d803709ae81cc0cd87a39ee78a9769e3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 Structured Trade & Investment Finance A Multilateral Emerging Market ECA: A Key Driver for Sustainable Development Paul Mudde Senior Vice President Reputation Management & Sustainable Development ABN AMRO bank
Structured Trade & Investment Finance A Multilateral Emerging Market ECA: A Key Driver for Sustainable Development Paul Mudde Senior Vice President Reputation Management & Sustainable Development ABN AMRO bank
 Structured Trade & Investment Finance Agenda I. Introduction II. The Rationale for EMECA III. The Role of EMECA IV. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market V. Summary & Conclusions ABN AMRO bank
Structured Trade & Investment Finance Agenda I. Introduction II. The Rationale for EMECA III. The Role of EMECA IV. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market V. Summary & Conclusions ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Main Considerations: 1. Debt Constraints Emerging Markets 2. Official Flow Constraints 3. Ambitious UN new Millennium Goals 4. Importance of Private Capital Flows 5. Support for Exports from Emerging Markets 6. Support for Intra-Regional Trade 7. Level Playing Field OECD Exporters & Exporters Emerging markets 8. No Dedicated Program to support Trade between Emerging Markets Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Main Considerations: 1. Debt Constraints Emerging Markets 2. Official Flow Constraints 3. Ambitious UN new Millennium Goals 4. Importance of Private Capital Flows 5. Support for Exports from Emerging Markets 6. Support for Intra-Regional Trade 7. Level Playing Field OECD Exporters & Exporters Emerging markets 8. No Dedicated Program to support Trade between Emerging Markets Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Debt Constraints EM Stock of Total Debt Developing Countries by Region in Bln. US$m Source: OECD & World Bank Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Debt Constraints EM Stock of Total Debt Developing Countries by Region in Bln. US$m Source: OECD & World Bank Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Debt Constraints EM Composition of Debt of Developing Countries in Bln. US$m Source: OECD & World Bank Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Debt Constraints EM Composition of Debt of Developing Countries in Bln. US$m Source: OECD & World Bank Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Debt Constraints EM: Debt Indicators All Developing Countries EDT /XGS: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Exports Goods & Services EDT/GNI: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Gross National Income Source: World Bank Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Debt Constraints EM: Debt Indicators All Developing Countries EDT /XGS: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Exports Goods & Services EDT/GNI: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Gross National Income Source: World Bank Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
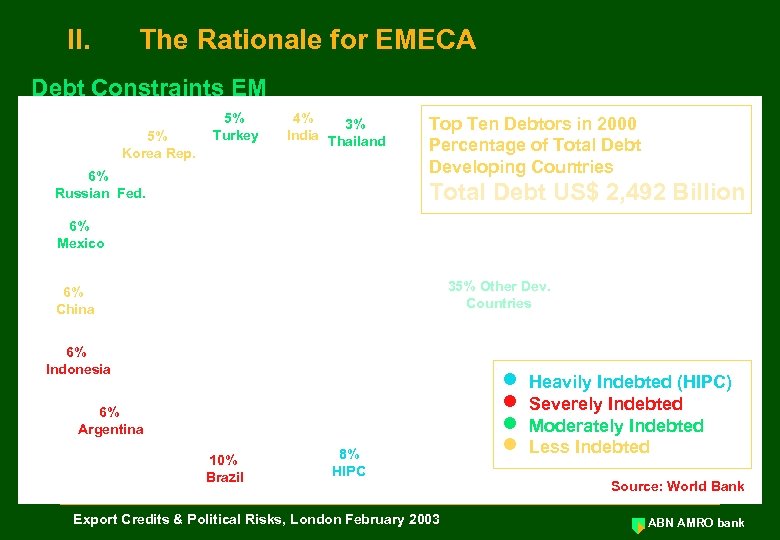 II. The Rationale for EMECA Debt Constraints EM 5% Korea Rep. 5% Turkey 4% 3% India Thailand 6% Russian Fed. Top Ten Debtors in 2000 Percentage of Total Debt Developing Countries Total Debt US$ 2, 492 Billion 6% Mexico 35% Other Dev. Countries 6% China 6% Indonesia 6% Argentina 10% Brazil 8% HIPC Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 n n Heavily Indebted (HIPC) Severely Indebted Moderately Indebted Less Indebted Source: World Bank ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Debt Constraints EM 5% Korea Rep. 5% Turkey 4% 3% India Thailand 6% Russian Fed. Top Ten Debtors in 2000 Percentage of Total Debt Developing