0b75c0f2477246ca4835f677476e5e3b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Study on Development and Application of MAS for Impact Analysis of Large-scale Shopping Center Development ZJ. Shen, M. Kawakami, P. Chen Kanazawa University, Japan 2006. DDSS
Study on Development and Application of MAS for Impact Analysis of Large-scale Shopping Center Development ZJ. Shen, M. Kawakami, P. Chen Kanazawa University, Japan 2006. DDSS
 Contents Introduction Location Regulations for B-shops Framework of Shopsim-MAS Policy Scenarios Evaluation Discussion and Further Research
Contents Introduction Location Regulations for B-shops Framework of Shopsim-MAS Policy Scenarios Evaluation Discussion and Further Research
 Background The commercial environment of many local cities in Japan is experiencing decline in their centre areas. Local governments have developed all kinds of city center generation policies to constrain this trend and revitalize the central city commercial environment. It is difficult to evaluate the potential impact of current policies on the city future due to the uncertainty inherent in urban system. MAS simulation is reconized as a tool to visualize impact of planning policies for presenting the complexity of the urban system.
Background The commercial environment of many local cities in Japan is experiencing decline in their centre areas. Local governments have developed all kinds of city center generation policies to constrain this trend and revitalize the central city commercial environment. It is difficult to evaluate the potential impact of current policies on the city future due to the uncertainty inherent in urban system. MAS simulation is reconized as a tool to visualize impact of planning policies for presenting the complexity of the urban system.
 Introduction Picture of center area in metropolitan prosperous commercial street in Osaka
Introduction Picture of center area in metropolitan prosperous commercial street in Osaka
 Introduction Pictures of center area in local city Decline of commercial environment
Introduction Pictures of center area in local city Decline of commercial environment
 Introduction Pictures of large-shopping mall In suburban area
Introduction Pictures of large-shopping mall In suburban area
 Contents Introduction Location Regulations for B-shops Framework of Shopsim-MAS Policy Scenarios Evaluation Discussion and Further Research
