131a0a014fd0992e0b94431cb3b23689.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Summary and Outlook Roy Holt 23 May 2008 With apologies for being incomplete
Summary and Outlook Roy Holt 23 May 2008 With apologies for being incomplete
 EIC White Papers 2007 – an astounding year Available at: • NSAC LRP 2007 home page • Rutgers Town Meeting page • http: //www. bnl. gov/eic n The Electron Ion Collider (EIC) White Paper n The GPD/DVCS White Paper n Position Paper: e+A Physics at an Electron Ion Collider n The e. RHIC machine: Accelerator Position Paper n ELIC Zero’th Order Design Report
EIC White Papers 2007 – an astounding year Available at: • NSAC LRP 2007 home page • Rutgers Town Meeting page • http: //www. bnl. gov/eic n The Electron Ion Collider (EIC) White Paper n The GPD/DVCS White Paper n Position Paper: e+A Physics at an Electron Ion Collider n The e. RHIC machine: Accelerator Position Paper n ELIC Zero’th Order Design Report
 The EIC Working Group 17 C. Aidala, 28 E. Aschenauer, 10 J. Annand, 1 J. Arrington, 26 R. Averbeck, 3 M. Baker, 26 K. Boyle, 28 W. Brooks, 28 A. Bruell, 19 A. Caldwell, 28 J. P. Chen, 2 R. Choudhury, 10 E. Christy, 8 B. Cole, 4 D. De Florian, 3 R. Debbe, 26, 24 -1 A. Deshpande*, 18 K. Dow, 26 A. Drees, 3 J. Dunlop, 2 D. Dutta, 7 F. Ellinghaus, 28 R. Ent, 18 R. Fatemi, 18 W. Franklin, 28 D. Gaskell, 16 G. Garvey, 12, 24 -1 M. Grosse-Perdekamp, 1 K. Hafidi, 18 D. Hasell, 26 T. Hemmick, 1 R. Holt, 8 E. Hughes, 22 C. Hyde-Wright, 5 G. Igo, 14 K. Imai, 10 D. Ireland, 26 B. Jacak, 15 P. Jacobs, 28 M. Jones, 10 R. Kaiser, 17 D. Kawall, 11 C. Keppel, 7 E. Kinney, 18 M. Kohl, 9 H. Kowalski, 17 K. Kumar, 2 V. Kumar, 21 G. Kyle, 13 J. Lajoie, 16 M. Leitch, 27 A. Levy, 27 J. Lichtenstadt, 10 K. Livingstone, 20 W. Lorenzon, 145. Matis, 12 N. Makins, 6 G. Mallot, 18 M. Miller, 18 R. Milner*, 2 A. Mohanty, 3 D. Morrison, 26 Y. Ning, 15 G. Odyniec, 13 C. Ogilvie, 2 L. Pant, 26 V. Pantuyev, 21 S. Pate, 26 P. Paul, 12 J. -C. Peng, 18 R. Redwine, 1 P. Reimer, 15 H. -G. Ritter, 10 G. Rosner, 25 A. Sandacz, 7 J. Seele, 12 R. Seidl, 10 B. Seitz, 2 P. Shukla, 15 E. Sichtermann, 18 F. Simon, 3 P. Sorensen, 3 P. Steinberg, 24 M. Stratmann, 22 M. Strikman, 18 B. Surrow, 18 E. Tsentalovich, 11 V. Tvaskis, 3 T. Ullrich, 3 R. Venugopalan, 3 W. Vogelsang, 28 C. Weiss, 15 H. Wieman, 15 N. Xu, 3 Z. Xu, 8 W. Zajc. 1 Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL; 2 Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Mumbai, India; 3 Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY; 4 University of Buenos Aires, Argentina; 5 University of California, Los Angeles, CA; 6 CERN, Geneva, Switzerland; 7 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO; 8 Columbia University, New York, NY; 9 DESY, Hamburg, Germany; 10 University of Glasgow, Scotland, United Kingdom; 11 Hampton University, Hampton, VA; 12 University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, IL; 13 Iowa State University, Ames, IA; 14 University of Kyoto, Japan; 15 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA; 16 Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM; 17 University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA; 18 MIT, Cambridge, MA; 19 Max Planck Institüt für Physik, Munich, Germany; 20 University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI; 21 New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, NM; 22 Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA; 23 Penn State University, PA; 24 RIKEN, Wako, Japan; 24 -1 RIKEN-BNL Research Center, BNL, Upton, NY; 25 Soltan Institute for Nuclear Studies, Warsaw, Poland; 26 SUNY, Stony Brook, NY; 27 Tel Aviv University, Israel; 28 Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility, Newport News, VA -95 Scientists, 28 Institutions, 9 countries *Contact People
