07a230504776778efa20fd490874583e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45

Student Orientation An Abhinav Perspective Kedar Soni, Director Abhinav Vidyalay & Jr. College, Dombivli Visit Us: www. abhinav. ac. in

How do we Learn? An introduction to the functioning & development of our brain
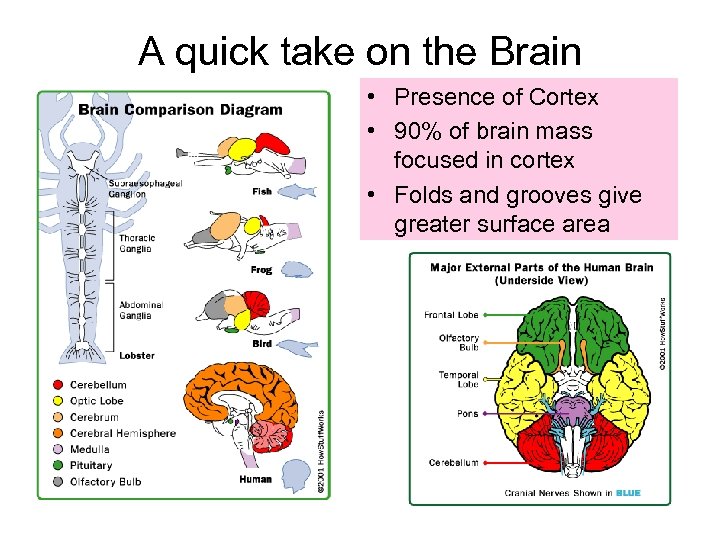
A quick take on the Brain • Presence of Cortex • 90% of brain mass focused in cortex • Folds and grooves give greater surface area
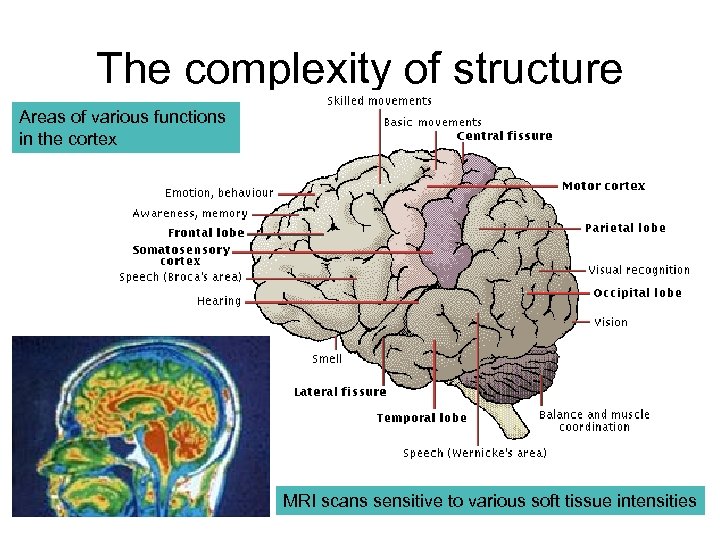
The complexity of structure Areas of various functions in the cortex MRI scans sensitive to various soft tissue intensities
Which picture engrosses you the most?
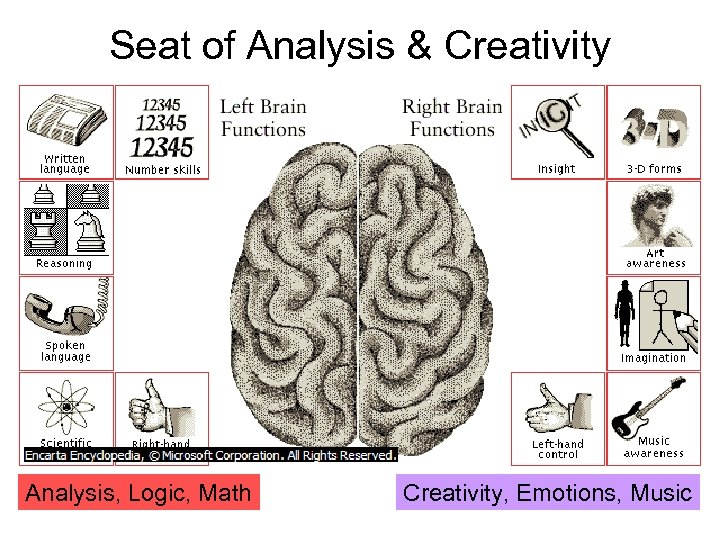
Seat of Analysis & Creativity Analysis, Logic, Math Creativity, Emotions, Music
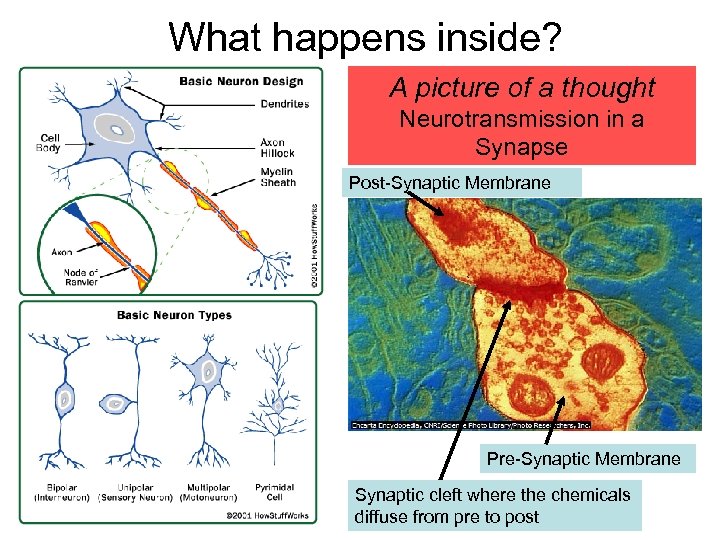
What happens inside? A picture of a thought Neurotransmission in a Synapse Post-Synaptic Membrane Pre-Synaptic Membrane Synaptic cleft where the chemicals diffuse from pre to post
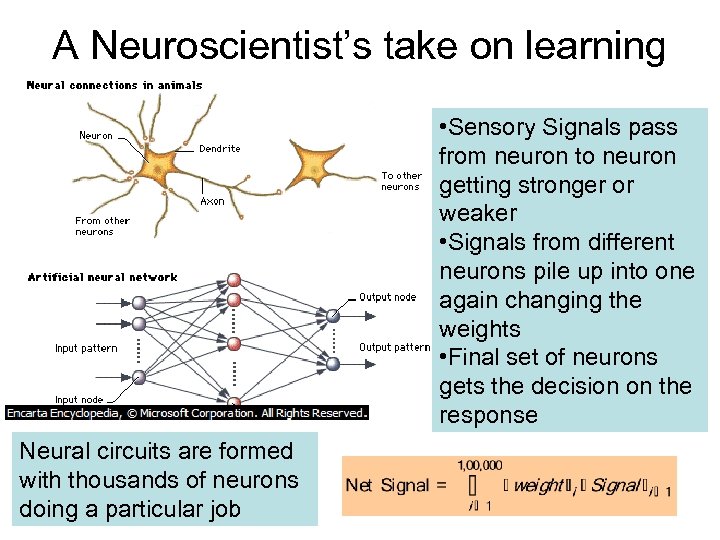
A Neuroscientist’s take on learning • Sensory Signals pass from neuron to neuron getting stronger or weaker • Signals from different neurons pile up into one again changing the weights • Final set of neurons gets the decision on the response Neural circuits are formed with thousands of neurons doing a particular job
