1. Вводное, возбудимость.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57

Subject: Introduction in a course of normal physiology Lecture plan: 1. 2. 3. 4. Physiology definition, communication with other sciences Stages of development of physiology Methods of physiological researches Concept about regulation of functions

Physiology, definition, communication by other sciences Physiology (the physis-nature, logоsscience) the science studying functions of live organisms, systems, bodies, cages, and also mechanisms of regulation of these functions. The physiology considers organism functions in an interconnection and taking into account influence of factors of environment.

The physiology belongs to biological sciences and it is closely connected with anatomy, histology, bionics, chemistry, physics, cybernetics.

Stages of development of physiology I. Догарвеевский, (empirical) from Hippocrates to Garvey II. Гарвеевский (1628 -1878) III. Павловский stage IV. Modern - neurocybernetic.

Methods of physiological researches: I. The sharp a) vivisection) m of the isolated bodies II. The chronic The Iii. Kliniko-physiological IV. The auxiliary methods

Regulation of functions of an organism Nervous regulation In a basis the reflex, a reflex arch with Ts. NS participation lies 2. Humoral regulation At participation of chemicals, circulating in blood (BAV) 1. 3. Metabolic regulation 1.

Now regulation consider as uniform neurohumoral, in which the great value is played by kreatorny communications.

Subject: "Excitability, excitability parameters. Bioelectric phenomena". Lecture plan: 1. Physiological properties of excitable fabrics. 2. Excitability, its phases. 3. Excitability parameters (excitement-reobaza threshold, useful time, accommodation, lability). 4. The electric phenomena in excitable fabrics.

Excitability is a property of living tissues to answer irritation with excitement process. Excitement is the difficult process, being characterized physiological, biophysical, biochemical and structural changes in fabrics.

Excitability parameters 1. The threshold of excitement is the minimum force of an irritant which causes excitement, i. e. the minimum response. 2. Reobaza is the minimum current expressed in Volts. 3. Useful time is the smallest time during which the irritating incentive in one реобазу has to work. 4. Hronaksiya is time during which the current equal doubled реобазе, causes excitement.

Excitability parameters 5. Accommodation is an adaptation of excitable fabric to slowly accruing force of an irritant. 6. Lability is a functional mobility. Measure of lability is the maximum quantity of impulses which can reproduce in unit of time (in sec. ) excitable fabric according to a rhythm of caused irritations. - nervous fabric: – 500– 1000 имп / sec. ; – the abolyutny refractory period – 1– 2 ms. - muscle: – 250– 330 имп / sec. ; – the abolyutny refractory period – 4– 5 ms. - synapse: – 100– 125 имп / sec. ; – the abolyutny refractory period – 8– 10 ms.
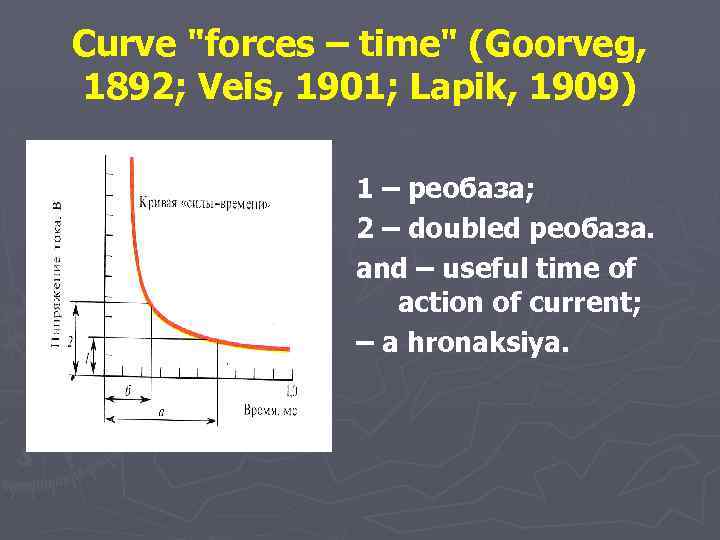
Curve "forces – time" (Goorveg, 1892; Veis, 1901; Lapik, 1909) 1 – реобаза; 2 – doubled реобаза. and – useful time of action of current; – a hronaksiya.
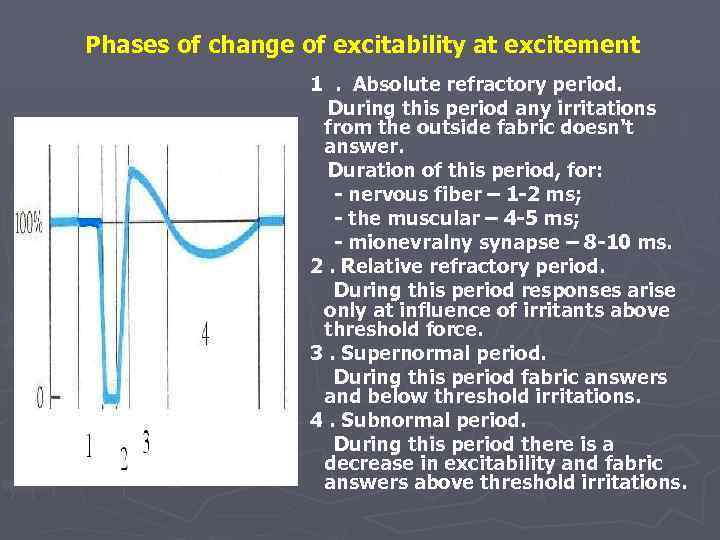
Phases of change of excitability at excitement 1. Absolute refractory period. During this period any irritations from the outside fabric doesn't answer. Duration of this period, for: - nervous fiber – 1 -2 ms; - the muscular – 4 -5 ms; - mionevralny synapse – 8 -10 ms. 2. Relative refractory period. During this period responses arise only at influence of irritants above threshold force. 3. Supernormal period. During this period fabric answers and below threshold irritations. 4. Subnormal period. During this period there is a decrease in excitability and fabric answers above threshold irritations.

