465ddb2c8645fdb213659e2d09cda6de.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Sue want to build a model to predict movie ratings. She has a matrix of data, where for M movies and U users she has collected ratings between 1 and 5. Not all users have rated all movies. These entries are indicated by a “? ”. Sue has build a model that can predict unrated movies for any user u in the database. The model always predicts a real number, q, between 1 and 5. To further optimize her predictions she decides to train another model that maps her predictions q to new rating estimates q’. To train this model she uses all observed ratings in the database (i. e. ignoring “? ”) and fits a neural network as follows: Here “i” runs over all observed ratings, and |. | denotes the absolute value. 1) Derive the gradients 2) Give pseudo-code for a stochastic gradient descent algorithm for learning “a” and “b”. 3) Given a fixed step-size, explain if this algorithm will converge after infinitely many gradient updates? 4) Jimmy has another algorithm that also predicts ratings. Sue and Jimmy decide to combine their models and compute a bagged estimate. Calling Sue prediction q_sue and Jimmy prediction q_jim give an expression for a combined prediction using bagging. 5) Explain whether bagging increases or decreases variance and why.

Bayesian Learning

Probabilities
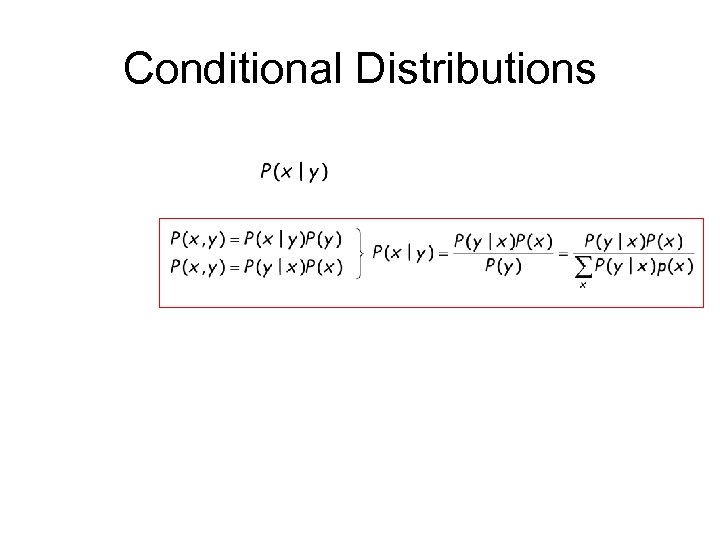
Conditional Distributions

(Conditional) Independence
Example C. I.
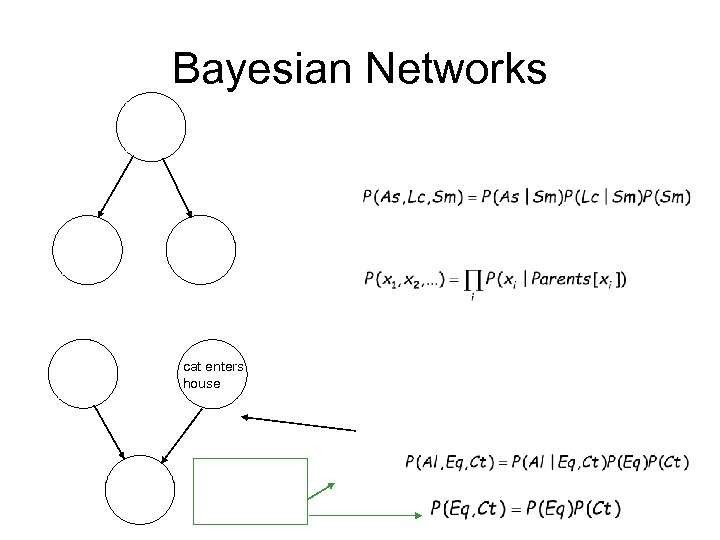
Bayesian Networks cat enters house
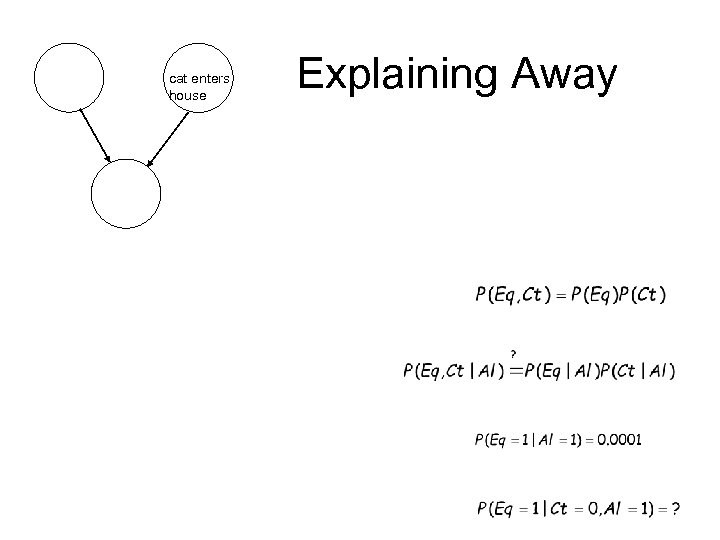
cat enters house Explaining Away
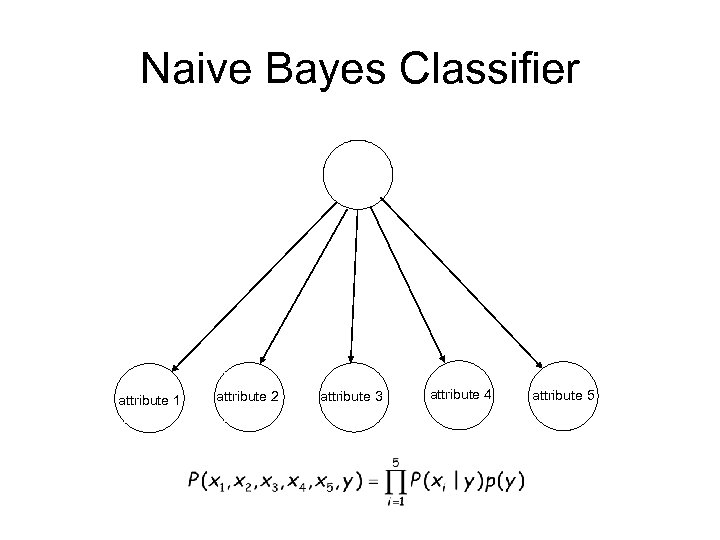
Naive Bayes Classifier attribute 1 attribute 2 attribute 3 attribute 4 attribute 5