Contents Introduction Location Regulations for B-shops Framework of Shopsim-MAS Policy Scenarios Evaluation Discussion and Further Research
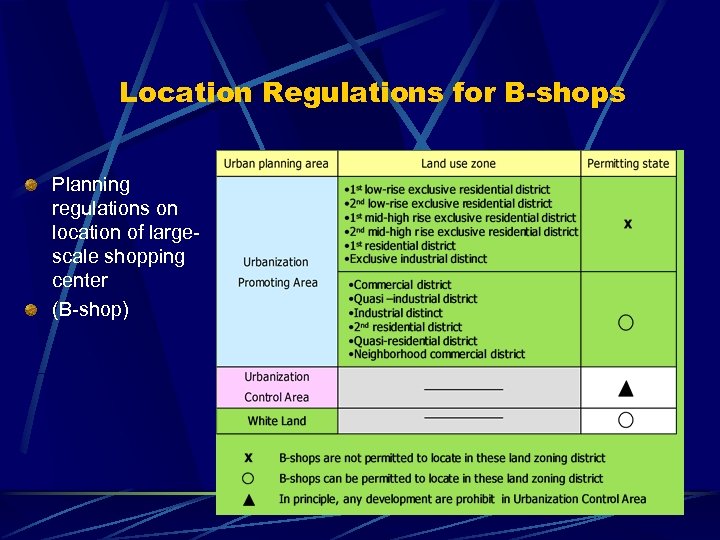 Location Regulations for B-shops Planning regulations on location of largescale shopping center (B-shop)
Location Regulations for B-shops Planning regulations on location of largescale shopping center (B-shop)
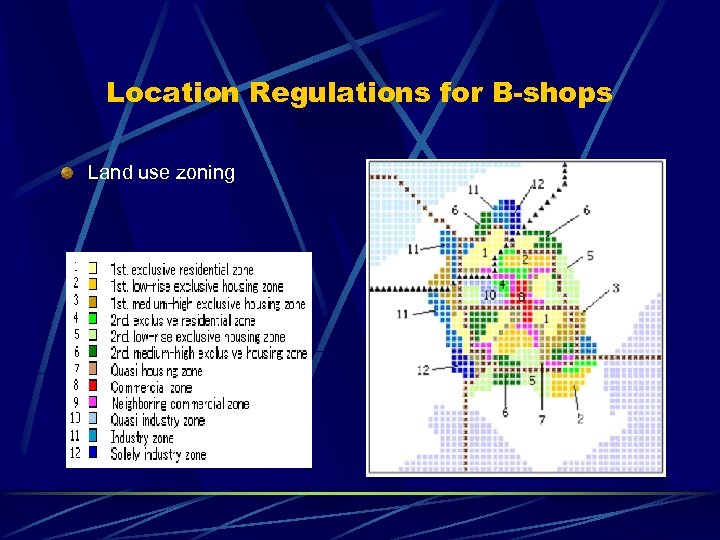 Location Regulations for B-shops Land use zoning
Location Regulations for B-shops Land use zoning
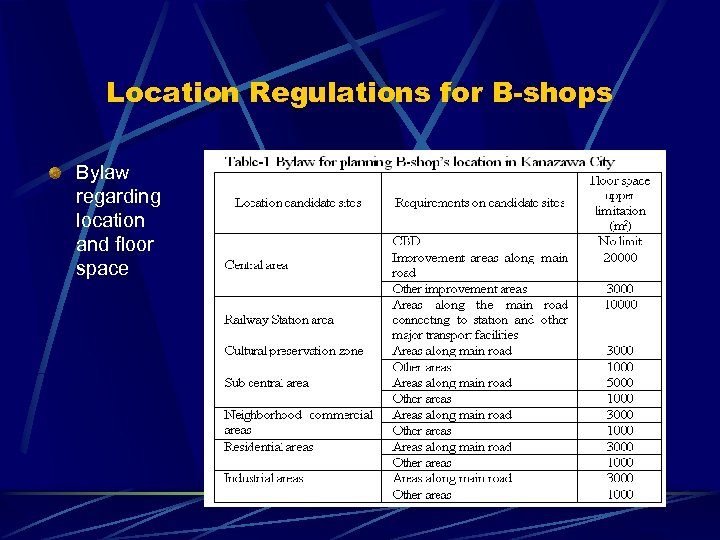 Location Regulations for B-shops Bylaw regarding location and floor space
Location Regulations for B-shops Bylaw regarding location and floor space
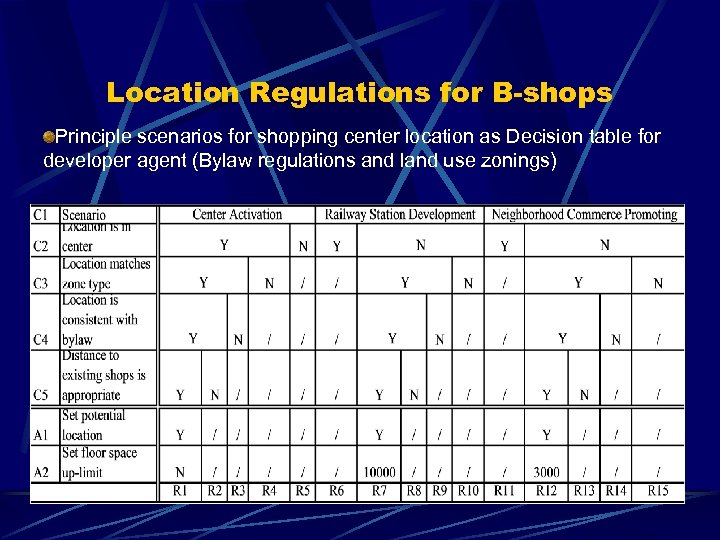 Location Regulations for B-shops Principle scenarios for shopping center location as Decision table for developer agent (Bylaw regulations and land use zonings)
Location Regulations for B-shops Principle scenarios for shopping center location as Decision table for developer agent (Bylaw regulations and land use zonings)
 Location Regulations for B-shops The location alternatives are limited in the possible areas according to land use zonings regulation and bylaw regarding large-scale shopping mall. These location alternatives reflect the different scenarios of commercial development.
Location Regulations for B-shops The location alternatives are limited in the possible areas according to land use zonings regulation and bylaw regarding large-scale shopping mall. These location alternatives reflect the different scenarios of commercial development.
 Contents Introduction Location Regulations for B-shops Framework of Shopsim-MAS Policy Scenarios Evaluation Discussion and Further Research
Contents Introduction Location Regulations for B-shops Framework of Shopsim-MAS Policy Scenarios Evaluation Discussion and Further Research
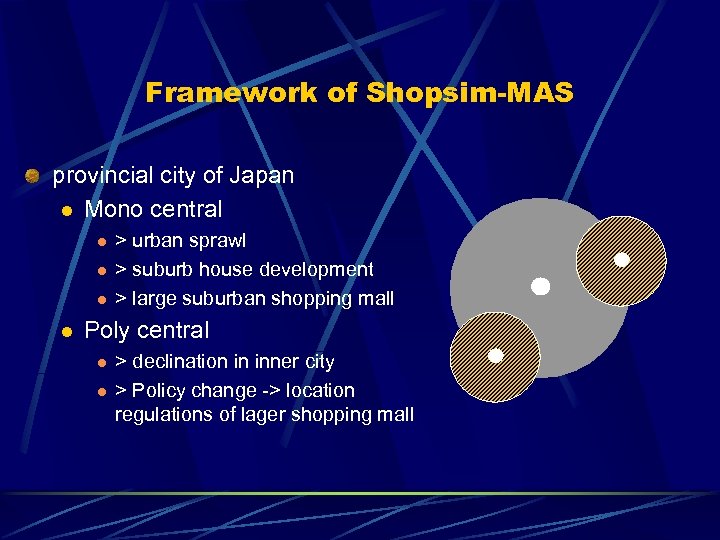 Framework of Shopsim-MAS provincial city of Japan l Mono central l l > urban sprawl > suburb house development > large suburban shopping mall Poly central l l > declination in inner city > Policy change -> location regulations of lager shopping mall
Framework of Shopsim-MAS provincial city of Japan l Mono central l l > urban sprawl > suburb house development > large suburban shopping mall Poly central l l > declination in inner city > Policy change -> location regulations of lager shopping mall