The EIC Working Group 17 C. Aidala, 28 E. Aschenauer, 10 J. Annand, 1 J. Arrington, 26 R. Averbeck, 3 M. Baker, 26 K. Boyle, 28 W. Brooks, 28 A. Bruell, 19 A. Caldwell, 28 J. P. Chen, 2 R. Choudhury, 10 E. Christy, 8 B. Cole, 4 D. De Florian, 3 R. Debbe, 26, 24 -1 A. Deshpande*, 18 K. Dow, 26 A. Drees, 3 J. Dunlop, 2 D. Dutta, 7 F. Ellinghaus, 28 R. Ent, 18 R. Fatemi, 18 W. Franklin, 28 D. Gaskell, 16 G. Garvey, 12, 24 -1 M. Grosse-Perdekamp, 1 K. Hafidi, 18 D. Hasell, 26 T. Hemmick, 1 R. Holt, 8 E. Hughes, 22 C. Hyde-Wright, 5 G. Igo, 14 K. Imai, 10 D. Ireland, 26 B. Jacak, 15 P. Jacobs, 28 M. Jones, 10 R. Kaiser, 17 D. Kawall, 11 C. Keppel, 7 E. Kinney, 18 M. Kohl, 9 H. Kowalski, 17 K. Kumar, 2 V. Kumar, 21 G. Kyle, 13 J. Lajoie, 16 M. Leitch, 27 A. Levy, 27 J. Lichtenstadt, 10 K. Livingstone, 20 W. Lorenzon, 145. Matis, 12 N. Makins, 6 G. Mallot, 18 M. Miller, 18 R. Milner*, 2 A. Mohanty, 3 D. Morrison, 26 Y. Ning, 15 G. Odyniec, 13 C. Ogilvie, 2 L. Pant, 26 V. Pantuyev, 21 S. Pate, 26 P. Paul, 12 J. -C. Peng, 18 R. Redwine, 1 P. Reimer, 15 H. -G. Ritter, 10 G. Rosner, 25 A. Sandacz, 7 J. Seele, 12 R. Seidl, 10 B. Seitz, 2 P. Shukla, 15 E. Sichtermann, 18 F. Simon, 3 P. Sorensen, 3 P. Steinberg, 24 M. Stratmann, 22 M. Strikman, 18 B. Surrow, 18 E. Tsentalovich, 11 V. Tvaskis, 3 T. Ullrich, 3 R. Venugopalan, 3 W. Vogelsang, 28 C. Weiss, 15 H. Wieman, 15 N. Xu, 3 Z. Xu, 8 W. Zajc. 1 Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL; 2 Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Mumbai, India; 3 Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY; 4 University of Buenos Aires, Argentina; 5 University of California, Los Angeles, CA; 6 CERN, Geneva, Switzerland; 7 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO; 8 Columbia University, New York, NY; 9 DESY, Hamburg, Germany; 10 University of Glasgow, Scotland, United Kingdom; 11 Hampton University, Hampton, VA; 12 University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, IL; 13 Iowa State University, Ames, IA; 14 University of Kyoto, Japan; 15 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA; 16 Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM; 17 University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA; 18 MIT, Cambridge, MA; 19 Max Planck Institüt für Physik, Munich, Germany; 20 University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI; 21 New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, NM; 22 Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA; 23 Penn State University, PA; 24 RIKEN, Wako, Japan; 24 -1 RIKEN-BNL Research Center, BNL, Upton, NY; 25 Soltan Institute for Nuclear Studies, Warsaw, Poland; 26 SUNY, Stony Brook, NY; 27 Tel Aviv University, Israel; 28 Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility, Newport News, VA -95 Scientists, 28 Institutions, 9 countries *Contact People
 NSAC 2007 Long Range Plan “An Electron-Ion Collider (EIC) with polarized beams has been embraced by the U. S. nuclear science community as embodying the vision for reaching the next QCD frontier. EIC would provide unique capabilities for the study of QCD well beyond those available at existing facilities worldwide and complementary to those planned for the next generation of accelerators in Europe and Asia. In support of this new direction: We recommend the allocation of resources to develop accelerator and detector technology necessary to lay the foundation for a polarized Electron Ion Collider. The EIC would explore the new QCD frontier of strong color fields in nuclei and precisely image the gluons in the proton. ”
NSAC 2007 Long Range Plan “An Electron-Ion Collider (EIC) with polarized beams has been embraced by the U. S. nuclear science community as embodying the vision for reaching the next QCD frontier. EIC would provide unique capabilities for the study of QCD well beyond those available at existing facilities worldwide and complementary to those planned for the next generation of accelerators in Europe and Asia. In support of this new direction: We recommend the allocation of resources to develop accelerator and detector technology necessary to lay the foundation for a polarized Electron Ion Collider. The EIC would explore the new QCD frontier of strong color fields in nuclei and precisely image the gluons in the proton. ”
 Introduction The EIC will explore the most compelling issues in nuclear science and technology. n Profound issues in nuclear physics – Structure of visible matter – Role of gluons in hadronic matter – Fundamental symmetries n New facilities on the horizon n Concluding statement