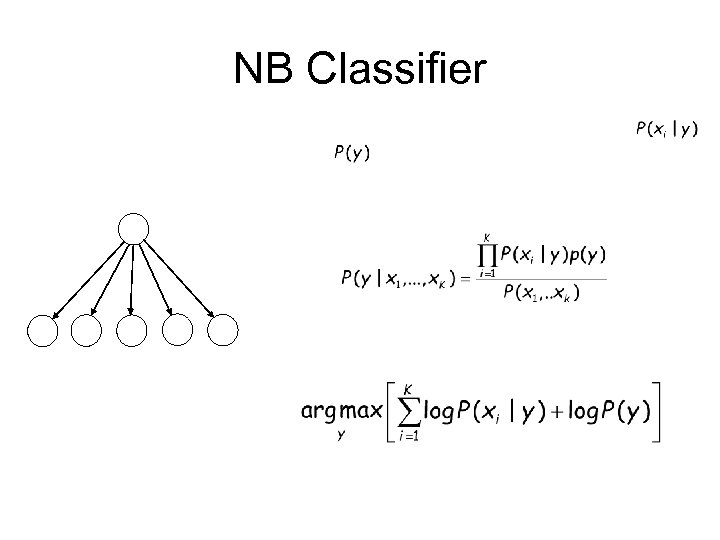
NB Classifier
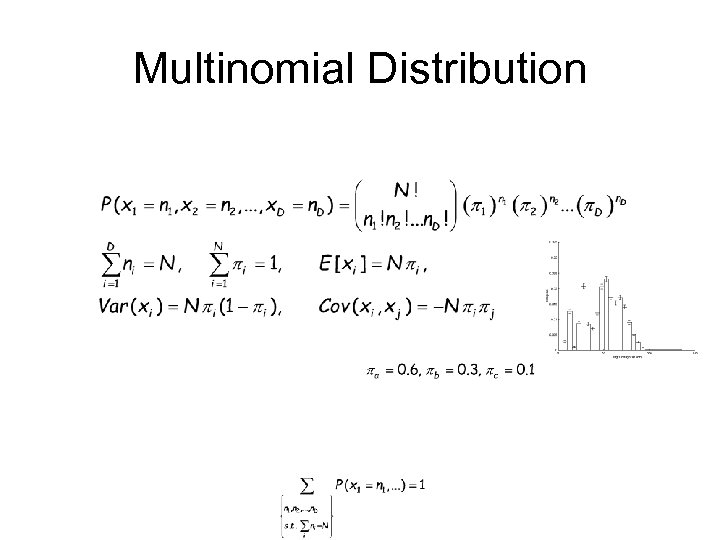
Multinomial Distribution
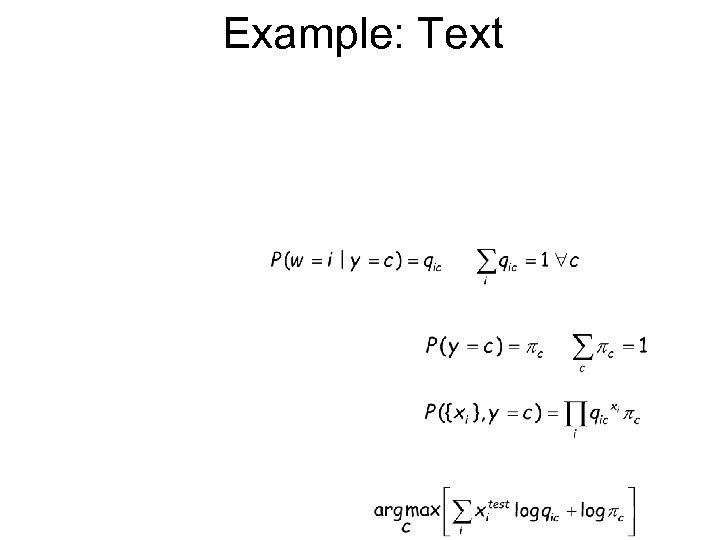
Example: Text
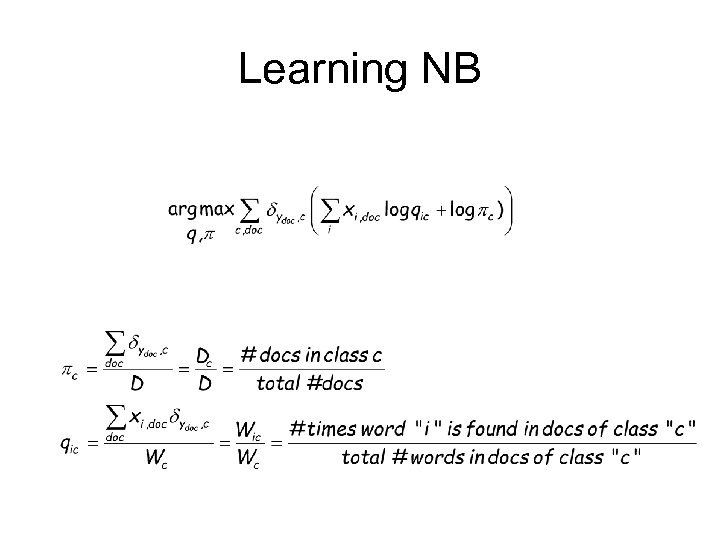
Learning NB
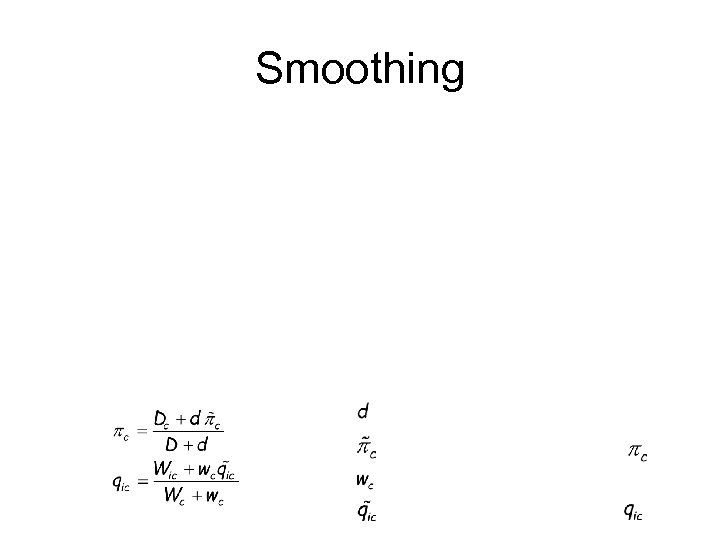
Smoothing

Document Clustering
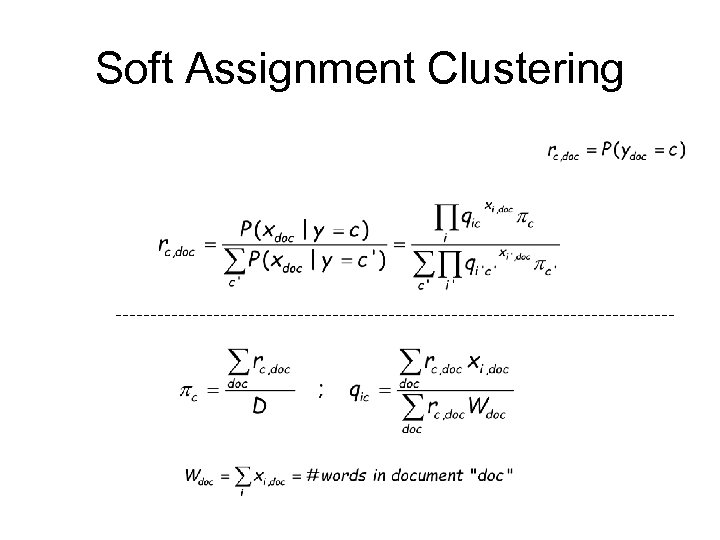
Soft Assignment Clustering
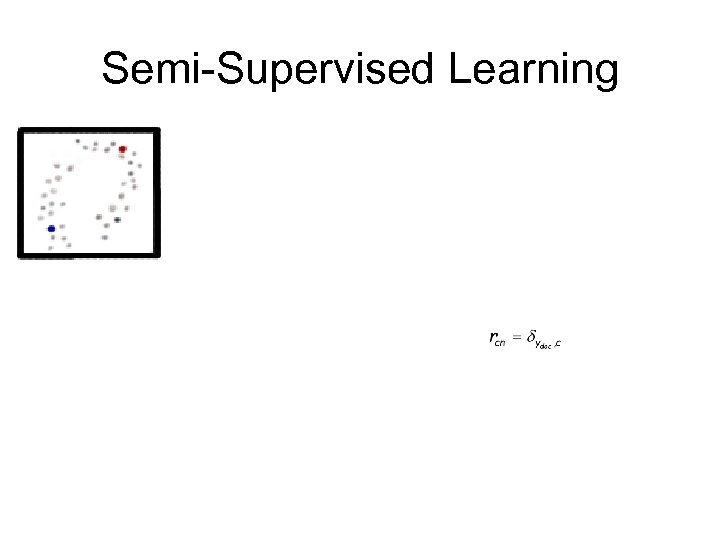
Semi-Supervised Learning
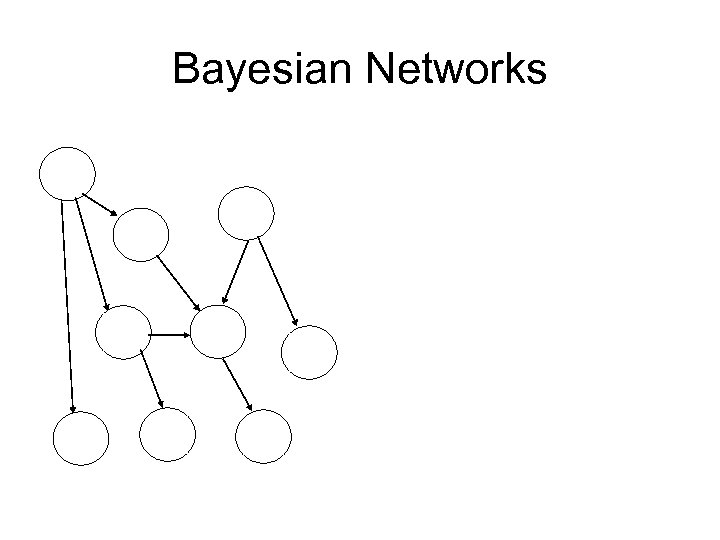
Bayesian Networks
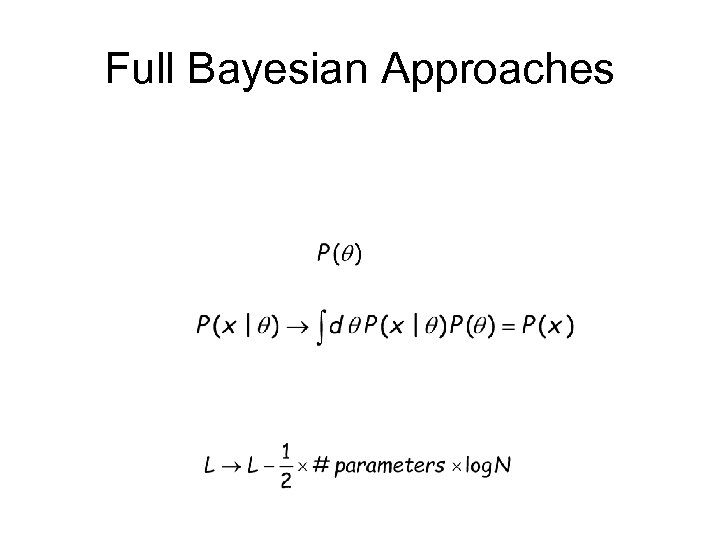
Full Bayesian Approaches

Conclusions
465ddb2c8645fdb213659e2d09cda6de.ppt