subjunctive_mood.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 25

Subjunctive Mood

I wish I could fly. I wish I had one.

Mood is a grammatical category which indicates the attitude of the speaker towards the action expressed by the verb from the point of view of its reality.

Moods in the English Language v the Indicative Mood I do a lot of travelling, you know. v the Imperative Mood Please, help me! v the Subjunctive Mood Oh, if I were free now!

The Subjunctive Mood shows that the action or state expressed by the verb is presented as a non-fact, as something imaginary or desired. The Subjunctive Mood has no tense forms to denote time relations. Its forms indicate only whether an action is thought of as prior or not to the moment of speech.
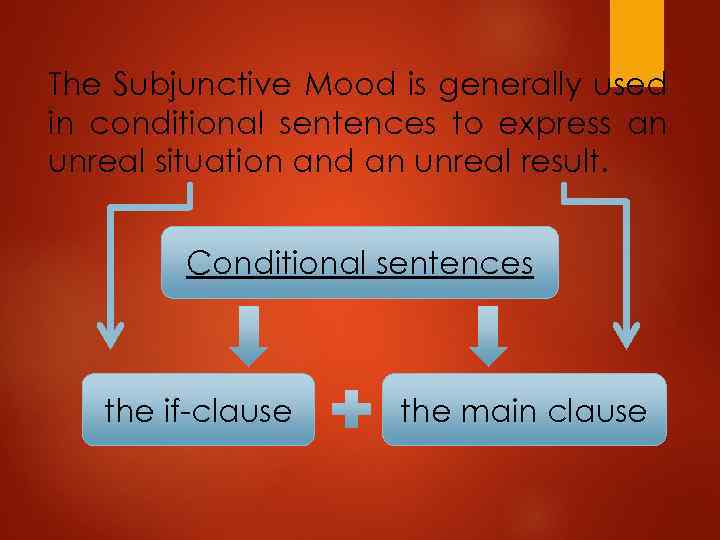
The Subjunctive Mood is generally used in conditional sentences to express an unreal situation and an unreal result. Conditional sentences the if-clause the main clause


Zero Conditional Real actions -100% Situations that are always true if something happens. if-clause present simple main clause , present simple If you have a chance, do it. /real actions/ If we take the snow into the house, it melts.

Conditional 1 the "real" conditional as it is used for real or possible situations makes statements about the real world if-clause present simple main clause , future simple If it rains, we will stay at home. He will arrive late if he doesn’t hurry up. He will arrive late unless he hurries up.


Conditional 2 things which are not real, or are not known to be true. the "unreal" conditional as it is used for unreal - impossible or improbable – situations; it provides an imaginary result for a given situation if-clause main clause past simple , would + infinitive If he studied more, he would pass the exam. They would buy a new house if they had more money.

The verb 'to be', when used in the 2 nd conditional, is always conjugated as 'were'. If I were you, I would follow his advice. He would do it for her if it were possible. If it were not for the storm, we would arrive on time.


The Use regret: If only I had studied harder when I was young. . . missed opportunities: If you had arrived earlier you would have seen the procession. criticism of others: If you hadn't spent so much money, we would be well off now.

Conditional 3 the "past" conditional as it concerns only past situations with hypothetical results if-clause past perfect , main clause would + perfect infinitive If he had known that, he would have decided differently. Jane would have found a new job if she had stayed in Boston.

Mixed Conditional v unreal past situations with hypothetical present or future results If you had taken the medicine yesterday, you would be better now. v unreal situations referring to no particular time with hypothetical results referring to the past If she were not so absent-minded, she would not have lost the way.
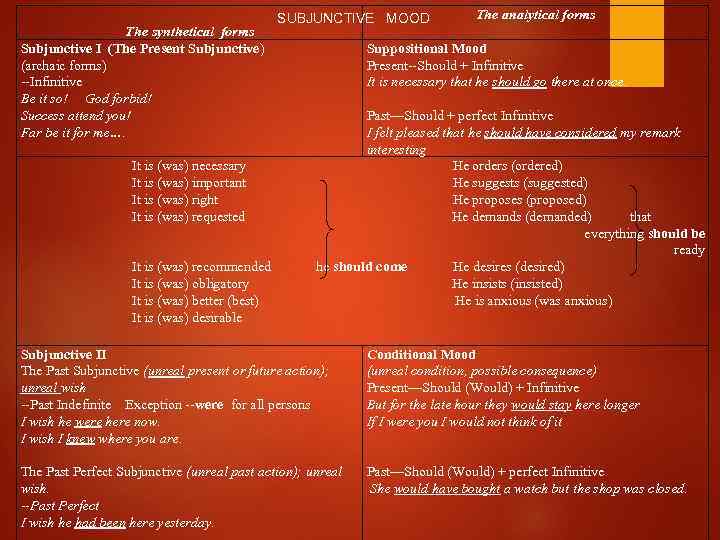
The synthetical forms Subjunctive I (The Present Subjunctive) (archaic forms) --Infinitive Be it so! God forbid! Success attend you! Far be it for me…. It is (was) necessary It is (was) important It is (was) right It is (was) requested It is (was) recommended It is (was) obligatory It is (was) better (best) It is (was) desirable SUBJUNCTIVE MOOD The analytical forms Suppositional Mood Present--Should + Infinitive It is necessary that he should go there at once. Past—Should + perfect Infinitive I felt pleased that he should have considered my remark interesting He orders (ordered) He suggests (suggested) He proposes (proposed) He demands (demanded) that everything should be ready he should come He desires (desired) He insists (insisted) He is anxious (was anxious) Subjunctive II The Past Subjunctive (unreal present or future action); unreal wish --Past Indefinite Exception --were for all persons I wish he were here now. I wish I knew where you are. Conditional Mood (unreal condition, possible consequence) Present—Should (Would) + Infinitive But for the late hour they would stay here longer If I were you I would not think of it The Past Perfect Subjunctive (unreal past action); unreal wish. Past Perfect I wish he had been here yesterday. Past—Should (Would) + perfect Infinitive She would have bought a watch but the shop was closed.

