Exploration 1, Chapter 3.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 57
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 CCNA EXPLORATION 1 CHAPTER 3 Application layer functionality and protocols By Zhamanov Azamat
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 CCNA EXPLORATION 1 CHAPTER 3 Application layer functionality and protocols By Zhamanov Azamat
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 In this chapter, you will learn to: • Describe how the functions of the three upper OSI model layers provide network services to end user applications. • Describe how the TCP/IP Application Layer protocols provide the services specified by the upper layers of the OSI model. • Define how people use the Application Layer to communicate across the information network. • Describe the function of well-known TCP/IP applications, such as the World Wide Web and email, and their related services (HTTP, DNS, SMB, DHCP, SMTP/POP, and Telnet).
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 In this chapter, you will learn to: • Describe how the functions of the three upper OSI model layers provide network services to end user applications. • Describe how the TCP/IP Application Layer protocols provide the services specified by the upper layers of the OSI model. • Define how people use the Application Layer to communicate across the information network. • Describe the function of well-known TCP/IP applications, such as the World Wide Web and email, and their related services (HTTP, DNS, SMB, DHCP, SMTP/POP, and Telnet).
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 In this chapter you will learn to: • Explain how protocols ensure services running on one kind of device can send to and receive data from many different network devices. • Use network analysis tools to examine and explain how common user applications work.
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 In this chapter you will learn to: • Explain how protocols ensure services running on one kind of device can send to and receive data from many different network devices. • Use network analysis tools to examine and explain how common user applications work.
 Suleyman Demirel University, Summer 2012 Speaking rules Use a common language 2. Wait your turn 3. Signal when stared 4. Signal when finished 1.
Suleyman Demirel University, Summer 2012 Speaking rules Use a common language 2. Wait your turn 3. Signal when stared 4. Signal when finished 1.
 Suleyman Demirel University, Summer 2012 Common speaking rules
Suleyman Demirel University, Summer 2012 Common speaking rules