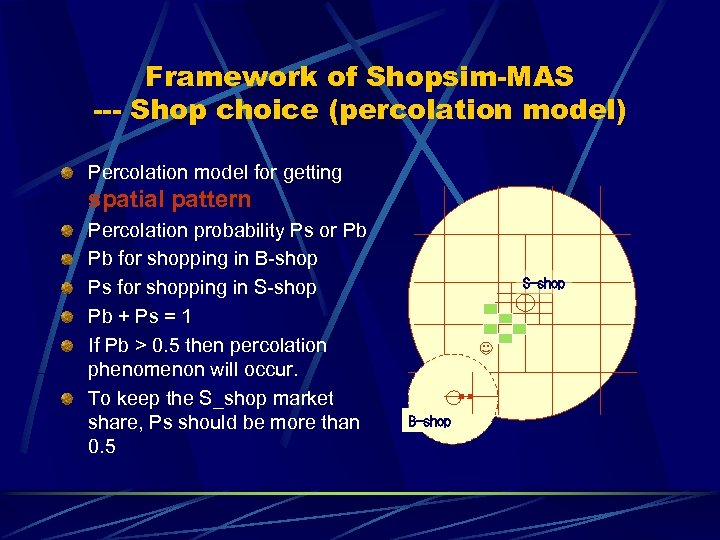 Framework of Shopsim-MAS --- Shop choice (percolation model) Percolation model for getting spatial pattern Percolation probability Ps or Pb Pb for shopping in B-shop Ps for shopping in S-shop Pb + Ps = 1 If Pb > 0. 5 then percolation phenomenon will occur. To keep the S_shop market share, Ps should be more than 0. 5 S-shop B-shop
Framework of Shopsim-MAS --- Shop choice (percolation model) Percolation model for getting spatial pattern Percolation probability Ps or Pb Pb for shopping in B-shop Ps for shopping in S-shop Pb + Ps = 1 If Pb > 0. 5 then percolation phenomenon will occur. To keep the S_shop market share, Ps should be more than 0. 5 S-shop B-shop
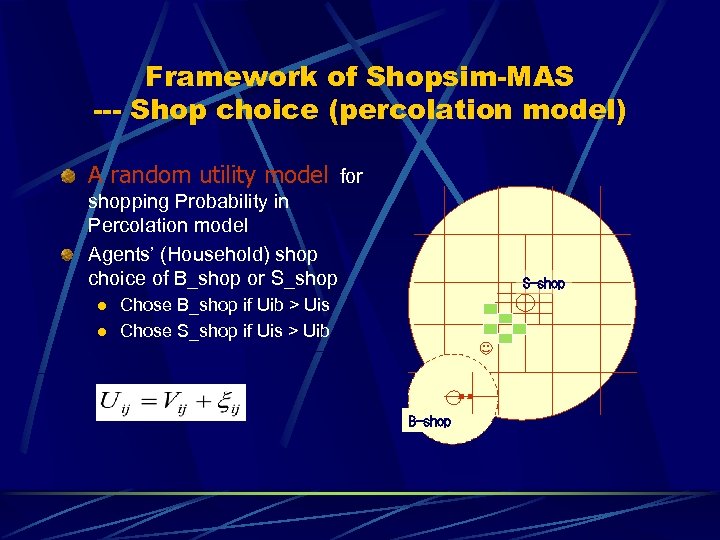 Framework of Shopsim-MAS --- Shop choice (percolation model) A random utility model for shopping Probability in Percolation model Agents’ (Household) shop choice of B_shop or S_shop l l S-shop Chose B_shop if Uib > Uis Chose S_shop if Uis > Uib B-shop
Framework of Shopsim-MAS --- Shop choice (percolation model) A random utility model for shopping Probability in Percolation model Agents’ (Household) shop choice of B_shop or S_shop l l S-shop Chose B_shop if Uib > Uis Chose S_shop if Uis > Uib B-shop
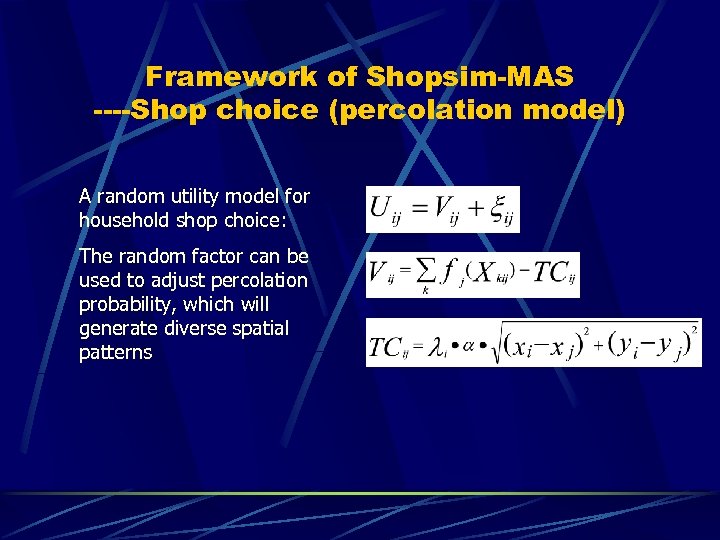 Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----Shop choice (percolation model) A random utility model for household shop choice: The random factor can be used to adjust percolation probability, which will generate diverse spatial patterns
Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----Shop choice (percolation model) A random utility model for household shop choice: The random factor can be used to adjust percolation probability, which will generate diverse spatial patterns
 Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----shop choice model According to local regulations of large scale shopping mall, influence factors of percolation probability should be set as location (set as decision table )and floor area. Xkij is the kth attribute describing store j attracting household i. , l price: X 1 j =Pj and l floor space: X 2 j =Sj (Price Pj is added by authors) l distance: Cij is a measure of the disutility of travel between site of household i and site of shop j. (Cij is added by authors) Shopping choice in simulation based on utility is deterministic process, as random factor to control individual choice.
Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----shop choice model According to local regulations of large scale shopping mall, influence factors of percolation probability should be set as location (set as decision table )and floor area. Xkij is the kth attribute describing store j attracting household i. , l price: X 1 j =Pj and l floor space: X 2 j =Sj (Price Pj is added by authors) l distance: Cij is a measure of the disutility of travel between site of household i and site of shop j. (Cij is added by authors) Shopping choice in simulation based on utility is deterministic process, as random factor to control individual choice.
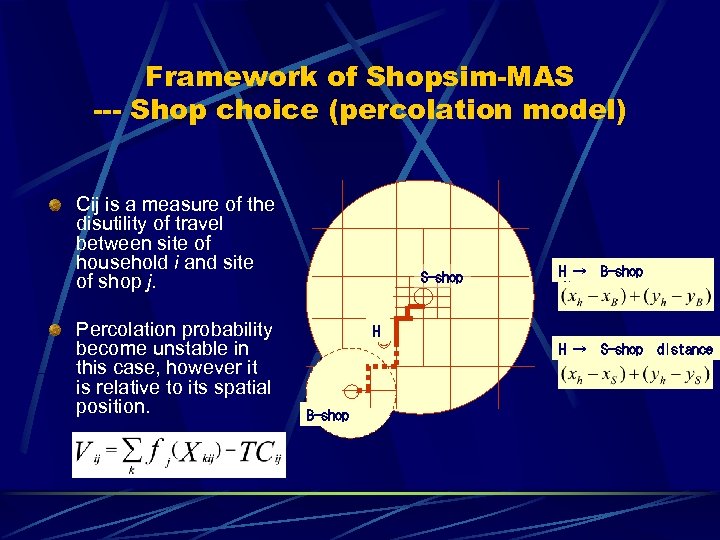 Framework of Shopsim-MAS --- Shop choice (percolation model) Cij is a measure of the disutility of travel between site of household i and site of shop j. Percolation probability become unstable in this case, however it is relative to its spatial position. S-shop H → B-shop distance H H → S-shop distance B-shop
Framework of Shopsim-MAS --- Shop choice (percolation model) Cij is a measure of the disutility of travel between site of household i and site of shop j. Percolation probability become unstable in this case, however it is relative to its spatial position. S-shop H → B-shop distance H H → S-shop distance B-shop
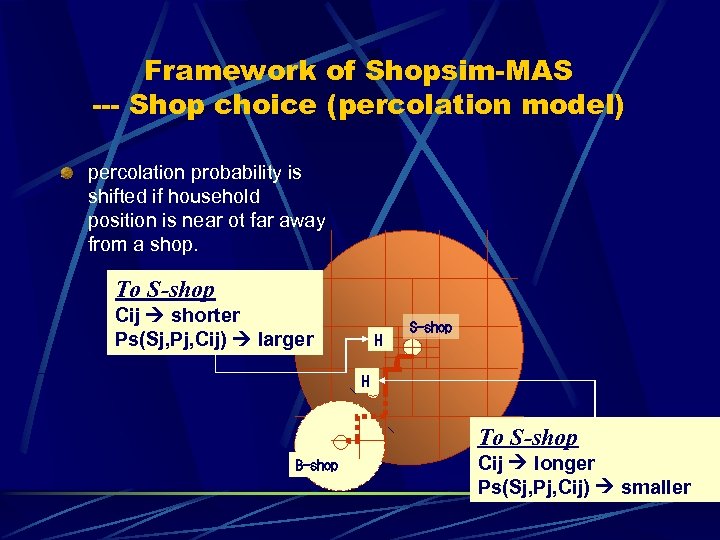 Framework of Shopsim-MAS --- Shop choice (percolation model) percolation probability is shifted if household position is near ot far away from a shop. To S-shop Cij shorter Ps(Sj, Pj, Cij) larger H S-shop H To S-shop B-shop Cij longer Ps(Sj, Pj, Cij) smaller
Framework of Shopsim-MAS --- Shop choice (percolation model) percolation probability is shifted if household position is near ot far away from a shop. To S-shop Cij shorter Ps(Sj, Pj, Cij) larger H S-shop H To S-shop B-shop Cij longer Ps(Sj, Pj, Cij) smaller
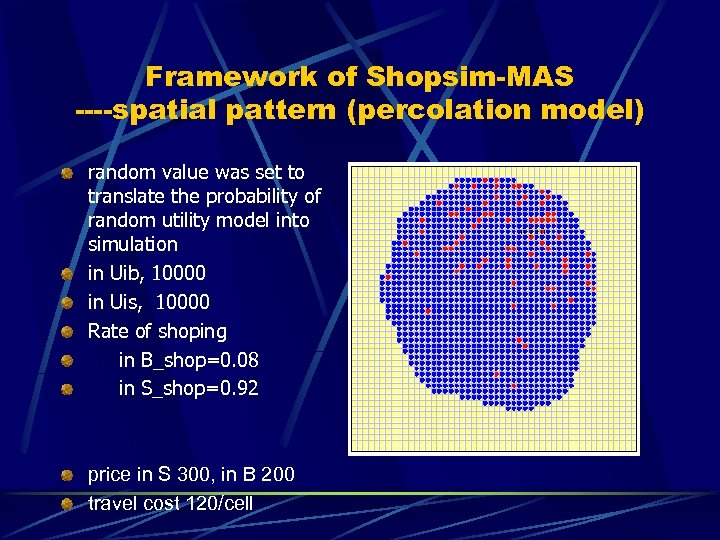 Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----spatial pattern (percolation model) random value was set to translate the probability of random utility model into simulation in Uib, 10000 in Uis, 10000 Rate of shoping in B_shop=0. 08 in S_shop=0. 92 price in S 300, in B 200 travel cost 120/cell
Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----spatial pattern (percolation model) random value was set to translate the probability of random utility model into simulation in Uib, 10000 in Uis, 10000 Rate of shoping in B_shop=0. 08 in S_shop=0. 92 price in S 300, in B 200 travel cost 120/cell
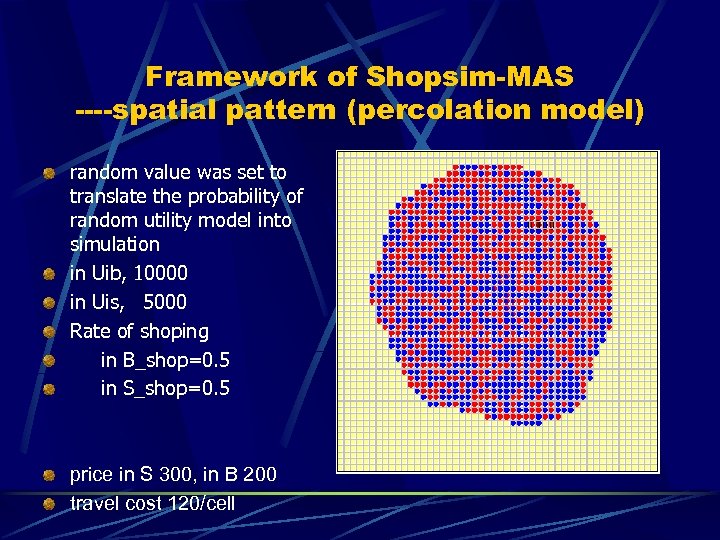 Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----spatial pattern (percolation model) random value was set to translate the probability of random utility model into simulation in Uib, 10000 in Uis, 5000 Rate of shoping in B_shop=0. 5 in S_shop=0. 5 price in S 300, in B 200 travel cost 120/cell
Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----spatial pattern (percolation model) random value was set to translate the probability of random utility model into simulation in Uib, 10000 in Uis, 5000 Rate of shoping in B_shop=0. 5 in S_shop=0. 5 price in S 300, in B 200 travel cost 120/cell
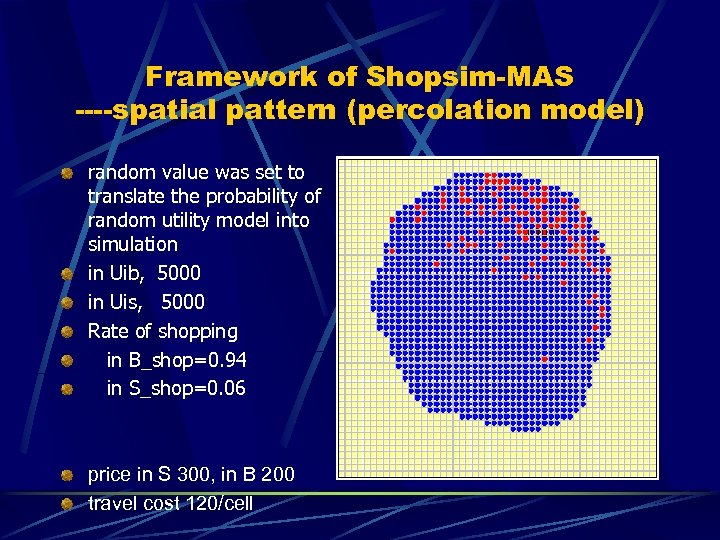 Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----spatial pattern (percolation model) random value was set to translate the probability of random utility model into simulation in Uib, 5000 in Uis, 5000 Rate of shopping in B_shop=0. 94 in S_shop=0. 06 price in S 300, in B 200 travel cost 120/cell
Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----spatial pattern (percolation model) random value was set to translate the probability of random utility model into simulation in Uib, 5000 in Uis, 5000 Rate of shopping in B_shop=0. 94 in S_shop=0. 06 price in S 300, in B 200 travel cost 120/cell
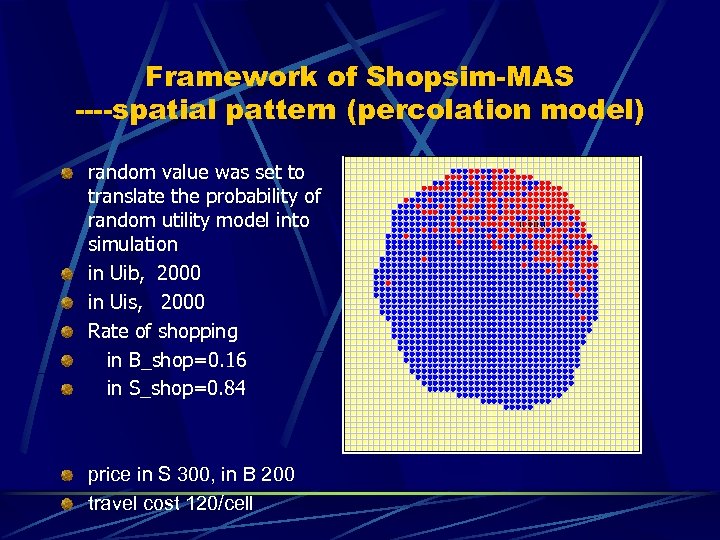 Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----spatial pattern (percolation model) random value was set to translate the probability of random utility model into simulation in Uib, 2000 in Uis, 2000 Rate of shopping in B_shop=0. 16 in S_shop=0. 84 price in S 300, in B 200 travel cost 120/cell
Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----spatial pattern (percolation model) random value was set to translate the probability of random utility model into simulation in Uib, 2000 in Uis, 2000 Rate of shopping in B_shop=0. 16 in S_shop=0. 84 price in S 300, in B 200 travel cost 120/cell
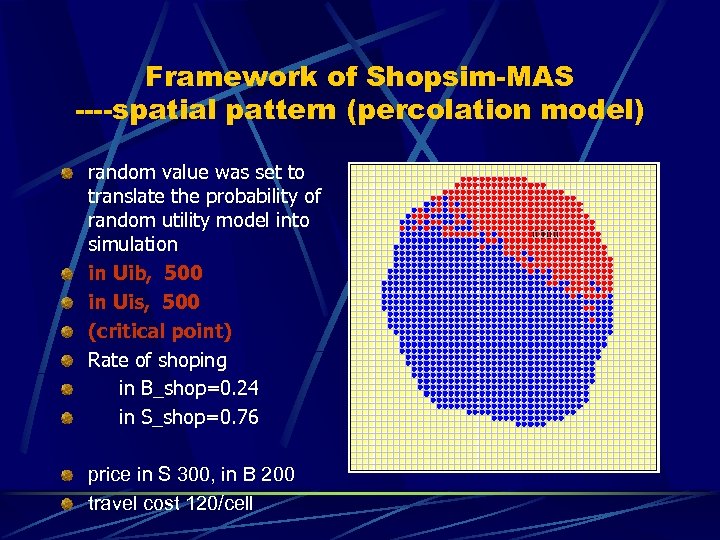 Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----spatial pattern (percolation model) random value was set to translate the probability of random utility model into simulation in Uib, 500 in Uis, 500 (critical point) Rate of shoping in B_shop=0. 24 in S_shop=0. 76 price in S 300, in B 200 travel cost 120/cell
Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----spatial pattern (percolation model) random value was set to translate the probability of random utility model into simulation in Uib, 500 in Uis, 500 (critical point) Rate of shoping in B_shop=0. 24 in S_shop=0. 76 price in S 300, in B 200 travel cost 120/cell
 Framework of Shopsim-MAS ---shop choice model Therefore, percolation Probability of B_shop or S_shop is decided by Pj, Sj and Cij. For translating probability of random utility model into agent’s individual behavior, a random variable is defined. If percolation probability changed gradually, the spatial pattern of percolation will be changed gradually. This phenomenon can be used in the market share simulation using MAS. However, how about fitness of Individual shopping choice based on ramdam utility and percolation probability in simulation is still a further study.
Framework of Shopsim-MAS ---shop choice model Therefore, percolation Probability of B_shop or S_shop is decided by Pj, Sj and Cij. For translating probability of random utility model into agent’s individual behavior, a random variable is defined. If percolation probability changed gradually, the spatial pattern of percolation will be changed gradually. This phenomenon can be used in the market share simulation using MAS. However, how about fitness of Individual shopping choice based on ramdam utility and percolation probability in simulation is still a further study.