The bioelectric phenomena in excitable fabrics ► 1791 – for the first time are found by Galvani ► 1896 – Chagovets assumed that at the heart of their emergence the ionic mechanism lies. ► 1902 Bernstein offered the membrane ionic theory. ► 1949 -1952 gg. - Hodzhkin, Huxley, Katts developed the membrane and ion theory of biopotentials for which got the Nobel Prize.
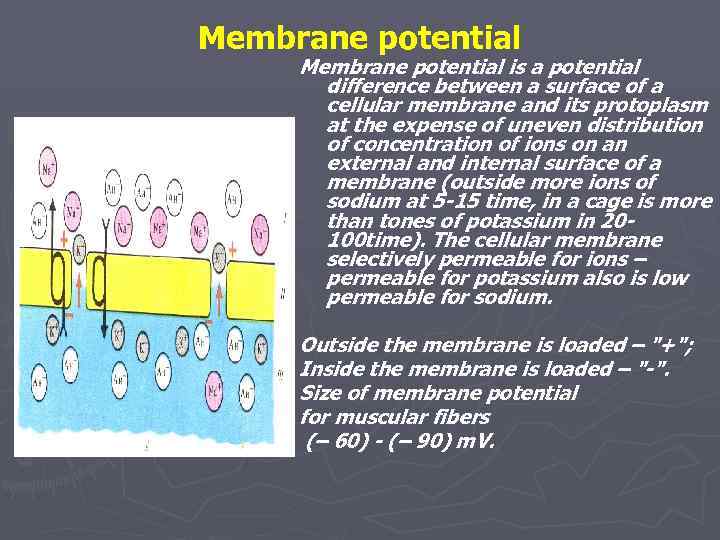
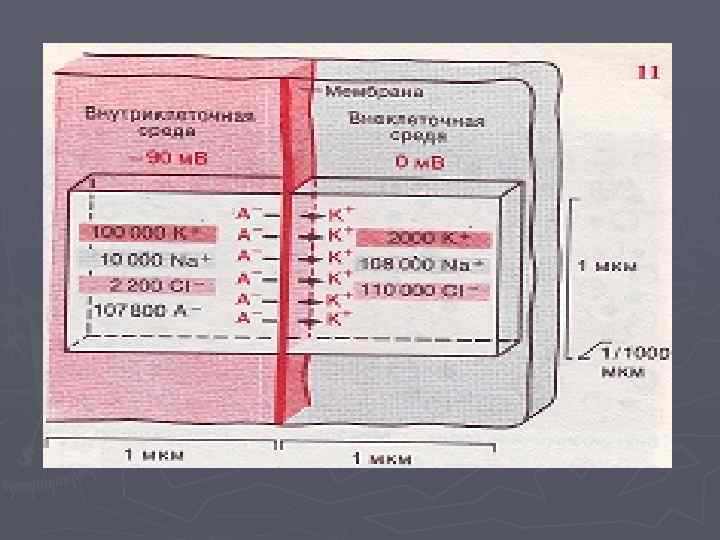
Membrane potential is a potential difference between a surface of a cellular membrane and its protoplasm at the expense of uneven distribution of concentration of ions on an external and internal surface of a membrane (outside more ions of sodium at 5 -15 time, in a cage is more than tones of potassium in 20100 time). The cellular membrane selectively permeable for ions – permeable for potassium also is low permeable for sodium. Outside the membrane is loaded – "+"; Inside the membrane is loaded – "-". Size of membrane potential for muscular fibers (– 60) - (– 90) m. V.
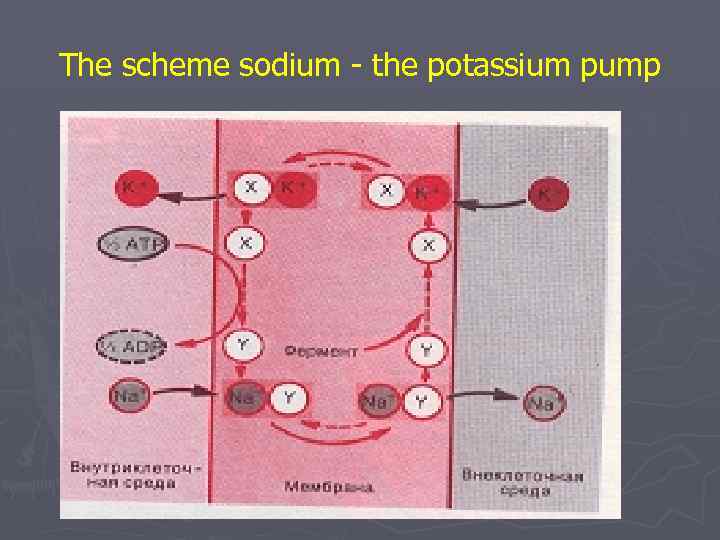
The scheme sodium - the potassium pump

