8943d59ff528c992a12ad91c16a3dee6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Summary of Prev. Lecture n Parametric Test Continue n Significance of Pearson’s C using t-Statistic n n Correlation is not different from 0 Significance of Regression Parameters n n n Validity: t-statistic Meaning: F-test Nonparametric Test n Chi-Square Statistic n n n Meaning of the correlation between two nominal or categorical data H 0: the observed Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient using t-statistic n n statistic is not significantly different from zero Correlation between two strong ordered data Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test using K-S D-statistic n Correlation between two weak ordered data GIS and Spatial Analysis 1
Summary of Prev. Lecture n Parametric Test Continue n Significance of Pearson’s C using t-Statistic n n Correlation is not different from 0 Significance of Regression Parameters n n n Validity: t-statistic Meaning: F-test Nonparametric Test n Chi-Square Statistic n n n Meaning of the correlation between two nominal or categorical data H 0: the observed Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient using t-statistic n n statistic is not significantly different from zero Correlation between two strong ordered data Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test using K-S D-statistic n Correlation between two weak ordered data GIS and Spatial Analysis 1
 Point Pattern Descriptor 1. 2. Points and point pattern Central Tendency (7) n 3. Jinmu Choi Overview (2) n Geography KHU Mean center, weighted mean center, median center Dispersion (4) n Standard distance, Standard deviational ellipses Summary and Next… GIS and Spatial Analysis 2
Point Pattern Descriptor 1. 2. Points and point pattern Central Tendency (7) n 3. Jinmu Choi Overview (2) n Geography KHU Mean center, weighted mean center, median center Dispersion (4) n Standard distance, Standard deviational ellipses Summary and Next… GIS and Spatial Analysis 2
 Point Feature n Statistics vs. Spatial Statistics n n n Location and attribute Spatial data: point, line, polygon Points n n Little or no spatial extent A house on a city map The location of events or incidences Representative points or the geometric centroids of a polygon GIS and Spatial Analysis 3
Point Feature n Statistics vs. Spatial Statistics n n n Location and attribute Spatial data: point, line, polygon Points n n Little or no spatial extent A house on a city map The location of events or incidences Representative points or the geometric centroids of a polygon GIS and Spatial Analysis 3
