ff3e6a7cdeebeb48f1ffcdb8c1341476.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Successful Intervention Plans from Start to Finish Amanda Geidel, Director of Special Education Assistant Professor of Education Concordia University, Nebraska Amanda. geidel@cune. edu
Successful Intervention Plans from Start to Finish Amanda Geidel, Director of Special Education Assistant Professor of Education Concordia University, Nebraska Amanda. geidel@cune. edu
 Do you ever feel like this?
Do you ever feel like this?
 Do you ever want to give up?
Do you ever want to give up?
 Success in inclusive education… n “…is about changing the general education teachers’ beliefs so that they hold the least dangerous assumption about students’ capabilities and have high expectations for student achievement. ” l Jorgensen, Schuh & Nisbet 2006
Success in inclusive education… n “…is about changing the general education teachers’ beliefs so that they hold the least dangerous assumption about students’ capabilities and have high expectations for student achievement. ” l Jorgensen, Schuh & Nisbet 2006
 Seven Steps in the Special Education Process: Pre-referral n Referral n Evaluation n Identification n IEP writing n IEP implementation n Yearly evaluation and re-writing of IEP n
Seven Steps in the Special Education Process: Pre-referral n Referral n Evaluation n Identification n IEP writing n IEP implementation n Yearly evaluation and re-writing of IEP n
 Identification Process: n 1 – Student has difficulty in class n 2 – Pre-referral services begin, either Rt. I or SAT n 3 – No improvement? Referral for Special Education?
Identification Process: n 1 – Student has difficulty in class n 2 – Pre-referral services begin, either Rt. I or SAT n 3 – No improvement? Referral for Special Education?
 Whether RTI or SAT… Pre-referral Planning Includes: n 1) Identifying the problem(s) n 2) Gathering baseline data n 3) Writing a goal(s) n 4) Planning Intervention(s) n 5) Data collection and follow-up plans.
Whether RTI or SAT… Pre-referral Planning Includes: n 1) Identifying the problem(s) n 2) Gathering baseline data n 3) Writing a goal(s) n 4) Planning Intervention(s) n 5) Data collection and follow-up plans.
 So, what’s the problem? n Be sure to focus on ONE problem per intervention goal n Describe each problem with detail and clarity n What is the difference between what is expected and what is occurring?
