exploration 1, chapter 7(osi data link).pptx
- Количество слайдов: 68
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 EXPLORATION 1, Chapter 7 OSI Data Link Zhamanov Azamat
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 EXPLORATION 1, Chapter 7 OSI Data Link Zhamanov Azamat
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to: • Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission. • Describe how the Data Link layer prepares data for transmission on network media. • Describe the different types of media access control methods. • Identify several common logical network topologies and describe how the logical topology determines the media access control method for that network.
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to: • Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission. • Describe how the Data Link layer prepares data for transmission on network media. • Describe the different types of media access control methods. • Identify several common logical network topologies and describe how the logical topology determines the media access control method for that network.
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to: • Explain the purpose of encapsulating packets into frames to facilitate media access. • Describe the Layer 2 frame structure and identify generic fields. • Explain the role of key frame header and trailer fields, including addressing, Qo. S, type of protocol, and Frame Check Sequence.
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to: • Explain the purpose of encapsulating packets into frames to facilitate media access. • Describe the Layer 2 frame structure and identify generic fields. • Explain the role of key frame header and trailer fields, including addressing, Qo. S, type of protocol, and Frame Check Sequence.
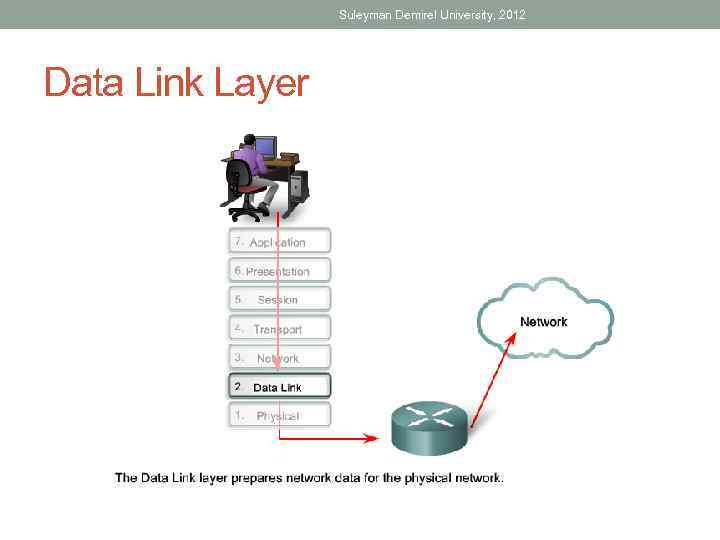 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link Layer
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link Layer
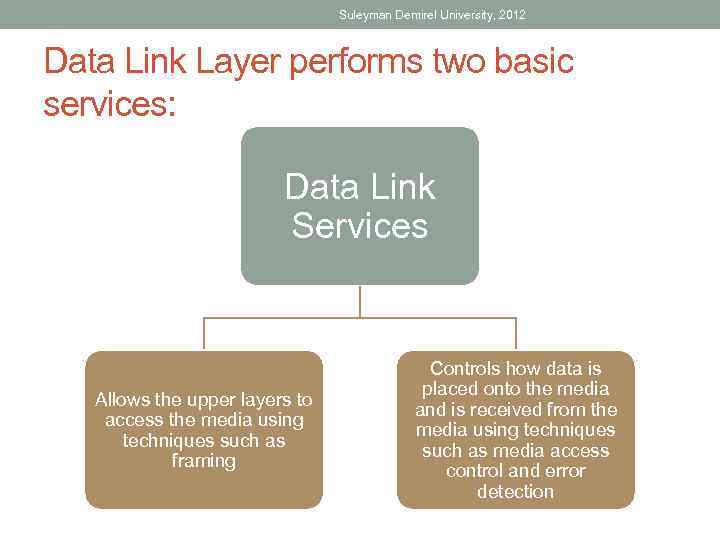 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link Layer performs two basic services: Data Link Services Allows the upper layers to access the media using techniques such as framing Controls how data is placed onto the media and is received from the media using techniques such as media access control and error detection
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link Layer performs two basic services: Data Link Services Allows the upper layers to access the media using techniques such as framing Controls how data is placed onto the media and is received from the media using techniques such as media access control and error detection
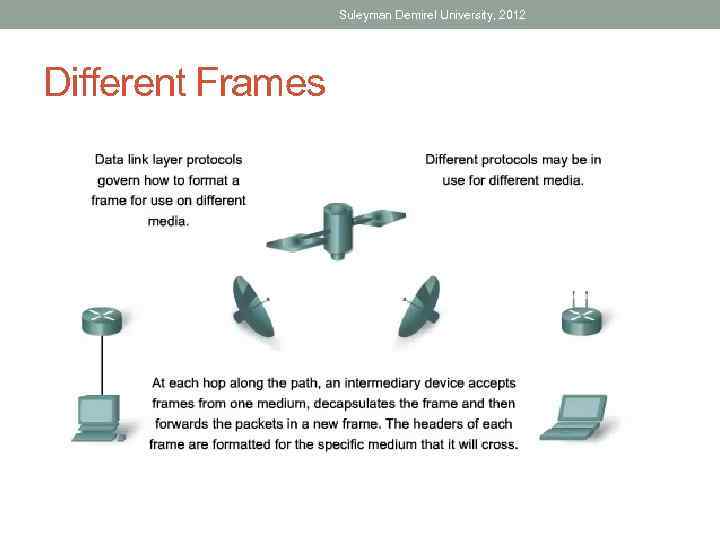 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Different Frames
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Different Frames
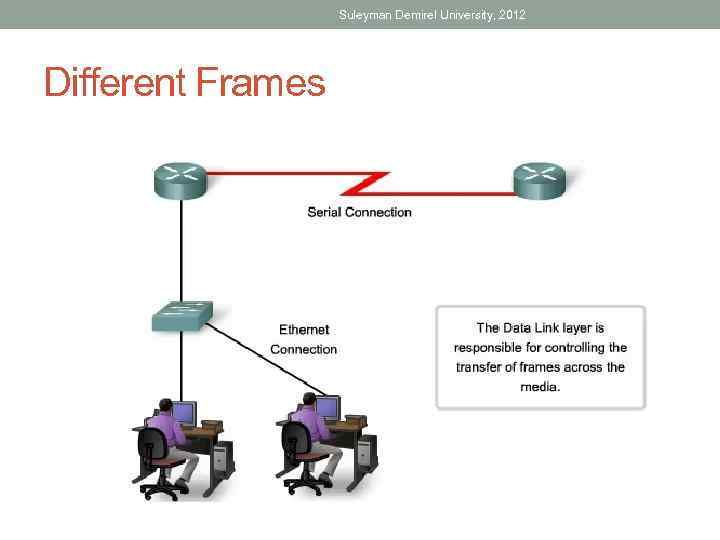 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Different Frames
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Different Frames
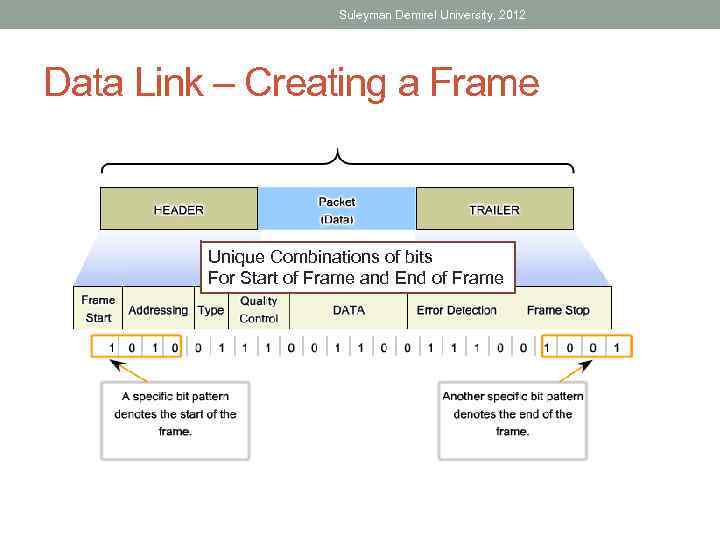 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link – Creating a Frame Unique Combinations of bits For Start of Frame and End of Frame
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link – Creating a Frame Unique Combinations of bits For Start of Frame and End of Frame