Introduction The EIC will explore the most compelling issues in nuclear science and technology. n Profound issues in nuclear physics – Structure of visible matter – Role of gluons in hadronic matter – Fundamental symmetries n New facilities on the horizon n Concluding statement
 Explore the structure of visible matter n What is the internal landscape of the hadron? – Benchmark: Spatial, spin, flavor and gluonic structure n What is the nature of the nuclear force that binds protons and neutrons into nuclei? – Frontier: QCD properties of nuclear force – Mysteries: QCD effects in nuclei “If, in some cataclysm, all of scientific knowledge were to be destroyed, and only one sentence passed on to the next generation, what statement would contain the most information in the fewest words? I believe it is the atomic hypothesis, that all things are made of atoms -- little particles that move around in perpetual motion, attracting each other when they are a little distance apart, but repelling upon being squeezed into one another. In that one sentence, there is an enormous amount of information about the world, if just a little imagination and thinking are applied. ” - R. Feynman
Explore the structure of visible matter n What is the internal landscape of the hadron? – Benchmark: Spatial, spin, flavor and gluonic structure n What is the nature of the nuclear force that binds protons and neutrons into nuclei? – Frontier: QCD properties of nuclear force – Mysteries: QCD effects in nuclei “If, in some cataclysm, all of scientific knowledge were to be destroyed, and only one sentence passed on to the next generation, what statement would contain the most information in the fewest words? I believe it is the atomic hypothesis, that all things are made of atoms -- little particles that move around in perpetual motion, attracting each other when they are a little distance apart, but repelling upon being squeezed into one another. In that one sentence, there is an enormous amount of information about the world, if just a little imagination and thinking are applied. ” - R. Feynman
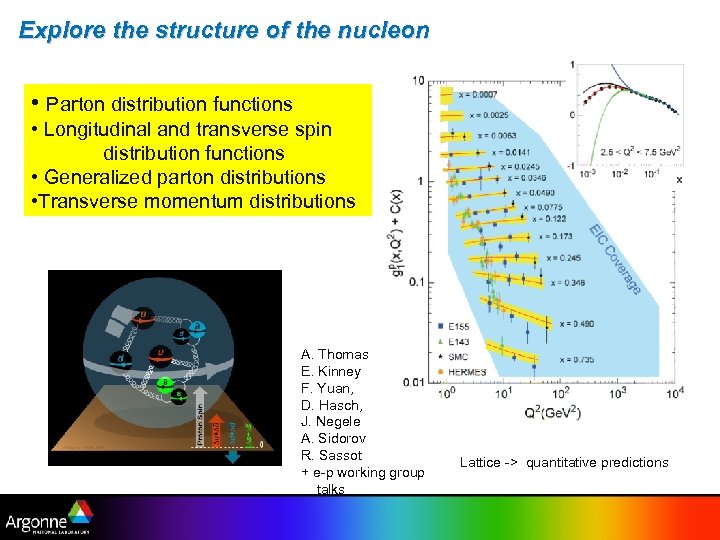 Explore the structure of the nucleon • Parton distribution functions • Longitudinal and transverse spin distribution functions • Generalized parton distributions • Transverse momentum distributions A. Thomas E. Kinney F. Yuan, D. Hasch, J. Negele A. Sidorov R. Sassot + e-p working group talks Lattice -> quantitative predictions
Explore the structure of the nucleon • Parton distribution functions • Longitudinal and transverse spin distribution functions • Generalized parton distributions • Transverse momentum distributions A. Thomas E. Kinney F. Yuan, D. Hasch, J. Negele A. Sidorov R. Sassot + e-p working group talks Lattice -> quantitative predictions
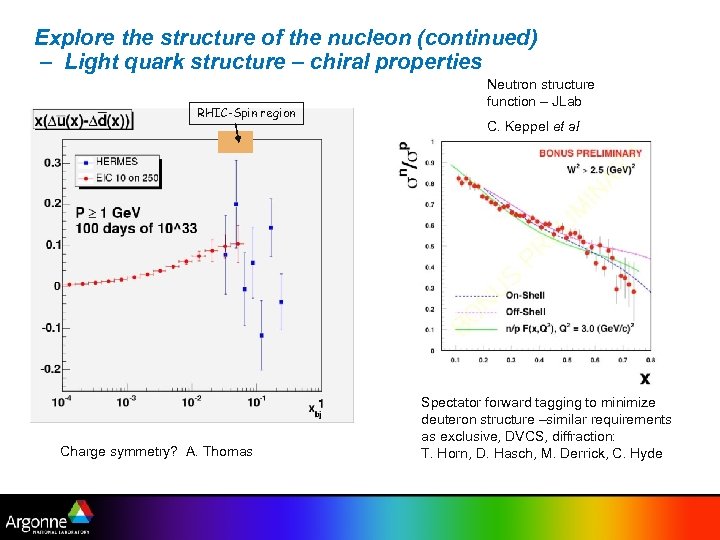 Explore the structure of the nucleon (continued) – Light quark structure – chiral properties RHIC-Spin region Charge symmetry? A. Thomas Neutron structure function – JLab C. Keppel et al Spectator forward tagging to minimize deuteron structure –similar requirements as exclusive, DVCS, diffraction: T. Horn, D. Hasch, M. Derrick, C. Hyde
Explore the structure of the nucleon (continued) – Light quark structure – chiral properties RHIC-Spin region Charge symmetry? A. Thomas Neutron structure function – JLab C. Keppel et al Spectator forward tagging to minimize deuteron structure –similar requirements as exclusive, DVCS, diffraction: T. Horn, D. Hasch, M. Derrick, C. Hyde
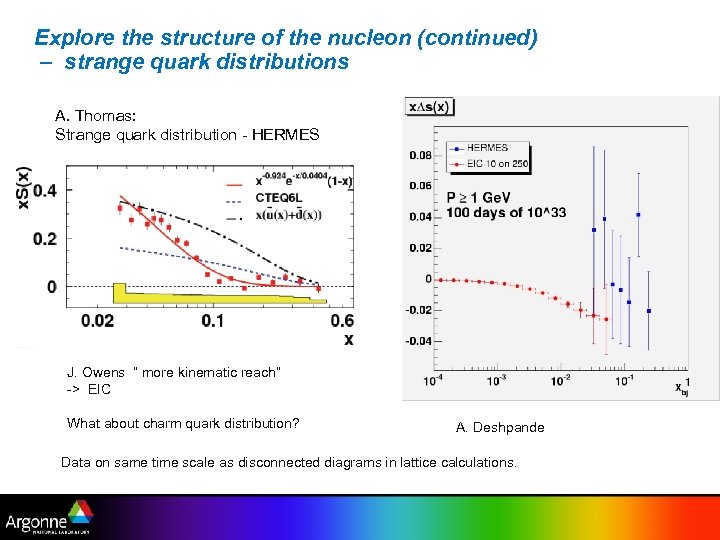 Explore the structure of the nucleon (continued) – strange quark distributions A. Thomas: Strange quark distribution - HERMES J. Owens ” more kinematic reach” -> EIC What about charm quark distribution? A. Deshpande Data on same time scale as disconnected diagrams in lattice calculations.
Explore the structure of the nucleon (continued) – strange quark distributions A. Thomas: Strange quark distribution - HERMES J. Owens ” more kinematic reach” -> EIC What about charm quark distribution? A. Deshpande Data on same time scale as disconnected diagrams in lattice calculations.