 Suleyman Demirel University, Summer 2012 Common speaking rules
Suleyman Demirel University, Summer 2012 Common speaking rules
 Suleyman Demirel University, Summer 2012 Common speaking rules Your ideas…
Suleyman Demirel University, Summer 2012 Common speaking rules Your ideas…
 Suleyman Demirel University, Summer 2012 Computer Networks rules Devices which are participating in Computer Networks are also using rules and that rules are called protocols Protocol is the set of rules
Suleyman Demirel University, Summer 2012 Computer Networks rules Devices which are participating in Computer Networks are also using rules and that rules are called protocols Protocol is the set of rules
 Suleyman Demirel University, Summer 2012 Computer Networks Layered Models To simply understand Computer Networks, engineers created two Computer Networks models and each of them consist of layers. Each layer consist of different types of protocols (set of rules)
Suleyman Demirel University, Summer 2012 Computer Networks Layered Models To simply understand Computer Networks, engineers created two Computer Networks models and each of them consist of layers. Each layer consist of different types of protocols (set of rules)
 Suleyman Demirel University, Summer 2012 Network models OSI TCP/IP • The OSI and TCP/IP reference models are layered, abstract representation created as a guideline for network protocol design.
Suleyman Demirel University, Summer 2012 Network models OSI TCP/IP • The OSI and TCP/IP reference models are layered, abstract representation created as a guideline for network protocol design.
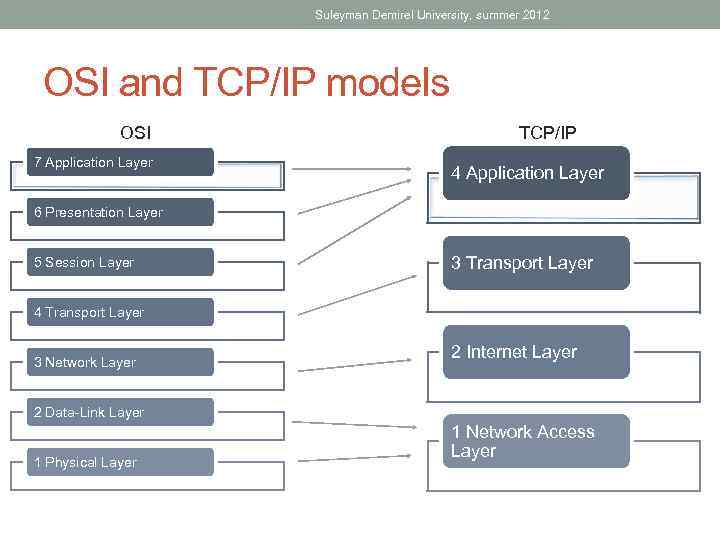 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 OSI and TCP/IP models OSI 7 Application Layer TCP/IP 4 Application Layer 6 Presentation Layer 5 Session Layer 3 Transport Layer 4 Transport Layer 3 Network Layer 2 Internet Layer 2 Data-Link Layer 1 Physical Layer 1 Network Access Layer
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 OSI and TCP/IP models OSI 7 Application Layer TCP/IP 4 Application Layer 6 Presentation Layer 5 Session Layer 3 Transport Layer 4 Transport Layer 3 Network Layer 2 Internet Layer 2 Data-Link Layer 1 Physical Layer 1 Network Access Layer
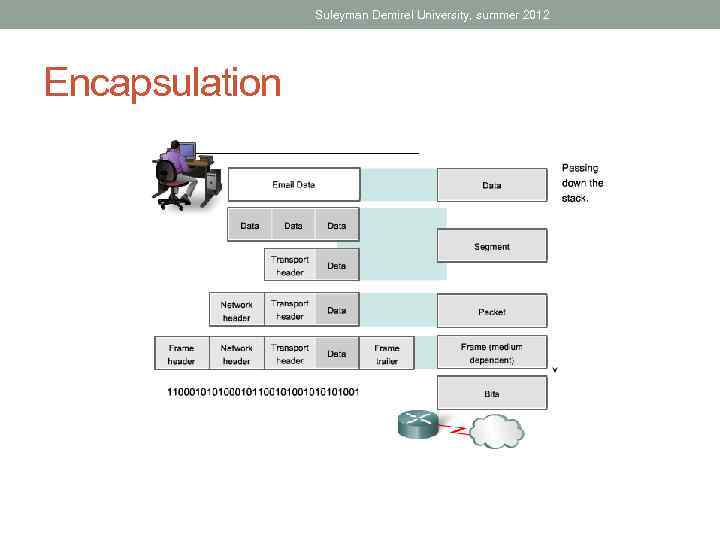 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Encapsulation
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Encapsulation