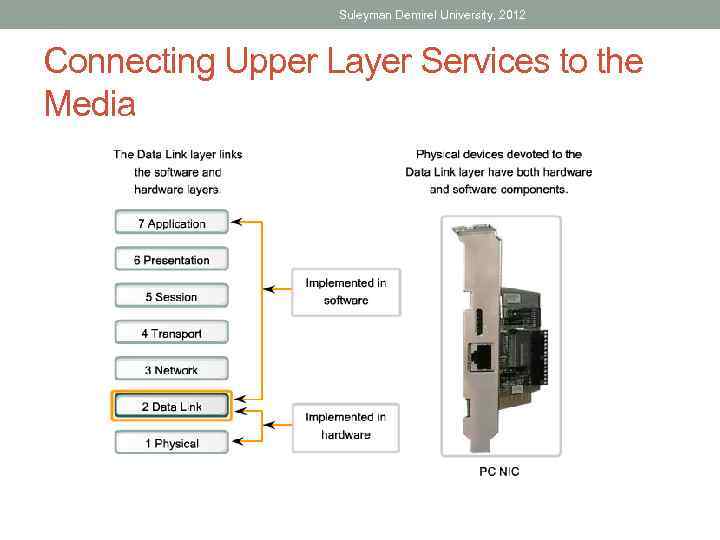 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Connecting Upper Layer Services to the Media
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Connecting Upper Layer Services to the Media
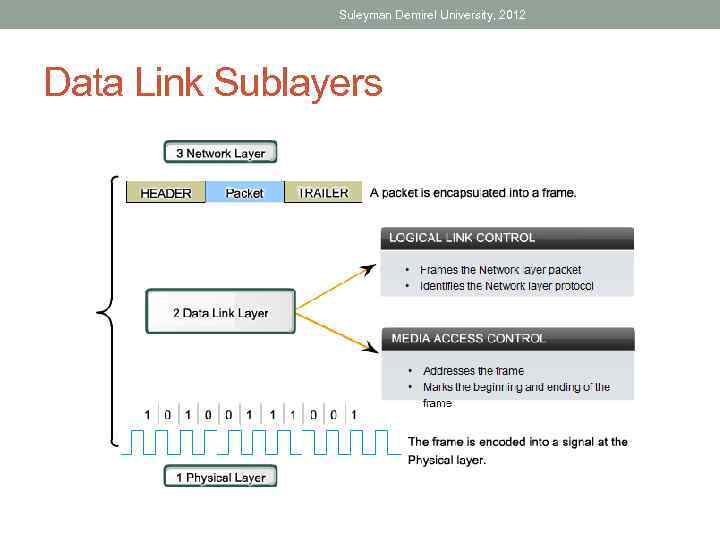
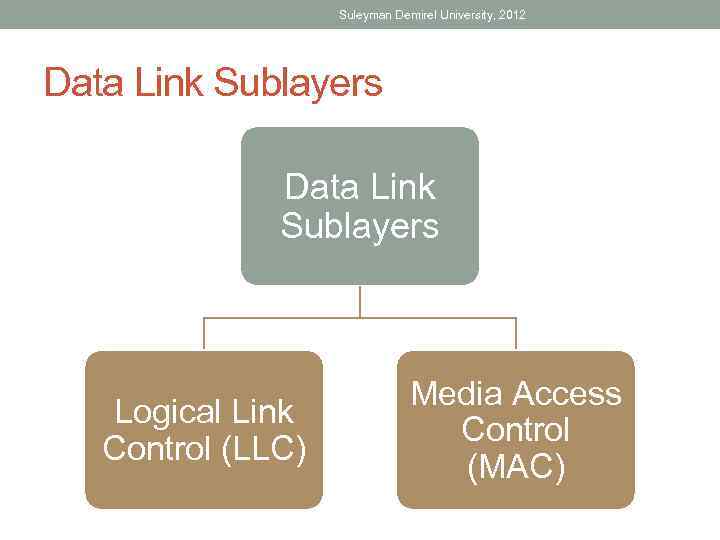 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link Sublayers Logical Link Control (LLC) Media Access Control (MAC)
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link Sublayers Logical Link Control (LLC) Media Access Control (MAC)
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Logical Link Control • Logical Link Control (LLC) places information in the frame that identifies which Network layer protocol is being used for the frame. This information allows multiple Layer 3 protocols, such as IP and IPX, to utilize the same network interface and media.
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Logical Link Control • Logical Link Control (LLC) places information in the frame that identifies which Network layer protocol is being used for the frame. This information allows multiple Layer 3 protocols, such as IP and IPX, to utilize the same network interface and media.
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Media Access Control • Media Access Control (MAC) provides Data Link layer addressing and delimiting of data according to the physical signaling requirements of the medium and the type of Data Link layer protocol in use.
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Media Access Control • Media Access Control (MAC) provides Data Link layer addressing and delimiting of data according to the physical signaling requirements of the medium and the type of Data Link layer protocol in use.
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link Layer • Prepares network data for the physical network • Provides a means for exchanging data over a common local media • The Data Link is responsible for controlling the transfer of frames across the media
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link Layer • Prepares network data for the physical network • Provides a means for exchanging data over a common local media • The Data Link is responsible for controlling the transfer of frames across the media
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link Sublayers
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link Sublayers
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 DATA LINK LAYER - STANDARDS
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 DATA LINK LAYER - STANDARDS
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link Standards International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) American National Standards Institute (ANSI) International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link Standards International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) American National Standards Institute (ANSI) International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 PLACING DATA ON THE MEDIA
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 PLACING DATA ON THE MEDIA
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Media Access Control • No Control • Control Based
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Media Access Control • No Control • Control Based
