launch project Expensive development
 Managing Risk • Project management tools • Phase gates • DFX X=market X=cost X= mfg X=reliability X=environment X= etc.
Managing Risk • Project management tools • Phase gates • DFX X=market X=cost X= mfg X=reliability X=environment X= etc.
 Organization • Functional • Matrix • Project
Organization • Functional • Matrix • Project
 Role of Project Leader • Direct Contact to the Market • Multilingual translator • Direct Engineering Manager (overall systems responsibility) • Walk around listener/problem solver/inspirer • Product Vision guardian • See around corners- anticipates problems
Role of Project Leader • Direct Contact to the Market • Multilingual translator • Direct Engineering Manager (overall systems responsibility) • Walk around listener/problem solver/inspirer • Product Vision guardian • See around corners- anticipates problems
 Ownership and Commitment • • • The individual power to make a difference Personal identification with project success Team shares responsibility Entire company supports projects success Recognition that business unit is dependant upon projects goals • Alignment of Rewards
Ownership and Commitment • • • The individual power to make a difference Personal identification with project success Team shares responsibility Entire company supports projects success Recognition that business unit is dependant upon projects goals • Alignment of Rewards
 Teams and team integration • • • Co-location Cross-functional training Team building TQ behaviors Successful Teams
Teams and team integration • • • Co-location Cross-functional training Team building TQ behaviors Successful Teams
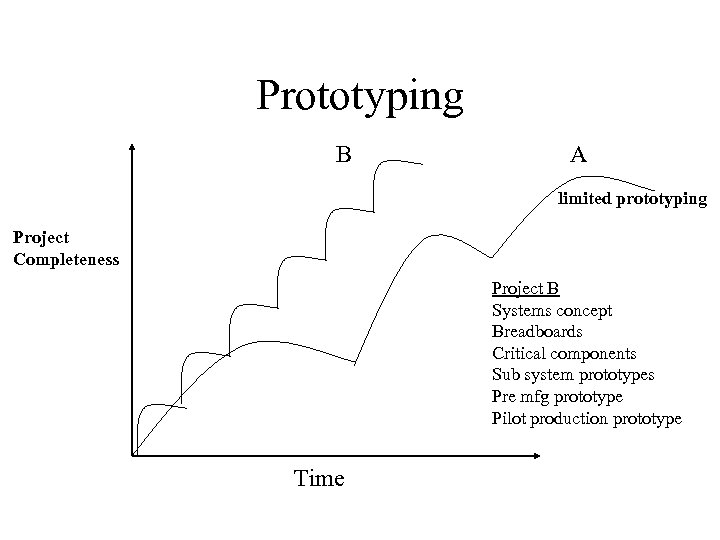 Prototyping B A limited prototyping Project Completeness Project B Systems concept Breadboards Critical components Sub system prototypes Pre mfg prototype Pilot production prototype Time
Prototyping B A limited prototyping Project Completeness Project B Systems concept Breadboards Critical components Sub system prototypes Pre mfg prototype Pilot production prototype Time
 Types of Prototypes • • • Models and Mockups Computer simulations Subsystem prototypes Mechanical prototypes Engineering prototypes Production prototypes
Types of Prototypes • • • Models and Mockups Computer simulations Subsystem prototypes Mechanical prototypes Engineering prototypes Production prototypes
 Leadership • What is the relationship between a great leader and the success of a technology? • What makes a great leader?
Leadership • What is the relationship between a great leader and the success of a technology? • What makes a great leader?