Principles of Neural Learning 1. Neurons that fire together, wire together. 2. Neurons are free to re-wire Corollaries: 1. Maximum neurons dedicated to learn a new skill 2. Once learnt most neurons are re-wired to other tasks and the learnt-skill circuit is optimized 3. Use it or lose it Conclusion: Natural & automatic response to stimuli No / few genetic constraints We can learn anything … anytime
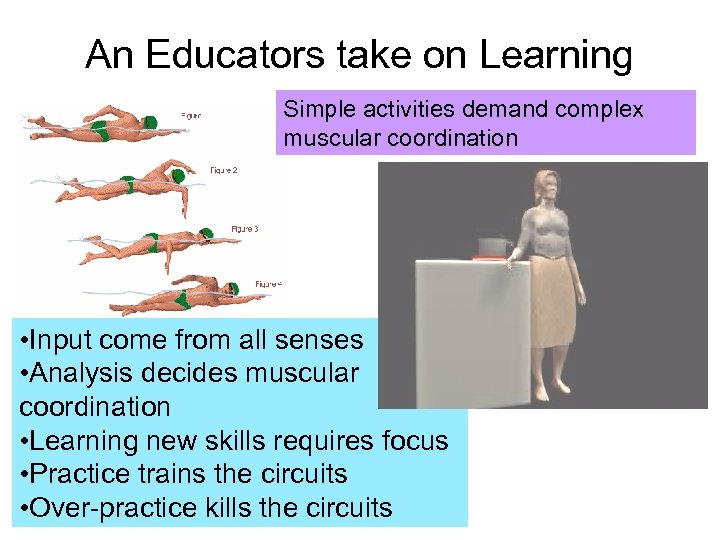
An Educators take on Learning Simple activities demand complex muscular coordination • Input come from all senses • Analysis decides muscular coordination • Learning new skills requires focus • Practice trains the circuits • Over-practice kills the circuits
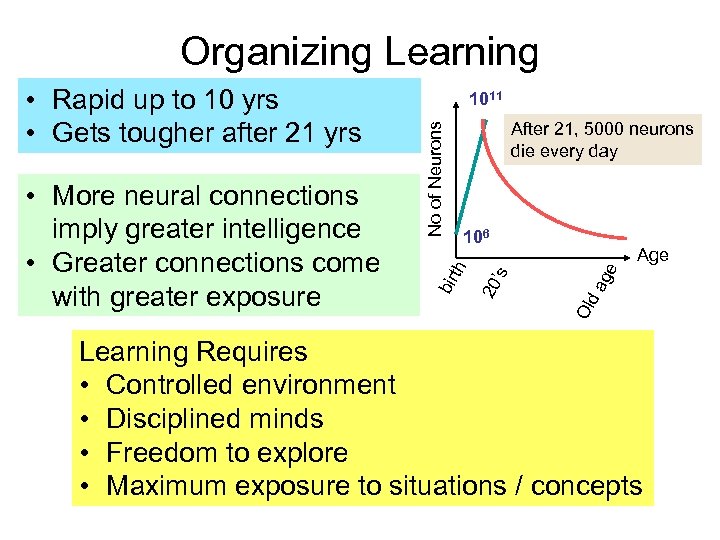
Organizing Learning After 21, 5000 neurons die every day ag e Age Old 20 ’s 106 th No of Neurons • More neural connections imply greater intelligence • Greater connections come with greater exposure 1011 bir • Rapid up to 10 yrs • Gets tougher after 21 yrs Learning Requires • Controlled environment • Disciplined minds • Freedom to explore • Maximum exposure to situations / concepts