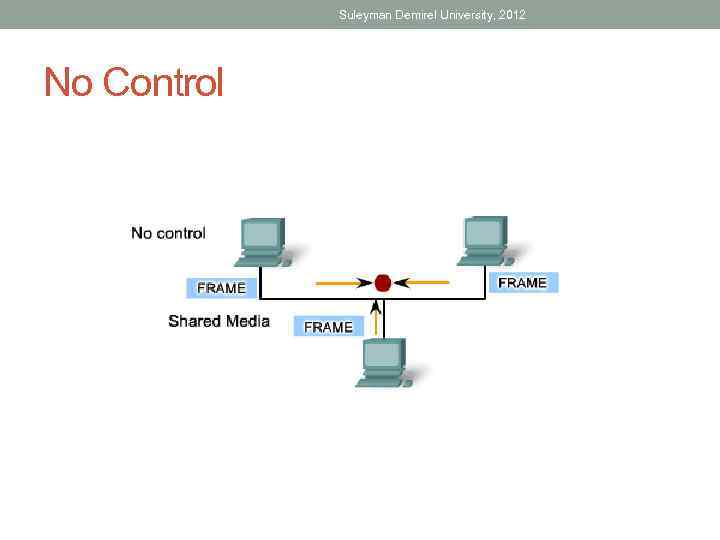 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 No Control
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 No Control
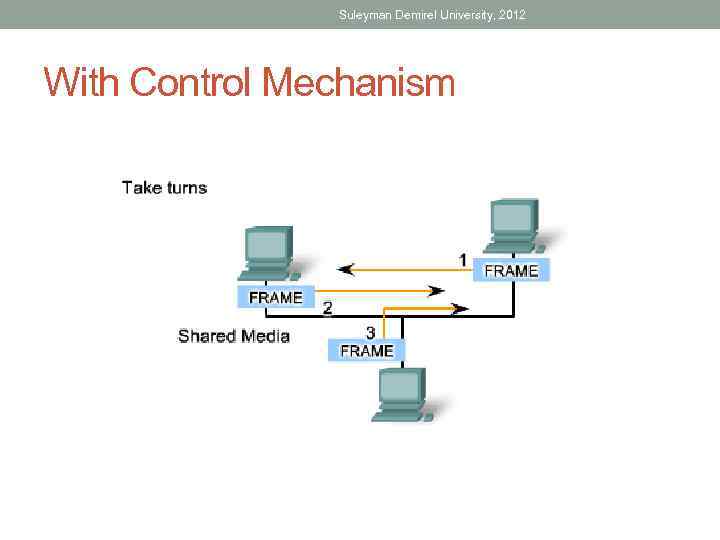 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 With Control Mechanism
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 With Control Mechanism
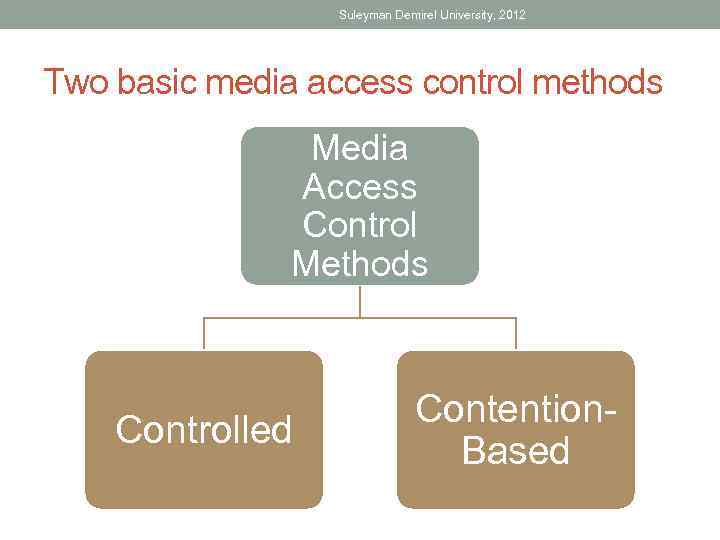 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Two basic media access control methods Media Access Control Methods Controlled Contention. Based
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Two basic media access control methods Media Access Control Methods Controlled Contention. Based
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Controlled • When using the controlled access method, network devices take turns, in sequence, to access the medium. • This method is also known as scheduled access or deterministic.
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Controlled • When using the controlled access method, network devices take turns, in sequence, to access the medium. • This method is also known as scheduled access or deterministic.
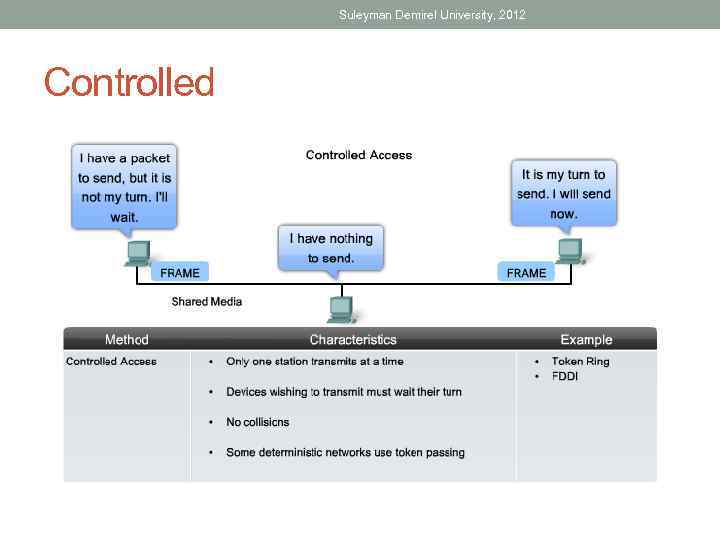 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Controlled
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Controlled
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Contention - Based • Also referred to as non-deterministic, contention-based methods allow any device to try to access the medium whenever it has data to send.
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Contention - Based • Also referred to as non-deterministic, contention-based methods allow any device to try to access the medium whenever it has data to send.
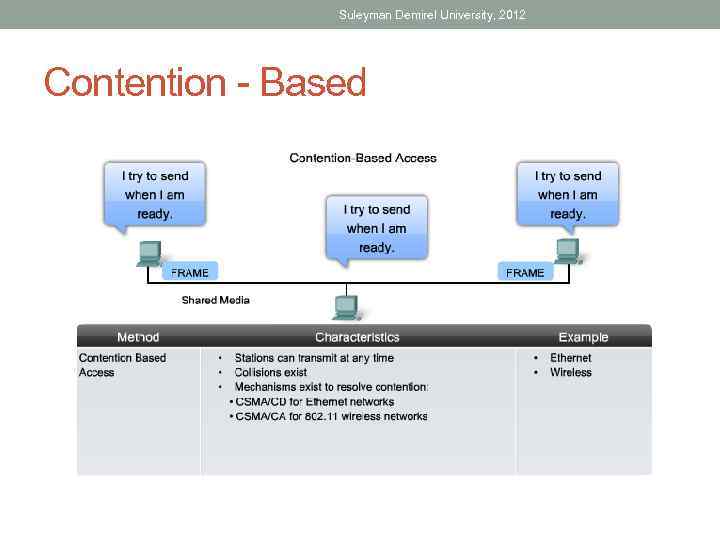 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Contention - Based
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Contention - Based
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Question • Duplex?
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Question • Duplex?
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Answer • Duplex commonly means double or twofold. • Example: Duplex Printing, double-sided printing
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Answer • Duplex commonly means double or twofold. • Example: Duplex Printing, double-sided printing
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Duplex in Computer Network Duplex Types Full Duplex Half Duplex
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Duplex in Computer Network Duplex Types Full Duplex Half Duplex
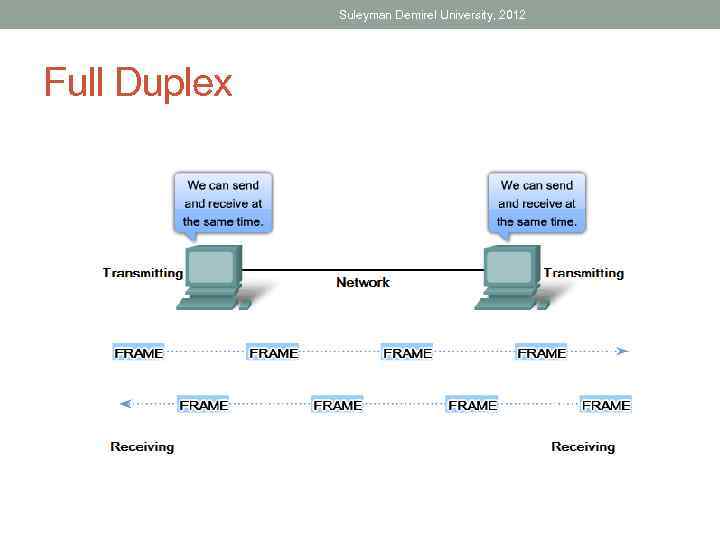 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Full Duplex
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Full Duplex
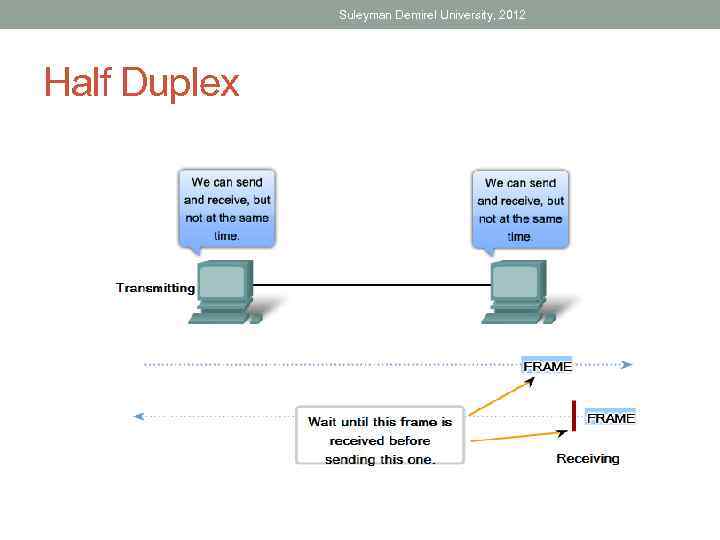 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Half Duplex
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Half Duplex
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 LOGICAL TOPOLOGY VS PHYSICAL TOPOLOGY
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 LOGICAL TOPOLOGY VS PHYSICAL TOPOLOGY
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Logical Topology • This arrangement consists of virtual connections between the nodes of a network independent of their physical layout.