 Point Pattern n Point pattern statistics n n To summarize the distribution of a set of points Descriptors n n n Centrographic measures: the description of any spatial relationship between individual points The magnitude of spatial dispersion of a given set of points The direction bias of a set of points GIS and Spatial Analysis 4
Point Pattern n Point pattern statistics n n To summarize the distribution of a set of points Descriptors n n n Centrographic measures: the description of any spatial relationship between individual points The magnitude of spatial dispersion of a given set of points The direction bias of a set of points GIS and Spatial Analysis 4
 Central Tendency n A representative value of a given set of values n n Median house value: quick impression on house price Most common style of houses: general idea about house style in the area Mean house income: socioeconomic condition in the area Spatial central tendency n Mean center, weighted mean center, median center GIS and Spatial Analysis 5
Central Tendency n A representative value of a given set of values n n Median house value: quick impression on house price Most common style of houses: general idea about house style in the area Mean house income: socioeconomic condition in the area Spatial central tendency n Mean center, weighted mean center, median center GIS and Spatial Analysis 5
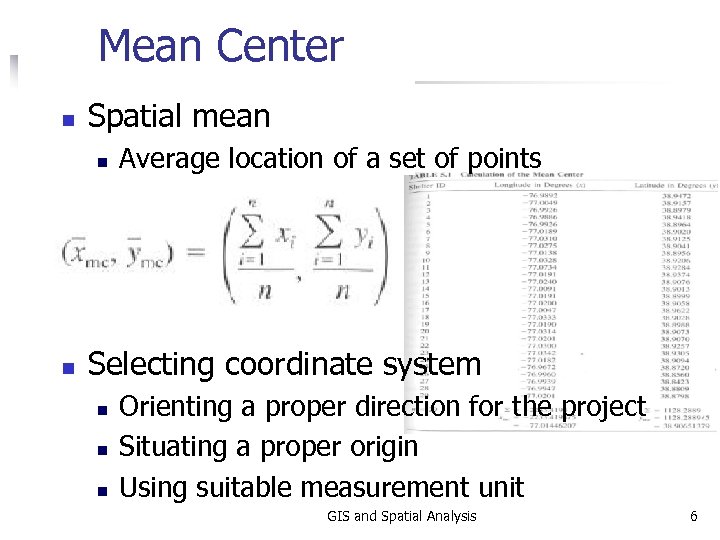 Mean Center n Spatial mean n n Average location of a set of points Selecting coordinate system n n n Orienting a proper direction for the project Situating a proper origin Using suitable measurement unit GIS and Spatial Analysis 6
Mean Center n Spatial mean n n Average location of a set of points Selecting coordinate system n n n Orienting a proper direction for the project Situating a proper origin Using suitable measurement unit GIS and Spatial Analysis 6
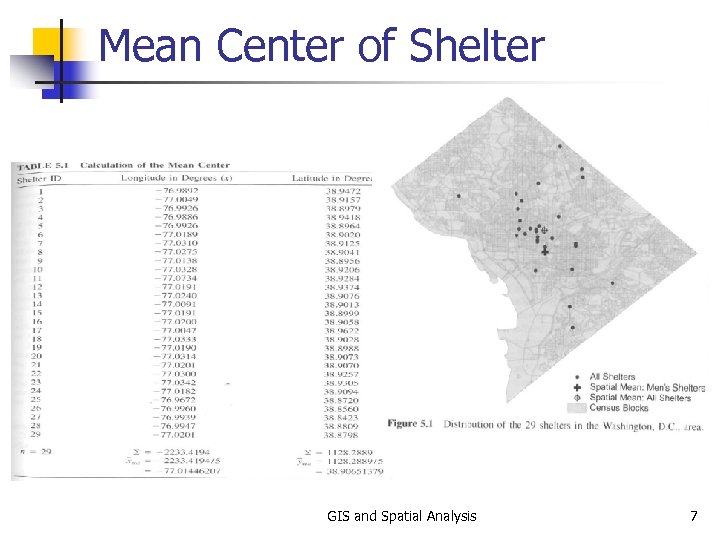 Mean Center of Shelter GIS and Spatial Analysis 7
Mean Center of Shelter GIS and Spatial Analysis 7
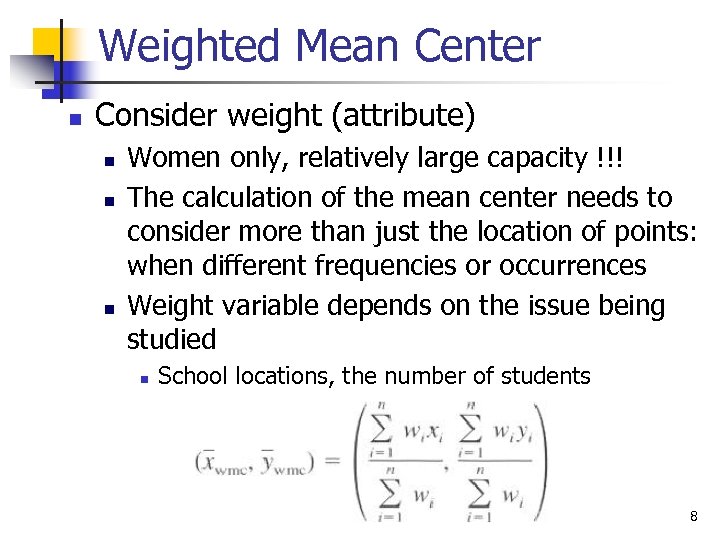 Weighted Mean Center n Consider weight (attribute) n n n Women only, relatively large capacity !!! The calculation of the mean center needs to consider more than just the location of points: when different frequencies or occurrences Weight variable depends on the issue being studied n School locations, the number of students GIS and Spatial Analysis 8
Weighted Mean Center n Consider weight (attribute) n n n Women only, relatively large capacity !!! The calculation of the mean center needs to consider more than just the location of points: when different frequencies or occurrences Weight variable depends on the issue being studied n School locations, the number of students GIS and Spatial Analysis 8
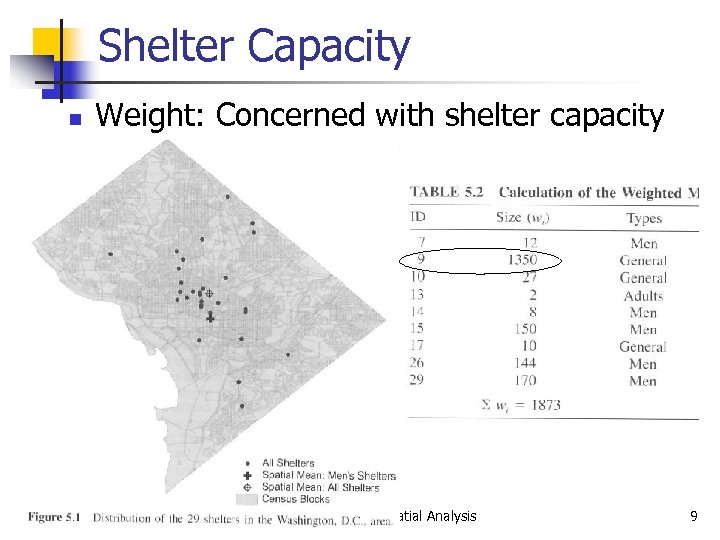 Shelter Capacity n Weight: Concerned with shelter capacity GIS and Spatial Analysis 9
