09e84dac14f6f348c286b09249fc7b29.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

SUCCESSION MANAGEMENT Building Your Talent Bench 1

agenda Why succession management Elements & tools Key success factors Challenges/reasons for failure Role of Top Management & HR Successful case studies

reasons for succession management • To develop a talent pipeline pool • To find out well in advance successors for each key position in the company • To ensure readiness of the individuals for taking over • • To ensure minimum disruption/smooth transition • Provide increased opportunities to high potential talent • Help individuals realize their career plans within the organization • Niche skils - supply gap • Hygiene To continuously foster organizational effectiveness

approach Organization Plan Talent Plan - Organization Strategy - People Strategy Track & Implement Plan -Succession Planning for Critical Roles -Talent Pipeline – High Potential - Talent Retention

Recent Research Data 40% of those surveyed said that company growth was limited because they didn’t have the right talent. 75% said that their company is chronically short of leadership talent. Failure rates are high (40 -50%) when executive talent is hired from outside. Two-thirds of employees have low to moderate confidence in their companies’ top executives; Employees say company leadership is a key contributor to job satisfaction, commitment and intent to stay; especially true for top talent. Recent surveys state that employees value most the leadership qualities of honesty and integrity. Only 1% of companies rate their succession management plans as excellent; two-thirds rate them as fair or worse. ─Mc. Kinsey, The War for Talent, Right’s People Brand Research Report, DDI Exec. Dev. & Succession Management
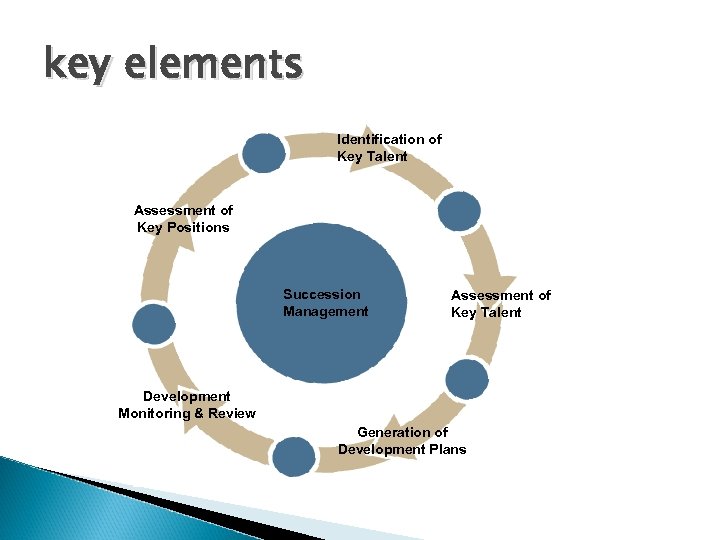
key elements Identification of Key Talent Assessment of Key Positions Succession Management Assessment of Key Talent Development Monitoring & Review Generation of Development Plans

Lets pause……. 1. 2. 3. 4. Have you lost high potential talent because they didn’t know they were on the list? If your executive team “got run over by a bus, ” would their replacements be able to step right in and be productive? Is anyone on the “top floors” or in the Boardroom worried about the status of your “talent bench? ” What lost opportunity costs has your organization incurred because it took a long time to replace a key leader? 7

Lets pause…. . 6. How does someone in your organization get selected to be a potential successor? 7. Do you have leadership development and talent management processes in place to grow successors? 8. If your organization has succession criteria, is it past focused or future oriented? 9. If you have a succession planning process, is it grounded in your business strategy? 10. Would your selection/promotion practices pass a “drop in” legal challenge? 8

key success factors • Secure senior level support • Align with future organizational strategy • Keep the process simple so that busy line managers do not find the process burdensome • Engage technology to support the process • Continual reinvention • Global approach Build or Buy ?
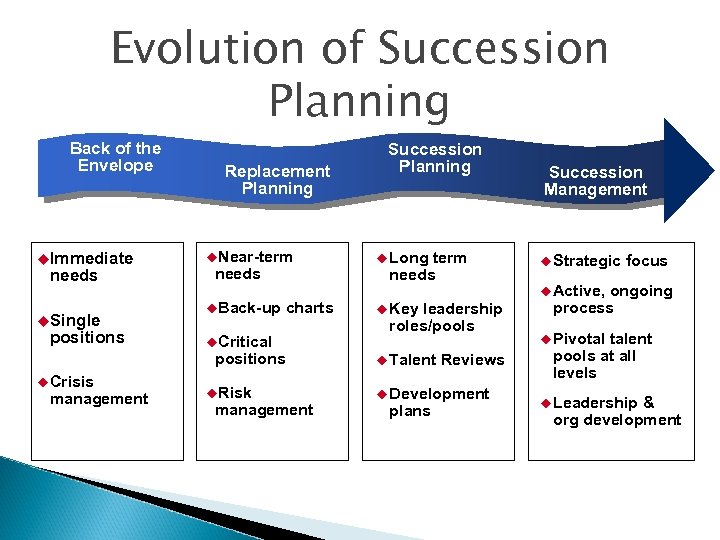
Evolution of Succession Planning Back of the Envelope u. Immediate needs u. Single positions Replacement Planning u. Near-term needs u. Back-up charts u. Critical positions u Crisis management u. Risk management Succession Planning u Long term needs u Key leadership roles/pools u Talent Reviews u Development plans Succession Management u Strategic focus u Active, ongoing process u Pivotal talent pools at all levels u Leadership & org development

why it fails. . • Succession management not linked to business strategy • Reactive approach – only when a position becomes vacant • Lack of ownership by top management • Line managers ignore development of the talent pool • No formal process to track candidates • Lack of objective, data based discussions

role of top management • Communicating their support • Share perspectives on the future leadership needs of the organization • Ensuring that it is perceived as management directive, not just a HR initiative • Volunteer to be part of succession management process • Ensure allocation of adequate resources

role of hr • Targeted processes • Ensure comprehensive assessment of talent • Creation of talent databases • Identification of future talent requirements: being pro -active • Structured & individualized development planning

