5fe665c1f2dd06ff72b476c8f3b8610b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43

 Studying Population • Demography is the statistical study of human populations • Demography is used to predict future population trends to determine where possible population increases/decreases will occur
Studying Population • Demography is the statistical study of human populations • Demography is used to predict future population trends to determine where possible population increases/decreases will occur
 Population Density • Average number of people living in a region, which is expressed in # of people/square mile. • Populations vary greatly throughout the world – Landforms – Climates – Water availability
Population Density • Average number of people living in a region, which is expressed in # of people/square mile. • Populations vary greatly throughout the world – Landforms – Climates – Water availability
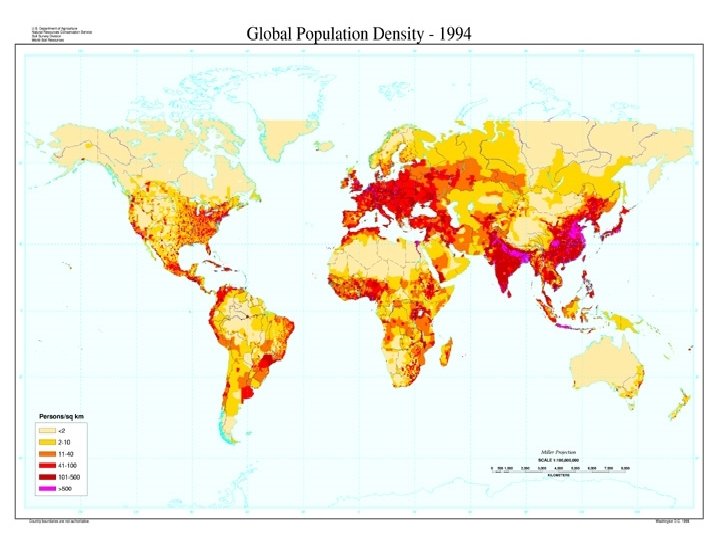
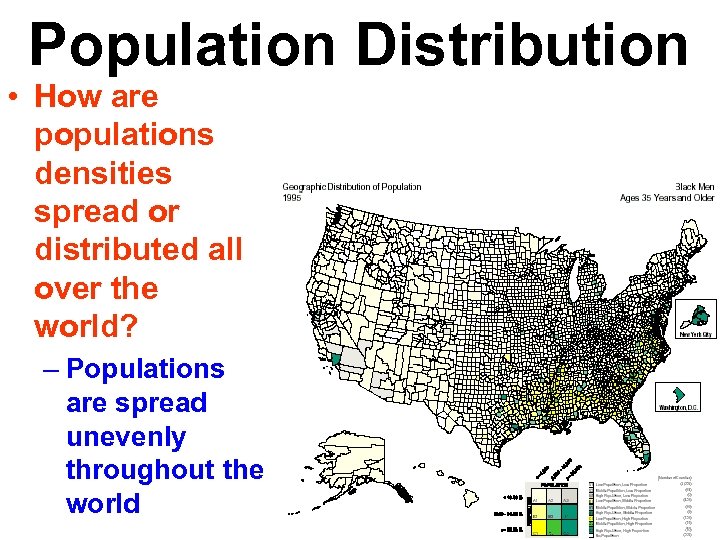 Population Distribution • How are populations densities spread or distributed all over the world? – Populations are spread unevenly throughout the world
Population Distribution • How are populations densities spread or distributed all over the world? – Populations are spread unevenly throughout the world
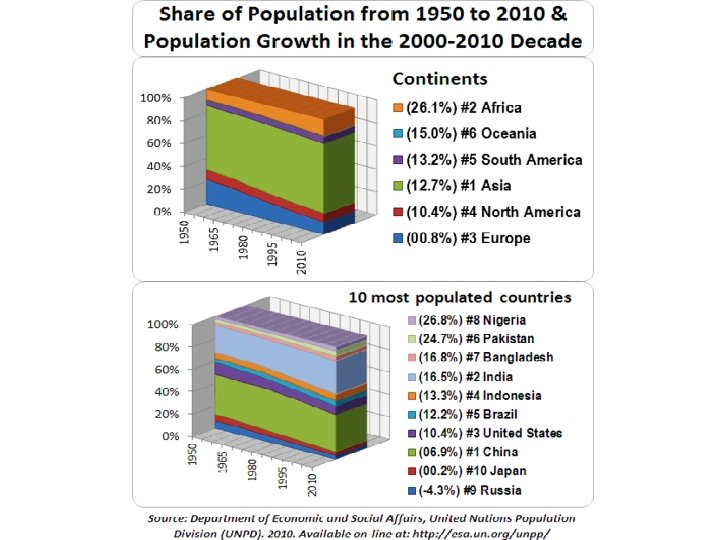
 Where do most people live? • 90% of the world population lives in the Northern Hemisphere – between 20 and 60 degrees North latitude – In low lands and areas with fertile soil • Example- river valleys
Where do most people live? • 90% of the world population lives in the Northern Hemisphere – between 20 and 60 degrees North latitude – In low lands and areas with fertile soil • Example- river valleys
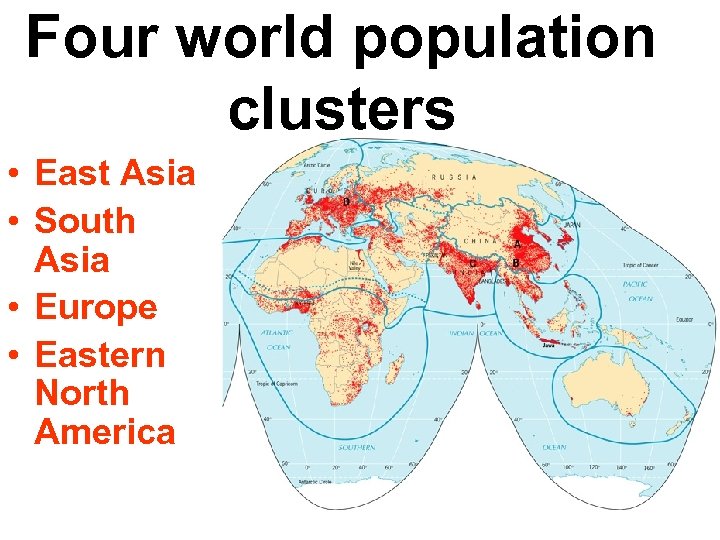 Four world population clusters • East Asia • South Asia • Europe • Eastern North America
Four world population clusters • East Asia • South Asia • Europe • Eastern North America
 Population Changes • 3 factors determine population changes – 1. Birth Rate – 2. Death Rate – 3. Migration
Population Changes • 3 factors determine population changes – 1. Birth Rate – 2. Death Rate – 3. Migration