Action potential Potential of action is a fluctuation of membrane potential during excitement (there is a membrane recharge).
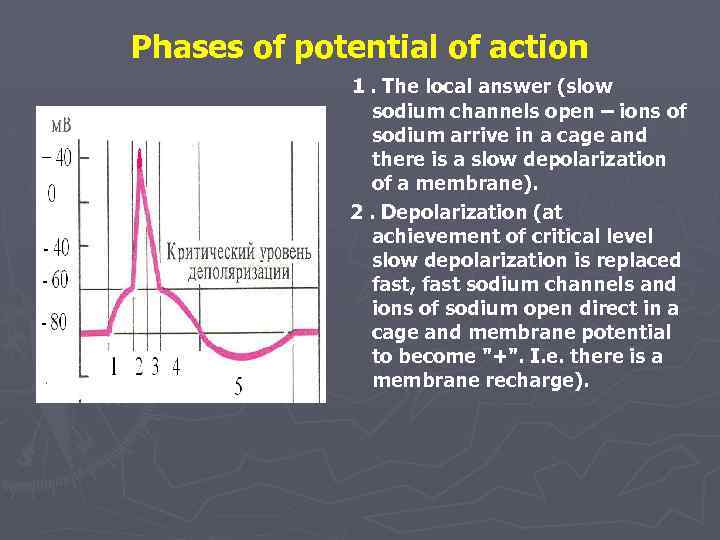
Phases of potential of action 1. The local answer (slow sodium channels open – ions of sodium arrive in a cage and there is a slow depolarization of a membrane). 2. Depolarization (at achievement of critical level slow depolarization is replaced fast, fast sodium channels and ions of sodium open direct in a cage and membrane potential to become "+". I. e. there is a membrane recharge).
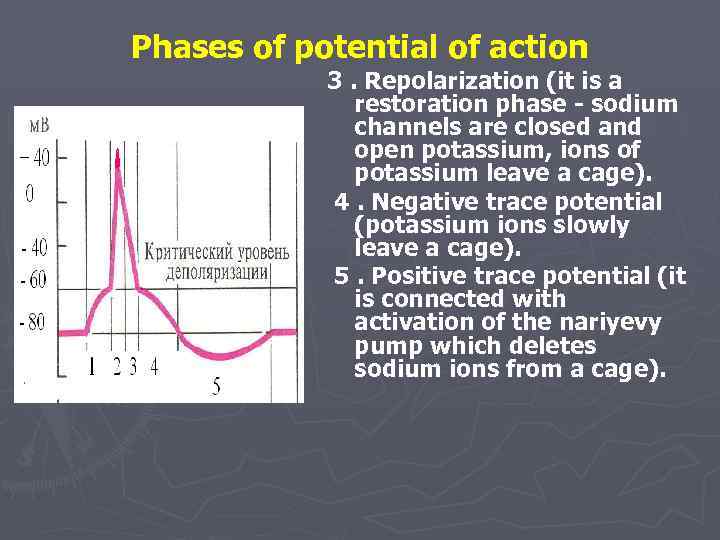
Phases of potential of action 3. Repolarization (it is a restoration phase - sodium channels are closed and open potassium, ions of potassium leave a cage). 4. Negative trace potential (potassium ions slowly leave a cage). 5. Positive trace potential (it is connected with activation of the nariyevy pump which deletes sodium ions from a cage).
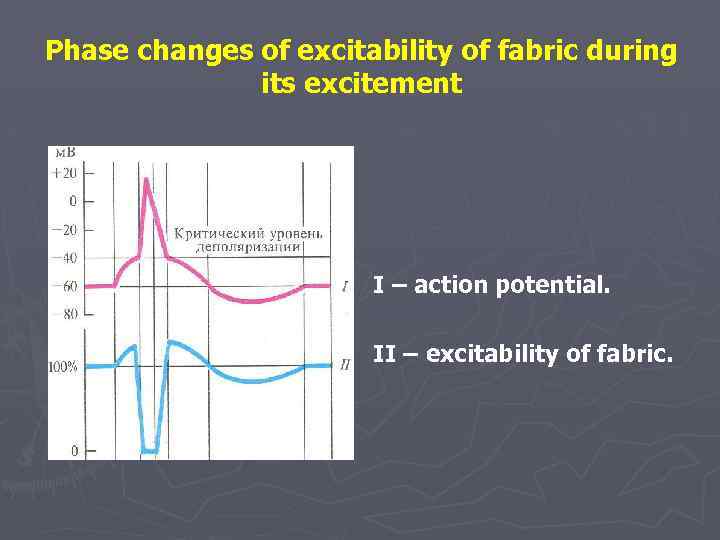
Phase changes of excitability of fabric during its excitement І – action potential. ІІ – excitability of fabric.