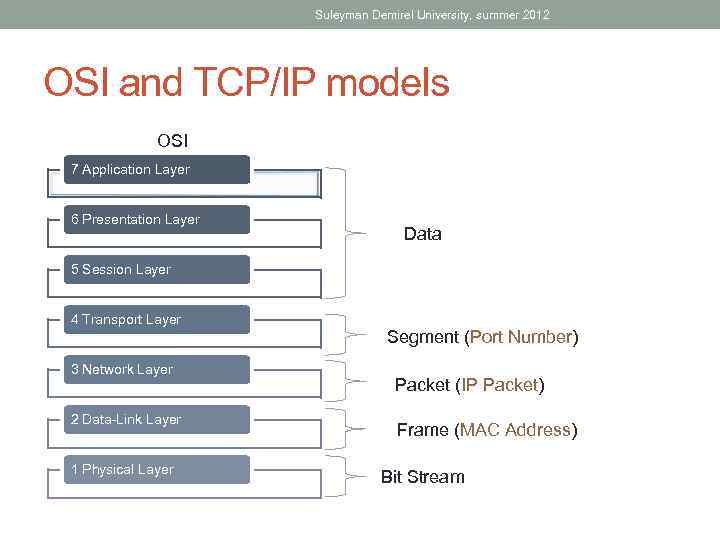 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 OSI and TCP/IP models OSI 7 Application Layer 6 Presentation Layer Data 5 Session Layer 4 Transport Layer 3 Network Layer 2 Data-Link Layer 1 Physical Layer Segment (Port Number) Packet (IP Packet) Frame (MAC Address) Bit Stream
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 OSI and TCP/IP models OSI 7 Application Layer 6 Presentation Layer Data 5 Session Layer 4 Transport Layer 3 Network Layer 2 Data-Link Layer 1 Physical Layer Segment (Port Number) Packet (IP Packet) Frame (MAC Address) Bit Stream
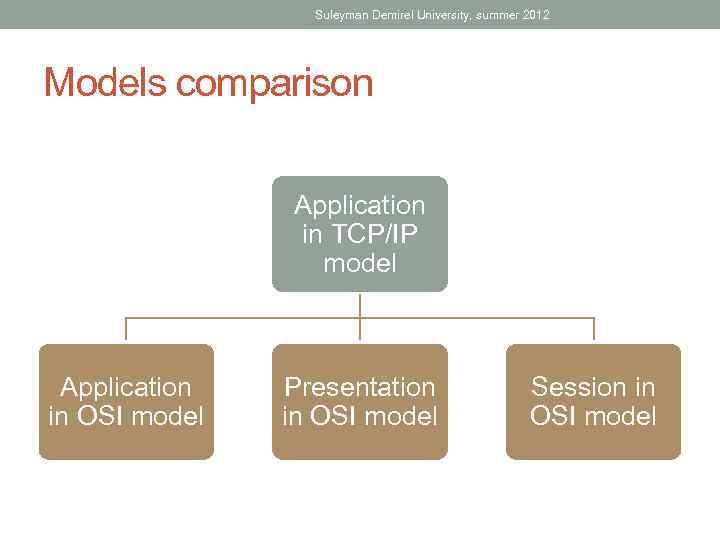 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Models comparison Application in TCP/IP model Application in OSI model Presentation in OSI model Session in OSI model
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Models comparison Application in TCP/IP model Application in OSI model Presentation in OSI model Session in OSI model
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Application Layer • Application layer services initiate the data transfer. • The Application layer prepares human communication for transmission over the data network. • Application layer receives data from the network and prepare it for human use.
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Application Layer • Application layer services initiate the data transfer. • The Application layer prepares human communication for transmission over the data network. • Application layer receives data from the network and prepare it for human use.
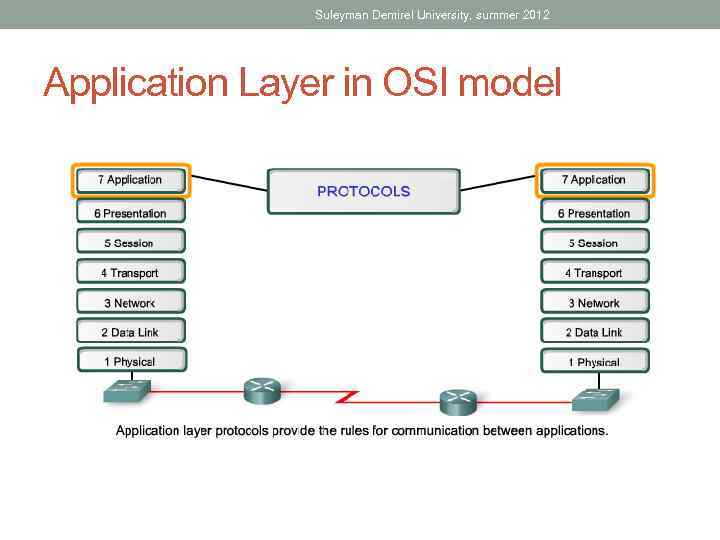 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Application Layer in OSI model
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Application Layer in OSI model
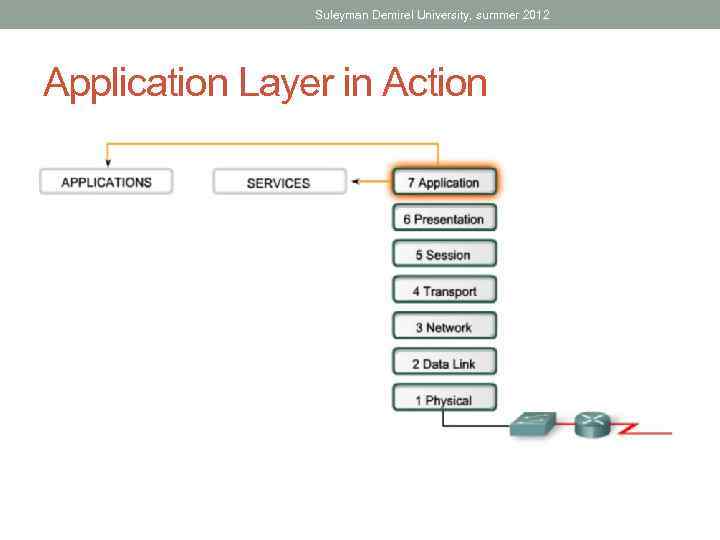 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Application Layer in Action
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Application Layer in Action
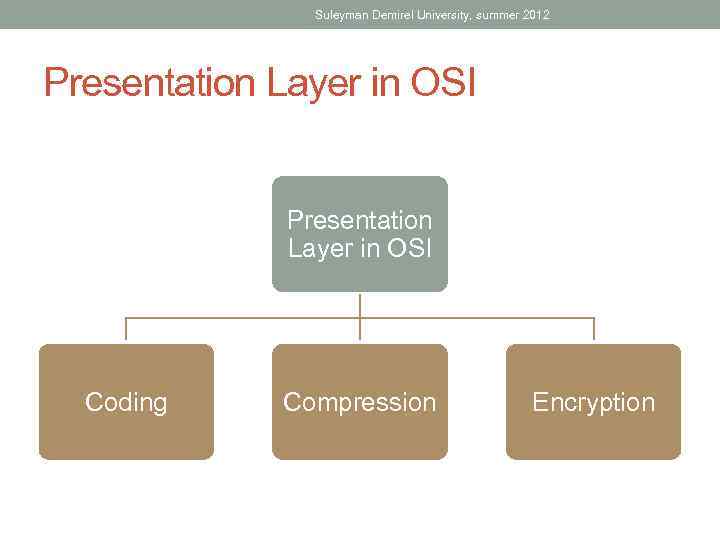 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Presentation Layer in OSI Coding Compression Encryption
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Presentation Layer in OSI Coding Compression Encryption
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Coding • Coding and conversion of Application layer data to ensure that data from the source device can be interpreted by the appropriate application
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Coding • Coding and conversion of Application layer data to ensure that data from the source device can be interpreted by the appropriate application
