5- общ ЦНС. Нервные центры.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

SUBJECT: General physiology of Ts. NS. General principles of regulation of functions. Nervous centers and their properties. Mechanisms of coordination and integrative activity of CNS. 1. PLAN: Ts. NS role in integrative, adaptive activity of an organism. Neuron - as a structural and functional unit of CNS. 2. Synapses, structure, functions. 3. Reflex principle of regulation of functions. 4. History of development of the reflex theory. 5. Methods of studying of CNS.
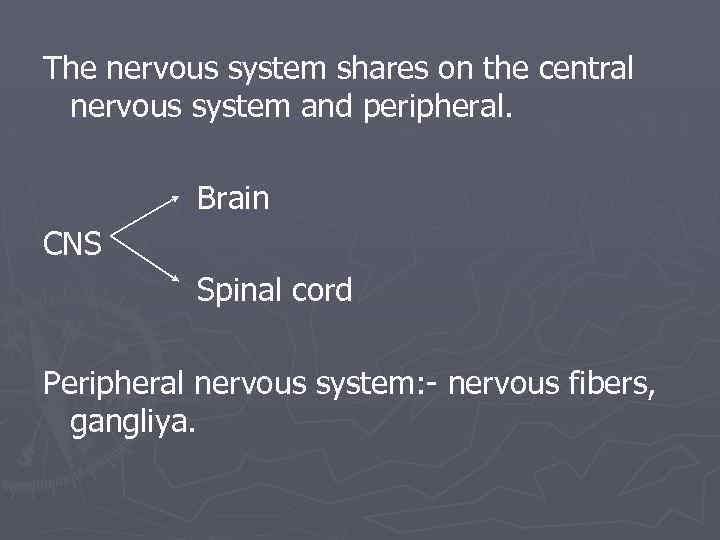
The nervous system shares on the central nervous system and peripheral. Brain CNS Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system: - nervous fibers, gangliya.

CNS carries out : 1. The individual adaptation of an organism to environment. 2. Integrative and coordinating functions. 3. Forms purposeful behavior. 4. Carries out the analysis and synthesis of the arrived incentives. 5. Forms a stream of efferent impulses. 6. Supports a tone of systems of an organism. At the heart of modern idea of CNS the neural theory lies.
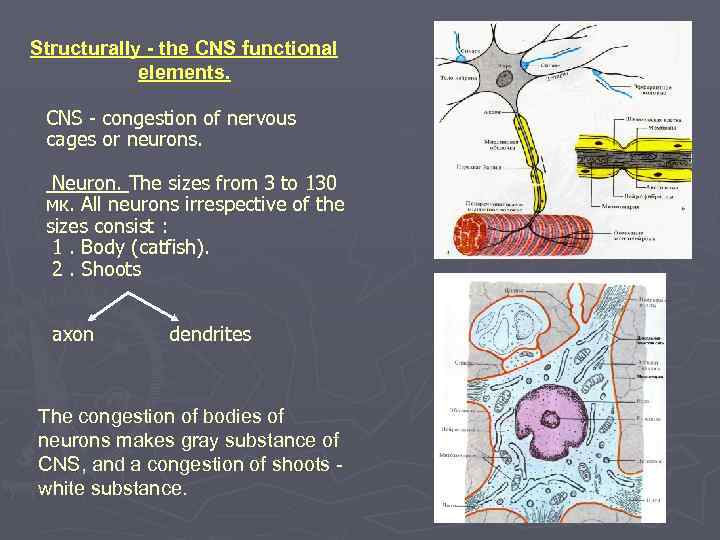
Structurally - the CNS functional elements. CNS - congestion of nervous cages or neurons. Neuron. The sizes from 3 to 130 мк. All neurons irrespective of the sizes consist : 1. Body (catfish). 2. Shoots axon dendrites The congestion of bodies of neurons makes gray substance of CNS, and a congestion of shoots white substance.

REFLEX PRINCIPLE REGULYATSY OF FUNCTION Activity of an organism is natural reflex reaction to incentive. In development of the reflex theory distinguish the next periods: 1. Cartesian (16 eyelids) 2. Sechenovsky 3. Pavlovsk 4. Modern, neurocybernetic.