Subject: "Physiological properties of muscles". Lecture plan: 1. Structure and functional value of muscles. 2. Physiological properties of muscles. 3. Types of muscular reductions. 4. Modern ideas of muscular reduction and relaxation. 5. Muscular exhaustion.

Types of muscular fabric: 1. Cross-striped muscles of a skeleton; 2. Cross-striped muscles of heart; 3. Smooth muscles. Skeletal muscles carry out following functions: - provide a pose of a body of the person; - move a body in space; - move separate parts of a body relatively each other; - are heat source (participate in thermal control).

Physiological properties of muscles 1. Excitability is an ability of a muscle to answer irritation with excitement; 2. Conductivity is an ability to carry out excitement along all muscular fiber; 3. The Sokratimost is an ability to change length or tension at excitement; 4. Elasticity is an ability of a muscle after reduction to accept an initial form; 5. Avtomatiya is an ability of fabric to be reduced at the expense of impulses arising in her without irritation from out of. 6. Plasticity is an ability to keep length given by stretching without tension change.

Speed of carrying out excitement: - in skeletal muscles – from 3, 5 to 14 m/s; - in the warm – from 0, 5 to 1 m/s; - in smooth muscles – from 0, 5 mm to 5 -10 cm/sec.

Types of reduction of muscles I. Depending on conditions in which there is a muscular reduction: - isometric mode; - isotonic mode. - auksotonichesky mode. II. From the quantitative party: - single muscular reduction; the summarized muscular reduction: a) incomplete summation; b) full summation. tetanus : a) gear tetanus ; b) smooth tetanus.
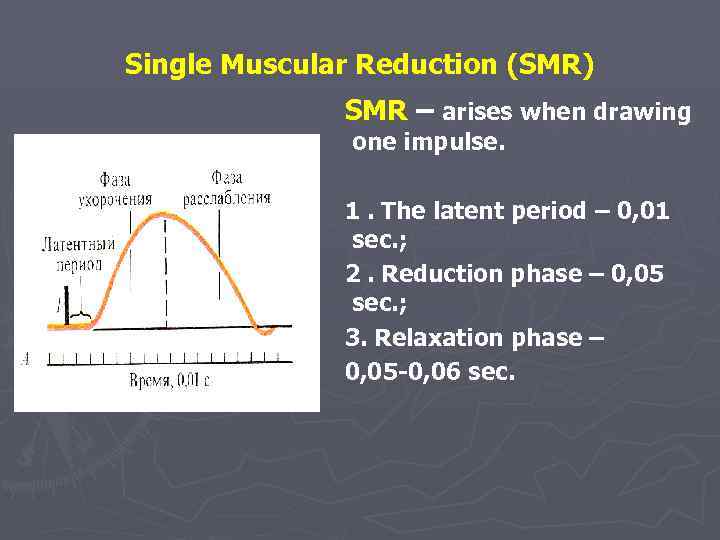
Single Muscular Reduction (SMR) SMR – arises when drawing one impulse. 1. The latent period – 0, 01 sec. ; 2. Reduction phase – 0, 05 sec. ; 3. Relaxation phase – 0, 05 -0, 06 sec.
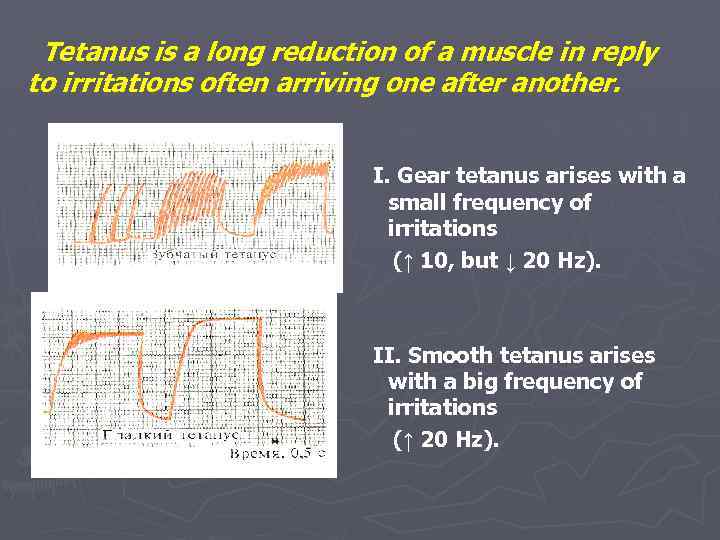
Tetanus is a long reduction of a muscle in reply to irritations often arriving one after another. I. Gear tetanus arises with a small frequency of irritations (↑ 10, but ↓ 20 Hz). II. Smooth tetanus arises with a big frequency of irritations (↑ 20 Hz).
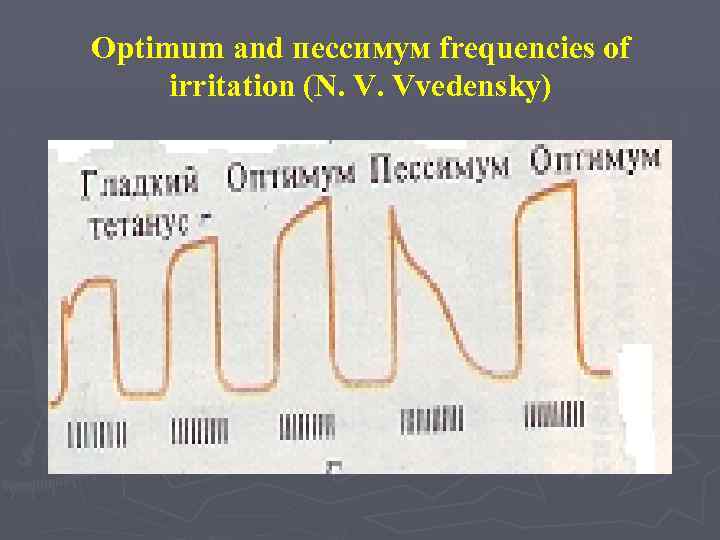
Optimum and пессимум frequencies of irritation (N. V. Vvedensky)