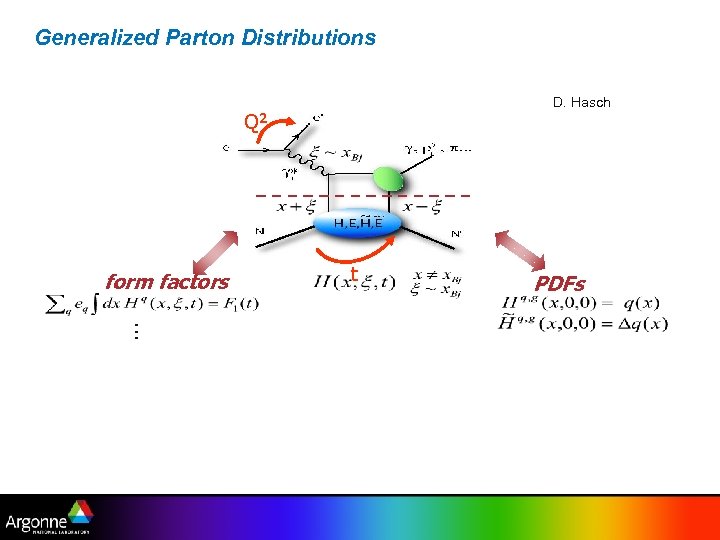 Generalized Parton Distributions D. Hasch Q 2 form factors t PDFs …
Generalized Parton Distributions D. Hasch Q 2 form factors t PDFs …
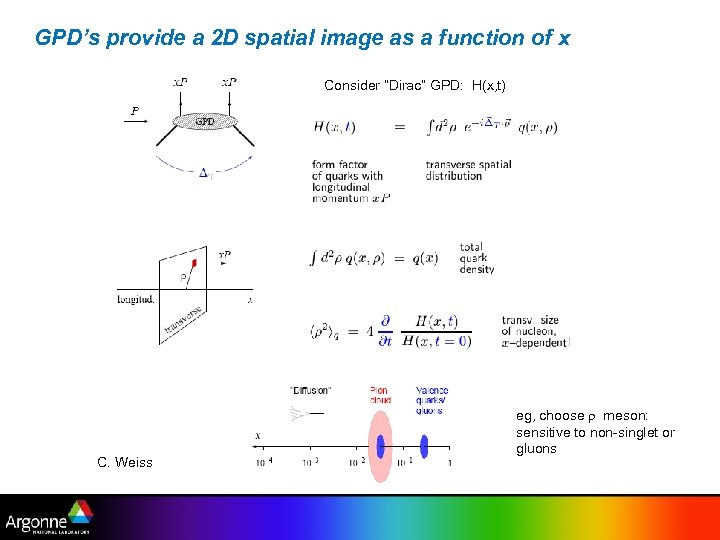 GPD’s provide a 2 D spatial image as a function of x Consider “Dirac” GPD: H(x, t) C. Weiss eg, choose r meson: sensitive to non-singlet or gluons
GPD’s provide a 2 D spatial image as a function of x Consider “Dirac” GPD: H(x, t) C. Weiss eg, choose r meson: sensitive to non-singlet or gluons
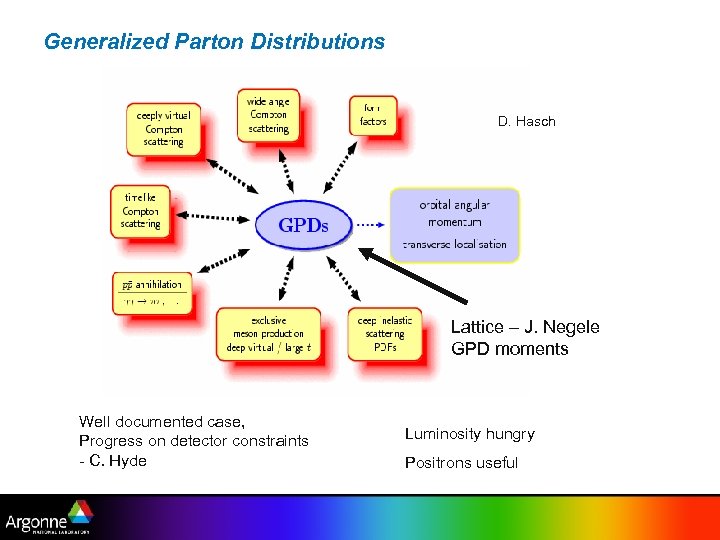 Generalized Parton Distributions D. Hasch Lattice – J. Negele GPD moments Well documented case, Progress on detector constraints - C. Hyde Luminosity hungry Positrons useful
Generalized Parton Distributions D. Hasch Lattice – J. Negele GPD moments Well documented case, Progress on detector constraints - C. Hyde Luminosity hungry Positrons useful
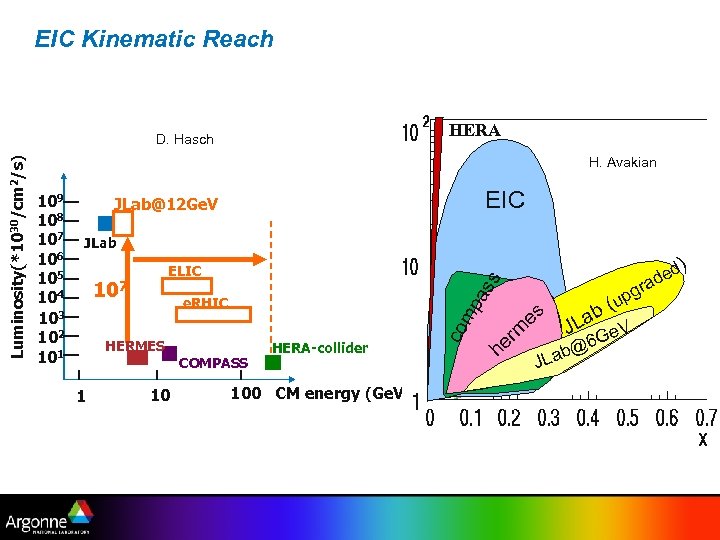 EIC Kinematic Reach 27 H. Avakian EIC JLab@12 Ge. V JLab 107 e. RHIC HERMES COMPASS 1 10 ) ed d gra ss ELIC pa 109 108 107 106 105 104 103 102 101 HERA-collider 100 CM energy (Ge. V) co m Luminosity(*1030/cm 2/s) Ge V HERA D. Hasch h m er es (up b a JL Ge. V 6 @ Lab J
EIC Kinematic Reach 27 H. Avakian EIC JLab@12 Ge. V JLab 107 e. RHIC HERMES COMPASS 1 10 ) ed d gra ss ELIC pa 109 108 107 106 105 104 103 102 101 HERA-collider 100 CM energy (Ge. V) co m Luminosity(*1030/cm 2/s) Ge V HERA D. Hasch h m er es (up b a JL Ge. V 6 @ Lab J
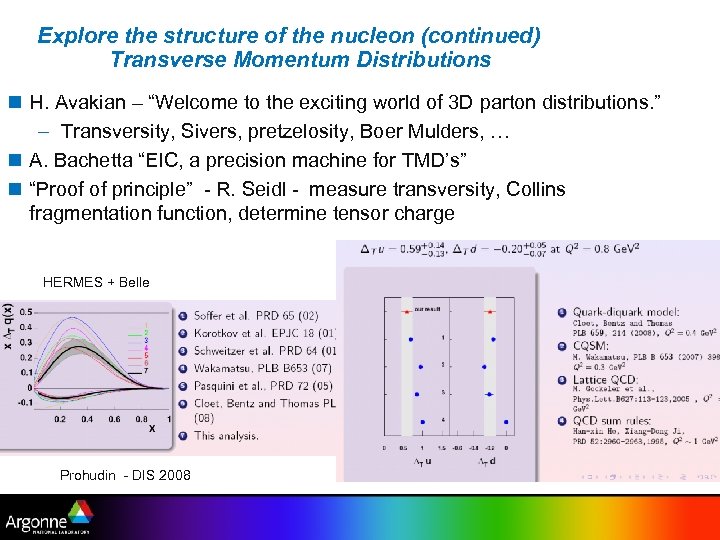 Explore the structure of the nucleon (continued) Transverse Momentum Distributions n H. Avakian – “Welcome to the exciting world of 3 D parton distributions. ” – Transversity, Sivers, pretzelosity, Boer Mulders, … n A. Bachetta “EIC, a precision machine for TMD’s” n “Proof of principle” - R. Seidl - measure transversity, Collins fragmentation function, determine tensor charge HERMES + Belle Prohudin - DIS 2008