 Birth Rate • Number of live birth’s each year for every 1000 people in a region
Birth Rate • Number of live birth’s each year for every 1000 people in a region
 Death Rate • Number of death’s each year for every 1000 people in a region
Death Rate • Number of death’s each year for every 1000 people in a region
 Migration • Process of moving from one place to live in another – Emigrants – Immigrants – Push and Pull Factors – Refugees
Migration • Process of moving from one place to live in another – Emigrants – Immigrants – Push and Pull Factors – Refugees
 Natural Increase • Population changes based solely on the birth and death rates
Natural Increase • Population changes based solely on the birth and death rates
 • Existing number of people is too large to be supported by available resources • Currently 6. 9 billion people on Earth – Population growing by 80 million each year
• Existing number of people is too large to be supported by available resources • Currently 6. 9 billion people on Earth – Population growing by 80 million each year
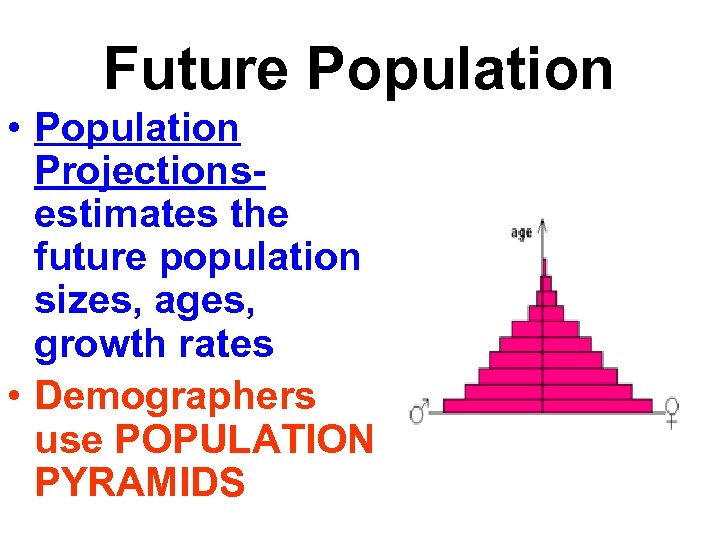 Future Population • Population Projectionsestimates the future population sizes, ages, growth rates • Demographers use POPULATION PYRAMIDS
Future Population • Population Projectionsestimates the future population sizes, ages, growth rates • Demographers use POPULATION PYRAMIDS
 Culture- All the features of a peoples way of life
Culture- All the features of a peoples way of life
 • Culture Trait- activities and behaviors used by people • Culture Region- an area where people have similar traits and beliefs • Ethnic Group- human population which shares ancestry and culture traits
• Culture Trait- activities and behaviors used by people • Culture Region- an area where people have similar traits and beliefs • Ethnic Group- human population which shares ancestry and culture traits
 3 causes for Culture Change • 1. Migration- movement of people and goods/services • 2. War- relocation of people who take their culture traits with them. • 3. Trade- people send a pieces of their culture to other places which affect that culture.