The optimum is the maximum (optimum) frequency of irritation at which тетанус reaches the greatest height. Pessimum is a big frequency of irritation at which amplitude тетануса decreases.

Mechanism of muscular reduction ► The mechanism of muscular reduction is explained by the "sliding" theory the developed Huxley and Hanson ► Muscular fiber consists from мофибрилл. ► Miofibrilla consist of sarkomer. ► Sarkomer is structurally functional unit of a muscle. ► Sarkomer is presented sokratitelny - proteins (a myosin, aktin, tropomyosin, troponin)

► Sarkomer is limited to Z membranes. ► In the center of a sarkomer there is an anisotropic disk (dark) which consists of several thousand threads of a myosin. ► On both ends of a sarkomer there are thin threads aktin – an isotropic (light) disk. Threads актина penetrate Z membrane. ► Miozinovye and aktinovy threads enter the ends into intervals of each other.
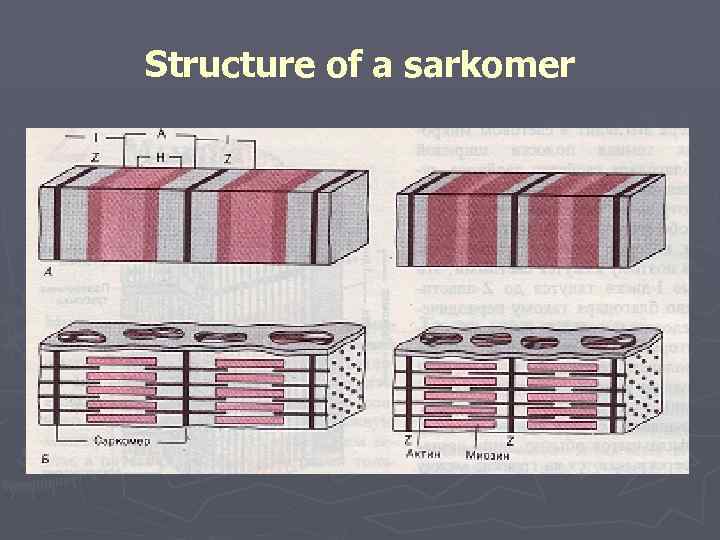
Structure of a sarkomer
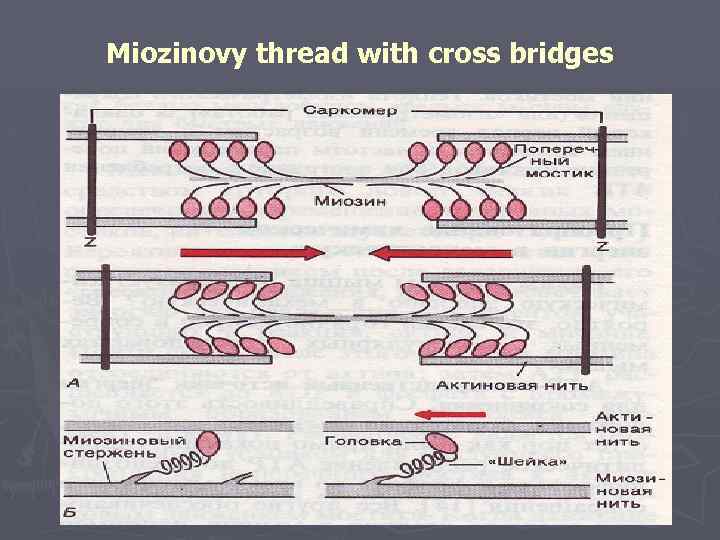
Miozinovy thread with cross bridges
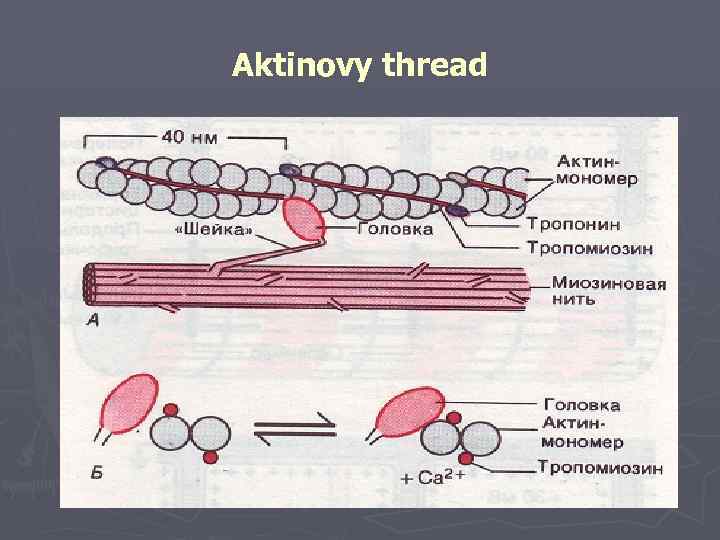
Aktinovy thread

►In the weakened condition миофибрилл molecules tropomyosin block attachments of cross bridges of a myosin to aktinovy threads. ►In the course of interaction aktin and a myosin the key role is played by calcium ions.