Explore the structure of the nucleon (continued) Transverse Momentum Distributions n H. Avakian – “Welcome to the exciting world of 3 D parton distributions. ” – Transversity, Sivers, pretzelosity, Boer Mulders, … n A. Bachetta “EIC, a precision machine for TMD’s” n “Proof of principle” - R. Seidl - measure transversity, Collins fragmentation function, determine tensor charge HERMES + Belle Prohudin - DIS 2008
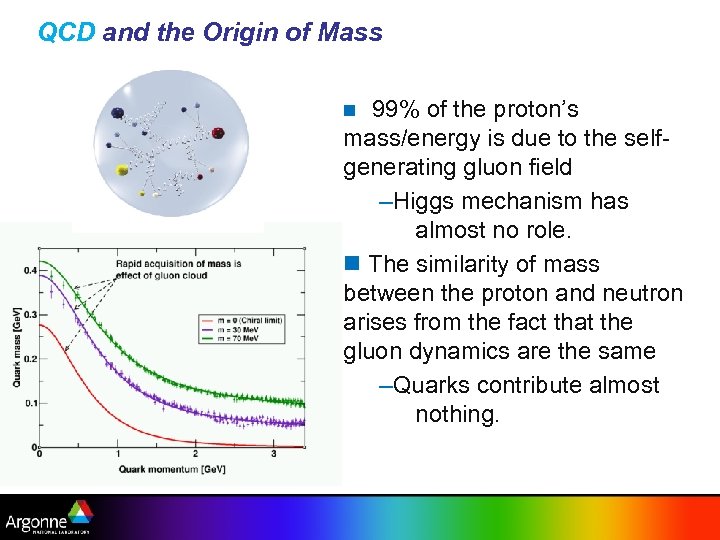 QCD and the Origin of Mass 99% of the proton’s mass/energy is due to the selfgenerating gluon field –Higgs mechanism has almost no role. n The similarity of mass between the proton and neutron arises from the fact that the gluon dynamics are the same –Quarks contribute almost nothing. n
QCD and the Origin of Mass 99% of the proton’s mass/energy is due to the selfgenerating gluon field –Higgs mechanism has almost no role. n The similarity of mass between the proton and neutron arises from the fact that the gluon dynamics are the same –Quarks contribute almost nothing. n
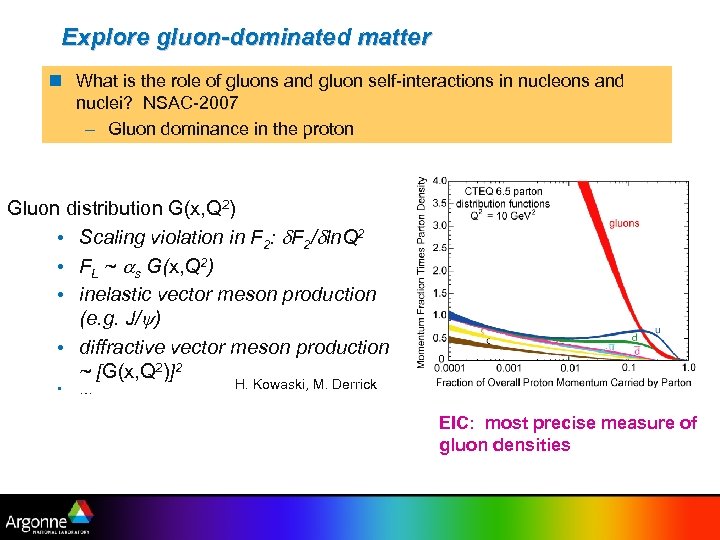 Explore gluon-dominated matter n What is the role of gluons and gluon self-interactions in nucleons and nuclei? NSAC-2007 – Gluon dominance in the proton Gluon distribution G(x, Q 2) • Scaling violation in F 2: d. F 2/dln. Q 2 • FL ~ as G(x, Q 2) • inelastic vector meson production (e. g. J/ ) • diffractive vector meson production ~ [G(x, Q 2)]2 • … H. Kowaski, M. Derrick EIC: most precise measure of gluon densities
Explore gluon-dominated matter n What is the role of gluons and gluon self-interactions in nucleons and nuclei? NSAC-2007 – Gluon dominance in the proton Gluon distribution G(x, Q 2) • Scaling violation in F 2: d. F 2/dln. Q 2 • FL ~ as G(x, Q 2) • inelastic vector meson production (e. g. J/ ) • diffractive vector meson production ~ [G(x, Q 2)]2 • … H. Kowaski, M. Derrick EIC: most precise measure of gluon densities
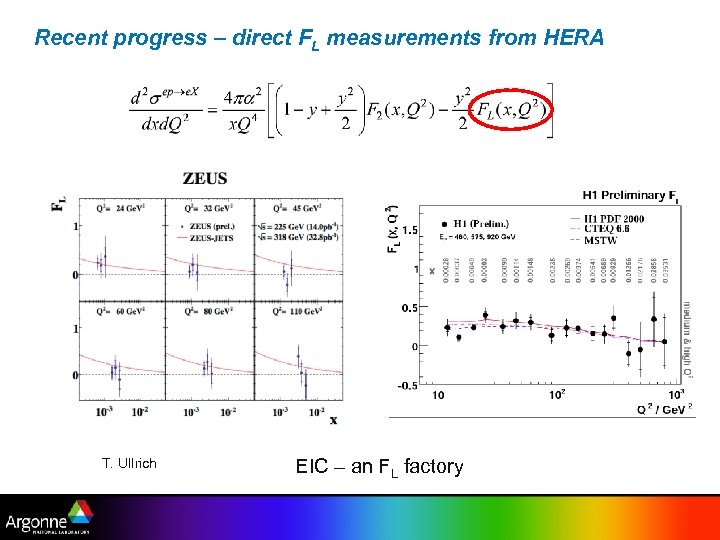 Recent progress – direct FL measurements from HERA T. Ullrich EIC – an FL factory