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Logical Topology • This arrangement consists of virtual connections between the nodes of a network independent of their physical layout.
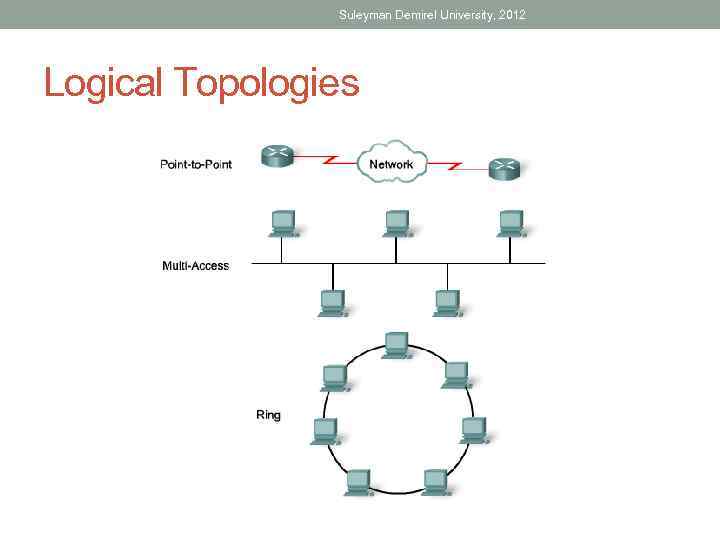 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Logical Topologies
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Logical Topologies
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Physical Topology • The physical topology is an arrangement of the nodes and the physical connections between them. • The representation of how the media is used to interconnect the devices is the physical topology. These will be covered in later chapters of this course.
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Physical Topology • The physical topology is an arrangement of the nodes and the physical connections between them. • The representation of how the media is used to interconnect the devices is the physical topology. These will be covered in later chapters of this course.
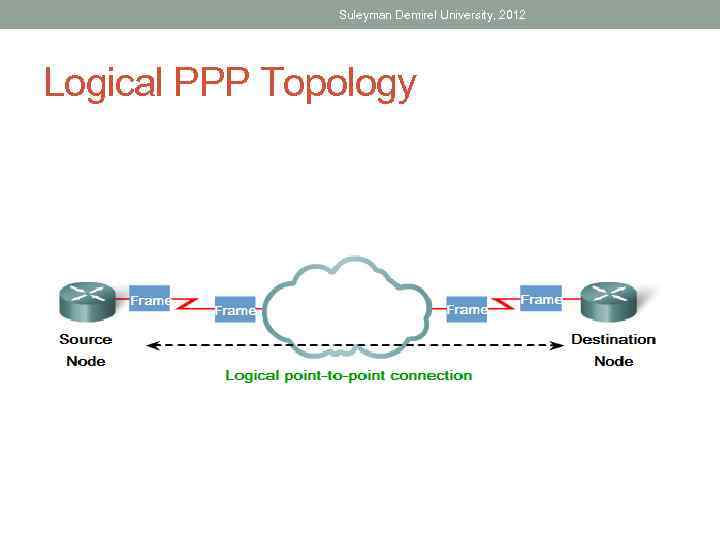 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Logical PPP Topology