►Starts the mechanism of muscular reduction of PD which reaching cross tubules captures lateral tanks which leave calcium ions in саркоплазму. ►Ions of calcium work on troponin which is deformed and immerses тропомиозин in a fillet between chains aktin, opening active sites for an attachment of a head of a miozinovy thread.
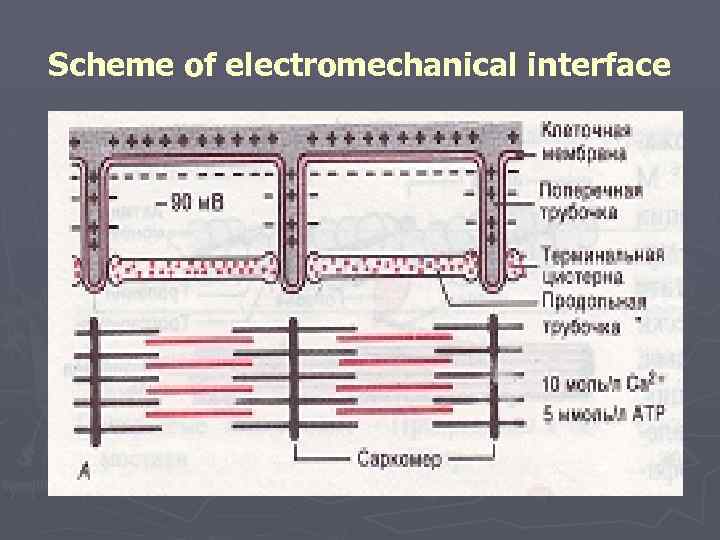
Scheme of electromechanical interface
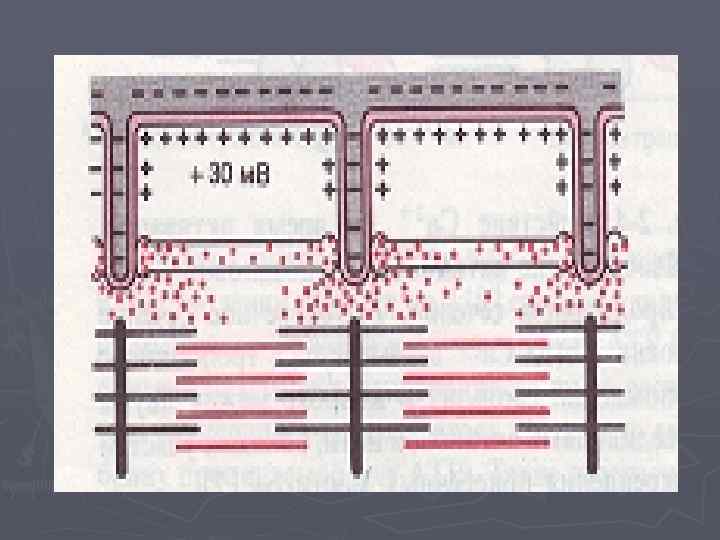
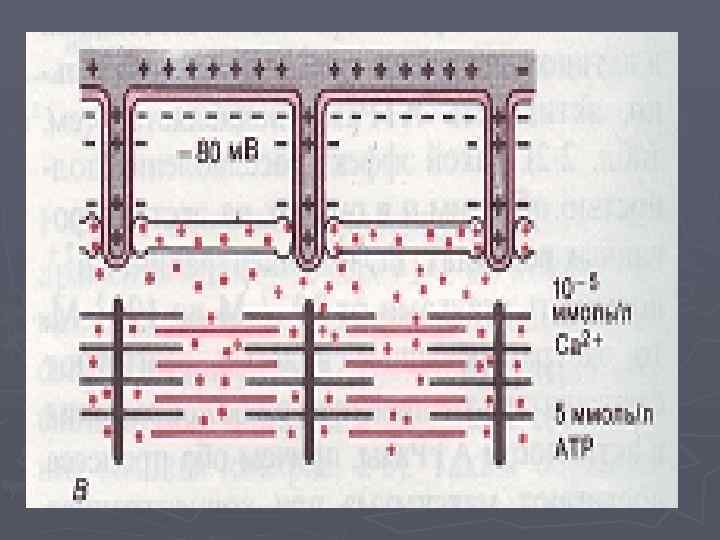

Mechanism of muscular reduction 1. Irritation → 2. Emergence of potential of action → 3. Carrying out it along a cellular membrane and in depth of fiber on cross tubules → 4. Release of Sa 2 + from lateral tanks sarkoplazmatichesky ретикулума and its diffusion to миофибриллам → 5. Interaction of Sa 2 + with troponiny → 6. Deformation troponin →