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Compression • Compression of the data in a manner that can be decompressed by the destination device.
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Compression • Compression of the data in a manner that can be decompressed by the destination device.
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Encryption • Encryption of the data for transmission and the decryption of data upon receipt by the destination.
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Encryption • Encryption of the data for transmission and the decryption of data upon receipt by the destination.
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Session Layer in OSI • Maintain dialogs between source and destination applications. • The Session layer handles the exchange of information to initiate dialogs, keep them active, and to restart sessions that are disrupted or idle for a long period of time.
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Session Layer in OSI • Maintain dialogs between source and destination applications. • The Session layer handles the exchange of information to initiate dialogs, keep them active, and to restart sessions that are disrupted or idle for a long period of time.
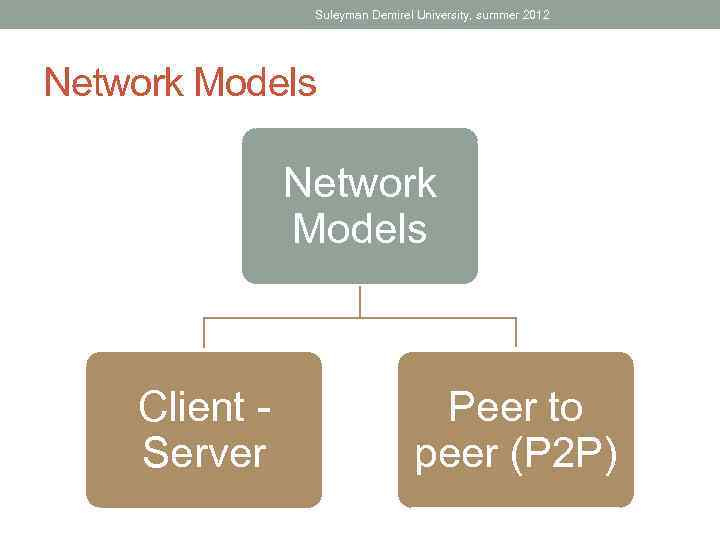 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Network Models Client Server Peer to peer (P 2 P)
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Network Models Client Server Peer to peer (P 2 P)
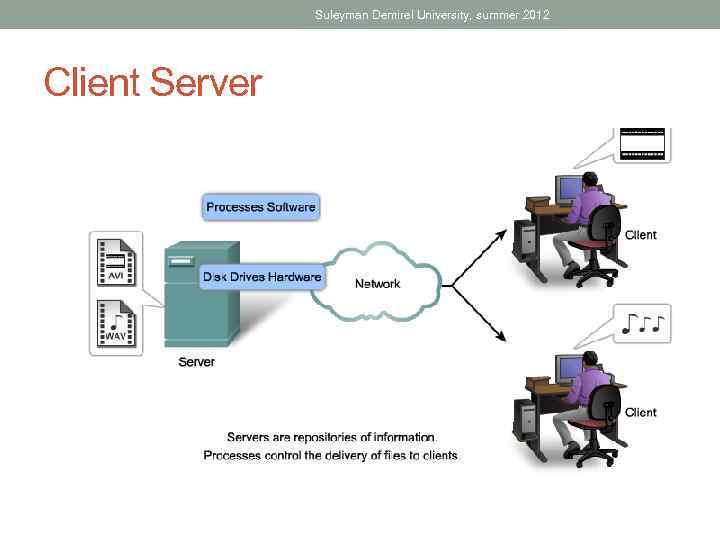 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Client Server
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Client Server
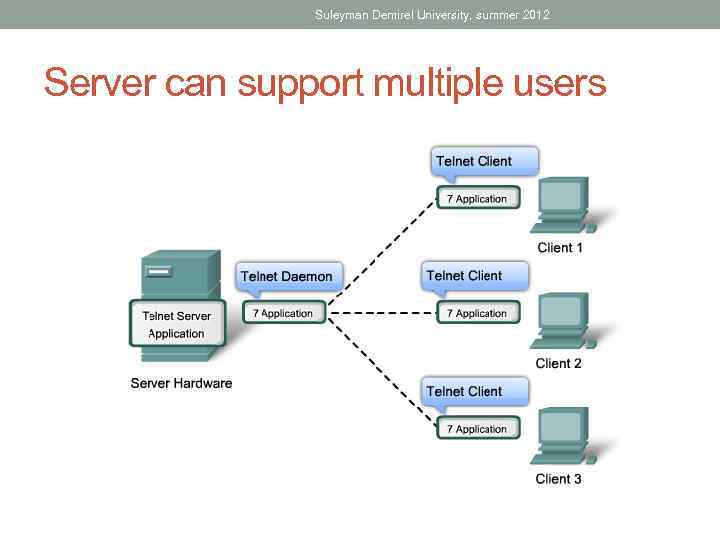 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Server can support multiple users
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Server can support multiple users
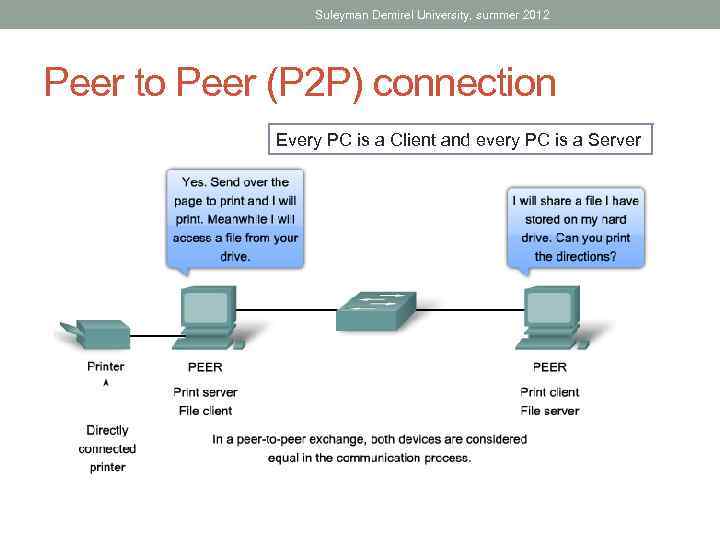 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Peer to Peer (P 2 P) connection Every PC is a Client and every PC is a Server
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Peer to Peer (P 2 P) connection Every PC is a Client and every PC is a Server
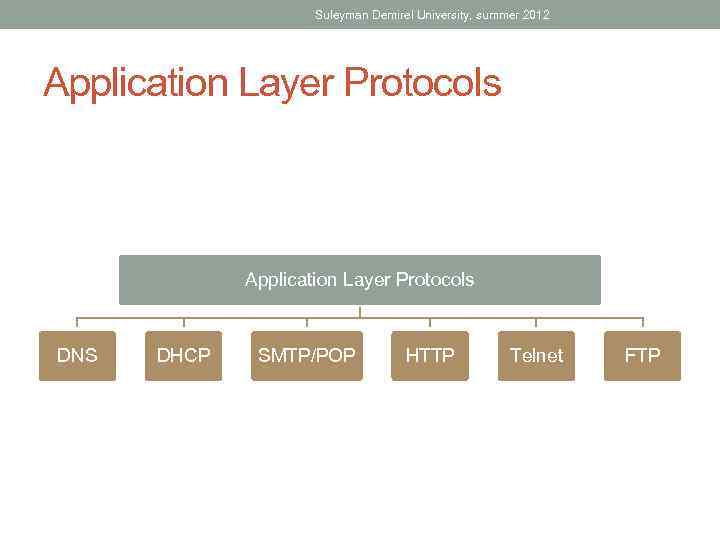 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Application Layer Protocols DNS DHCP SMTP/POP HTTP Telnet FTP
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Application Layer Protocols DNS DHCP SMTP/POP HTTP Telnet FTP
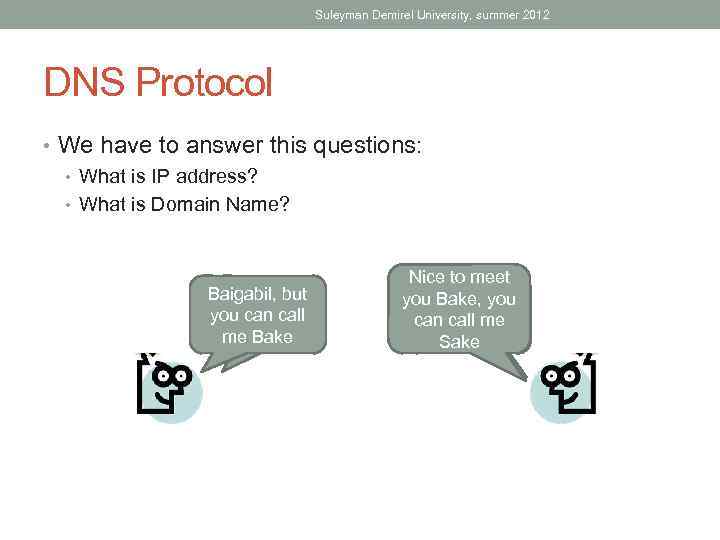 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DNS Protocol • We have to answer this questions: • What is IP address? • What is Domain Name? Baigabil, but Hello, my youname is can call me Bake Baigabil Nice to meet you Bake, you Hi, Baiga… can. What? call me Sake