So, what’s the problem? n Be sure to focus on ONE problem per intervention goal n Describe each problem with detail and clarity n What is the difference between what is expected and what is occurring?
 How do I collect baseline data? Look at previous report cards n Visit with others who know the child n Take observation notes or find someone to help do that n Look at your own documented scores on student work n Take some simple data n
How do I collect baseline data? Look at previous report cards n Visit with others who know the child n Take observation notes or find someone to help do that n Look at your own documented scores on student work n Take some simple data n
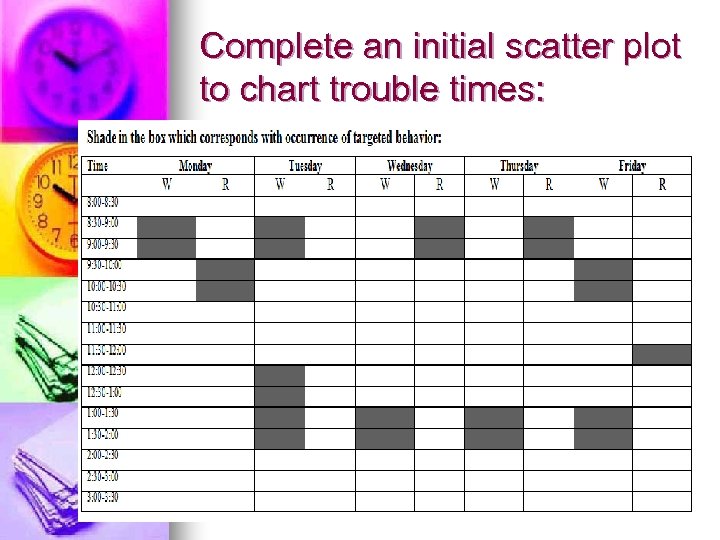 Complete an initial scatter plot to chart trouble times:
Complete an initial scatter plot to chart trouble times:
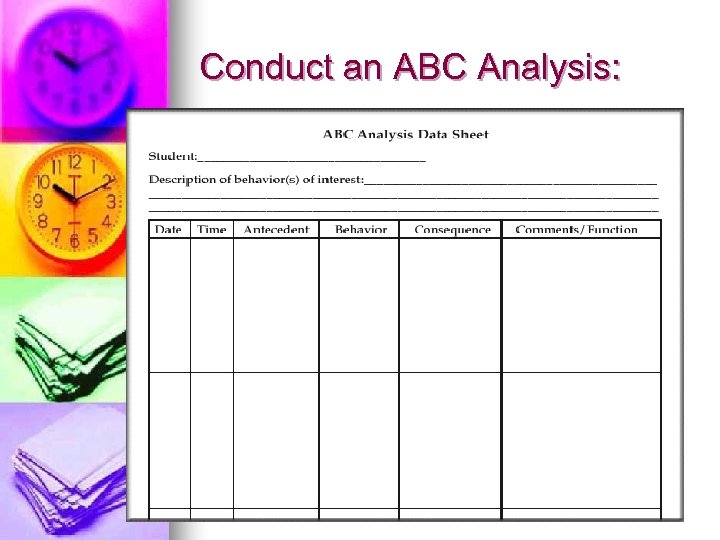 Conduct an ABC Analysis:
Conduct an ABC Analysis:
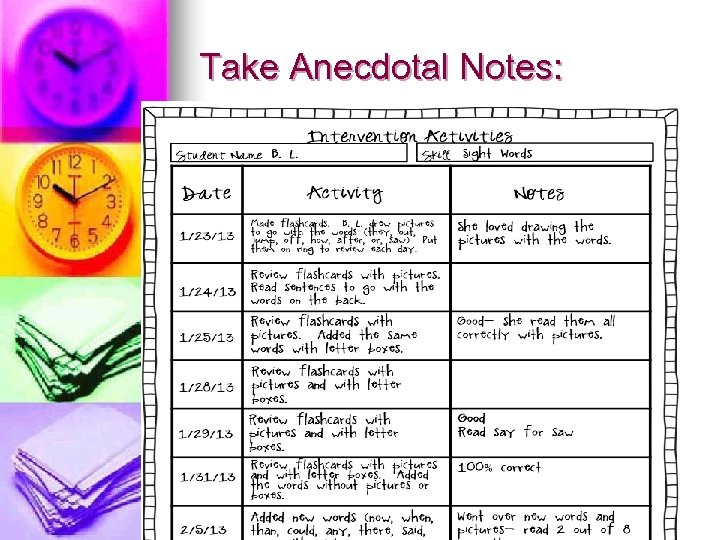 Take Anecdotal Notes:
Take Anecdotal Notes:
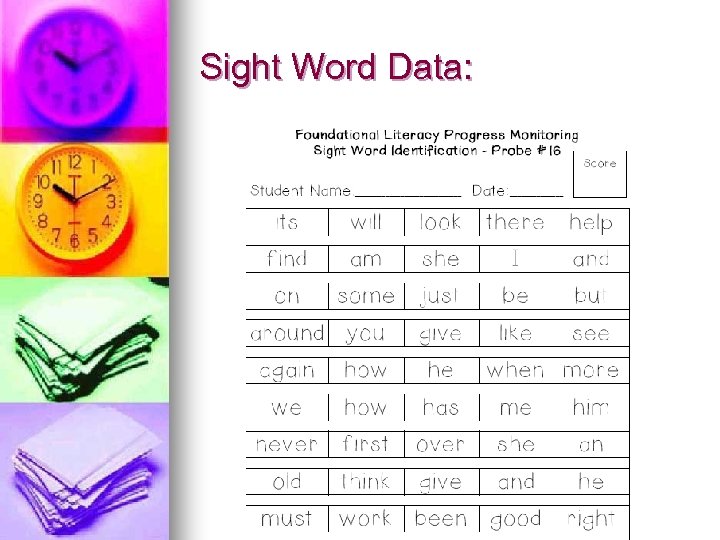 Sight Word Data:
Sight Word Data:
 Reading Strategy Data:
Reading Strategy Data:
 Running Record Data:
Running Record Data:
 Identify Reading Levels: n Independent – 0 -5 errors 95 -100% accuracy n Instructional – 6 -10 errors 90 -94% accuracy n Frustration – 11 or more errors 89% or below
Identify Reading Levels: n Independent – 0 -5 errors 95 -100% accuracy n Instructional – 6 -10 errors 90 -94% accuracy n Frustration – 11 or more errors 89% or below
 What goes into the goal? n Timeframe: how long will the intervention last/take? n Student’s expected behavior n Conditions (extra needed details) n Criteria
What goes into the goal? n Timeframe: how long will the intervention last/take? n Student’s expected behavior n Conditions (extra needed details) n Criteria
 Examples: By Dec. 22, Sara will volunteer to read a problem out loud, while in math class, on 9/10 opportunities. n By the end of 2 nd quarter, Jay will score at the instructional level, on 3 rd grade material, on 8/10 opportunities. n
Examples: By Dec. 22, Sara will volunteer to read a problem out loud, while in math class, on 9/10 opportunities. n By the end of 2 nd quarter, Jay will score at the instructional level, on 3 rd grade material, on 8/10 opportunities. n
 How can I intervene? Use available resources and tools for guidance n Seek input from colleagues and other professionals n Look at what needs to change in the environment or setting that will allow student success. n How will you motivate the student during the intervention? n