What’s Special About G 3? The Physiology • Connections are made rapidly in an infant • Then numbers rise, but not connections • In adolescence (primarily G 3) connections jumble • Chaos reigns and a lot is learnt & unlearnt • Body is also changing The Psychology • Confusion between goals & desires • Confusion about self – abilities & drawbacks • Cannot accept external interference – Rebellious Ideal for reshaping & casting into a final mould
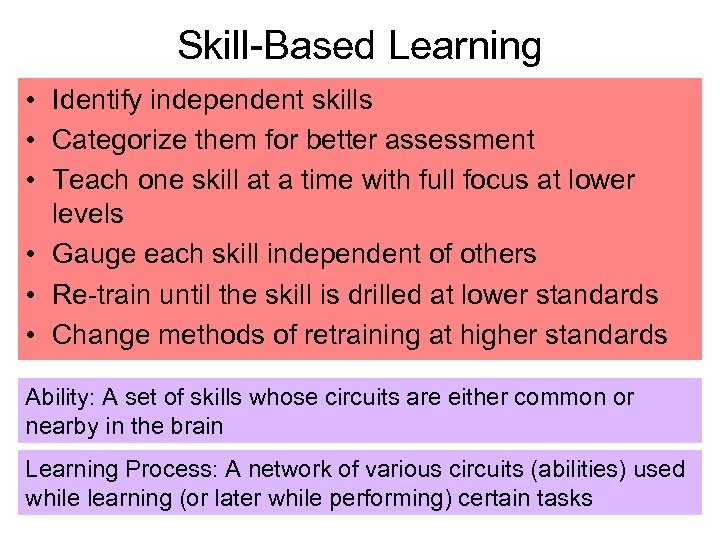
Skill-Based Learning • Identify independent skills • Categorize them for better assessment • Teach one skill at a time with full focus at lower levels • Gauge each skill independent of others • Re-train until the skill is drilled at lower standards • Change methods of retraining at higher standards Ability: A set of skills whose circuits are either common or nearby in the brain Learning Process: A network of various circuits (abilities) used while learning (or later while performing) certain tasks
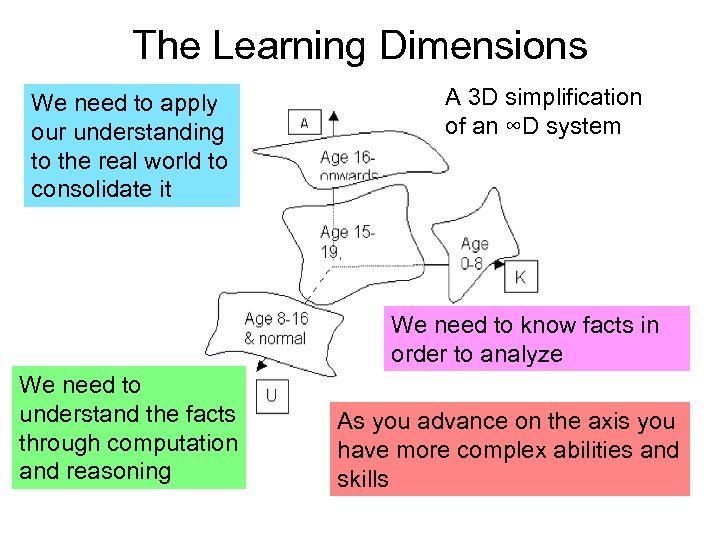