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DNS Protocol • We have to answer this questions: • What is IP address? • What is Domain Name? Baigabil, but Hello, my youname is can call me Bake Baigabil Nice to meet you Bake, you Hi, Baiga… can. What? call me Sake
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DNS Protocol • We have to answer this questions: • What is IP address? • What is Domain Name? 192. 168. 102. 11 Nice to meet Hi, 192… you What? gmail. com Baigabil I am 192. 168. 102. 11, Hello, I am but you can call 192. 168. 102. 11 me gmail. com IP address = Name Domain name = Nickname gmail. com Bake
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DNS Protocol • We have to answer this questions: • What is IP address? • What is Domain Name? 192. 168. 102. 11 Nice to meet Hi, 192… you What? gmail. com Baigabil I am 192. 168. 102. 11, Hello, I am but you can call 192. 168. 102. 11 me gmail. com IP address = Name Domain name = Nickname gmail. com Bake
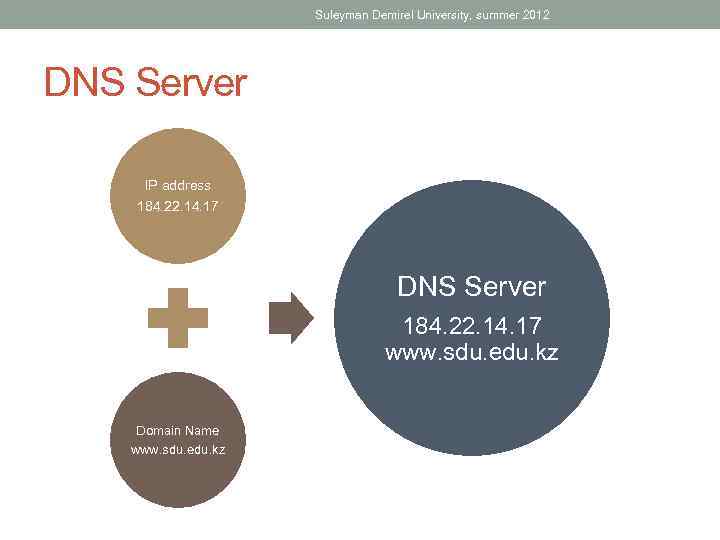 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DNS Server IP address 184. 22. 14. 17 DNS Server 184. 22. 14. 17 www. sdu. edu. kz Domain Name www. sdu. edu. kz
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DNS Server IP address 184. 22. 14. 17 DNS Server 184. 22. 14. 17 www. sdu. edu. kz Domain Name www. sdu. edu. kz
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DNS in Process
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DNS in Process
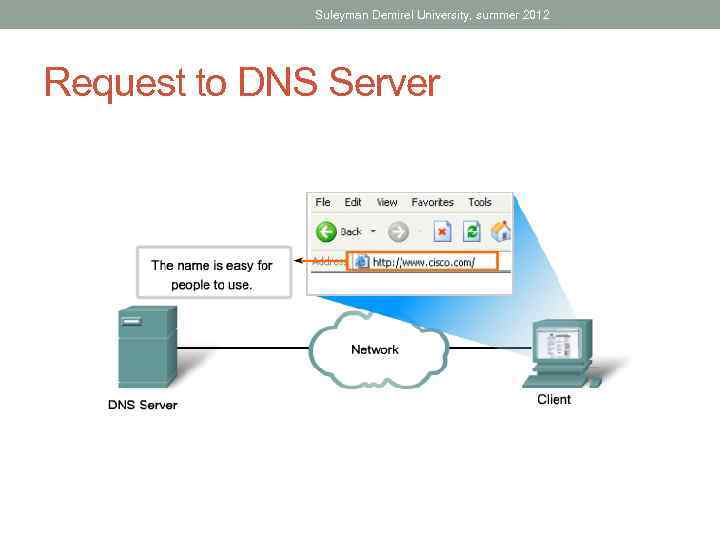 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Request to DNS Server
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Request to DNS Server
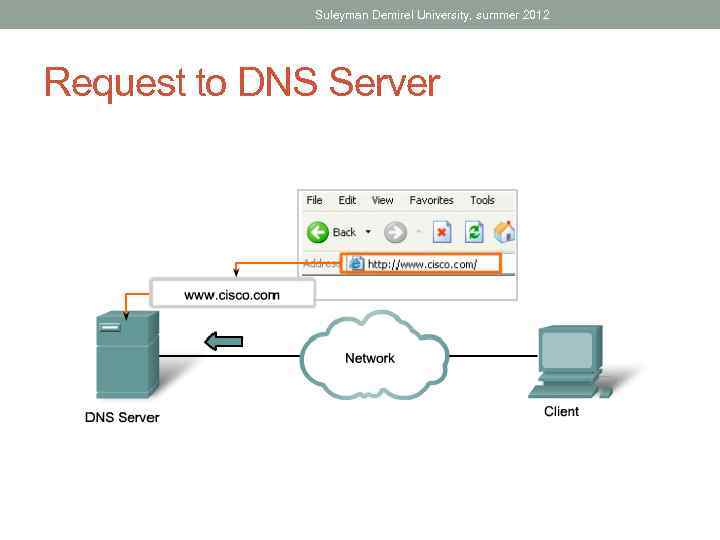 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Request to DNS Server
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Request to DNS Server
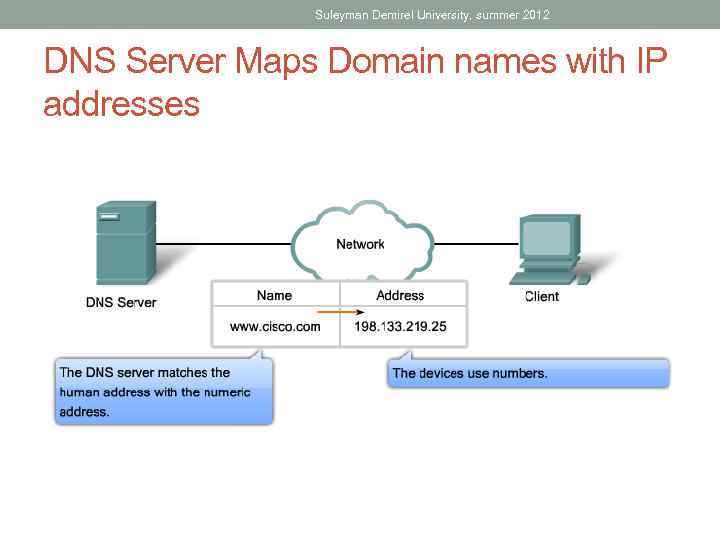 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DNS Server Maps Domain names with IP addresses
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DNS Server Maps Domain names with IP addresses
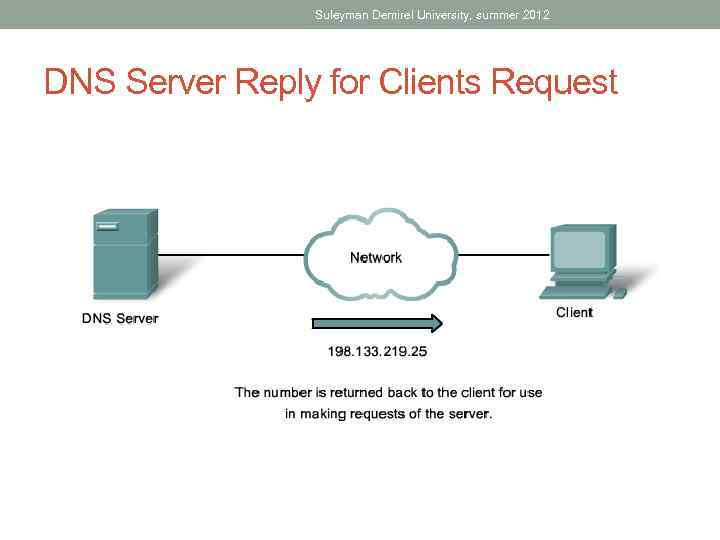 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DNS Server Reply for Clients Request
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DNS Server Reply for Clients Request
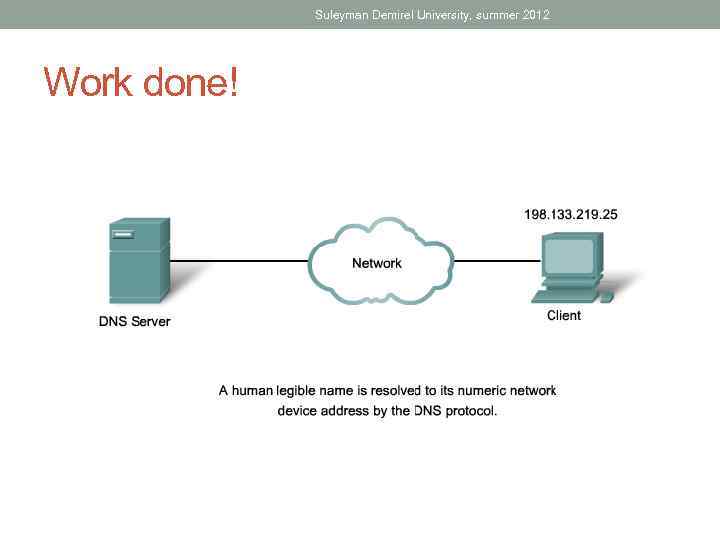 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Work done!