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Logical PPP Topology
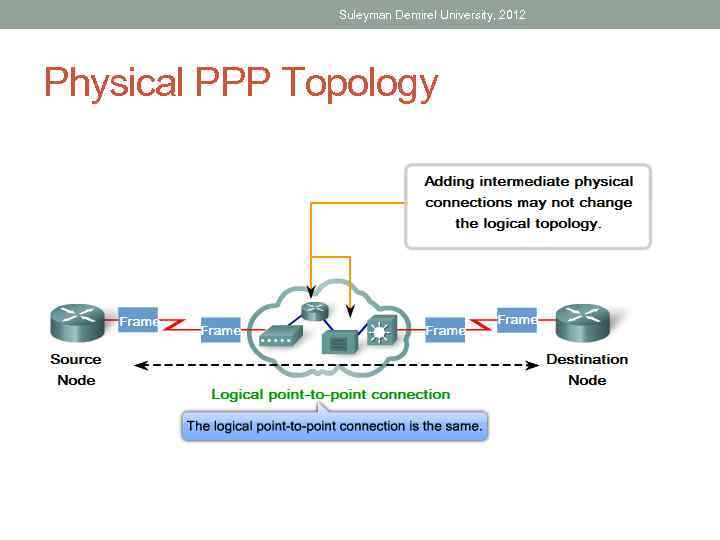 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Physical PPP Topology
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Physical PPP Topology
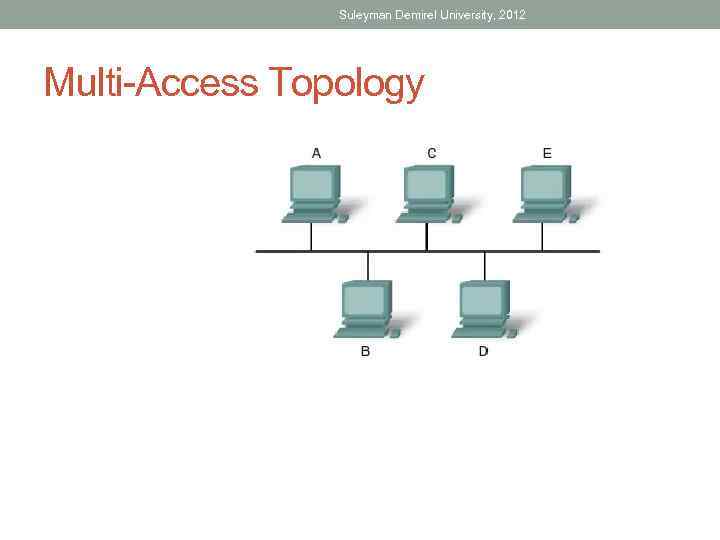 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Multi-Access Topology
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Multi-Access Topology
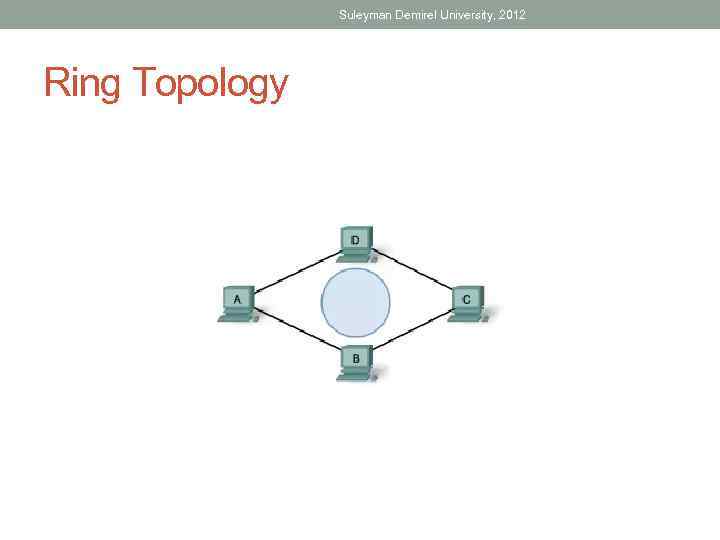 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Ring Topology
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Ring Topology
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 FRAMING
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 FRAMING
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Role of the Header
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Role of the Header
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Frame Trailer
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Frame Trailer
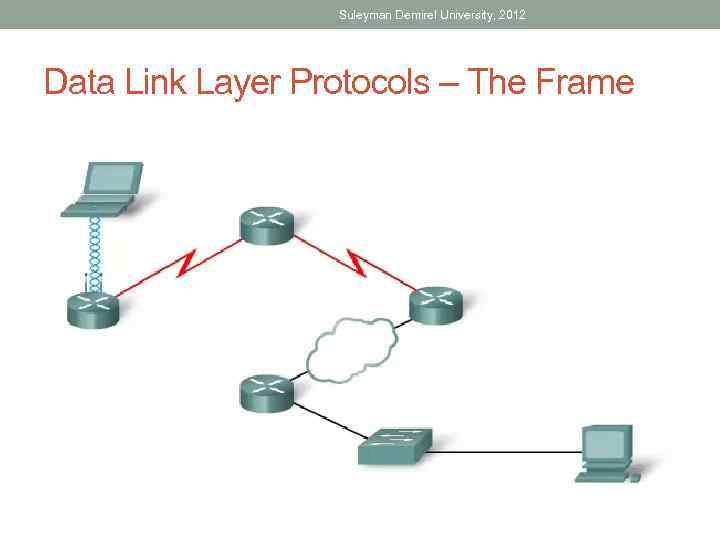 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link Layer Protocols – The Frame