The Learning Dimensions We need to apply our understanding to the real world to consolidate it A 3 D simplification of an ∞D system We need to know facts in order to analyze We need to understand the facts through computation and reasoning As you advance on the axis you have more complex abilities and skills
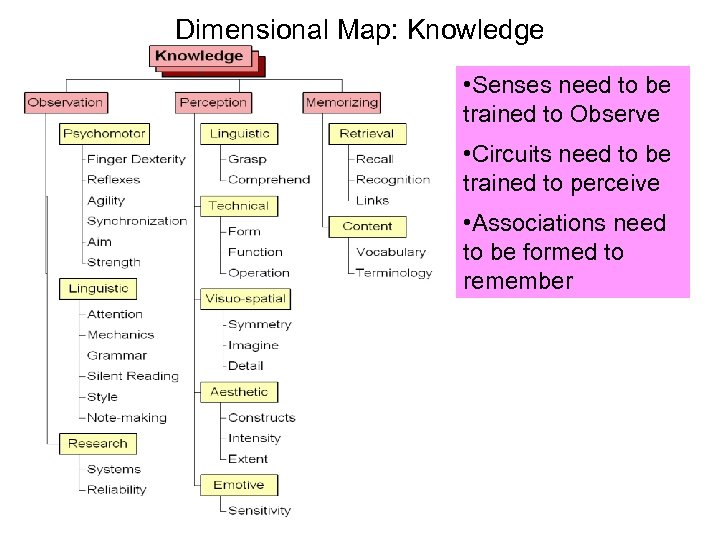
Dimensional Map: Knowledge • Senses need to be trained to Observe • Circuits need to be trained to perceive • Associations need to be formed to remember
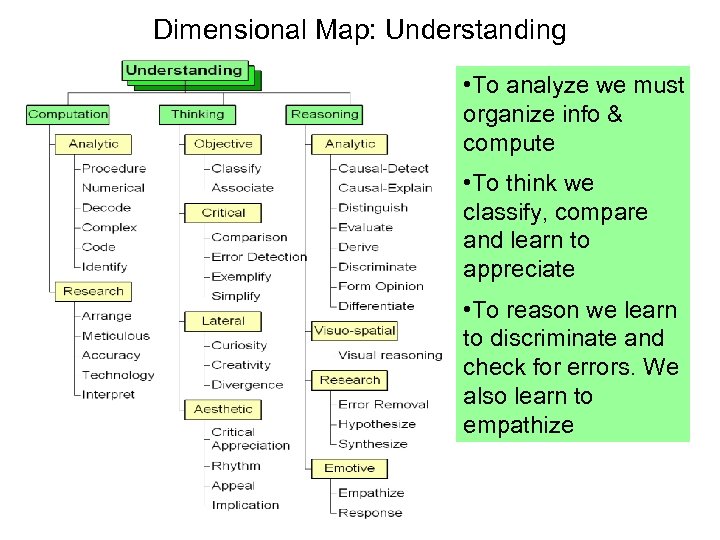
Dimensional Map: Understanding • To analyze we must organize info & compute • To think we classify, compare and learn to appreciate • To reason we learn to discriminate and check for errors. We also learn to empathize
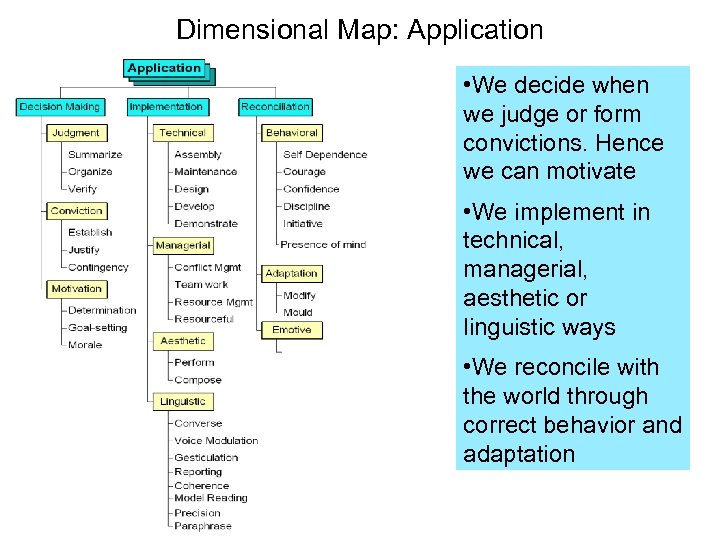
Dimensional Map: Application • We decide when we judge or form convictions. Hence we can motivate • We implement in technical, managerial, aesthetic or linguistic ways • We reconcile with the world through correct behavior and adaptation