 Great Leaders- Examples • Science: Craig Ventnor, Negroponte, Baltimore • Politics: Henry VIII, Gubernator, Mandela, Lincoln, FDR, Ghandi • Military: Patton, Marshall, Rommel, Van Braun • Business: Welch, Jobs, Gates, Murdoch • Cultural: Spears, Stewart, Trump, Murdoch, Beatles, Dr. Dre, Gerschwin • Other endeavors: Jesus, Hitler, Bin Laden
Great Leaders- Examples • Science: Craig Ventnor, Negroponte, Baltimore • Politics: Henry VIII, Gubernator, Mandela, Lincoln, FDR, Ghandi • Military: Patton, Marshall, Rommel, Van Braun • Business: Welch, Jobs, Gates, Murdoch • Cultural: Spears, Stewart, Trump, Murdoch, Beatles, Dr. Dre, Gerschwin • Other endeavors: Jesus, Hitler, Bin Laden
 Great Leaders- Examples • • • Science: Politics: Military: Business: Cultural Other endeavors
Great Leaders- Examples • • • Science: Politics: Military: Business: Cultural Other endeavors
 Great Leaders- What are their Characteristics in common? • • Consistency of message Integrity (Think Clinton) Psychological connection with people Understands people’s motivation and how to harness them Manage complexity Command respect (or fear) Confident & Assertive Form a good team
Great Leaders- What are their Characteristics in common? • • Consistency of message Integrity (Think Clinton) Psychological connection with people Understands people’s motivation and how to harness them Manage complexity Command respect (or fear) Confident & Assertive Form a good team
 Intelligence Characterizing Features: • Hire very smart people to work for you • Reading other people (emotional IQ)
Intelligence Characterizing Features: • Hire very smart people to work for you • Reading other people (emotional IQ)
 Vision • Characterizing Features: – Knows where the world is going, can see around corners – Able to adjust to changes
Vision • Characterizing Features: – Knows where the world is going, can see around corners – Able to adjust to changes
 Communication • Characterizing Features – Positive bias in communicating – See problems as opportunities – Motivate others by example
Communication • Characterizing Features – Positive bias in communicating – See problems as opportunities – Motivate others by example
 Confidence • Characterizing Features – I can do it and you can do it – If we execute, we’re going to win – Overcome objects why it wouldn’t work – Right decision: make a decision (many decisions are made too late) – Sometimes you can make a better decision with less information
Confidence • Characterizing Features – I can do it and you can do it – If we execute, we’re going to win – Overcome objects why it wouldn’t work – Right decision: make a decision (many decisions are made too late) – Sometimes you can make a better decision with less information
 Competence • Characterizing features – Can do what they say they are going to do – Ken Lay (example of “incompetence”) – Are leaders generalists? Zero odds that you are really good at everything. – Know what you don’t know and know who is good. – Know when to ask an intelligent question (be humble)
Competence • Characterizing features – Can do what they say they are going to do – Ken Lay (example of “incompetence”) – Are leaders generalists? Zero odds that you are really good at everything. – Know what you don’t know and know who is good. – Know when to ask an intelligent question (be humble)
 Emotional Intelligence (beyond IQ) Daniel Goleman (HBR November-December 1998) • Outstanding Performance driven by – Technical skills (e. g. accounting, engineering, etc. ) – Cognitive skills ( analytic reasoning) – Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Intelligence (beyond IQ) Daniel Goleman (HBR November-December 1998) • Outstanding Performance driven by – Technical skills (e. g. accounting, engineering, etc. ) – Cognitive skills ( analytic reasoning) – Emotional Intelligence
 What is Emotional Intelligence? • Self awareness – Recognize your own emotions and their effect on others (self-confidence, realistic self-assessment) • Self Regulation – Control disruptive impulses and moods (comfort with ambiguity, integrity)- shoot from the hip • Motivation – A passion to work that goes beyond money and status (optimism even in the face of failure)
What is Emotional Intelligence? • Self awareness – Recognize your own emotions and their effect on others (self-confidence, realistic self-assessment) • Self Regulation – Control disruptive impulses and moods (comfort with ambiguity, integrity)- shoot from the hip • Motivation – A passion to work that goes beyond money and status (optimism even in the face of failure)
 Emotional Intelligence (cont. ) • Empathy – Understanding the emotional drives of others (expertise in building and retaining talent) • Social Skill – ability to find common ground and build rapport (effectiveness in leading change)
Emotional Intelligence (cont. ) • Empathy – Understanding the emotional drives of others (expertise in building and retaining talent) • Social Skill – ability to find common ground and build rapport (effectiveness in leading change)
 Other considerations • What about Toughness? – Do you need to be tough to be a Leader? – How about ruthless? • How about optimistic? • How about “energy level” • How about being an introvert (or extrovert)
Other considerations • What about Toughness? – Do you need to be tough to be a Leader? – How about ruthless? • How about optimistic? • How about “energy level” • How about being an introvert (or extrovert)
 Jack Welch- an example of leadership • Took over GE in 1980. • Succeeded a person totally different from himself • Started to make immediate, drastic changes
Jack Welch- an example of leadership • Took over GE in 1980. • Succeeded a person totally different from himself • Started to make immediate, drastic changes
 Jack Welch • • GE was not broken when Jack Welch took over His Mantra: 1. Be #1 or #2? Why? 2. Three circles of businesses. Why? 3. Fix, Sell or Close? Why? Applications of this for start-ups? Neutron Jack He eliminating 122, 000 positions! Isn’t this the height of cruelty!