Shelter Capacity n Weight: Concerned with shelter capacity GIS and Spatial Analysis 9
 Median Center n Minimum distance location from all points Median center n Median center with weight n n Weight can be + or - GIS and Spatial Analysis 10
Median Center n Minimum distance location from all points Median center n Median center with weight n n Weight can be + or - GIS and Spatial Analysis 10
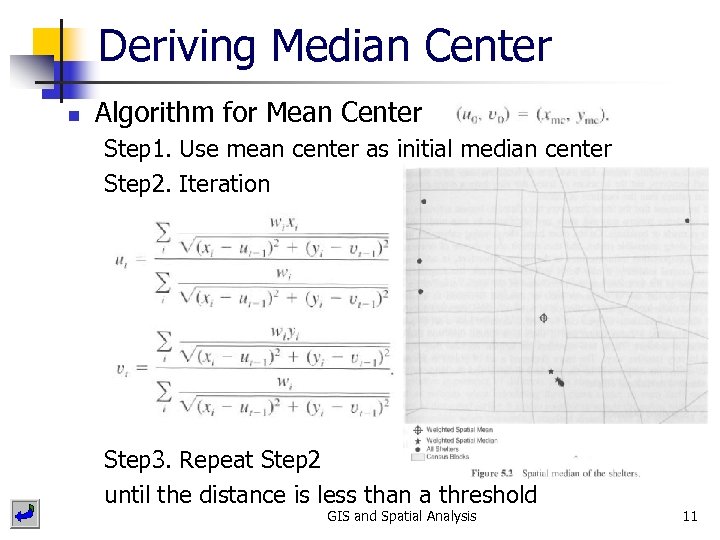 Deriving Median Center n Algorithm for Mean Center Step 1. Use mean center as initial median center Step 2. Iteration Step 3. Repeat Step 2 until the distance is less than a threshold GIS and Spatial Analysis 11
Deriving Median Center n Algorithm for Mean Center Step 1. Use mean center as initial median center Step 2. Iteration Step 3. Repeat Step 2 until the distance is less than a threshold GIS and Spatial Analysis 11
 Standard Distance n Relationship between two sets of points n n Forest fire locations vs. camping cabin locations Dispersion: forest fire Orientation: camping cabin along routes Standard distance n The average deviation from the spatial mean n Weighted standard distance GIS and Spatial Analysis 12
Standard Distance n Relationship between two sets of points n n Forest fire locations vs. camping cabin locations Dispersion: forest fire Orientation: camping cabin along routes Standard distance n The average deviation from the spatial mean n Weighted standard distance GIS and Spatial Analysis 12
 Standard Distance of Shelter n Comparing the results from the men-only and women-only shelters offers some insights n Location and spatial dispersion size GIS and Spatial Analysis 13
Standard Distance of Shelter n Comparing the results from the men-only and women-only shelters offers some insights n Location and spatial dispersion size GIS and Spatial Analysis 13
 Different Reference Frame n Weighted standard distance Standard distance of Japan’s largest cities with population 3. 27746 n Standard distance of Brazil’s largest cities with population 8. 84955 -> Brazil much more dispersed interurban structure n n Scaled weighted standard distance n n n by the average distance between cities in each country Japan’s case: 0. 2379 Brazil’s case: 0. 0272 GIS and Spatial Analysis 14
Different Reference Frame n Weighted standard distance Standard distance of Japan’s largest cities with population 3. 27746 n Standard distance of Brazil’s largest cities with population 8. 84955 -> Brazil much more dispersed interurban structure n n Scaled weighted standard distance n n n by the average distance between cities in each country Japan’s case: 0. 2379 Brazil’s case: 0. 0272 GIS and Spatial Analysis 14