How do we know, how much you Learn? An introduction to Skill Based Assessments

Assessment Methodology • Since inputs to the brain have various channel, so must the outputs • Assessment must be Oral as well as through Observation, along with written Therefore various types: • Group Assignments (AG) • Individual Assignments (AI) • Home, Objective & Tutorials • Practical (Pr) • Written (W) • Project-Work (P) – To. K (VE) & Stimulus (GK)
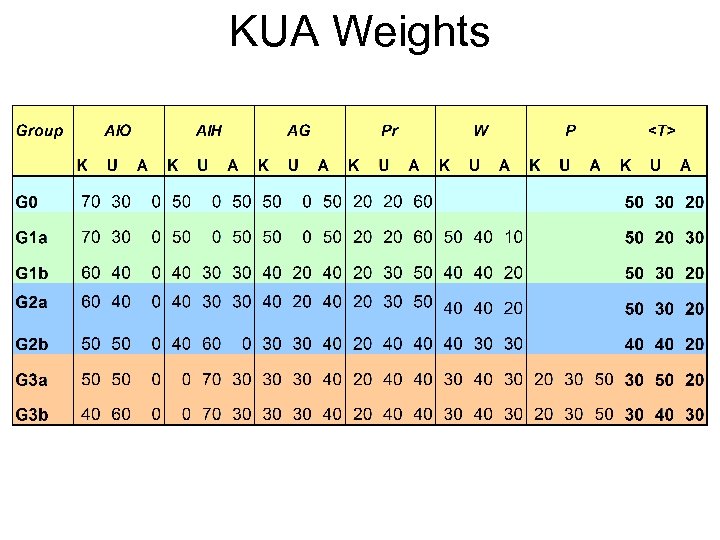
KUA Weights
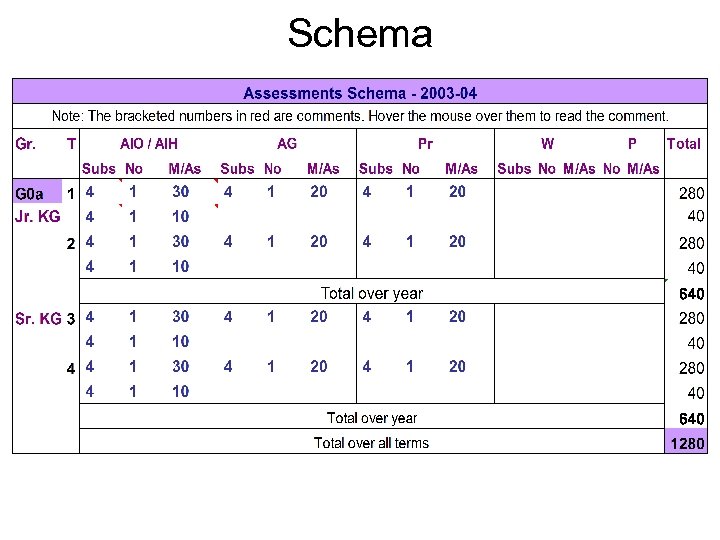
Schema
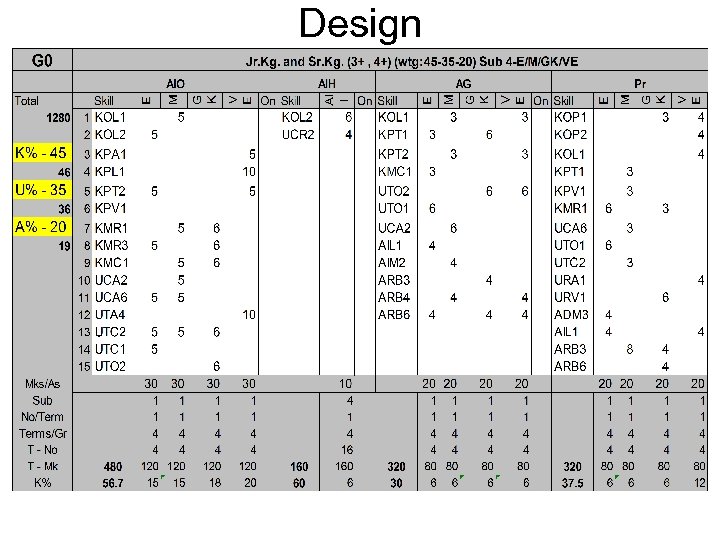
Design
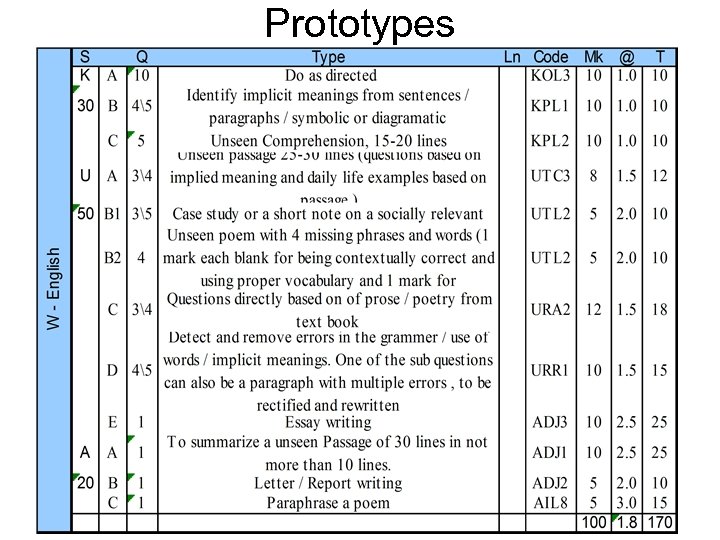
Prototypes
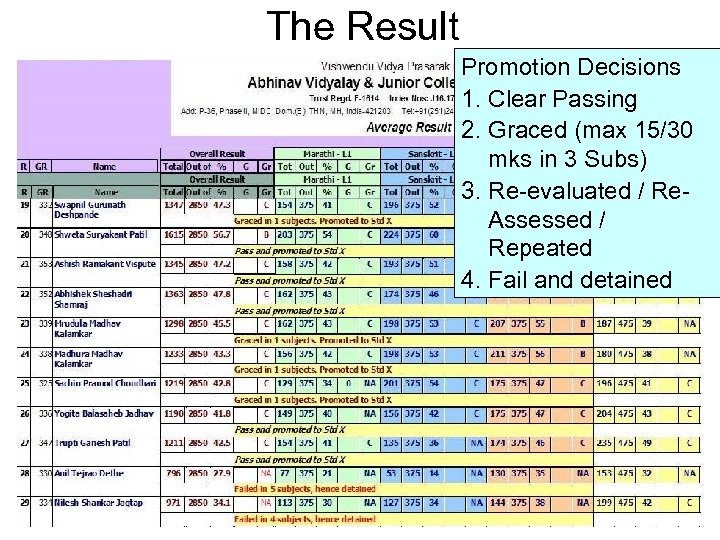
The Result Promotion Decisions 1. Clear Passing 2. Graced (max 15/30 mks in 3 Subs) 3. Re-evaluated / Re. Assessed / Repeated 4. Fail and detained