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Data Link Layer Protocols – The Frame
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Frame Structure
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Frame Structure
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 FOLLOW DATA THROUGH AN INTERNET
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 FOLLOW DATA THROUGH AN INTERNET
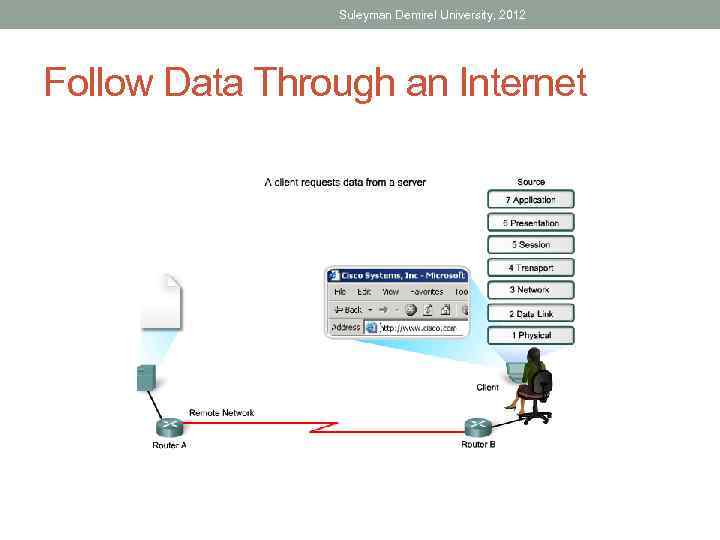 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
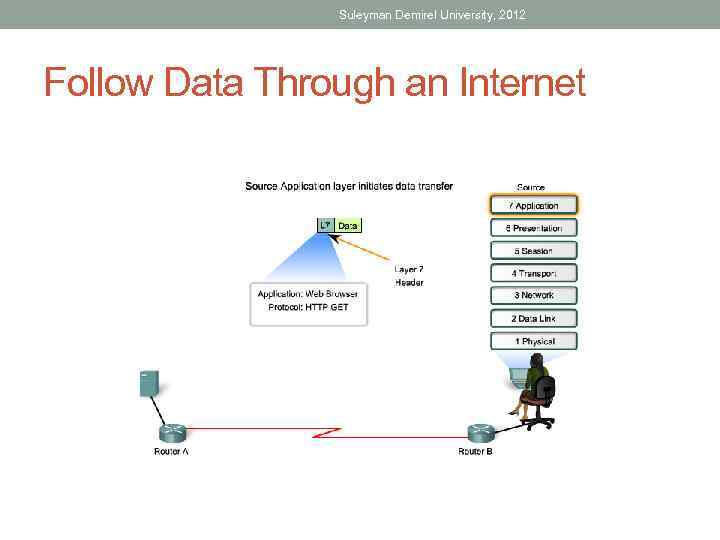 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
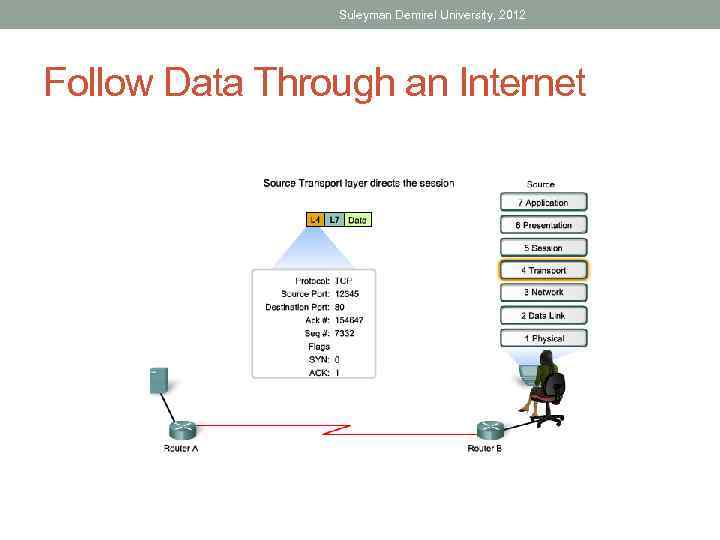 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
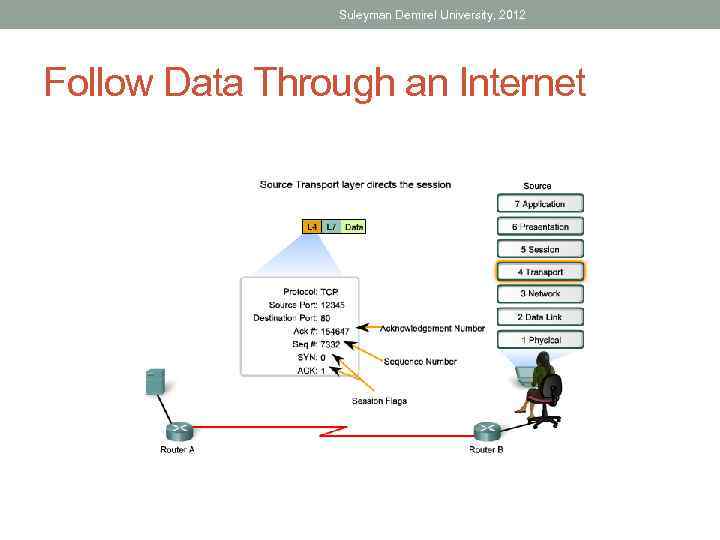 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
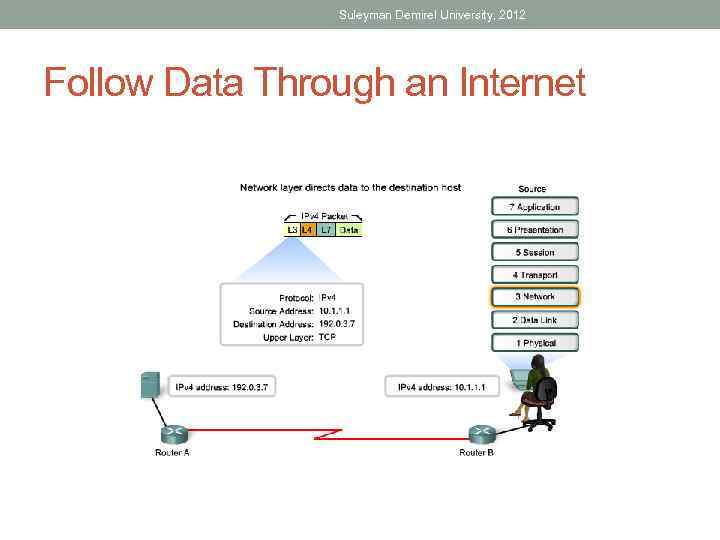 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
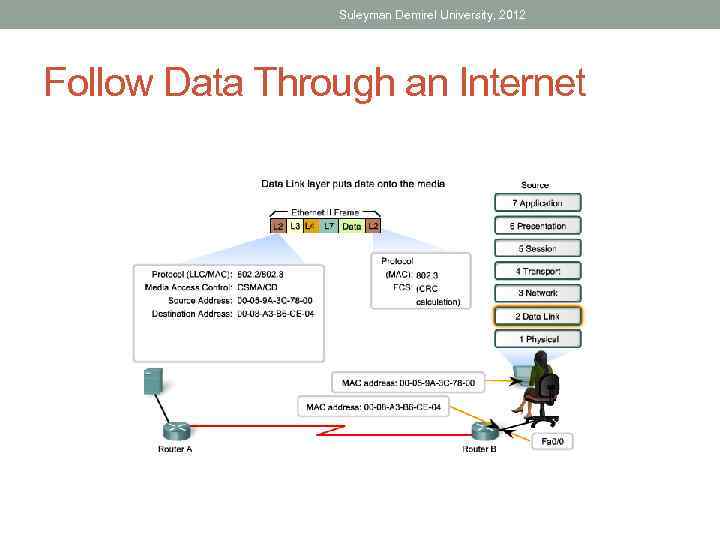 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
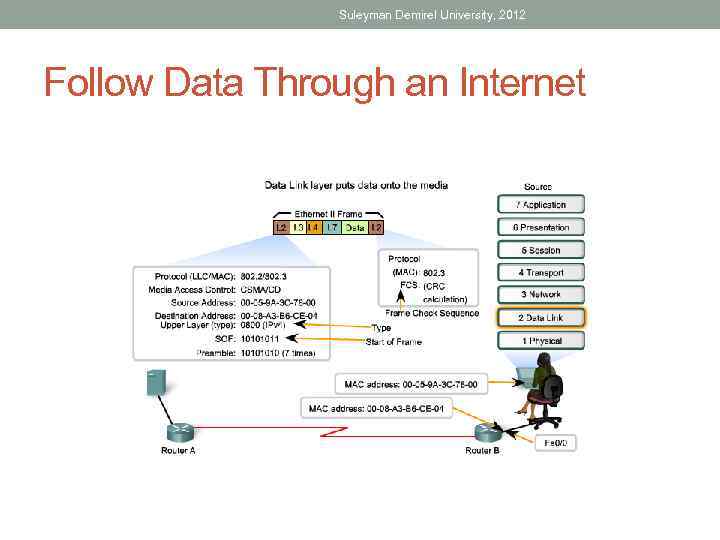 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
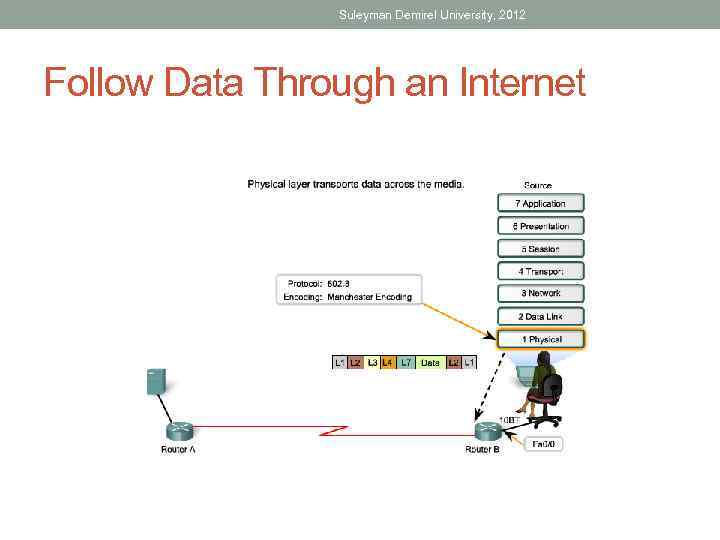 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
