da4a18b2e9ec4d10377b8564ecbee0c2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Subdural Empyema complicating Sinusitis in Immunocompetent adults Authors Institutions

Introduction w Bacterial sinusitis is a common infection in adults w Posterior invasion through sinus walls causes subdural empyema w Prompt neurosurgery and antibiotics are needed for successful treatment w We report two causes of subdural empyema in patients who had sinusitis as underlying cause

Case One w 30 year old male was admitted via ER w Two weeks h/o head ache w Two days h/o intermittent fever, vomiting, facial twitching and tenderness over frontal region of head

Background w Was seen in ER 3 days prior with headache and fever w Febrile, no nuchal rigidity w Had CT head – Pansinusitis w Discharged with amoxicillin-clavulunate w Did not take antibiotics for two days due to lack of insurance
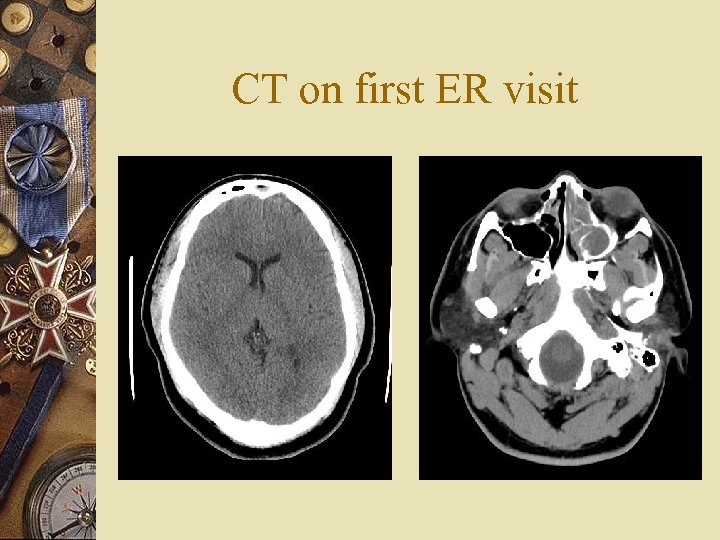
CT on first ER visit

Other History w PMH: Migraine, remote h/o seizure w PSH: None w Social: Non-smoker, no alcohol use w Family: None significant w Medications: None

Physical Exam w Temp 37. 9 o C, BP 90/49, PR 52 w Drowsy, symmetrical facial twitching and nose wrinkling w Tenderness over frontal sinuses w Mild neck stiffness
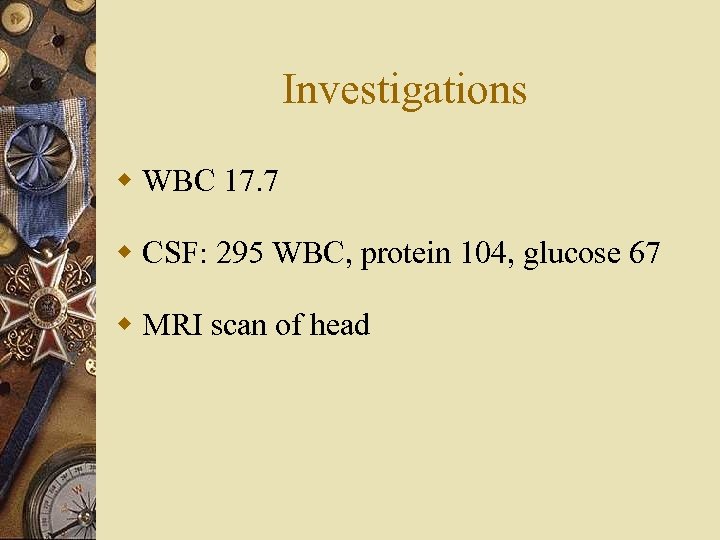
Investigations w WBC 17. 7 w CSF: 295 WBC, protein 104, glucose 67 w MRI scan of head
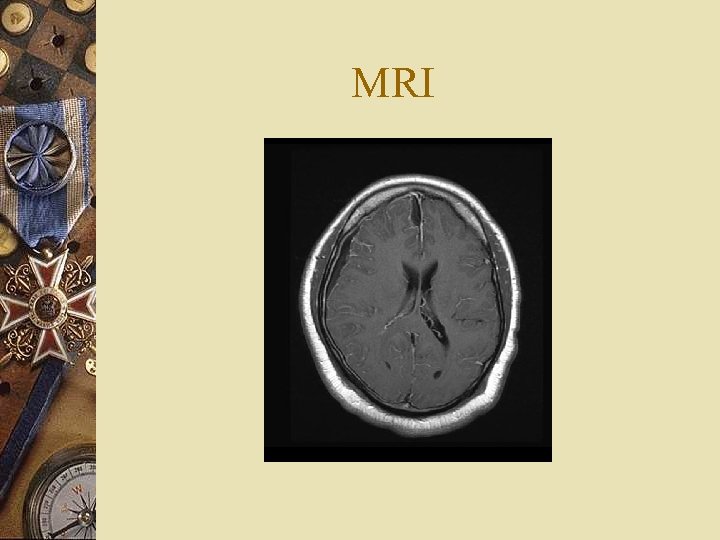
MRI