Countries Total Debt US$ 2, 492 Billion 6% Mexico 35% Other Dev. Countries 6% China 6% Indonesia 6% Argentina 10% Brazil 8% HIPC Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 n n Heavily Indebted (HIPC) Severely Indebted Moderately Indebted Less Indebted Source: World Bank ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Main Consequences of Debt Problem Emerging Markets: • Financial Crises in various EM (Asia, Brazil, Russia, Turkey, Argentina) • Local Currency Devaluation • Payment Defaults & Private Sector Bankruptcies • Loss of Jobs and large Social Damages • EM Governments enhance process of Liberalisation & Privatisation Response of Financial Markets: • Credit Crunch • Increased Pricing • London Club Rescheduling • Commercial Work-outs Response IMF, ECAs, MLAs, Bilateral Donors • IMF / MLA Support combined with Conditions re. Liberalisation & Privatisation • Bilateral Aid Loans (e. g. Balance of Payment support) • Technical Assistance • Paris Club Rescheduling (Since 1983: 352 Agreements covering US$ 406 Bln. ) • HIPC Debt Relief & Chapter 11 for Sovereigns Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Main Consequences of Debt Problem Emerging Markets: • Financial Crises in various EM (Asia, Brazil, Russia, Turkey, Argentina) • Local Currency Devaluation • Payment Defaults & Private Sector Bankruptcies • Loss of Jobs and large Social Damages • EM Governments enhance process of Liberalisation & Privatisation Response of Financial Markets: • Credit Crunch • Increased Pricing • London Club Rescheduling • Commercial Work-outs Response IMF, ECAs, MLAs, Bilateral Donors • IMF / MLA Support combined with Conditions re. Liberalisation & Privatisation • Bilateral Aid Loans (e. g. Balance of Payment support) • Technical Assistance • Paris Club Rescheduling (Since 1983: 352 Agreements covering US$ 406 Bln. ) • HIPC Debt Relief & Chapter 11 for Sovereigns Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Official Flow Constraints & Importance of Private Flows Net MLT Capital Flows to Developing Countries in Bln. US$ Source: World Bank Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Official Flow Constraints & Importance of Private Flows Net MLT Capital Flows to Developing Countries in Bln. US$ Source: World Bank Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Gross Official Flows in Bln. US$ Official Flow Constraints Gross Official Flows to Developing Countries in Bln. US$ Source: World Bank Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Gross Official Flows in Bln. US$ Official Flow Constraints Gross Official Flows to Developing Countries in Bln. US$ Source: World Bank Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Official Flow Constraints (IMF) Source: IMF Stock of Debt Developing Countries to IMF in Bln. US$m Source: OECD, BU & IMF Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Official Flow Constraints (IMF) Source: IMF Stock of Debt Developing Countries to IMF in Bln. US$m Source: OECD, BU & IMF Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA 2000 Official Flow Constraints (OECD DAC) Bilateral Aid 2000: Total US$ 43. 3 Billion Bilateral OECD DAC Aid by Income Group Total Aid all DAC Members in Mln US$ 10, 886 7, 789 32 1, 839 11, 358 11, 739 Source: OECD Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA 2000 Official Flow Constraints (OECD DAC) Bilateral Aid 2000: Total US$ 43. 3 Billion Bilateral OECD DAC Aid by Income Group Total Aid all DAC Members in Mln US$ 10, 886 7, 789 32 1, 839 11, 358 11, 739 Source: OECD Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Official Flow Constraints (OECD DAC) 2000: Net ODA as a % of GNI UN Target 0. 7 OECD Average: 0. 39 Source: OECD Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Official Flow Constraints (OECD DAC) 2000: Net ODA as a % of GNI UN Target 0. 