RESEARCH TSNS METHODS 1. Ekstirpation (removal: partial, full) 2. Irritations (electric, chemical) 3. The radio isotope 4. Modeling (physical, mathematical, conceptual) 5. EEG (registration of electric potentials) 6. Stereotaksichesky technique. 7. Development of conditioned reflexes 8. Computer tomography 9. Patalogoanatomichesky method

Ts. NS carries out two functions reflex and conduction. Reflex activity is carried out at the expense of reflexes. REFLEX – the reaction of an organism which is arising on irritation of receptors and carried out with participation of Ts. NS.

Under natural conditions reflex reaction happens at threshold and nadporogovy irritation of an entrance of a reflex arch – a receptive field. RECEPTIVE FIELD - a certain site with the receptor cages which irritation initiates reflex reaction. Receptive fields of different reflexes have a certain localization, and receptor cages - the corresponding specialization.
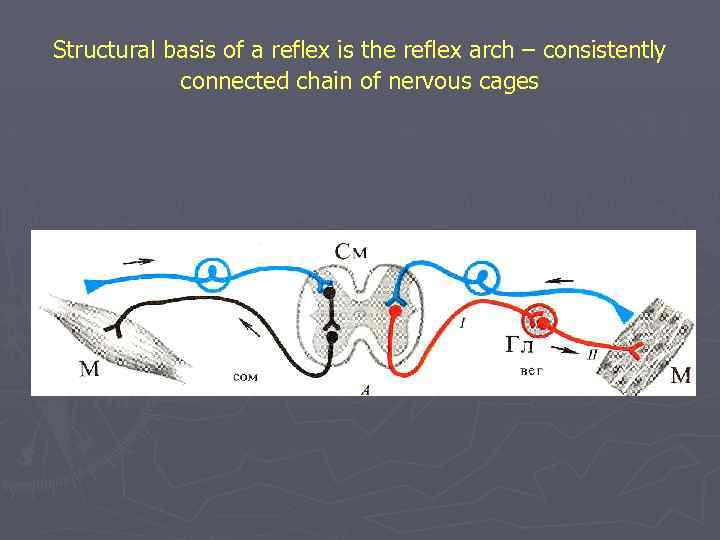
Structural basis of a reflex is the reflex arch – consistently connected chain of nervous cages
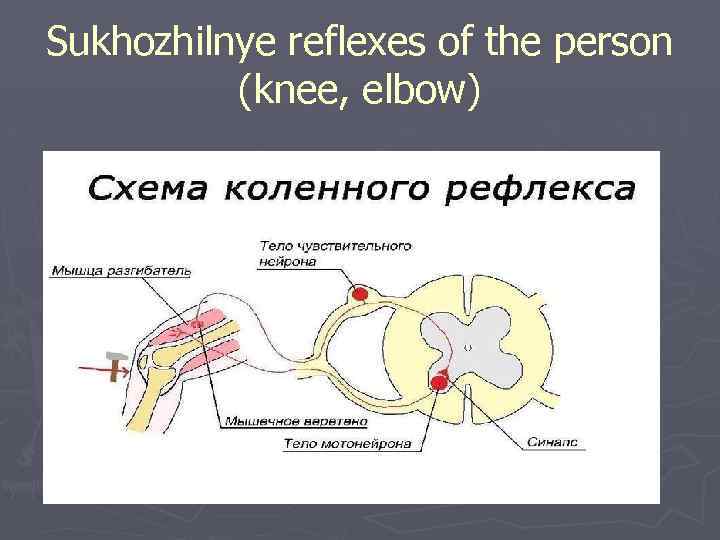
Sukhozhilnye reflexes of the person (knee, elbow)

TIME of the REFLEX is the time necessary for implementation of a reflex, it consists of 5 components: - the latent period of a receptor time for excitement passing on afferentny nervous fibers - the central time of a reflex (time of transfer of excitement in Ts. NS from afferentny neuron to efferent) - time of passing of excitement on efferent nervous fibers - the latent period of an effector