Management w Commenced on cefotaxime, vancomycin, metronidazole w Debridement of subdural empyema w Cultures grew viridans Streptococcus w Developed seizures and hemiplegia - repeat debridement with craniectomy w Treated with 6 weeks ABX, with resolution of hemiplegia

Case Two w 55 year old male w Does not routinely seek medical care w Feeling generally unwell for few weeks w Took few doses of Levofloxacin given by physician friend w Was having intermittent headache, fever and increasingly lethargic w Seen previous day in urgent care, advised to follow with PCP

History continued w Came again with lethargy for 16 hrs, f/b decreased consciousness w PMH : Asthma w PSH: Nasal surgery and knee surgery w Social: Non smoker, no alcohol use w Medications: Advair and Fluticasone

Physical Examination w Temperature 36. 8 o C, PR 91, BP 125/71 w Did not follow commands, obtunded w Mild menigismus w No grimace on percussion over sinuses w Moderate gingivitis

Investigations w Na 127 w WBC 20. 9 w CT brain
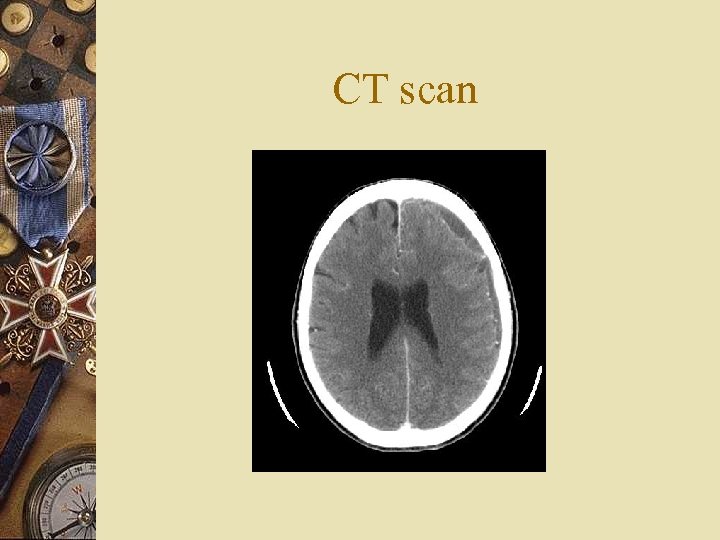
CT scan

Management w Commenced on cefotaxime, vancomycin and metronidazole w Emergent fronto-parietal subdural evacuation w Functional endoscopic sinus surgery w Culture of the subdural empyema grew Streptococcus intermedius w Good recovery and was transferred to rehabilitation