Recent progress – direct FL measurements from HERA T. Ullrich EIC – an FL factory
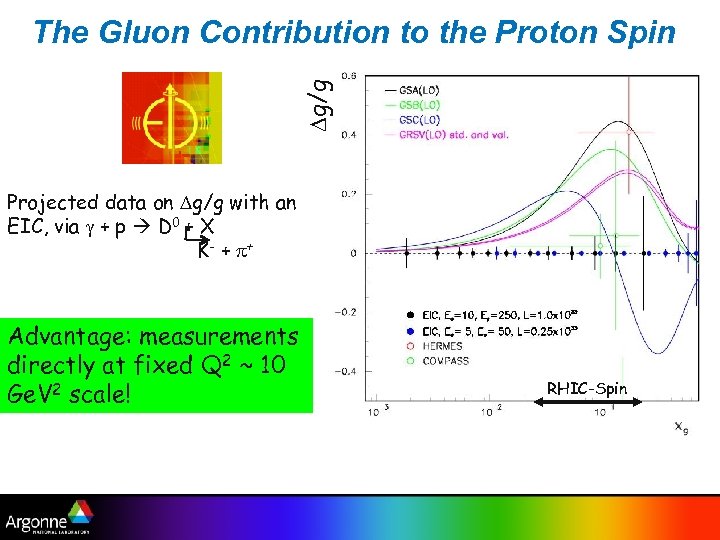 Dg/g The Gluon Contribution to the Proton Spin Projected data on Dg/g with an EIC, via g + p D 0 + X K - + p+ Advantage: measurements directly at fixed Q 2 ~ 10 Ge. V 2 scale! RHIC-Spin
Dg/g The Gluon Contribution to the Proton Spin Projected data on Dg/g with an EIC, via g + p D 0 + X K - + p+ Advantage: measurements directly at fixed Q 2 ~ 10 Ge. V 2 scale! RHIC-Spin
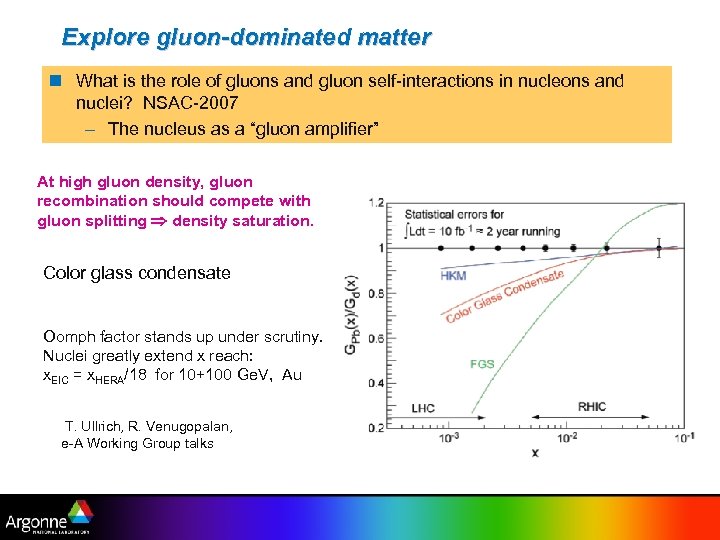 Explore gluon-dominated matter n What is the role of gluons and gluon self-interactions in nucleons and nuclei? NSAC-2007 – The nucleus as a “gluon amplifier” At high gluon density, gluon recombination should compete with gluon splitting density saturation. Color glass condensate Oomph factor stands up under scrutiny. Nuclei greatly extend x reach: x. EIC = x. HERA/18 for 10+100 Ge. V, Au T. Ullrich, R. Venugopalan, e-A Working Group talks
Explore gluon-dominated matter n What is the role of gluons and gluon self-interactions in nucleons and nuclei? NSAC-2007 – The nucleus as a “gluon amplifier” At high gluon density, gluon recombination should compete with gluon splitting density saturation. Color glass condensate Oomph factor stands up under scrutiny. Nuclei greatly extend x reach: x. EIC = x. HERA/18 for 10+100 Ge. V, Au T. Ullrich, R. Venugopalan, e-A Working Group talks
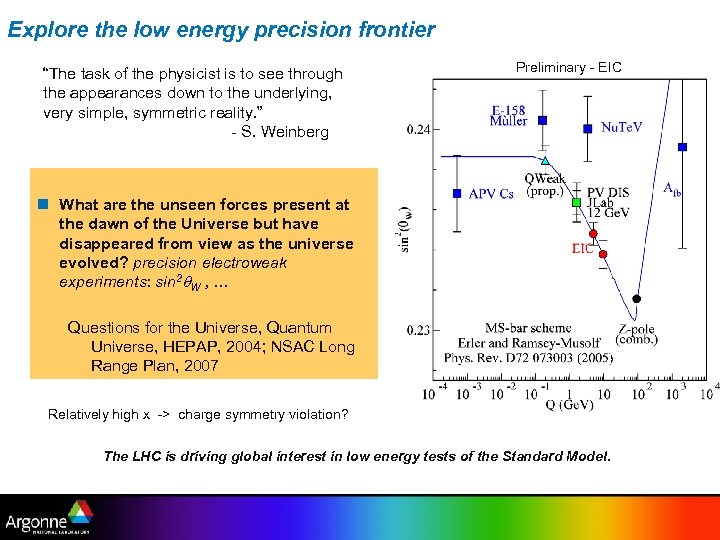 Explore the low energy precision frontier “The task of the physicist is to see through the appearances down to the underlying, very simple, symmetric reality. ” - S. Weinberg Preliminary - EIC n What are the unseen forces present at the dawn of the Universe but have disappeared from view as the universe evolved? precision electroweak experiments: sin 2 q. W , … Questions for the Universe, Quantum Universe, HEPAP, 2004; NSAC Long Range Plan, 2007 Relatively high x -> charge symmetry violation? The LHC is driving global interest in low energy tests of the Standard Model.