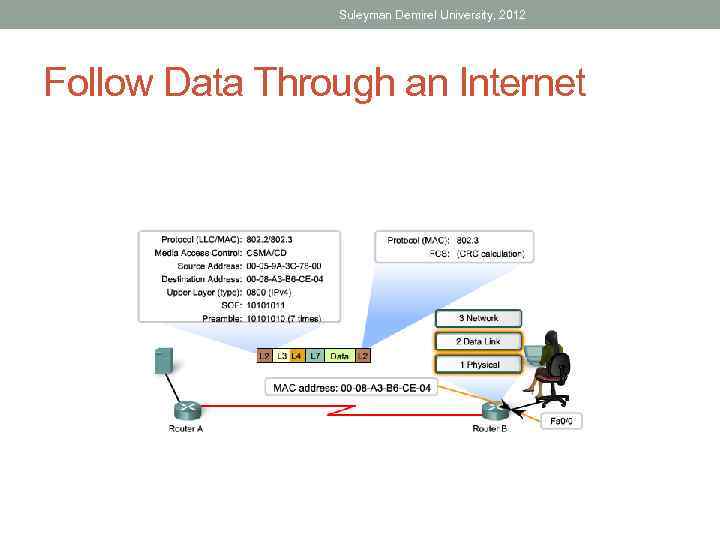 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
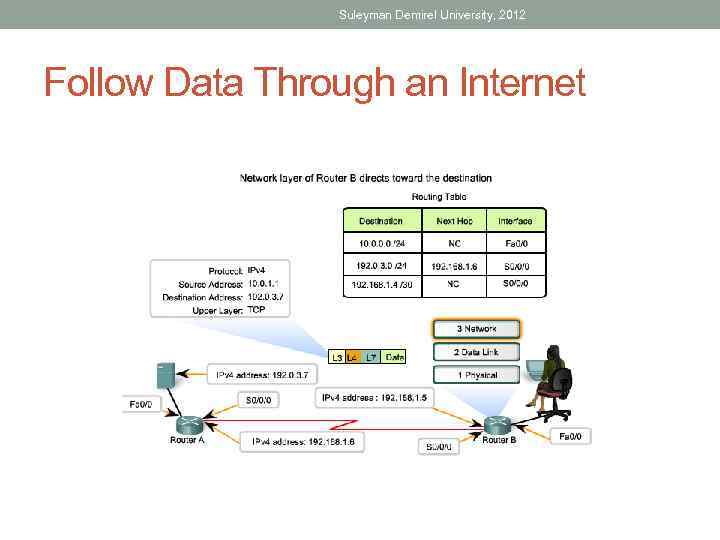 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
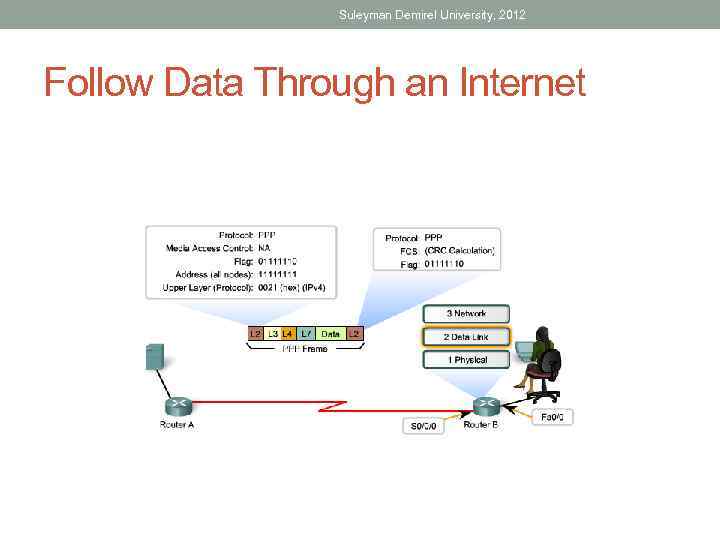 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
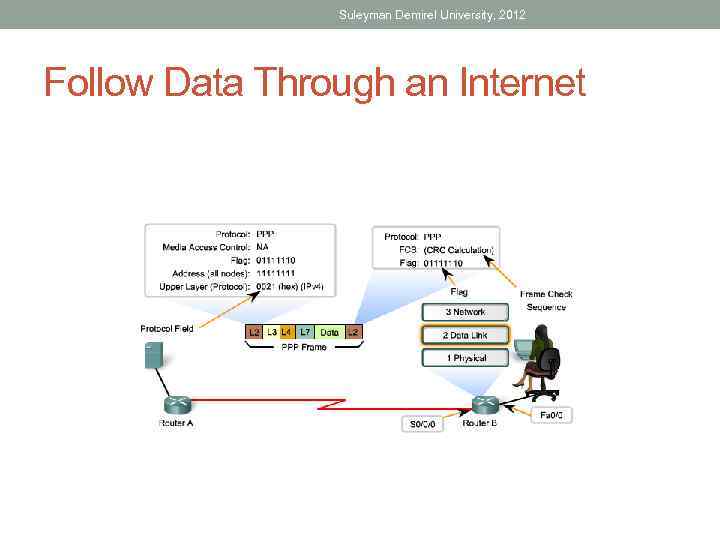 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
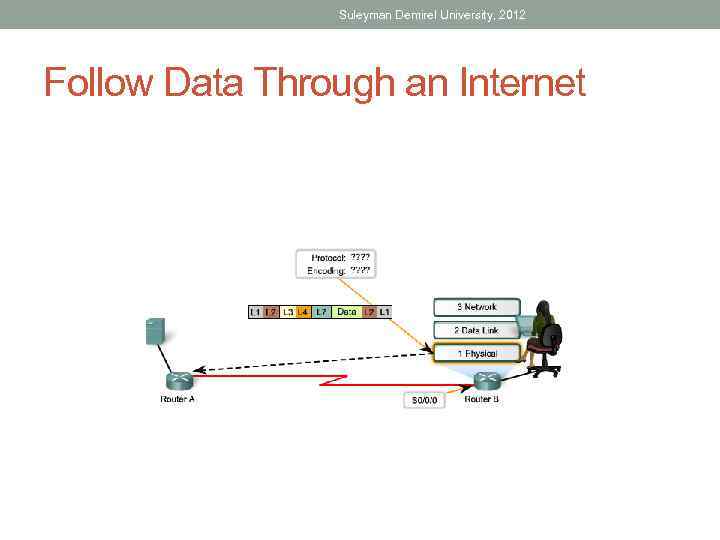 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
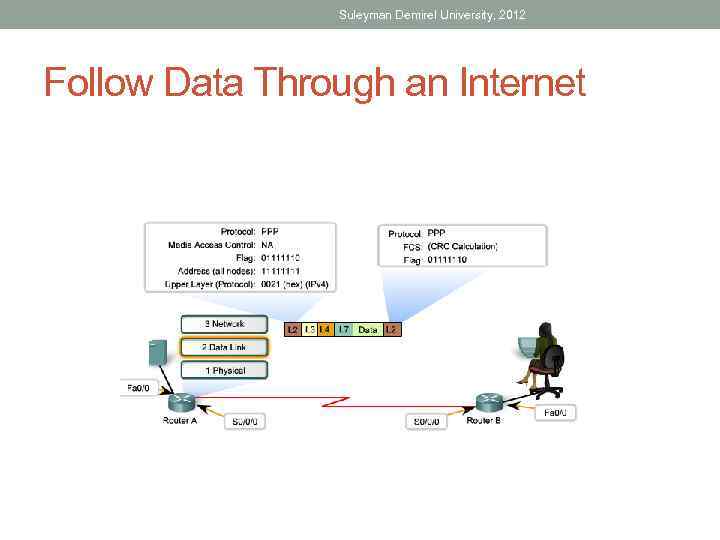 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
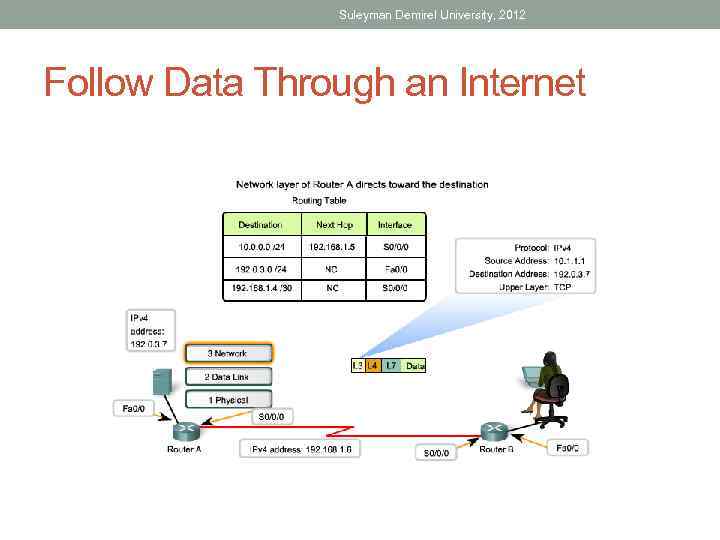 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
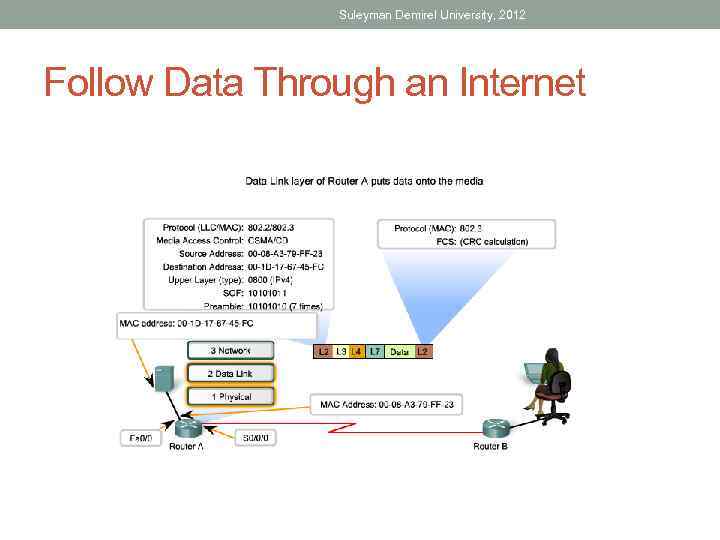 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
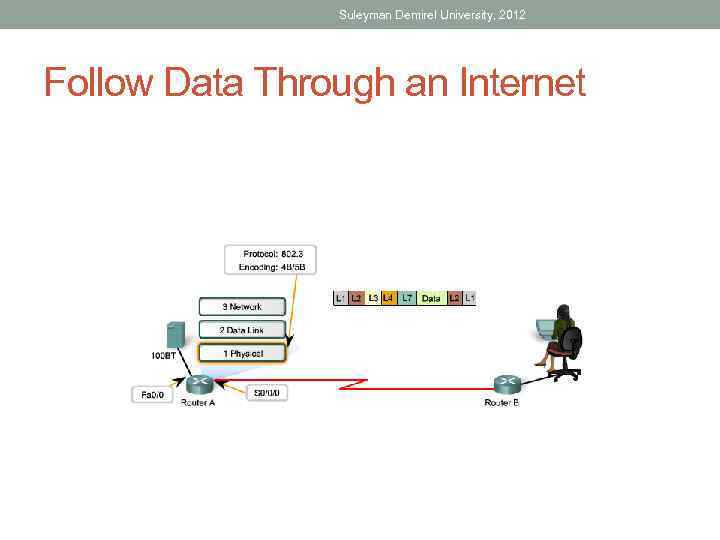 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
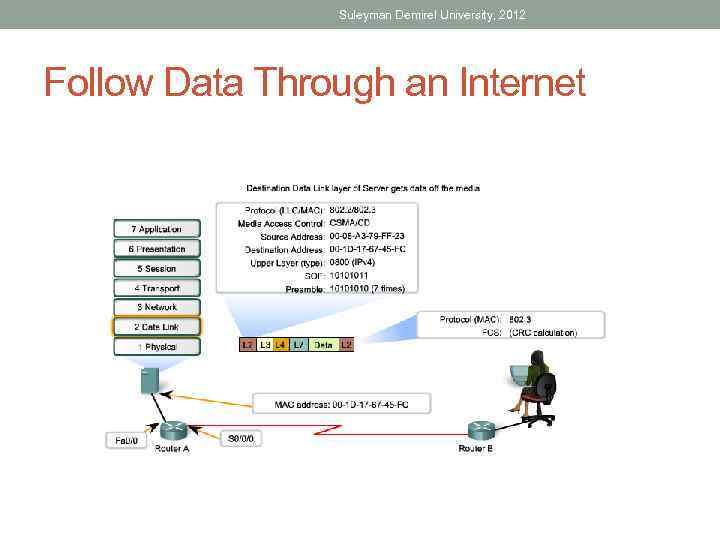 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
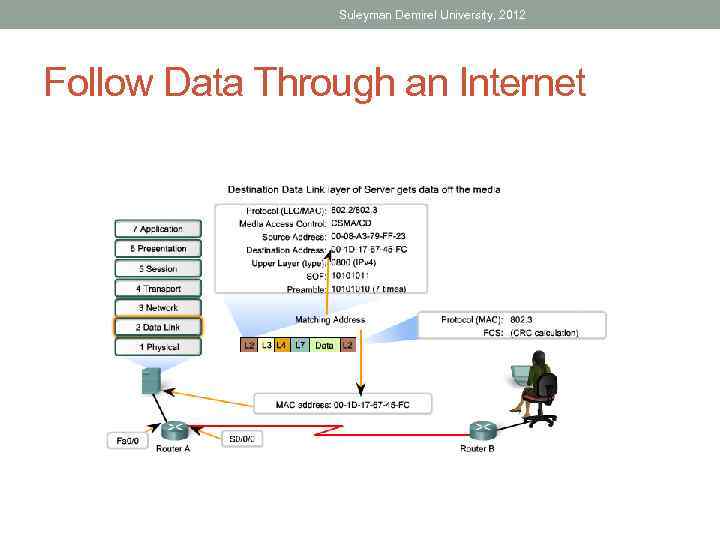 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
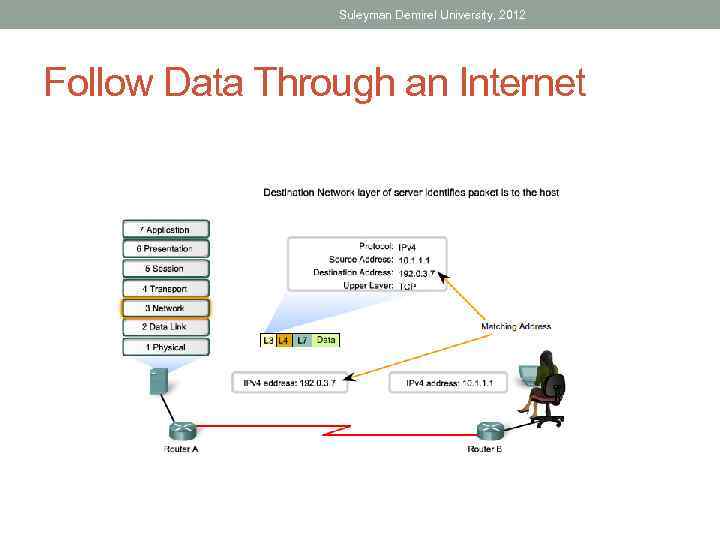 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