Jack Welch • • GE was not broken when Jack Welch took over His Mantra: 1. Be #1 or #2? Why? 2. Three circles of businesses. Why? 3. Fix, Sell or Close? Why? Applications of this for start-ups? Neutron Jack He eliminating 122, 000 positions! Isn’t this the height of cruelty!
 Jack Welch • Workout- Town meetings where anyone can question the chief. Is there an equivalent for small companies? • Can small companies use “Best Practices? ” • Developing Leaders- How do you develop anything when you are in start-up mode? • Stretch Goals • What are the lessons of “service businesses for start-ups? • Focus on Quality. What are the benefits?
Jack Welch • Workout- Town meetings where anyone can question the chief. Is there an equivalent for small companies? • Can small companies use “Best Practices? ” • Developing Leaders- How do you develop anything when you are in start-up mode? • Stretch Goals • What are the lessons of “service businesses for start-ups? • Focus on Quality. What are the benefits?
 Another take http: //www. nwlink. com/~donclark/leader/leadcon. html • • • Be technically proficient - As a leader, you must know your job and have a solid familiarity with your employees' tasks. Seek responsibility and take responsibility for your actions - Search for ways to guide your organization to new heights. And when things go wrong, they always do sooner or later -- do not blame others. Analyze the situation, take corrective action, and move on to the next challenge. Make sound and timely decisions - Use good problem solving, decision making, and planning tools. Set the example - Be a good role model for your employees. They must not only hear what they are expected to do, but also see. We must become the change we want to see Mahatma Gandhi Know your people and look out for their well-being - Know human nature and the importance of sincerely caring for your workers. Keep your workers informed - Know how to communicate with not only them, but also seniors and other key people. Develop a sense of responsibility in your workers - Help to develop good character traits that will help them carry out their professional responsibilities. Ensure that tasks are understood, supervised, and accomplished - Communication is the key to this responsibility. Train as a team - Although many so called leaders call their organization, department, section, etc. a team; they are not really teams. . . they are just a group of people doing their jobs. Use the full capabilities of your organization - By developing a team spirit, you will be able to employ your organization, department, section, etc. to its fullest capabilities
Another take http: //www. nwlink. com/~donclark/leader/leadcon. html • • • Be technically proficient - As a leader, you must know your job and have a solid familiarity with your employees' tasks. Seek responsibility and take responsibility for your actions - Search for ways to guide your organization to new heights. And when things go wrong, they always do sooner or later -- do not blame others. Analyze the situation, take corrective action, and move on to the next challenge. Make sound and timely decisions - Use good problem solving, decision making, and planning tools. Set the example - Be a good role model for your employees. They must not only hear what they are expected to do, but also see. We must become the change we want to see Mahatma Gandhi Know your people and look out for their well-being - Know human nature and the importance of sincerely caring for your workers. Keep your workers informed - Know how to communicate with not only them, but also seniors and other key people. Develop a sense of responsibility in your workers - Help to develop good character traits that will help them carry out their professional responsibilities. Ensure that tasks are understood, supervised, and accomplished - Communication is the key to this responsibility. Train as a team - Although many so called leaders call their organization, department, section, etc. a team; they are not really teams. . . they are just a group of people doing their jobs. Use the full capabilities of your organization - By developing a team spirit, you will be able to employ your organization, department, section, etc. to its fullest capabilities
 Nature vs Nurture • Are Leaders made or born? – While leaders appear to be born, hybrid model seems most valid – Is ambition genetic?