Explore the low energy precision frontier “The task of the physicist is to see through the appearances down to the underlying, very simple, symmetric reality. ” - S. Weinberg Preliminary - EIC n What are the unseen forces present at the dawn of the Universe but have disappeared from view as the universe evolved? precision electroweak experiments: sin 2 q. W , … Questions for the Universe, Quantum Universe, HEPAP, 2004; NSAC Long Range Plan, 2007 Relatively high x -> charge symmetry violation? The LHC is driving global interest in low energy tests of the Standard Model.
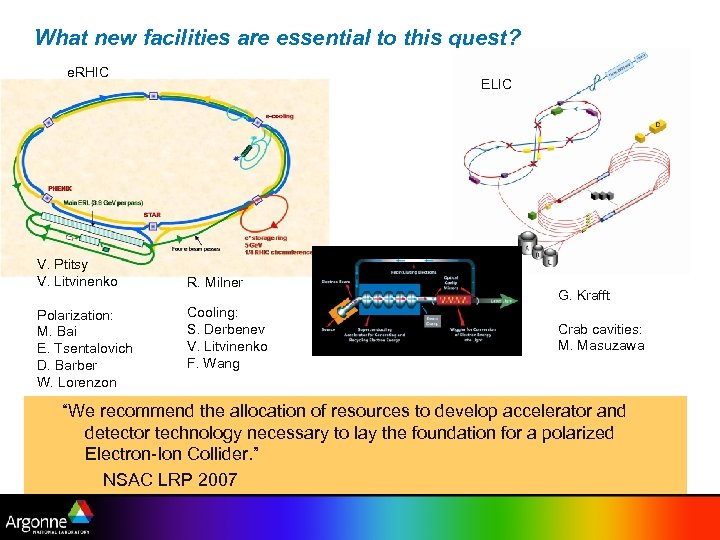 What new facilities are essential to this quest? e. RHIC V. Ptitsy V. Litvinenko Polarization: M. Bai E. Tsentalovich D. Barber W. Lorenzon ELIC R. Milner Cooling: S. Derbenev V. Litvinenko F. Wang G. Krafft Crab cavities: M. Masuzawa “We recommend the allocation of resources to develop accelerator and detector technology necessary to lay the foundation for a polarized Electron-Ion Collider. ” NSAC LRP 2007
What new facilities are essential to this quest? e. RHIC V. Ptitsy V. Litvinenko Polarization: M. Bai E. Tsentalovich D. Barber W. Lorenzon ELIC R. Milner Cooling: S. Derbenev V. Litvinenko F. Wang G. Krafft Crab cavities: M. Masuzawa “We recommend the allocation of resources to develop accelerator and detector technology necessary to lay the foundation for a polarized Electron-Ion Collider. ” NSAC LRP 2007
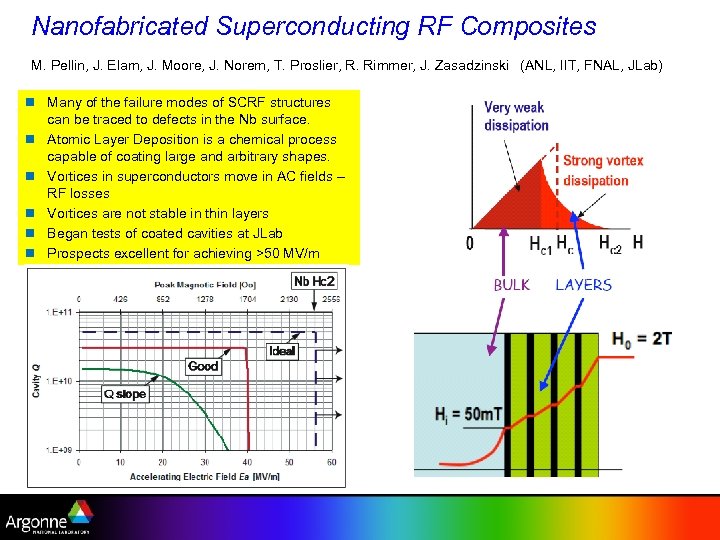 Nanofabricated Superconducting RF Composites M. Pellin, J. Elam, J. Moore, J. Norem, T. Proslier, R. Rimmer, J. Zasadzinski (ANL, IIT, FNAL, JLab) n Many of the failure modes of SCRF structures can be traced to defects in the Nb surface. n Atomic Layer Deposition is a chemical process capable of coating large and arbitrary shapes. n Vortices in superconductors move in AC fields – RF losses n Vortices are not stable in thin layers n Began tests of coated cavities at JLab n Prospects excellent for achieving >50 MV/m
Nanofabricated Superconducting RF Composites M. Pellin, J. Elam, J. Moore, J. Norem, T. Proslier, R. Rimmer, J. Zasadzinski (ANL, IIT, FNAL, JLab) n Many of the failure modes of SCRF structures can be traced to defects in the Nb surface. n Atomic Layer Deposition is a chemical process capable of coating large and arbitrary shapes. n Vortices in superconductors move in AC fields – RF losses n Vortices are not stable in thin layers n Began tests of coated cavities at JLab n Prospects excellent for achieving >50 MV/m
 An application of our technology Hampton University Proton Therapy Institute – online in 2010 Cynthia Keppel – Scientific and Technical Director
An application of our technology Hampton University Proton Therapy Institute – online in 2010 Cynthia Keppel – Scientific and Technical Director
 World Community in 2015 and Beyond n Three new major facilities investigating nuclear physics at hadronic level (QCD): GSI, J-PARC and 12 -Ge. V JLab n Two new facilities that explore nuclei at the partonic level: RHIC with upgrades and LHC n Two new proposed facilities that can take our field to the next level: EIC, Project X (FNAL) n Petascale computing facilities are imminent, Exascale is on the way. n Outstanding opportunities for the future
World Community in 2015 and Beyond n Three new major facilities investigating nuclear physics at hadronic level (QCD): GSI, J-PARC and 12 -Ge. V JLab n Two new facilities that explore nuclei at the partonic level: RHIC with upgrades and LHC n Two new proposed facilities that can take our field to the next level: EIC, Project X (FNAL) n Petascale computing facilities are imminent, Exascale is on the way. n Outstanding opportunities for the future
 The International Picture Nu. PECC activities – EIC study group approved at the meeting in Bucharest on 10/27/2007 with G. Rosner, chair – Charge is to produce a report outlining: • The science possibilities • The interest among European groups • Possible links with proposals outside Europe n Glasgow meeting in Fall 2008. n
The International Picture Nu. PECC activities – EIC study group approved at the meeting in Bucharest on 10/27/2007 with G. Rosner, chair – Charge is to produce a report outlining: • The science possibilities • The interest among European groups • Possible links with proposals outside Europe n Glasgow meeting in Fall 2008. n
 The International Picture (continued) n OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development) Global Science Forum – Nuclear Physics Working Group- report on ‘optimal evolution of Nuclear Physics at an international level during the next 10 -15 years’ n Membership – 14 countries n Two projects may be ‘Global’ due to size – EURISOL – EIC F. Willeke, S. Chattopadhyay