7 OECD Average: 0. 39 Source: OECD Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Ambitious Development Goals for the new Millennium UN Millennium Development Goals: 1. Eradicate extreme Poverty & Hunger 2. Achieve universal Primary Education 3. Promote gender equality & empower Women 4. Reduce Child mortality 5. Improve Maternal Health 6. Combat HIV / AIDS 7. Ensure Environmental Sustainability 8. Develop Global Partnership for Development WB Estimate: US$ 40 - 60 Billion of additional Aid per Annum Internationally Agreed Aid Target: Actual Average OECD DAC Countries: To meet Millennium Goals: Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 0. 7% of GDP 0. 39% of GDP (2000) 0. 49% of GDP ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Ambitious Development Goals for the new Millennium UN Millennium Development Goals: 1. Eradicate extreme Poverty & Hunger 2. Achieve universal Primary Education 3. Promote gender equality & empower Women 4. Reduce Child mortality 5. Improve Maternal Health 6. Combat HIV / AIDS 7. Ensure Environmental Sustainability 8. Develop Global Partnership for Development WB Estimate: US$ 40 - 60 Billion of additional Aid per Annum Internationally Agreed Aid Target: Actual Average OECD DAC Countries: To meet Millennium Goals: Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 0. 7% of GDP 0. 39% of GDP (2000) 0. 49% of GDP ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Importance of Private Capital Flows to Emerging Markets Net MLT Private Flows to Developing Countries by Source in Bln. US$ Source: World Bank Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Importance of Private Capital Flows to Emerging Markets Net MLT Private Flows to Developing Countries by Source in Bln. US$ Source: World Bank Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Importance of Private Capital Flows to Emerging Markets Key Developments re Private Capital Flows: • Importance of FDI (approx. 30% mergers & acquisitions) • Volatility of Debt Flows (Bank Loans / Bonds) • Concentration in Financial Markets • BIS II Solvency Rules (2006) Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Importance of Private Capital Flows to Emerging Markets Key Developments re Private Capital Flows: • Importance of FDI (approx. 30% mergers & acquisitions) • Volatility of Debt Flows (Bank Loans / Bonds) • Concentration in Financial Markets • BIS II Solvency Rules (2006) Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
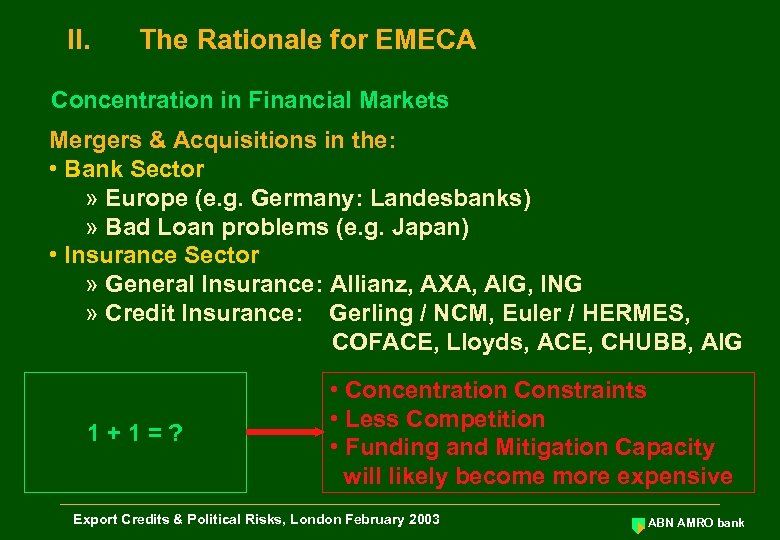 II. The Rationale for EMECA Concentration in Financial Markets Mergers & Acquisitions in the: • Bank Sector » Europe (e. g. Germany: Landesbanks) » Bad Loan problems (e. g. Japan) • Insurance Sector » General Insurance: Allianz, AXA, AIG, ING » Credit Insurance: Gerling / NCM, Euler / HERMES, COFACE, Lloyds, ACE, CHUBB, AIG 1+1=? • Concentration Constraints • Less Competition • Funding and Mitigation Capacity will likely become more expensive Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Concentration in Financial Markets Mergers & Acquisitions in the: • Bank Sector » Europe (e. g. Germany: Landesbanks) » Bad Loan problems (e. g. Japan) • Insurance Sector » General Insurance: Allianz, AXA, AIG, ING » Credit Insurance: Gerling / NCM, Euler / HERMES, COFACE, Lloyds, ACE, CHUBB, AIG 1+1=? • Concentration Constraints • Less Competition • Funding and Mitigation Capacity will likely become more expensive Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA BIS II Solvency Changes for Sovereigns Borrowers Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA BIS II Solvency Changes for Sovereigns Borrowers Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Supporting