Conclusion §Subdural empyema is uncommon but potentially fatal complication of sinusitis. §Suspect subdural empyema in patients with sinusitis plus any of the following: -altered mental status -nuchal rigidity -seizures -focal neurological changes. §MRI is more sensitive than CT for diagnosis.
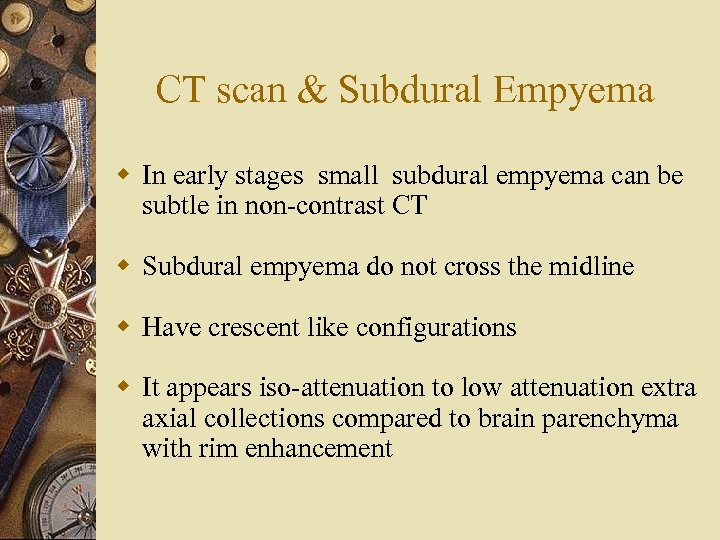
CT scan & Subdural Empyema w In early stages small subdural empyema can be subtle in non-contrast CT w Subdural empyema do not cross the midline w Have crescent like configurations w It appears iso-attenuation to low attenuation extra axial collections compared to brain parenchyma with rim enhancement
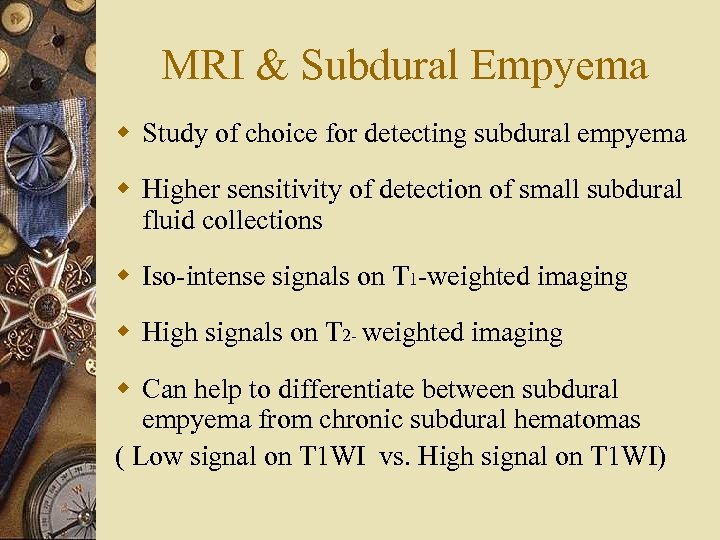
MRI & Subdural Empyema w Study of choice for detecting subdural empyema w Higher sensitivity of detection of small subdural fluid collections w Iso-intense signals on T 1 -weighted imaging w High signals on T 2 - weighted imaging w Can help to differentiate between subdural empyema from chronic subdural hematomas ( Low signal on T 1 WI vs. High signal on T 1 WI)

References Ziai WC, Lewin JJ 3 rd. Update in the diagnosis and management of central nervous system infections. Neurol Clin. 2008 May; 2(2): 42768, viii. Foerster BR, Thurnher MM, Malani PN et al. Intracranial infections: clinical and imaging characteristics. Acta Radiol. 2007 Oct; 48(8): 875 -93.

Thank You
da4a18b2e9ec4d10377b8564ecbee0c2.ppt