The International Picture (continued) n OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development) Global Science Forum – Nuclear Physics Working Group- report on ‘optimal evolution of Nuclear Physics at an international level during the next 10 -15 years’ n Membership – 14 countries n Two projects may be ‘Global’ due to size – EURISOL – EIC F. Willeke, S. Chattopadhyay
 Columbus’ vision Look! Purple mountains! Spacious skies! Fruited plains! … Is someone writing this down? - adapted from G. Larson Yes! white papers, NSAC LRP 2007, but we need an even more compelling case by next NP LRP (2012 -13)
Columbus’ vision Look! Purple mountains! Spacious skies! Fruited plains! … Is someone writing this down? - adapted from G. Larson Yes! white papers, NSAC LRP 2007, but we need an even more compelling case by next NP LRP (2012 -13)
 Concluding Statement n EIC research can penetrate some of the most profound mysteries and questions of 21 st century physics. n Technology is improving at an astounding rate: – Accelerator design, cavity improvement, energy recovery, crab cavities, cooling, polarization, polarimetry, detectors, petascale computing, … n There are interesting new opportunities worldwide. The next 10 years will be even more exciting than the last 10 years. n We must put forward a most compelling case for the EIC on the time scale of the next LRP.
Concluding Statement n EIC research can penetrate some of the most profound mysteries and questions of 21 st century physics. n Technology is improving at an astounding rate: – Accelerator design, cavity improvement, energy recovery, crab cavities, cooling, polarization, polarimetry, detectors, petascale computing, … n There are interesting new opportunities worldwide. The next 10 years will be even more exciting than the last 10 years. n We must put forward a most compelling case for the EIC on the time scale of the next LRP.
 Summary n Fourth EIC workshop has been a resounding success. n Clear and substantial progress was demonstrated since the last EIC workshop. n Essential to lay the foundation for the next Long Range Planning Exercise. must develop a clear path forward. n Next Workshop - Berkeley - December 11 -13, 2008 Peter Jacobs
Summary n Fourth EIC workshop has been a resounding success. n Clear and substantial progress was demonstrated since the last EIC workshop. n Essential to lay the foundation for the next Long Range Planning Exercise. must develop a clear path forward. n Next Workshop - Berkeley - December 11 -13, 2008 Peter Jacobs
 Many thanks to Steering Committee • Abhay Deshpande, Stony Brook, RBRC (Co-Chair/Contact person) • Rolf Ent, Jlab • Charles Hyde, ODU/UBP, France • Peter Jacobs, LBL Working Groups and Convenors • Richard Milner, MIT (Co-Chair/Contact person) • ep Physics • Thomas Ulrich, BNL • Antje Bruell, JLAB • Raju Venugopalan, BNL • Ernst Sichterman, LBL • Antje Bruell, Jlab • Werner Vogelsang, BNL • Christian Weiss, JLAB • e. A Physics International Advisory Committee • Vadim Guzey, JLAB • Dave Morrison, BNL n Jochen Bartels (DESY) • Thomas Ullrich, BNL n Allen Caldwell (MPI, Munich) • Raju Venugopalan, BNL n Albert De Roeck (CERN) • Detector n Walter Henning (ANL) • Elke Aschenauer, JLAB • Edward Kinney, Colorado n Dave Hertzog (UIUC) • Bernd Surrow, MIT n Xiangdong Ji (U. Maryland) • Electron Beam Polarimetry n Robert Klanner (U. Hamburg) • Wolfgang Lorenzon, Michigan n Katsunobu Oide (KEK) n Naohito Saito (KEK) n Uli Wienands (SLAC)
Many thanks to Steering Committee • Abhay Deshpande, Stony Brook, RBRC (Co-Chair/Contact person) • Rolf Ent, Jlab • Charles Hyde, ODU/UBP, France • Peter Jacobs, LBL Working Groups and Convenors • Richard Milner, MIT (Co-Chair/Contact person) • ep Physics • Thomas Ulrich, BNL • Antje Bruell, JLAB • Raju Venugopalan, BNL • Ernst Sichterman, LBL • Antje Bruell, Jlab • Werner Vogelsang, BNL • Christian Weiss, JLAB • e. A Physics International Advisory Committee • Vadim Guzey, JLAB • Dave Morrison, BNL n Jochen Bartels (DESY) • Thomas Ullrich, BNL n Allen Caldwell (MPI, Munich) • Raju Venugopalan, BNL n Albert De Roeck (CERN) • Detector n Walter Henning (ANL) • Elke Aschenauer, JLAB • Edward Kinney, Colorado n Dave Hertzog (UIUC) • Bernd Surrow, MIT n Xiangdong Ji (U. Maryland) • Electron Beam Polarimetry n Robert Klanner (U. Hamburg) • Wolfgang Lorenzon, Michigan n Katsunobu Oide (KEK) n Naohito Saito (KEK) n Uli Wienands (SLAC)
 Many thanks to Workshop Organizing Committee: Alberto Accardi - Hampton/JLab Andrei Afanasev - Hampton/JLab Eric Christy - Hampton Abhay Deshpande - Stony Brook/RBRC Rolf Ent - JLab/Hampton Cynthia Keppel - Hampton/JLab Lia Merminga - JLab Richard Milner - MIT Thomas Roser - BNL
Many thanks to Workshop Organizing Committee: Alberto Accardi - Hampton/JLab Andrei Afanasev - Hampton/JLab Eric Christy - Hampton Abhay Deshpande - Stony Brook/RBRC Rolf Ent - JLab/Hampton Cynthia Keppel - Hampton/JLab Lia Merminga - JLab Richard Milner - MIT Thomas Roser - BNL