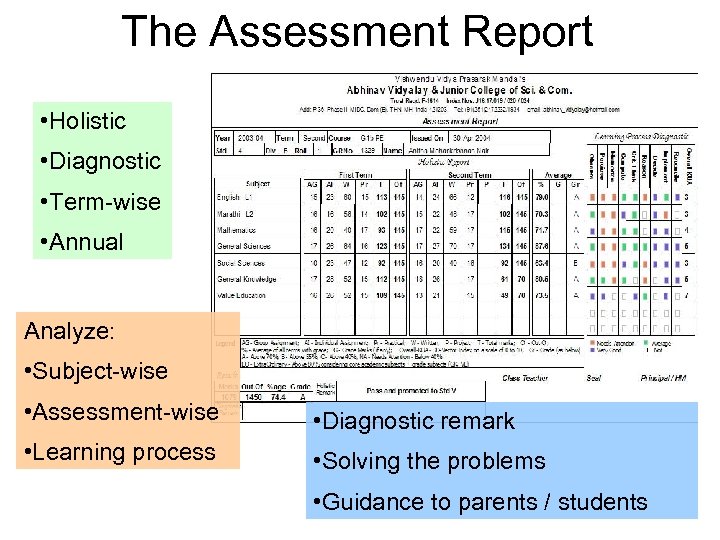
The Assessment Report • Holistic • Diagnostic • Term-wise • Annual Analyze: • Subject-wise • Assessment-wise • Diagnostic remark • Learning process • Solving the problems • Guidance to parents / students
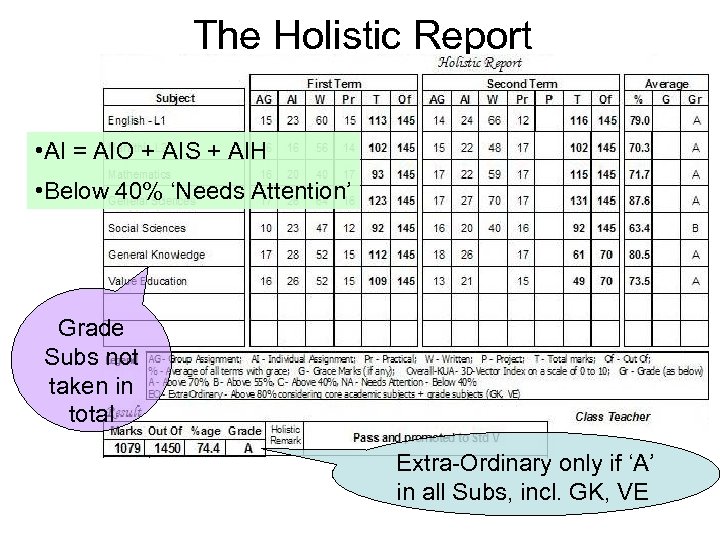
The Holistic Report • AI = AIO + AIS + AIH • Below 40% ‘Needs Attention’ Grade Subs not taken in total Extra-Ordinary only if ‘A’ in all Subs, incl. GK, VE
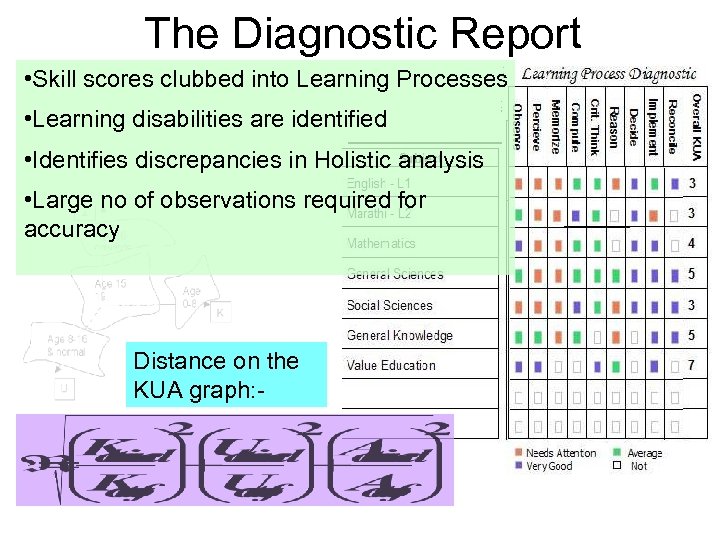
The Diagnostic Report • Skill scores clubbed into Learning Processes • Learning disabilities are identified • Identifies discrepancies in Holistic analysis • Large no of observations required for accuracy Distance on the KUA graph: -