3 causes for Culture Change • 1. Migration- movement of people and goods/services • 2. War- relocation of people who take their culture traits with them. • 3. Trade- people send a pieces of their culture to other places which affect that culture.
 • Acculturation- Individual or group adopts some traits to that of another culture (language, religion) • Innovation- new ideas which are accepted by culture (baggy pants, Tattoos) • Diffusion- ideas or innovations spread from one person to another and are adopted. (music, fashion)
• Acculturation- Individual or group adopts some traits to that of another culture (language, religion) • Innovation- new ideas which are accepted by culture (baggy pants, Tattoos) • Diffusion- ideas or innovations spread from one person to another and are adopted. (music, fashion)
 • Globalization- the process in which connections around the world increase and cultures merge • Traditionalism- cultures which follow longtime historical practices or ways of life and who sometimes oppose many modern innovations.
• Globalization- the process in which connections around the world increase and cultures merge • Traditionalism- cultures which follow longtime historical practices or ways of life and who sometimes oppose many modern innovations.
 World Language and World Religion
World Language and World Religion
 • Dialect- regional variety of language • Major vs. Minor Languagealmost every country in the world has a major and a minor language.
• Dialect- regional variety of language • Major vs. Minor Languagealmost every country in the world has a major and a minor language.
 Religion • Ethnic Religion- Focuses on one ethnic group and generally spreads into culture • Animist Religion- People who believe in the presence of the spirits and the forces of nature • Polytheism- belief in many gods • Monotheism- belief in one god • Henotheism- belief in one god without denying the existence of other gods.
Religion • Ethnic Religion- Focuses on one ethnic group and generally spreads into culture • Animist Religion- People who believe in the presence of the spirits and the forces of nature • Polytheism- belief in many gods • Monotheism- belief in one god • Henotheism- belief in one god without denying the existence of other gods.
 Examples of Religion • Ethnic Religion- Jews/Muslims • Animists- Voodoo • Polytheism- Hinduism • Monotheism- Christianity
Examples of Religion • Ethnic Religion- Jews/Muslims • Animists- Voodoo • Polytheism- Hinduism • Monotheism- Christianity
 • Missionariespeople who help spread religion around the world.
• Missionariespeople who help spread religion around the world.
 Types of Government • Autocracy- government run by a single person who has unlimited powers (North Korea) – Totalitarianism- Absolute power – Absolute Monarchy- King or queen with absolute power • Constitutional Monarchy- King or queen who rules along with elected officials and both must abide to a constitution (United Kingdom)
Types of Government • Autocracy- government run by a single person who has unlimited powers (North Korea) – Totalitarianism- Absolute power – Absolute Monarchy- King or queen with absolute power • Constitutional Monarchy- King or queen who rules along with elected officials and both must abide to a constitution (United Kingdom)
 • Oligarchy- Government run by a few powerful people (South Africa) • Communism- Economic and political system in which the government controls and owns all the means of production. (China) • Socialism- Free enterprise system of economy in which the government owns and controls some of the means of production. (Canada)
• Oligarchy- Government run by a few powerful people (South Africa) • Communism- Economic and political system in which the government controls and owns all the means of production. (China) • Socialism- Free enterprise system of economy in which the government owns and controls some of the means of production. (Canada)
 • Democracy- Government run by the people, either directly or through elected officials or representatives. (USA) – Direct Democracy- citizens participated directly in the decision making process – Representative Democracy- voters elect officials to make decisions in their interest – Republic- Political order in which the power lies with the citizens who vote representatives to be responsible for some of the decision making process (USA)
• Democracy- Government run by the people, either directly or through elected officials or representatives. (USA) – Direct Democracy- citizens participated directly in the decision making process – Representative Democracy- voters elect officials to make decisions in their interest – Republic- Political order in which the power lies with the citizens who vote representatives to be responsible for some of the decision making process (USA)
 Types of Economies • Market Economy- Economy which the people freely choose what to buy and sell – Free Enterprise- System which lets competition among businesses determine the price of a product – Capitalism- business, industry, and resources are privately owned
Types of Economies • Market Economy- Economy which the people freely choose what to buy and sell – Free Enterprise- System which lets competition among businesses determine the price of a product – Capitalism- business, industry, and resources are privately owned
 • Command Economy- The government decides what to produce, where to make it, and what price to sell it at • Traditional or Subsistence Economy- People who make goods for themselves and sell whatever they have left over
• Command Economy- The government decides what to produce, where to make it, and what price to sell it at • Traditional or Subsistence Economy- People who make goods for themselves and sell whatever they have left over
 4 Types of Economic Activities • 1. Primary- economic activity that uses natural resources directly (farming, fishing, mining) • 2. Secondary- Use of raw materials to produce or manufacture something new (wheat to flour, lumber to plywood) • 3. Tertiary- Provides a service to people or businesses (teacher, dry cleaner, grocer) • 4. Quaternary- requires workers to have a specialized skill or training (doctor, scientist, engineer)
4 Types of Economic Activities • 1. Primary- economic activity that uses natural resources directly (farming, fishing, mining) • 2. Secondary- Use of raw materials to produce or manufacture something new (wheat to flour, lumber to plywood) • 3. Tertiary- Provides a service to people or businesses (teacher, dry cleaner, grocer) • 4. Quaternary- requires workers to have a specialized skill or training (doctor, scientist, engineer)
 How to measure the development of a country Gross Domestic Product- GDP- Total value of goods and services which were built within a country per year. Gross National Product- GNP- Total value of goods and services which a country produces either foreign or domestic per year.