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Work done!
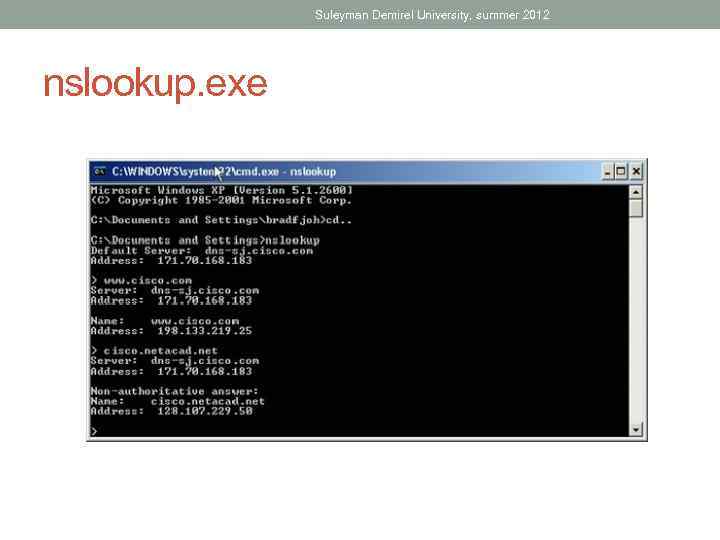 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 nslookup. exe
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 nslookup. exe
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Hierarchy of DNS Servers • Root Level Domain Servers • . kz - Kazakhstan • . uz - Uzbekistan • . com - a business or industry • . ru - Russia • . org - a non-profit organization • Top Level Domain Servers • ok. kz • nur. kz • Secondary Level Domain Servers • mail. ok. kz • www. ok. kz
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Hierarchy of DNS Servers • Root Level Domain Servers • . kz - Kazakhstan • . uz - Uzbekistan • . com - a business or industry • . ru - Russia • . org - a non-profit organization • Top Level Domain Servers • ok. kz • nur. kz • Secondary Level Domain Servers • mail. ok. kz • www. ok. kz
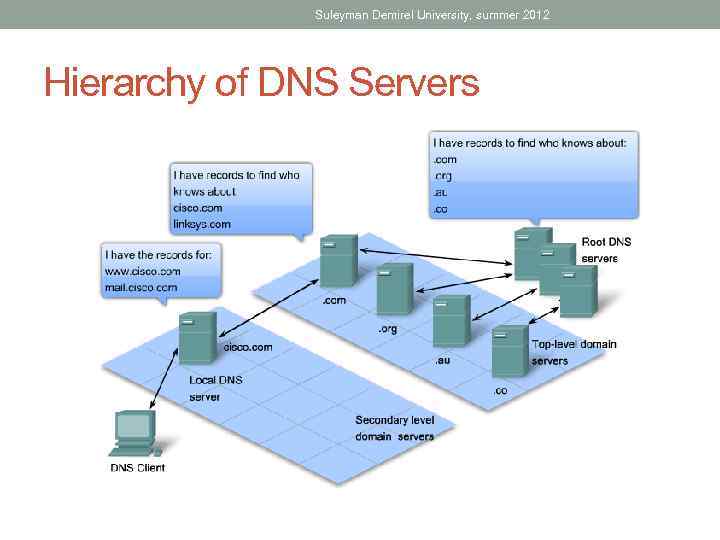 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Hierarchy of DNS Servers
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Hierarchy of DNS Servers
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 HTTP – Hypertext Transfer Protocol • Hypertext?
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 HTTP – Hypertext Transfer Protocol • Hypertext?