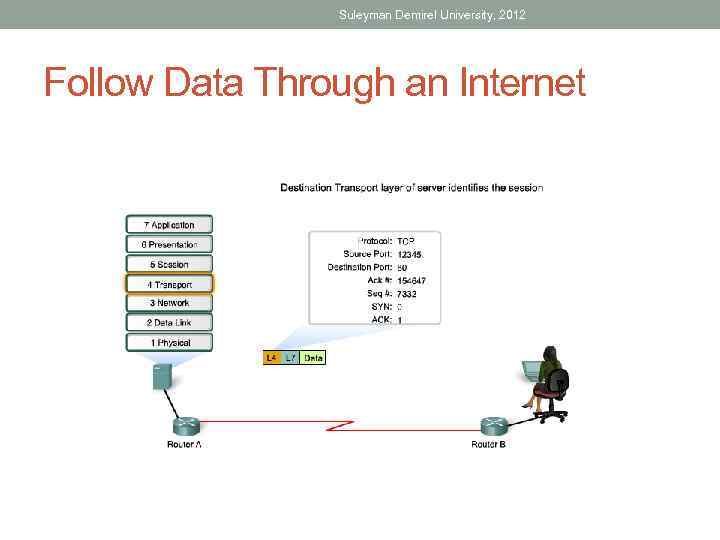 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
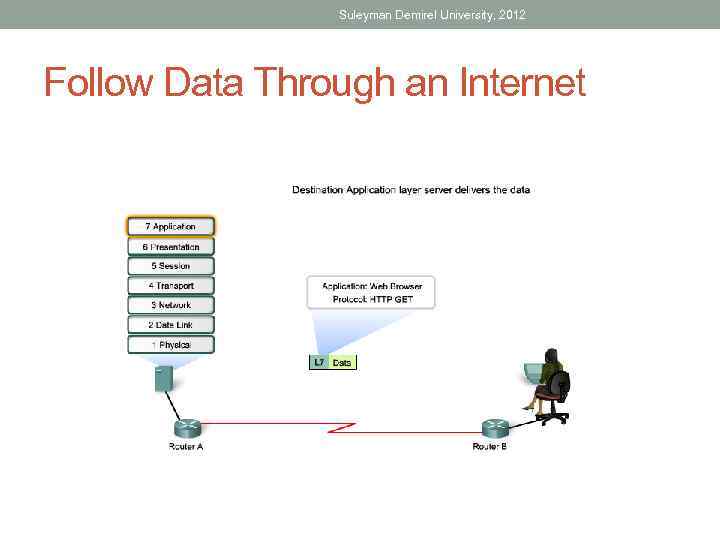 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Follow Data Through an Internet
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 MAC Address • Is divide into two parts • OUI , Organizationally Unique Identifier, 24 bits • Rest 24 bits are belong to identify device in the organization • Stored in ROM (Read Only Memory) • MAC Address consist of 48 bits, it is 2^48 or 281 474 976 710 656 addresses. • By evaluation of IEEE this range is enough till 2100 year. • Example • 01: 23: 45: 67: 89: ab
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 MAC Address • Is divide into two parts • OUI , Organizationally Unique Identifier, 24 bits • Rest 24 bits are belong to identify device in the organization • Stored in ROM (Read Only Memory) • MAC Address consist of 48 bits, it is 2^48 or 281 474 976 710 656 addresses. • By evaluation of IEEE this range is enough till 2100 year. • Example • 01: 23: 45: 67: 89: ab
 Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Q/A
Suleyman Demirel University, 2012 Q/A