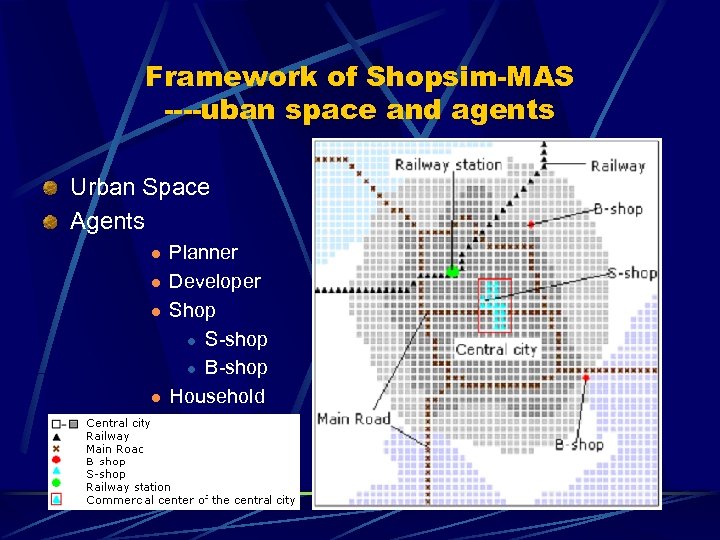 Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----uban space and agents Urban Space Agents l l Planner Developer Shop l S-shop l B-shop Household
Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----uban space and agents Urban Space Agents l l Planner Developer Shop l S-shop l B-shop Household
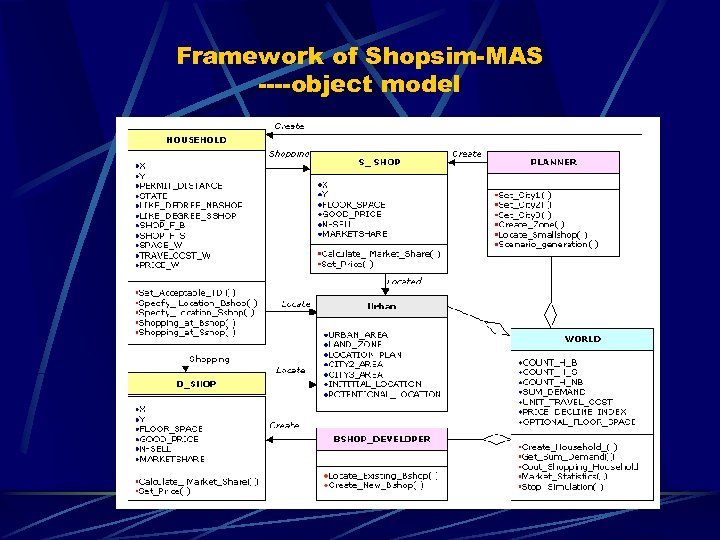 Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----object model
Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----object model
 Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----Simulation Process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The user of Shopsim-MAS defines a policy scenario to be implemented. -> decision table The planner agent sets the spatial structure and initiates the scenario. S-shop agents and existing B-shop agents are created in the urban space. Household agents are created and distributed to the whole central city urban planning area. The developer agent places the new B-shop in urban space according to defined scenarios. The user sets the initial values of parameters. For clear simulation results, random value is set as 500 under critical point. Households then decide where to go shopping until their demands are fulfilled (demands of each household=50).
Framework of Shopsim-MAS ----Simulation Process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The user of Shopsim-MAS defines a policy scenario to be implemented. -> decision table The planner agent sets the spatial structure and initiates the scenario. S-shop agents and existing B-shop agents are created in the urban space. Household agents are created and distributed to the whole central city urban planning area. The developer agent places the new B-shop in urban space according to defined scenarios. The user sets the initial values of parameters. For clear simulation results, random value is set as 500 under critical point. Households then decide where to go shopping until their demands are fulfilled (demands of each household=50).
 Contents Introduction Location Regulations for B-shops Framework of Shopsim-MAS Policy Scenarios Evaluation Discussion and Further Research
Contents Introduction Location Regulations for B-shops Framework of Shopsim-MAS Policy Scenarios Evaluation Discussion and Further Research
 Policy Scenarios Evaluation ----Define four cases of scenario Base Scenario No new B-shop are permitted to develop Centre Activation(CA) B-shop can only locate in the centre commercial area without upper limitation for floor space. Railway Station Development (RSD) B-shop can only be opened near the station, with an upper limitation of 10000 m 2. Neighbouring Commerce Promotion (NCP) B-shop can only locate in neighbour commercial area, with an upper limitation of 3000 m 2.
Policy Scenarios Evaluation ----Define four cases of scenario Base Scenario No new B-shop are permitted to develop Centre Activation(CA) B-shop can only locate in the centre commercial area without upper limitation for floor space. Railway Station Development (RSD) B-shop can only be opened near the station, with an upper limitation of 10000 m 2. Neighbouring Commerce Promotion (NCP) B-shop can only locate in neighbour commercial area, with an upper limitation of 3000 m 2.