2. CLASSIFICATION OF REFLEXES 1. On a way of calling: - unconditioned reflexes - the conditional 2. In the receptor location: eksterotseptivny (painful, temperature, tactile) interotseptivny - Propriotseptivnye (elbow, knee, ахиллов)
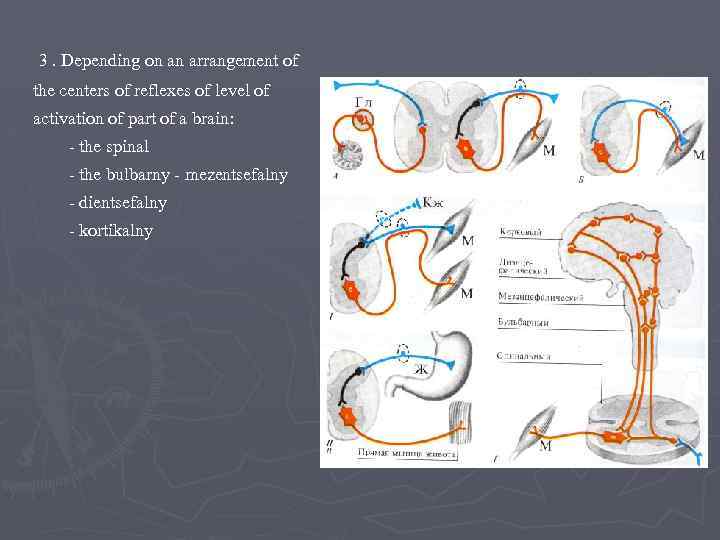
3. Depending on an arrangement of the centers of reflexes of level of activation of part of a brain: - the spinal - the bulbarny - mezentsefalny - dientsefalny - kortikalny

4. On biological value - the food - the defensive - sexual, etc. 5. On nature of response: - the motor - sekretorny - sosudodvigatelny 6. On response duration - fazichesky - the tonic 7. By quantity of neurons: - the two-neural - three-neural and more 8. By quantity of synapses - monosinaptichesky - polisinaptichesky 9. True, false
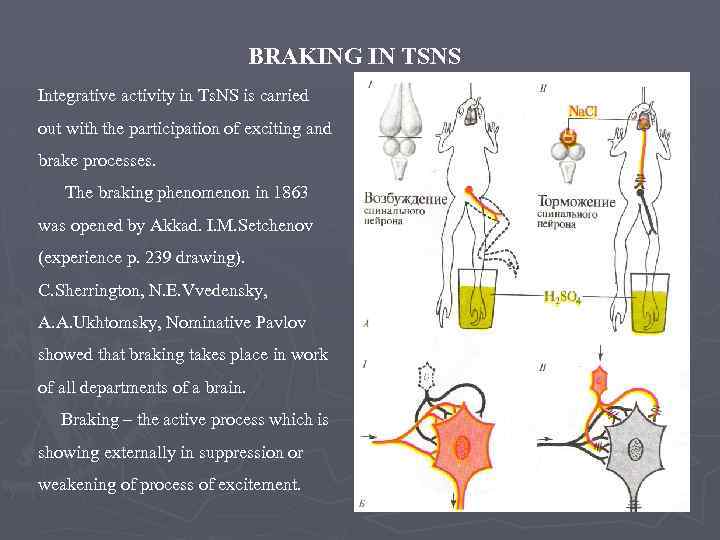
BRAKING IN TSNS Integrative activity in Ts. NS is carried out with the participation of exciting and brake processes. The braking phenomenon in 1863 was opened by Akkad. I. M. Setchenov (experience p. 239 drawing). C. Sherrington, N. E. Vvedensky, A. A. Ukhtomsky, Nominative Pavlov showed that braking takes place in work of all departments of a brain. Braking – the active process which is showing externally in suppression or weakening of process of excitement.