A Learning Environment An introduction to the technology & philosophy of our systems
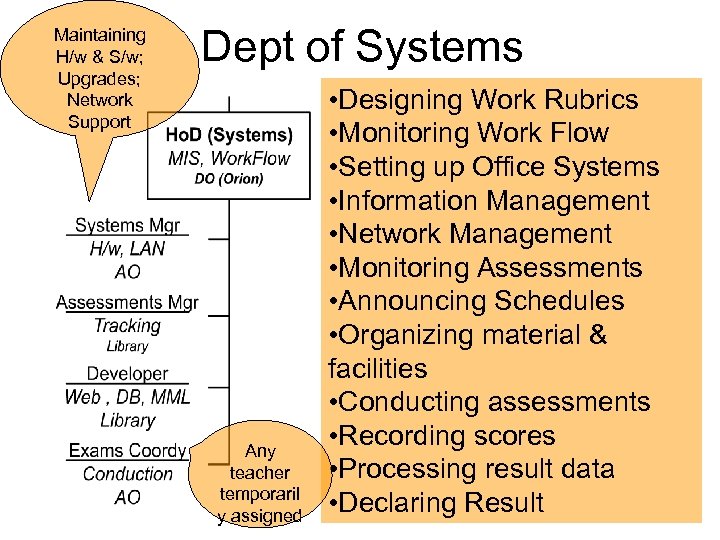
Maintaining H/w & S/w; Upgrades; Network Support Dept of Systems Any teacher temporaril y assigned • Designing Work Rubrics • Monitoring Work Flow • Setting up Office Systems • Information Management • Network Management • Monitoring Assessments • Announcing Schedules • Organizing material & facilities • Conducting assessments • Recording scores • Processing result data • Declaring Result
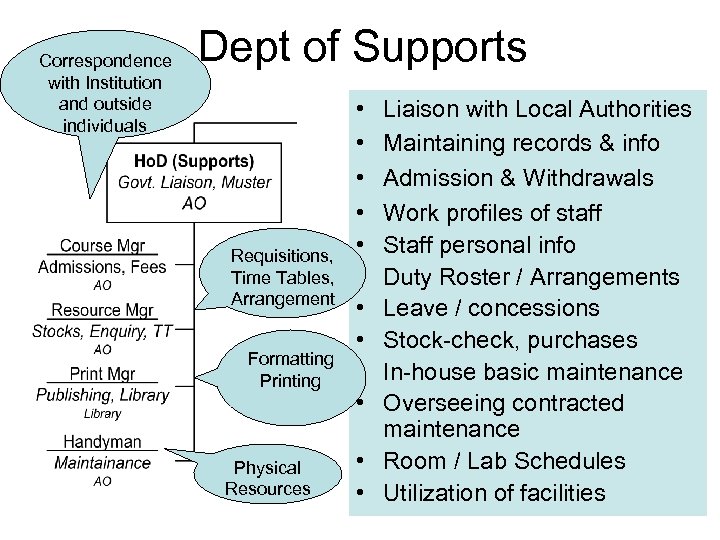
Correspondence with Institution and outside individuals Dept of Supports Requisitions, Time Tables, Arrangement Formatting Printing Physical Resources • • • Liaison with Local Authorities Maintaining records & info Admission & Withdrawals Work profiles of staff Staff personal info Duty Roster / Arrangements Leave / concessions Stock-check, purchases In-house basic maintenance Overseeing contracted maintenance • Room / Lab Schedules • Utilization of facilities
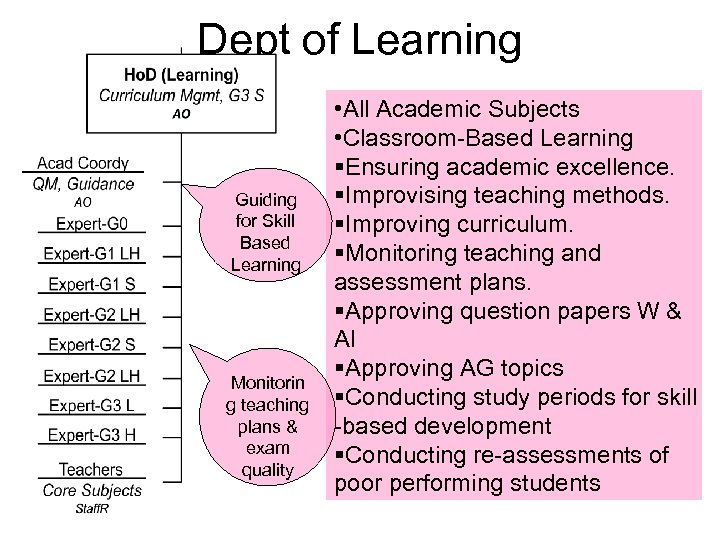
Dept of Learning Guiding for Skill Based Learning Monitorin g teaching plans & exam quality • All Academic Subjects • Classroom-Based Learning §Ensuring academic excellence. §Improvising teaching methods. §Improving curriculum. §Monitoring teaching and assessment plans. §Approving question papers W & AI §Approving AG topics §Conducting study periods for skill -based development §Conducting re-assessments of poor performing students
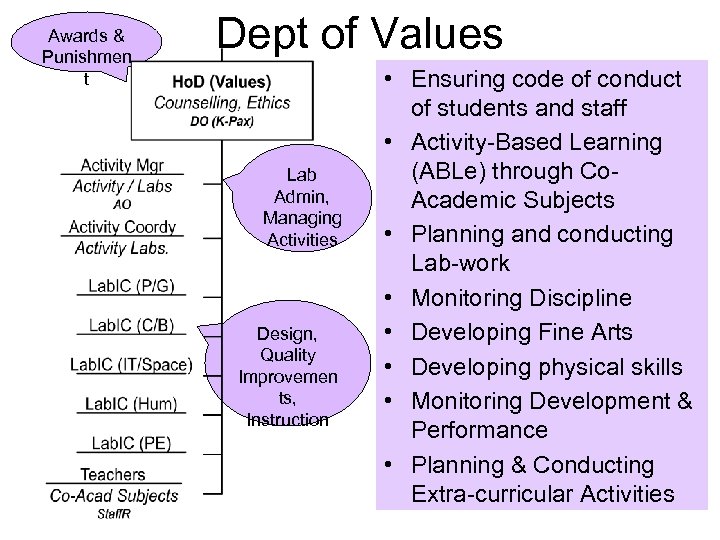
Awards & Punishmen t Dept of Values Lab Admin, Managing Activities Design, Quality Improvemen ts, Instruction • Ensuring code of conduct of students and staff • Activity-Based Learning (ABLe) through Co. Academic Subjects • Planning and conducting Lab-work • Monitoring Discipline • Developing Fine Arts • Developing physical skills • Monitoring Development & Performance • Planning & Conducting Extra-curricular Activities