Mechanism of muscular reduction 7. Immersion тропомиозина in aktinovy fillets → 8. Interaction of cross bridges with the active centers актина → 9. The sliding of aktinovy threads leading to shortening миофибриллы → 10. Activation of the calcic pump → 11. Decrease in concentration of free ions of Sa 2 + in саркоплазме → 12. Detachment of cross bridges → 13. Relaxation миофибрилл

Physiological features of smooth muscles ► Are less excitable, than skeletal (the threshold of excitement is higher, the hronaksiya is longer) ► PD is insignificant and stable, equal 60 -70 m. V ► Refractory period =1 -3 sek ► The latent period to 0, 25 sec. ► Duration of compulsory health insurance is up to 1 min. ► Possess plasticity and automatism ► Иннервируются VNS

The exhaustion is a temporary loss of operability of a cage, body or the whole organism caused work and disappearing after rest. There is a concept about, outdoor activities, (I. M. Setchenov).

Subject: "Physiological properties of nervous fibers. N. E. Vvedensky's doctrine about a parabiosis. Action of a direct current on excitable fabrics. Polar laws, electrotone, katodichesky depression". Lecture plan: 1. Structurally – physiological features of nervous fiber 2. Physiological properties of nervous fiber. 3. Excitement distribution on nervous fibers. 4. Speed of carrying out excitement. 5. Laws of carrying out excitement. Relative not fatigue of a nerve. 6. Parabiosis, phases. 7. Action of a direct current.
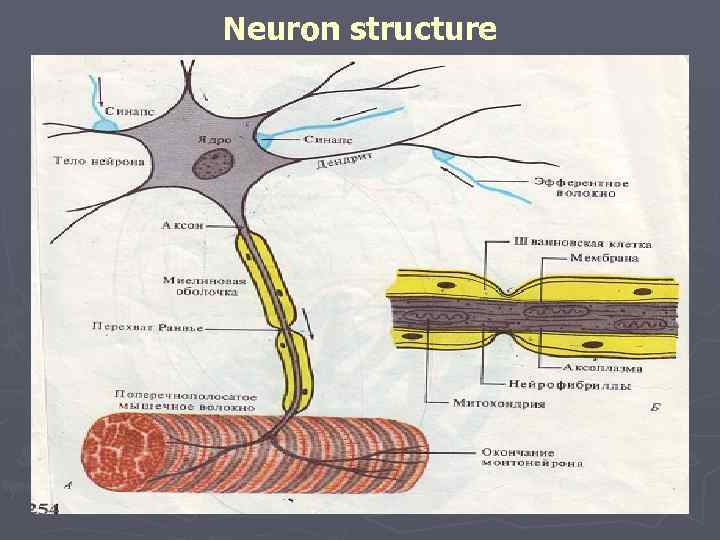
Neuron structure

Structure of nervous fiber ► Share on miyelinoy (pulpy) and bezmiyelinovy (bezmyakotny). ► Bezmiyelinovye consist of the axial cylinder covered with a membrane. In the cylinder is available аксоплазма with organellas. ► Myelin fiber in addition has a myelin cover which interrupts, forming Ranvye's interceptions.

Physiological svoystvanervny fiber Excitability. 2. Conductivity. 1.
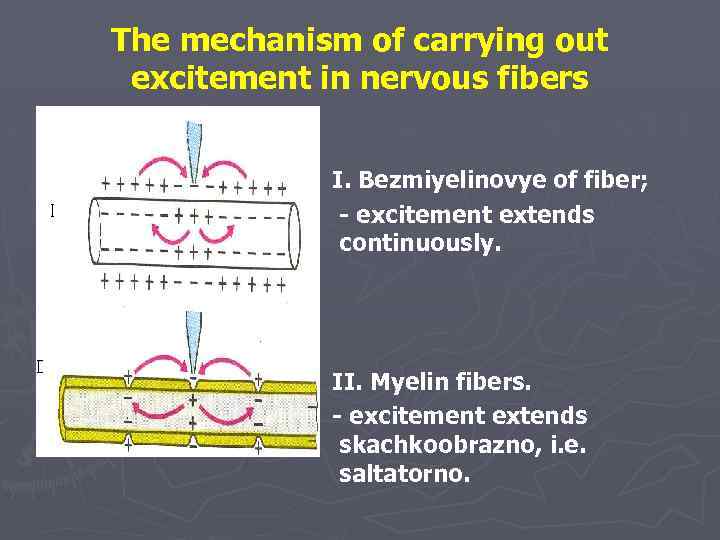
The mechanism of carrying out excitement in nervous fibers I. Bezmiyelinovye of fiber; - excitement extends continuously. II. Myelin fibers. - excitement extends skachkoobrazno, i. e. saltatorno.
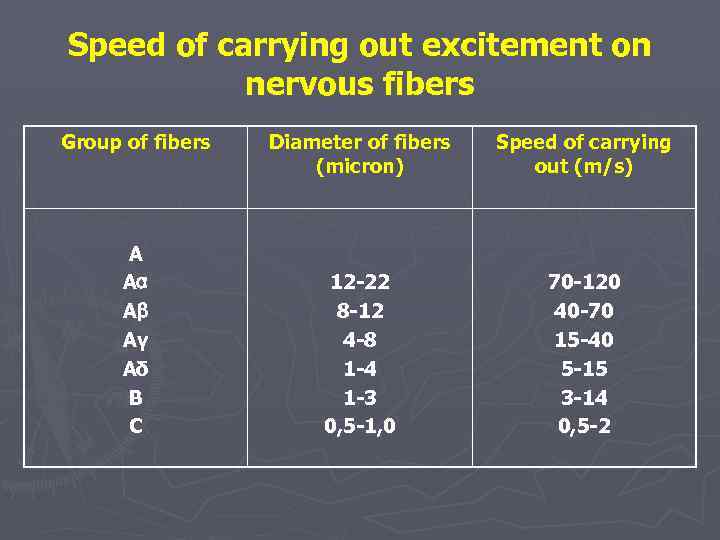
Speed of carrying out excitement on nervous fibers Group of fibers А Аα Аβ Аγ Аδ В С Diameter of fibers (micron) Speed of carrying out (m/s) 12 -22 8 -12 4 -8 1 -4 1 -3 0, 5 -1, 0 70 -120 40 -70 15 -40 5 -15 3 -14 0, 5 -2