Nature vs Nurture • Are Leaders made or born? – While leaders appear to be born, hybrid model seems most valid – Is ambition genetic?
 Nice exercise- what do I do about it? • How do you develop these characteristics- if you don’t have them all- or even if you do? – Let’s begin by everybody rating themselves (1 -5 on each, 5 high) • Do a “ 360”i. e. , ask people around you. – What are your biggest challenges? – What are you working on now that an improved behavior could favorably effect?
Nice exercise- what do I do about it? • How do you develop these characteristics- if you don’t have them all- or even if you do? – Let’s begin by everybody rating themselves (1 -5 on each, 5 high) • Do a “ 360”i. e. , ask people around you. – What are your biggest challenges? – What are you working on now that an improved behavior could favorably effect?
 – Create improvement model • Take from personal observations of leaders you admire, biographical readings, introspection • Create some specific goals to move yourself in the right direction for some improvement area e. g. , – Improve relationship with someone with whom problems now exist – Achieve a leadership position within a group – Create and execute an aggressive, candid, repetitious multifaceted communication plan – Evaluate what turns you on in a job- peel the onion to improve motivation – Get feedback from Coach (Could be a friend, mentor, spouse) – Listen! – Track progress • Iterate
– Create improvement model • Take from personal observations of leaders you admire, biographical readings, introspection • Create some specific goals to move yourself in the right direction for some improvement area e. g. , – Improve relationship with someone with whom problems now exist – Achieve a leadership position within a group – Create and execute an aggressive, candid, repetitious multifaceted communication plan – Evaluate what turns you on in a job- peel the onion to improve motivation – Get feedback from Coach (Could be a friend, mentor, spouse) – Listen! – Track progress • Iterate
 Some takeaways on this course How hard it is Key success factors • Importance of good management • Importance of Passion • Importance of Timing • Importance of (sound) Market Research • Importance of iteration/experimentation • Importance of a defensible business • Importance of networking • Multiplicity of Financing routes
Some takeaways on this course How hard it is Key success factors • Importance of good management • Importance of Passion • Importance of Timing • Importance of (sound) Market Research • Importance of iteration/experimentation • Importance of a defensible business • Importance of networking • Multiplicity of Financing routes
 Some thoughts on some of today’s major issues and how this might affect you • Globalization – Market – Sources • Need for New Leaders • Rapidly Changing Environment • Fast Changing technologies • Companies die suddenly Globalize yourself! Think about what you do best. Technical + Market skills + Management Half life of many “truths”~3 -5 years Continuous learning Look for small but fast growing technology Make bet and ride the curve (up) but be prepared to bail Choose company with “good problems” In-demand “core competencies= fungible skills Don’t wait until it falls down around you
Some thoughts on some of today’s major issues and how this might affect you • Globalization – Market – Sources • Need for New Leaders • Rapidly Changing Environment • Fast Changing technologies • Companies die suddenly Globalize yourself! Think about what you do best. Technical + Market skills + Management Half life of many “truths”~3 -5 years Continuous learning Look for small but fast growing technology Make bet and ride the curve (up) but be prepared to bail Choose company with “good problems” In-demand “core competencies= fungible skills Don’t wait until it falls down around you
 Example Energy- 2008 • Many technologies- none really new – – – Coal Gasification Tar sands Wind Solar turbine Solar Electric Scavenging Fuel Cells Ethanol Battery Conservation Power electronics Etc, etc • Will there be one “winner? ” • Is this finally the time? ? Or is it the 70’s redux. • Apply the tools you have learned in this class
Example Energy- 2008 • Many technologies- none really new – – – Coal Gasification Tar sands Wind Solar turbine Solar Electric Scavenging Fuel Cells Ethanol Battery Conservation Power electronics Etc, etc • Will there be one “winner? ” • Is this finally the time? ? Or is it the 70’s redux. • Apply the tools you have learned in this class
 E/ME 103 Management of Technology Spring 2008 • This has been a great class! – Committed – Innovative – Sophisticated • I have enjoyed teaching it! • Good Luck on the Final!
E/ME 103 Management of Technology Spring 2008 • This has been a great class! – Committed – Innovative – Sophisticated • I have enjoyed teaching it! • Good Luck on the Final!