Life @ Abhinav An introduction to the Schedules, Activities, etc.

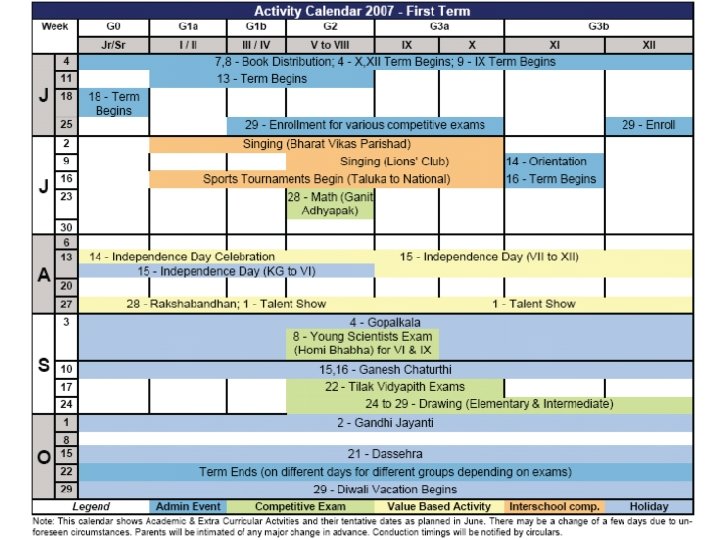
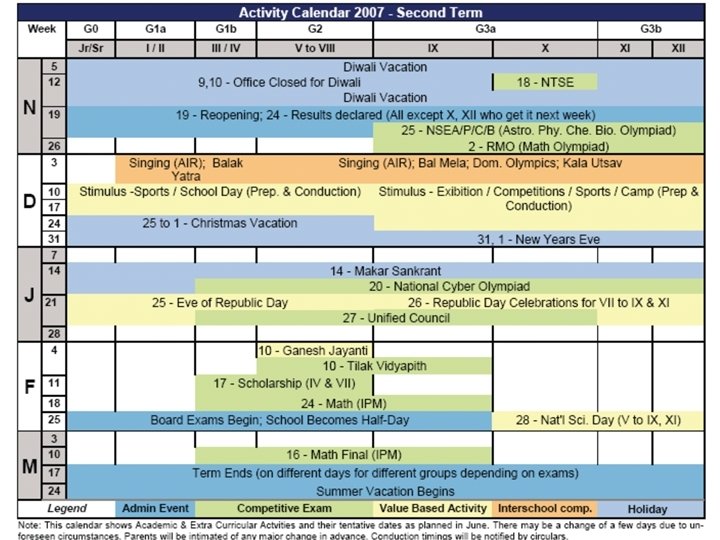
The Schedules • • Timings: 9: 00 to 2: 00 (M, T, W); 8: 00 to 2: 00 (T, F) Report outside the gate 5 min before Sometimes you may leave later than scheduled Saturdays usually off, sometimes Project-work or extra lectures • Two terms – – – First: XI – 1 st Wk Aug to 3 rd Wk Oct Second: 3 rd Wk Nov to 1 st Wk Apr Third: XII – 2 nd Wk Apr to 3 rd Wk Oct Fourth: 2 nd Wk Nov to 3 rd Wk Jan
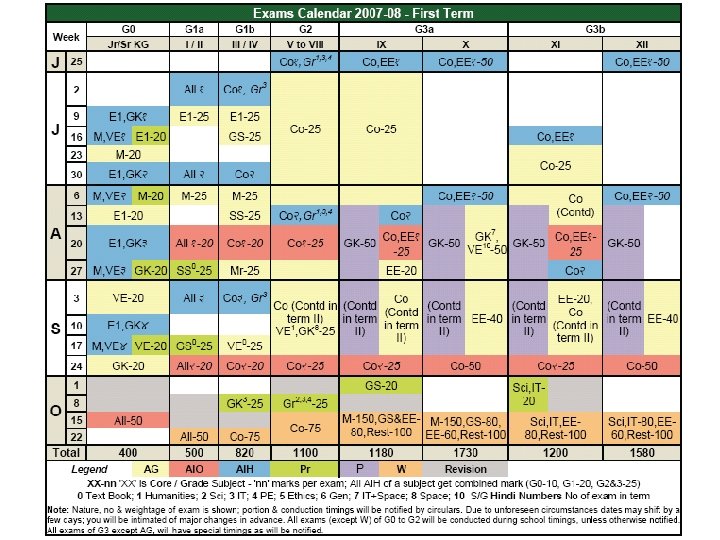
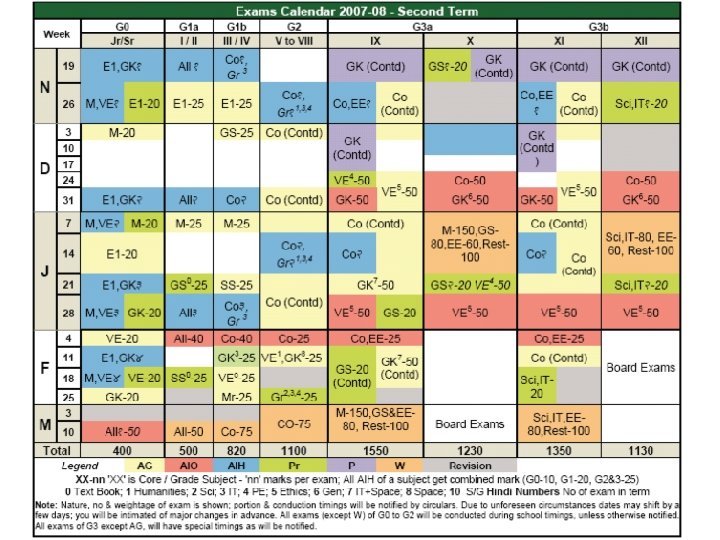

The Academics • Teachers are here to teach. . . So you have a right to ask questions • They may answer some Q’s later • Unless you ask/discuss, you will not understand truly • Also, you have a right to be wrong • Discussion mandatory for all exams / labs

Groups • Assignment Groups – 18 / 12 per class in College / School – Each group has 3 -4 members defined by Do. V – Three batches: • Alpha: A & C – a 1 to a 6, B – a 7 to a 8 • Beta: A & C – b 1 to b 6, B – b 7 to b 8 • Gamma: A & C – g 1 to g 6, B – g 7 to g 8 • Project Groups – 2 -3 assignment groups joined together

Use of Groups • Assignment Groups – Science Labs: a, b, g have separate practical – Any extra assignment given • Project Groups – Stimulus Project

The Activities • Participation is not compulsory but is expected from everyone • Planning is fluid – we may include some new activities if many students interested & time permits • Games kits kept in all classes for recess, also quadrangle available • Premises available after hours for practice

FTP & LAN • Logons to LAN • What’s the big deal about the LAN? – Info about the Institution – Past papers, rules & policies – Academic Webs • Web & FTP – Downloads – Blogs – Stimulus & Icon

Uniform & Other Rules • • • Without uniform, permissible until 15 th Aug Civil dress must be decent No ornaments / fancy hair-do’s No fancy or costly gadgets Once in you don’t go out until dismissed

Olympiads • The HBCSE Presentation • The Astronomy Olympiad presentation
07a230504776778efa20fd490874583e.ppt