Laws of carrying out excitement in nerves. 1. 2. 3. Anatomic and physiological integrity of nervous fiber. Bilateral carrying out excitement. The isolated carrying out excitement.

Relative not fatigue of nervous fiber ► Relative not fatigue of nervous fiber is caused by low power expenditure of a nerve at excitement and fast the resintezy. ► In the nitrogen atmosphere the nerve gets tired.
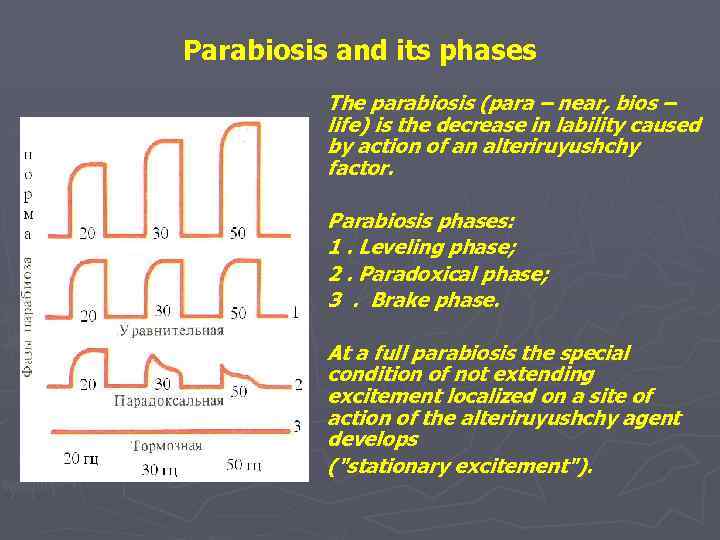
Parabiosis and its phases The parabiosis (para – near, bios – life) is the decrease in lability caused by action of an alteriruyushchy factor. Parabiosis phases: 1. Leveling phase; 2. Paradoxical phase; 3. Brake phase. At a full parabiosis the special condition of not extending excitement localized on a site of action of the alteriruyushchy agent develops ("stationary excitement").

Action of a direct current on excitable fabric current (Pflyuger 1759) ► Laws of polar action of a direct current 1. The irritant action occurs only at the time of short circuit and disconnection. 2. At short circuit of excitement arises on the cathode, at disconnection on the anode. 3. The switching blow of a direct current is stronger than the razmykatelny.
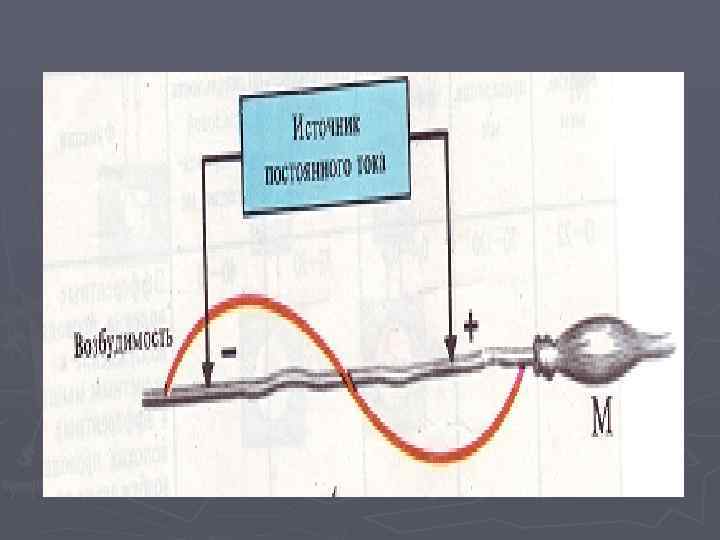

►Katelektroton is an increase of excitability and conductivity under the cathode at action of a direct current ►Anelektroton is a decrease in excitability and conductivity under the anode at action of a direct current

► The Katodichesky depression is a decrease in excitability and conductivity under the cathode at long action of a direct current. ► Anodichesky exaltation is an increase of excitability and conductivity under the anode at long action of a direct current.
1. Вводное, возбудимость.ppt