Talent houses

@ P&G • Rigorous leadership program - Build From Within • Each of the top 50 jobs has three replacement candidates lined up • Ensure each successor gets the experience to be ready for the next job • They train people to work in different countries and businesses so as to develop a deep bench globally • The disadvantage is that people did think in similar ways President & Chief Executive, P&G: From A. G. Lafley to Bob Mc. Donald in 2009. . . “Today I could show you the next generation of successors to current leaders, the generation after that, and the generation after that. ” - Moheet Nagrath, Head of Human Resources at P&G

@ GE • Jack Welch (Chairman & CEO, GE) submitted a list of 23 potential CEO candidates to the Management Development Board in 1994 • Successors reviewed every June and December by Board and Welch • No outside candidates considered • Succession plan was closely tied with management & leadership development plan • Leading contenders were put on various proving grounds & given cross business exposure • GE Board made regular visits to get impression of the candidates – natural style and approach From Jack Welch to Jeffrey Immelt in 2000. . . “From now on, choosing my successor is the most important decision I'll make. It occupies a considerable amount of thought almost every day. ” - Jack Welch, 1991

@ Wipro • Succession Planning program is called Talent Review & Planning (TRP) ü Identify employees who are ready to take over the critical roles immediately and over the next 1 -2 or 23 years • Developmental planning for each identified internal candidate - job rotation, training, coaching and performance counseling • They also keep track of potential external candidates, and establish touch points for attracting them at the appropriate time • Training could be through internal programs or onthe-job (local as well as global) to gain crossfunctional or cross-geographical exposure Azim Premji – succession plan disclosed to board of directors…

@ HUL • System of listers ü Continuous process of discussing people ü Identifying people at different levels ü For the distance they will be able to travel in their career • The process is centered on ü Identifying a list of potential candidates ü Placing them in specially chosen and challenging roles ü Then observing the outcomes Nitin Paranjpe joined HUL in 1987 as mgmt trainee, appointed as CEO & MD in 2008…

@ L&T • Six out of eight Executive Directors on the board are retiring within three years, including AM Naik (Chairman & MD, L&T) • The company is putting in place an interim leadership team to steer the company until 2015 • Two global consultants Mc. Kinsey & Bains are working on a succession plan for the company Successor yet to be identified for AM Naik…

@ airtel • Critical positions identified as part of OTR process basis: ü Impact on financials ü Exposure to brand ü Uniqueness of the skill (Supply in market) ü Span of influence & control ü Relevance of position – If redesign the org from scratch would this role be there ü Impact on customers / shareholders / investors ü External value (How much sought by competition) ü YLP, e. Leap, b. Leap, Shadow boards From Manoj Kohli to Sanjay Kapoor in 2010. . .
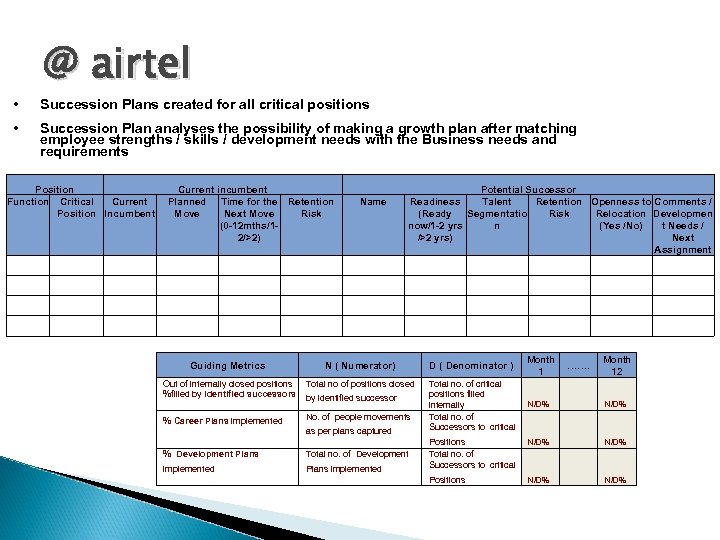
@ airtel • Succession Plans created for all critical positions • Succession Plan analyses the possibility of making a growth plan after matching employee strengths / skills / development needs with the Business needs and requirements Position Function Critical Current Position Incumbent Current incumbent Planned Time for the Retention Move Next Move Risk (0 -12 mths/12/>2) Potential Successor Readiness Talent Retention Openness to Comments / (Ready Segmentatio Risk Relocation Developmen now/1 -2 yrs n (Yes /No) t Needs / />2 yrs) Next Assignment Name Guiding Metrics N ( Numerator) Out of internally closed positions Total no of positions closed %filled by identified successors by identified successor % Career Plans implemented No. of people movements % Development Plans Total no. of Development implemented Plans implemented as per plans captured D ( Denominator ) Month ……. 1 Total no. of critical positions filled internally Total no. of Successors to critical N/D% Positions Total no. of Successors to critical Positions Month 12 N/D% N/D%

“Bosses are stewards of people’s talent

u! Thank yo
09e84dac14f6f348c286b09249fc7b29.ppt