How can I intervene? Use available resources and tools for guidance n Seek input from colleagues and other professionals n Look at what needs to change in the environment or setting that will allow student success. n How will you motivate the student during the intervention? n
 More modifying and intervening… What academic modifications or adaptations are needed? n Are there behavioral issues that need to be addressed? n How is/can the family be involved? n What social situations might impede progress? n
More modifying and intervening… What academic modifications or adaptations are needed? n Are there behavioral issues that need to be addressed? n How is/can the family be involved? n What social situations might impede progress? n
 A “must buy” for any teacher!
A “must buy” for any teacher!
 Make the Needed Adaptations for Student Success: n http: //www. grandviewlibrary. org/ Curriculum. Adaptations/Nine. Typ es. pdf n Adaptation grid. doc
Make the Needed Adaptations for Student Success: n http: //www. grandviewlibrary. org/ Curriculum. Adaptations/Nine. Typ es. pdf n Adaptation grid. doc
 Collecting data and making USE of it… Create simple data charts that you can record student scores/behaviors on quickly. n Ask others to monitor the same skills/behaviors when necessary. n Review the results daily/weekly n IF no progress is being made, revisit your intervention plans and revise where needed! n
Collecting data and making USE of it… Create simple data charts that you can record student scores/behaviors on quickly. n Ask others to monitor the same skills/behaviors when necessary. n Review the results daily/weekly n IF no progress is being made, revisit your intervention plans and revise where needed! n
 Resources: n Jorgensen, C. M. , Schuh, M. C. , & Nisbet, J. (2006). The inclusion facilitator’s guide. Baltimore, MD: Brookes. n Mc. Carney, S. B. (2006), Pre-Referral intervention manual (3 rd ed. ). Columbia, MO: Hawthorne. n Salend, S. J. (2008) Creating inclusive classrooms: Effective and reflective practices for all students. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Education.
Resources: n Jorgensen, C. M. , Schuh, M. C. , & Nisbet, J. (2006). The inclusion facilitator’s guide. Baltimore, MD: Brookes. n Mc. Carney, S. B. (2006), Pre-Referral intervention manual (3 rd ed. ). Columbia, MO: Hawthorne. n Salend, S. J. (2008) Creating inclusive classrooms: Effective and reflective practices for all students. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Education.