BRAKING MECHANISM. (Ekkls, Renshaw), proved existence of inserted structures, Renshaw, Purkinye's cells having communication with the motor neurons which excitement causes allocation of the brake mediator influencing a motor neuron. As a result braking process develops.
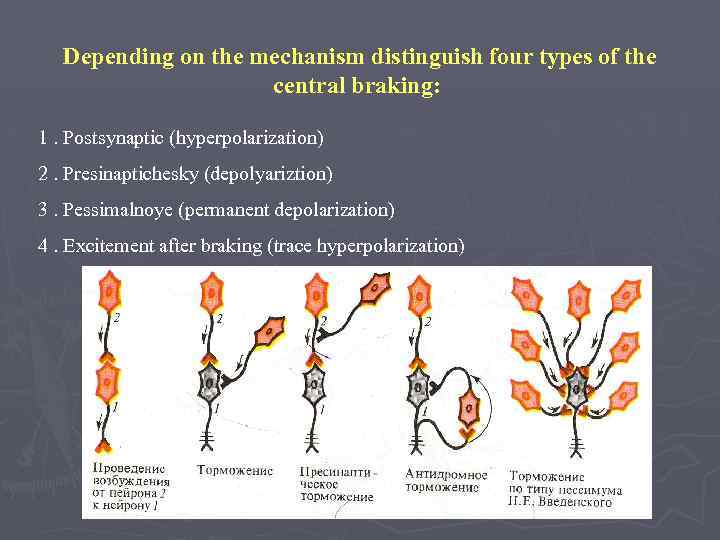
Depending on the mechanism distinguish four types of the central braking: 1. Postsynaptic (hyperpolarization) 2. Presinaptichesky (depolyariztion) 3. Pessimalnoye (permanent depolarization) 4. Excitement after braking (trace hyperpolarization)

The NERVOUS CENTER is a set of neurons (structures) of Ts. NS necessary for implementation of a reflex and regulation of separate functions of an organism.

PHYSIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF THE NERVOUS CENTERS (NC) 1. Unilateral carrying out excitement 2. Sinaptichesky delay. One synoptic delay equals 1 -2 ms (0, 5 ms on mediator allocation, 1, 5 ms on mediator diffusion). 3. High fatigue (exhaustion of stocks of a mediator, energy resources, adaptation of a postsynaptic receptor to a mediator) 4. Summation of excitement – (In 1863 I opened I. M. Setchenov) ability of NTs to summarize excitement of subthreshold force and to give the reflex act
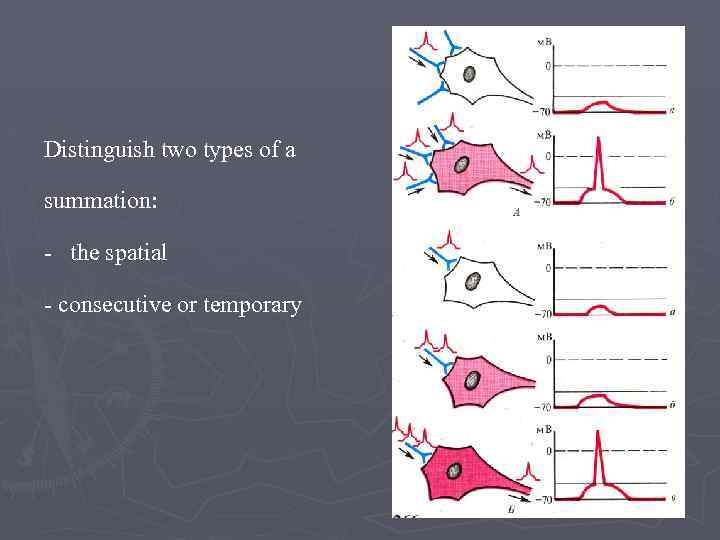
Distinguish two types of a summation: - the spatial - consecutive or temporary
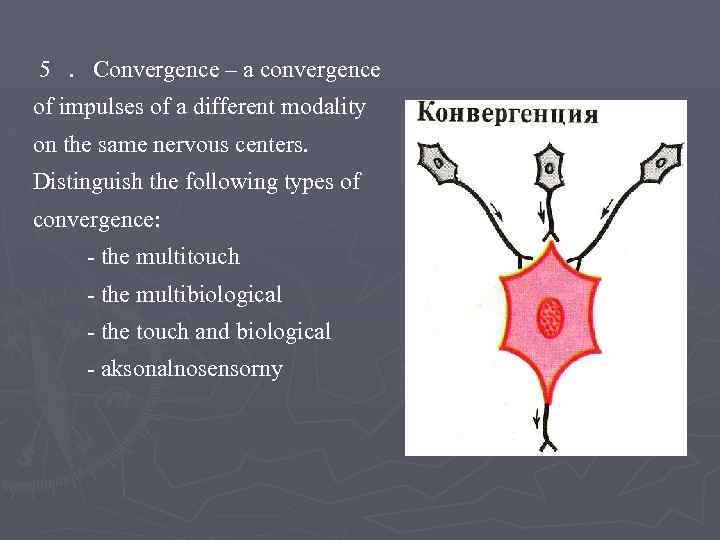
5. Convergence – a convergence of impulses of a different modality on the same nervous centers. Distinguish the following types of convergence: - the multitouch - the multibiological - the touch and biological - aksonalnosensorny
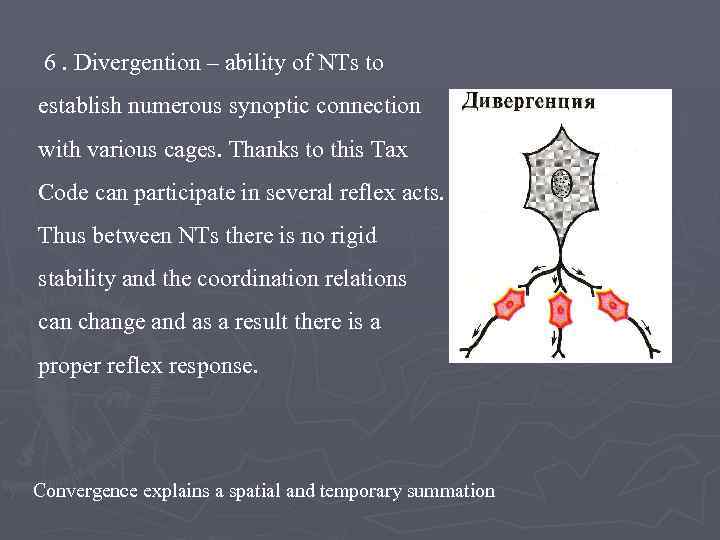
6. Divergention – ability of NTs to establish numerous synoptic connection with various cages. Thanks to this Tax Code can participate in several reflex acts. Thus between NTs there is no rigid stability and the coordination relations can change and as a result there is a proper reflex response. Convergence explains a spatial and temporary summation

7. Okklyuziya - "obstruction". Have partially blocked receptive fields. Nervous centers 8. The simplification – total reaction is higher than the arithmetic sum of reaction at the isolated irritation 9. Transformation of a rhythm and power of incentive 10. After-effect (reaction continuation after the irritation termination) - short-term (trace depolarization) - the long – circulation of impulses on the closed neural chains.
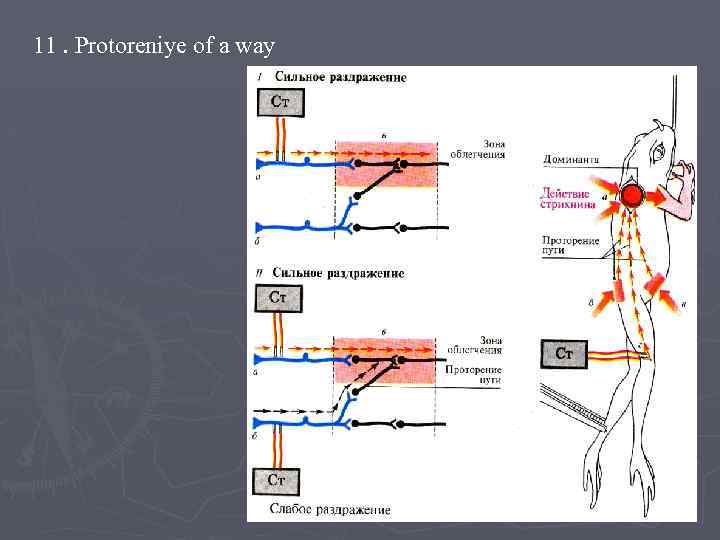
11. Protoreniye of a way