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 HTTP in Process
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 HTTP in Process
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 HTTP Request
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 HTTP Request
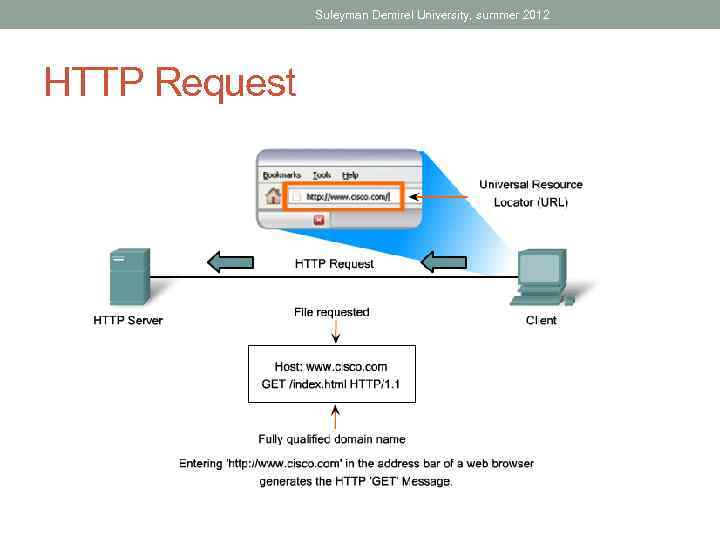 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 HTTP Request
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 HTTP Request
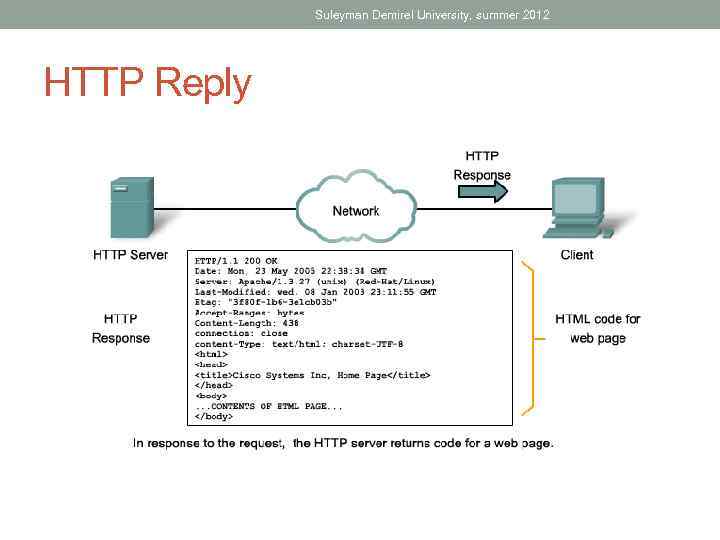 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 HTTP Reply
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 HTTP Reply
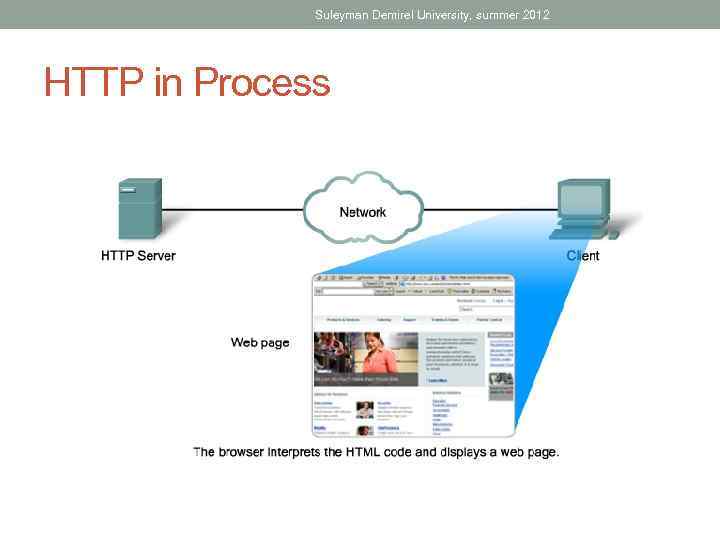 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 HTTP in Process
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 HTTP in Process
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Question • At least, what your friend have to know about you to be your friend?
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Question • At least, what your friend have to know about you to be your friend?
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Answer • Name
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Answer • Name
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Question • At least, what your friend’s computers have to know to make connection with your computer?
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Question • At least, what your friend’s computers have to know to make connection with your computer?
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Answer • IP address
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Answer • IP address
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol • DHCP allows a host to obtain an IP address dynamically when it connects to the network. The DHCP server is contacted an address requested. The DHCP server chooses an address from a configured range of addresses called a pool and assigns ("leases") it to the host for a set period.
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol • DHCP allows a host to obtain an IP address dynamically when it connects to the network. The DHCP server is contacted an address requested. The DHCP server chooses an address from a configured range of addresses called a pool and assigns ("leases") it to the host for a set period.
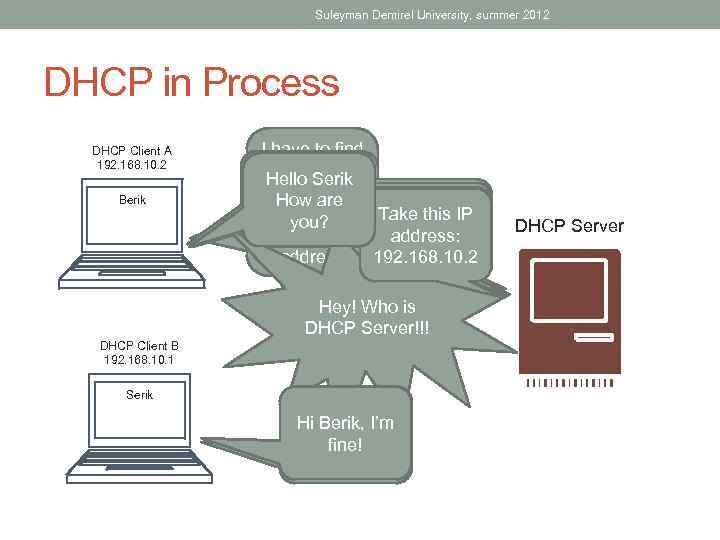 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DHCP in Process DHCP Client A 192. 168. 10. 2 Berik I have to find Without IP DHCP Hello tohave Now, you IHow Serik don’t I’m find Thank and address I’m serverare I’ll DHCP Scream! member How IP static DHCP him of not member ask Server the you? to network address Server? of network give me IP address Take DHCP heard give II am this IP am to the I Ihave. DHCP address: scream Server answer Server 192. 168. 10. 2 Hey! Who is DHCP Server!!! DHCP Client B 192. 168. 10. 1 Serik I Berik, I’m Hiheard the I’m not Relaxing scream fine! DHCP Server
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DHCP in Process DHCP Client A 192. 168. 10. 2 Berik I have to find Without IP DHCP Hello tohave Now, you IHow Serik don’t I’m find Thank and address I’m serverare I’ll DHCP Scream! member How IP static DHCP him of not member ask Server the you? to network address Server? of network give me IP address Take DHCP heard give II am this IP am to the I Ihave. DHCP address: scream Server answer Server 192. 168. 10. 2 Hey! Who is DHCP Server!!! DHCP Client B 192. 168. 10. 1 Serik I Berik, I’m Hiheard the I’m not Relaxing scream fine! DHCP Server