The following expressions are also used to introduce conditional clauses, especially of the first type: unless (= if. . . not), in case, provided or providing, on condition that.
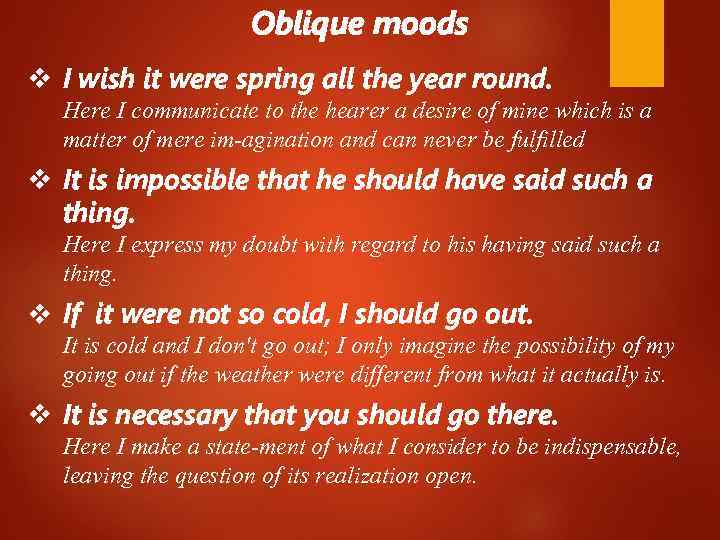
Oblique moods v I wish it were spring all the year round. Here I communicate to the hearer a desire of mine which is a matter of mere im agination and can never be fulfilled. v It is impossible that he should have said such a thing. Here I express my doubt with regard to his having said such a thing. v If it were not so cold, I should go out. It is cold and I don't go out; I only imagine the possibility of my going out if the weather were different from what it actually is. v It is necessary that you should go there. Here I make a state ment of what I consider to be indispensable, leaving the question of its realization open.

You’ve just found a genie and he’s going to grant you three wishes! If I…

q OTHER TYPES OF IF-SENTENCE q IF X IS, DO Y. the second part of the sentence is an imperative = the speaker is telling you what to do if a certain thing happens: e. g. If Penny calls, tell her I've gone to the hairdresser's. If I'm not here by seven, don't bother to wait for me. q IF YOU WILL DO A, I WILL DO В.

q IF X IS, Y IS. states a general truth, such as a scientific fact. Compare: A If you drop eggs, they break. = a general truth about eggs В If you drop that egg, it will break. =what will happen to this particular egg In such cases, if really means whenever or every time that. . .

Type I: IF I DO X, Y WILL BE THE RESULT Examples If I have enough time, I may go and see Jennie this evening. If you study really hard, you should pass your examinations. If they don't come soon, they might miss the first act. If you don't make an effort, you cannot expect to be successful.

Type II: IF I DID X, Y WOULD BE THE RESULT Examples: If I were you, I would take up a sport to keep fit. If you saved your money, you could afford a holiday abroad. If we could (i. e. , were able to: past) get to London before midday, we might be able to do some shopping in Oxford Street.

Type III: IF I HAD DONE X, Y WOULD HAVE BEEN THE RESULT Examples: If I hadn't come to Liverpool, we would never have met, darling. If you hadn't reacted so quickly, we might well have had an accident. If she had not been so hardworking, she might not have been manager today. If they had only asked us, they could have used the caravan with pleasure.
subjunctive_mood.pptx