How to measure the development of a country Gross Domestic Product- GDP- Total value of goods and services which were built within a country per year. Gross National Product- GNP- Total value of goods and services which a country produces either foreign or domestic per year.
 • Industrialization- process by which manufacturing based on machine power becomes widespread in an area • Literacy Rate- the percentage of people who can read and write in a country (over the age of 15) • Standard of Living- per capita, education levels, food consumption, food production, population size, and population prediction.
• Industrialization- process by which manufacturing based on machine power becomes widespread in an area • Literacy Rate- the percentage of people who can read and write in a country (over the age of 15) • Standard of Living- per capita, education levels, food consumption, food production, population size, and population prediction.
 More Developed vs. Less Developed
More Developed vs. Less Developed
 • More Developed – richest countries in the world – high levels of industrialization – high standard of livings – High GDP and GNP – Less than 25% of the worlds populations live in these countries. – They have a lot of infrastructure (all systems of transportation including roads, ports, highways. . . )
• More Developed – richest countries in the world – high levels of industrialization – high standard of livings – High GDP and GNP – Less than 25% of the worlds populations live in these countries. – They have a lot of infrastructure (all systems of transportation including roads, ports, highways. . . )

 • Less Developed – World’s poorest countries – Low standard of living – Low literacy rates, GNP, GDP – Majority of world populations lives here – High government corruption, birth rates, death rates, and infant mortality rates.
• Less Developed – World’s poorest countries – Low standard of living – Low literacy rates, GNP, GDP – Majority of world populations lives here – High government corruption, birth rates, death rates, and infant mortality rates.

 • Mid Income Countries – Features of both developed and developing countries. – Usually have modern cities or urban areas but poor rural or country areas. • Mexico • Thailand • Brazil • Malaysia
• Mid Income Countries – Features of both developed and developing countries. – Usually have modern cities or urban areas but poor rural or country areas. • Mexico • Thailand • Brazil • Malaysia
 3 Types of Boundaries • 1. Natural Boundary- follow a feature of the landscape • 2. Cultural Boundary- based on a cultural trait • 3. Geometric Boundary- usually follow a straight line with regard to the environment
3 Types of Boundaries • 1. Natural Boundary- follow a feature of the landscape • 2. Cultural Boundary- based on a cultural trait • 3. Geometric Boundary- usually follow a straight line with regard to the environment

 • Domestication- taming of animals • Urbanization- people moving from rural areas to live in urban areas • Shifting Cultivation- farmers clear trees for planting fields which are farmed for a few years until the soil is depleted of its nutrients and then it is abandoned. • Subsistence Agriculture- growing enough for your needs • World Cities- most important centers of economic power and wealth (NYC, Tokyo, London)
• Domestication- taming of animals • Urbanization- people moving from rural areas to live in urban areas • Shifting Cultivation- farmers clear trees for planting fields which are farmed for a few years until the soil is depleted of its nutrients and then it is abandoned. • Subsistence Agriculture- growing enough for your needs • World Cities- most important centers of economic power and wealth (NYC, Tokyo, London)
 • Nationalism- Feelings of pride and loyalty for ones own country • Terrorism- the use of fear and violence as a political force • United Nations- representatives from almost every country discuss international issues (goal- prevent war) • World Trade Organization- works to make trade between countries fair and organized.
• Nationalism- Feelings of pride and loyalty for ones own country • Terrorism- the use of fear and violence as a political force • United Nations- representatives from almost every country discuss international issues (goal- prevent war) • World Trade Organization- works to make trade between countries fair and organized.