12. Low lability 13. High sensitivity to a hypoxia 14. Selective sensitivity to pharmacological substances 15. Tone (background activity) 16. Plasticity

COORDINATION ACTIVITY. Coordination – interaction of neurons in NTs providing coordinated integrated activity of all centers as a result of which there is a proper reflex response.

The integrated, coordinate function is provided by the following regularities: Irradiation Concentration Induction – targeting of opposite process. Types of an induction: the simultaneous the consecutive the positive the negative
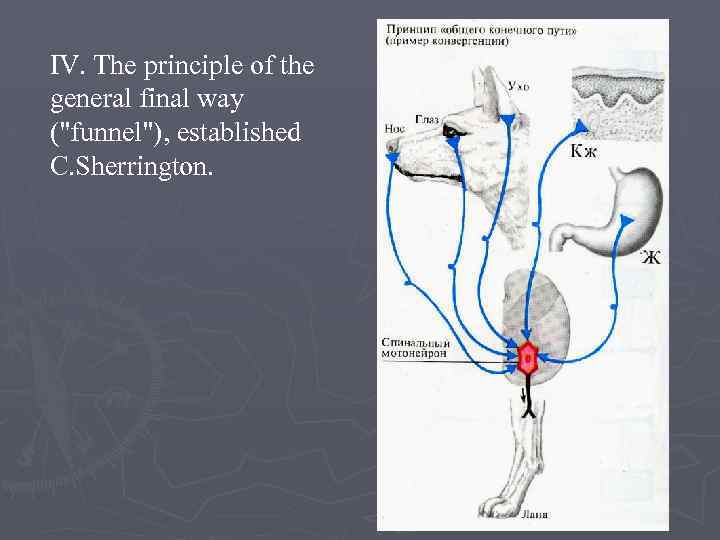
IV. The principle of the general final way ("funnel"), established C. Sherrington.
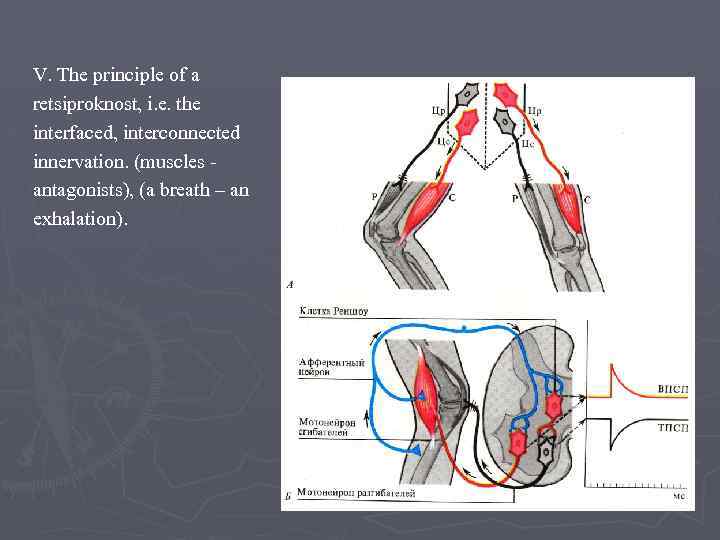
V. The principle of a retsiproknost, i. e. the interfaced, interconnected innervation. (muscles antagonists), (a breath – an exhalation).

VI. Principle of feedback VII. Dominant – I opened A. A. Ukhtomsky. The dominant – temporarily dominating center of excitement, is characterized by the following properties: ability to summarize excitement hypererethism firmness of excitement inertness of excitement the interfaced braking of other centers ability to attract the impulses coming to other centers.
5- общ ЦНС. Нервные центры.ppt