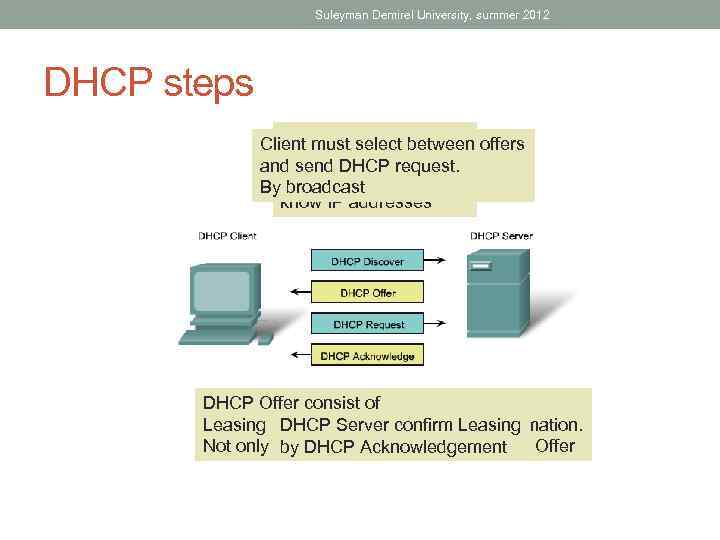 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DHCP steps DCHP Discover Client must select between offers sent by broadcast and send DHCP request. Bybecause Client doesn’t broadcast know IP addresses DHCP Offer consist of Leasing IP, Subnet, DNS, Gateway information. DHCP Server confirm Leasing Not only one. DHCP Acknowledgement by server can reply with DHCP Offer
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DHCP steps DCHP Discover Client must select between offers sent by broadcast and send DHCP request. Bybecause Client doesn’t broadcast know IP addresses DHCP Offer consist of Leasing IP, Subnet, DNS, Gateway information. DHCP Server confirm Leasing Not only one. DHCP Acknowledgement by server can reply with DHCP Offer
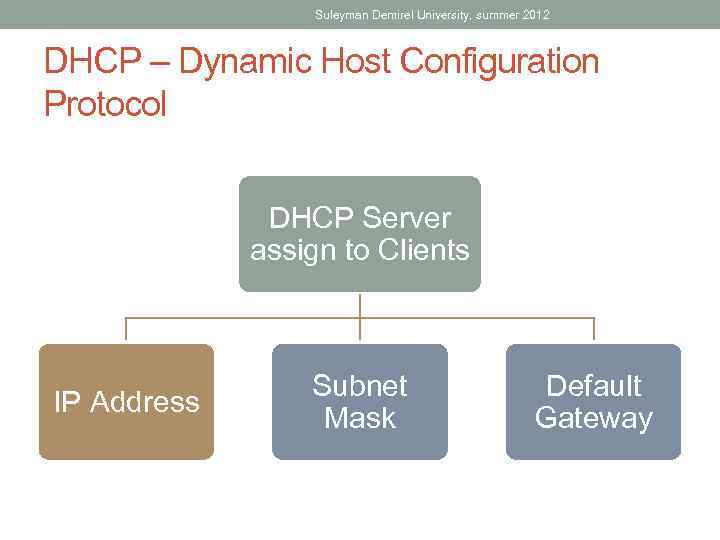 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP Server assign to Clients IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP Server assign to Clients IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Simple Mail Transfer Protocol/Post Office Protocol • E-mail, the most popular network service, has revolutionized how people communicate through its simplicity and speed. Yet to run on a computer or other end device, e-mail requires several applications and services. Two example Application layer protocols are Post Office Protocol (POP) and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), shown in the figure. As with HTTP, these protocols define client/server processes.
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Simple Mail Transfer Protocol/Post Office Protocol • E-mail, the most popular network service, has revolutionized how people communicate through its simplicity and speed. Yet to run on a computer or other end device, e-mail requires several applications and services. Two example Application layer protocols are Post Office Protocol (POP) and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), shown in the figure. As with HTTP, these protocols define client/server processes.
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Simple Mail Transfer Protocol/Post Office Protocol SMTP/POP Server Client(MUA) SMTP Protocol POP Protocol Client is using Application witch is called MUA Mail User Agent
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Simple Mail Transfer Protocol/Post Office Protocol SMTP/POP Server Client(MUA) SMTP Protocol POP Protocol Client is using Application witch is called MUA Mail User Agent
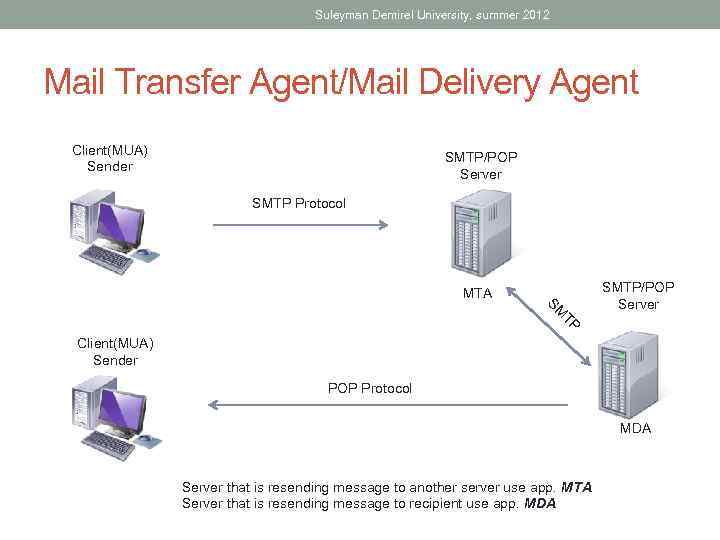 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Mail Transfer Agent/Mail Delivery Agent Client(MUA) Sender SMTP/POP Server SMTP Protocol MTA TP SM SMTP/POP Server Client(MUA) Sender POP Protocol MDA Server that is resending message to another server use app. MTA Server that is resending message to recipient use app. MDA
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Mail Transfer Agent/Mail Delivery Agent Client(MUA) Sender SMTP/POP Server SMTP Protocol MTA TP SM SMTP/POP Server Client(MUA) Sender POP Protocol MDA Server that is resending message to another server use app. MTA Server that is resending message to recipient use app. MDA
 Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Q/A
Suleyman Demirel University, summer 2012 Q/A