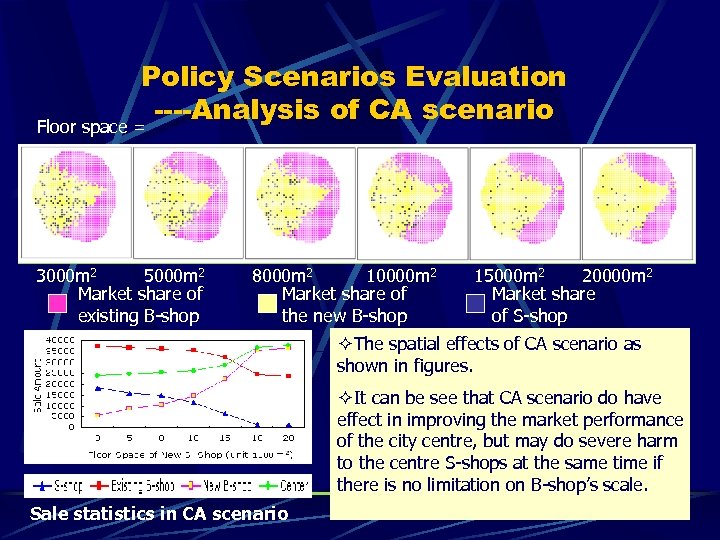 Policy Scenarios Evaluation ----Analysis of CA scenario Floor space = 3000 m 2 5000 m 2 Market share of existing B-shop 8000 m 2 10000 m 2 Market share of the new B-shop 15000 m 2 20000 m 2 Market share of S-shop ²The spatial effects of CA scenario as shown in figures. ²It can be see that CA scenario do have effect in improving the market performance of the city centre, but may do severe harm to the centre S-shops at the same time if there is no limitation on B-shop’s scale. Sale statistics in CA scenario
Policy Scenarios Evaluation ----Analysis of CA scenario Floor space = 3000 m 2 5000 m 2 Market share of existing B-shop 8000 m 2 10000 m 2 Market share of the new B-shop 15000 m 2 20000 m 2 Market share of S-shop ²The spatial effects of CA scenario as shown in figures. ²It can be see that CA scenario do have effect in improving the market performance of the city centre, but may do severe harm to the centre S-shops at the same time if there is no limitation on B-shop’s scale. Sale statistics in CA scenario
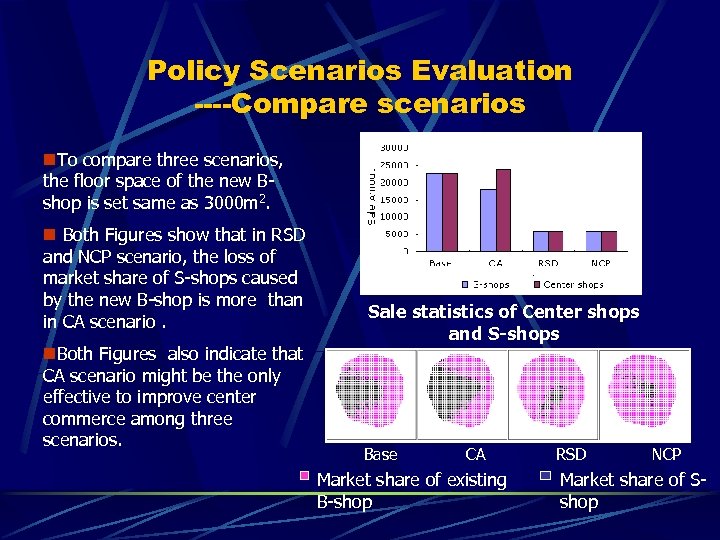 Policy Scenarios Evaluation ----Compare scenarios n. To compare three scenarios, the floor space of the new Bshop is set same as 3000 m 2. n Both Figures show that in RSD and NCP scenario, the loss of market share of S-shops caused by the new B-shop is more than in CA scenario. n. Both Figures also indicate that CA scenario might be the only effective to improve center commerce among three scenarios. Sale statistics of Center shops and S-shops Base CA Market share of existing B-shop RSD NCP Market share of Sshop
Policy Scenarios Evaluation ----Compare scenarios n. To compare three scenarios, the floor space of the new Bshop is set same as 3000 m 2. n Both Figures show that in RSD and NCP scenario, the loss of market share of S-shops caused by the new B-shop is more than in CA scenario. n. Both Figures also indicate that CA scenario might be the only effective to improve center commerce among three scenarios. Sale statistics of Center shops and S-shops Base CA Market share of existing B-shop RSD NCP Market share of Sshop
 Contents Introduction Location Regulations for B-shops Framework of Shopsim-MAS Policy Scenarios Evaluation Discussion and Further Research
Contents Introduction Location Regulations for B-shops Framework of Shopsim-MAS Policy Scenarios Evaluation Discussion and Further Research
 Discussion and Further Research The use of MAS for impact analysis of large scale shopping center development regulations is proposed in this paper. By introducing real urban land use zoning to form agent’s behavior constraints, the Shopsim-MAS simulate the virtual urban space in a more practical way in the context of urban planning. Percolation model and random utility model are employed in this simulation and spatial pattern of the market share influenced by urban bylaw and planning regulations can be visualized. The simulation results of four possible policy scenarios indicate that to develop new B-shop in the city center might be an effective measure to improve commercial activity of city centre. However, how about the behavior of households (random factors in this simulation that will influence the spatial pattern of market share) ?
Discussion and Further Research The use of MAS for impact analysis of large scale shopping center development regulations is proposed in this paper. By introducing real urban land use zoning to form agent’s behavior constraints, the Shopsim-MAS simulate the virtual urban space in a more practical way in the context of urban planning. Percolation model and random utility model are employed in this simulation and spatial pattern of the market share influenced by urban bylaw and planning regulations can be visualized. The simulation results of four possible policy scenarios indicate that to develop new B-shop in the city center might be an effective measure to improve commercial activity of city centre. However, how about the behavior of households (random factors in this simulation that will influence the spatial pattern of market share) ?