 Standard Deviational Ellipses n Directional bias n n Accidents along a section of a highway, not a circle Components of S. D. Ellipses n An angle of rotation n n Deviation along the major axis n n n Maximum bias direction of points Deviation along the minor axis n n Angle btw. North and the y-axis Perpendicular to the major axis + angle value: x = minor, y = major - angle value: x = major, y = minor GIS and Spatial Analysis 15
Standard Deviational Ellipses n Directional bias n n Accidents along a section of a highway, not a circle Components of S. D. Ellipses n An angle of rotation n n Deviation along the major axis n n n Maximum bias direction of points Deviation along the minor axis n n Angle btw. North and the y-axis Perpendicular to the major axis + angle value: x = minor, y = major - angle value: x = major, y = minor GIS and Spatial Analysis 15
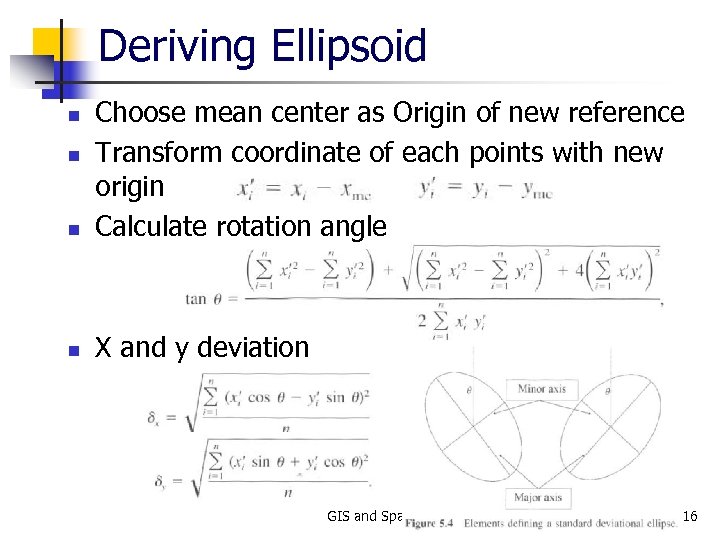 Deriving Ellipsoid n Choose mean center as Origin of new reference Transform coordinate of each points with new origin Calculate rotation angle n X and y deviation n n GIS and Spatial Analysis 16
Deriving Ellipsoid n Choose mean center as Origin of new reference Transform coordinate of each points with new origin Calculate rotation angle n X and y deviation n n GIS and Spatial Analysis 16
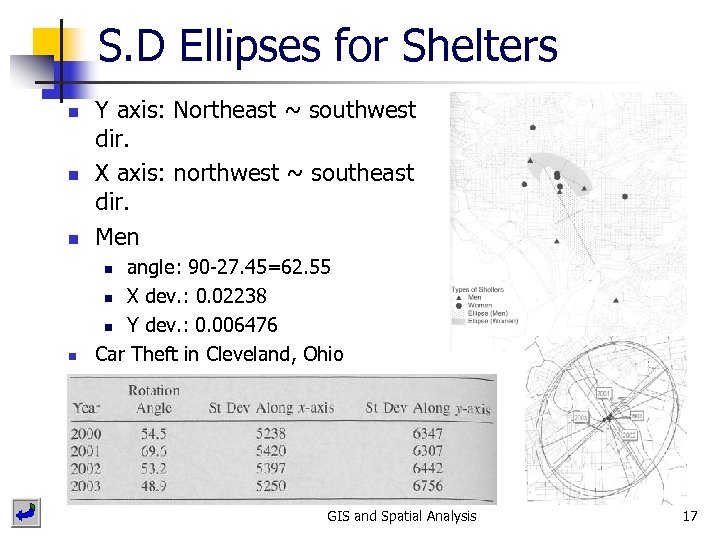 S. D Ellipses for Shelters n Y axis: Northeast ~ southwest dir. X axis: northwest ~ southeast dir. Men n angle: 90 -27. 45=62. 55 n X dev. : 0. 02238 n Y dev. : 0. 006476 Car Theft in Cleveland, Ohio n n n GIS and Spatial Analysis 17
S. D Ellipses for Shelters n Y axis: Northeast ~ southwest dir. X axis: northwest ~ southeast dir. Men n angle: 90 -27. 45=62. 55 n X dev. : 0. 02238 n Y dev. : 0. 006476 Car Theft in Cleveland, Ohio n n n GIS and Spatial Analysis 17
 Summary n Points and point pattern n Mean center: spatial mean Weighted mean center n n Min. distance center from all points Standard distance n n Spatial mean considering attributes Median center n n Locations and distribution of locations Average distribution of points from the mean center Standard deviational ellipses n Spatial distribution of points considering directional bias GIS and Spatial Analysis 18
Summary n Points and point pattern n Mean center: spatial mean Weighted mean center n n Min. distance center from all points Standard distance n n Spatial mean considering attributes Median center n n Locations and distribution of locations Average distribution of points from the mean center Standard deviational ellipses n Spatial distribution of points considering directional bias GIS and Spatial Analysis 18
 Next … • Lab: Point Pattern Descriptors • Lec: Point Pattern Analyzers • Read -. Chapter 6, pp. 218 -279 GIS and Spatial Analysis 19
Next … • Lab: Point Pattern Descriptors • Lec: Point Pattern Analyzers • Read -. Chapter 6, pp. 218 -279 GIS and Spatial Analysis 19