Exports from Developing Countries by Destination in Bln. US$ Source: Unctad Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Supporting Exports from Developing Countries by Destination in Bln. US$ Source: Unctad Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Supporting Exports from Developing Countries Exports of Manufactures have become more Important ! Composition of Exports Developing Countries in % of Total Exports 66% 54% Source: Unctad Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Supporting Exports from Developing Countries Exports of Manufactures have become more Important ! Composition of Exports Developing Countries in % of Total Exports 66% 54% Source: Unctad Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Supporting Exports from Developing Countries Focus on Private Sector Development in EM • Private Sector is the engine for Sustained Economic Growth • Private Sector is main source for job creation & employment • Employment is main Route to combat Poverty & to Improve Living Standards • Private sector is main source of (tax) income for Public Sector Expenditures in Health, Education, etc. Focus on the Support of Exports • Exports Income is key for GDP Growth of Developing Countries • Exports Income is key in solving Debt problem of Developing Countries • By Supporting Exports Future Crises can be Prevented Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Supporting Exports from Developing Countries Focus on Private Sector Development in EM • Private Sector is the engine for Sustained Economic Growth • Private Sector is main source for job creation & employment • Employment is main Route to combat Poverty & to Improve Living Standards • Private sector is main source of (tax) income for Public Sector Expenditures in Health, Education, etc. Focus on the Support of Exports • Exports Income is key for GDP Growth of Developing Countries • Exports Income is key in solving Debt problem of Developing Countries • By Supporting Exports Future Crises can be Prevented Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA BU New MLT Business in Bln. US$ ECAs play a Key role in supporting Exports to EM & Development of EM Berne Union Members MLT New Business Covered in Bln. US$ Source: Berne Union Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA BU New MLT Business in Bln. US$ ECAs play a Key role in supporting Exports to EM & Development of EM Berne Union Members MLT New Business Covered in Bln. US$ Source: Berne Union Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Supporting Intra Regional Trade: Key for Regional Development 2000 % Source: World Bank Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Supporting Intra Regional Trade: Key for Regional Development 2000 % Source: World Bank Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA Level Playing Field OECD Exporters & EM Exporters Bottlenecks for MLT Finance of exports from EM: • MLT Finance in Local Currency Not Available • MLT Finance in Hard Currency Hardly Available No adequate MLT Insurance / Guarantee Facilities for Financing Banks There is no ECA There is an ECA, but adequate cover is not Available. Most EM ECAs are only / mainly involved in ST Supplier Credits. Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Level Playing Field OECD Exporters & EM Exporters Bottlenecks for MLT Finance of exports from EM: • MLT Finance in Local Currency Not Available • MLT Finance in Hard Currency Hardly Available No adequate MLT Insurance / Guarantee Facilities for Financing Banks There is no ECA There is an ECA, but adequate cover is not Available. Most EM ECAs are only / mainly involved in ST Supplier Credits. Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
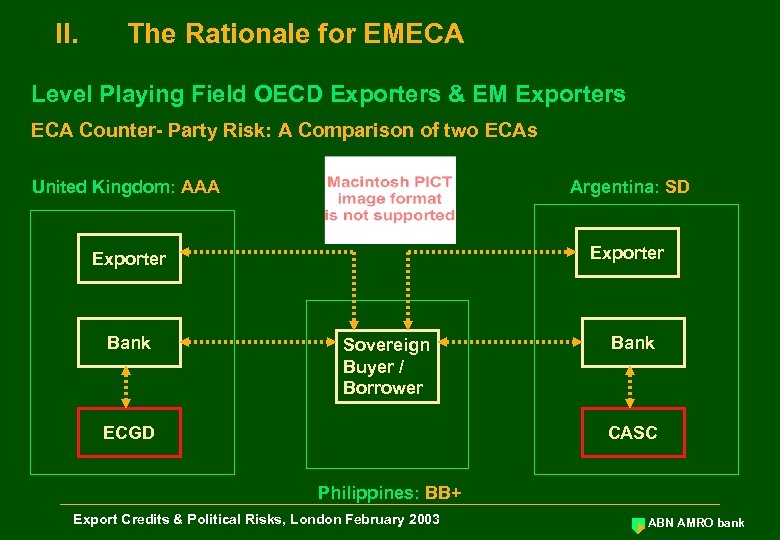 II. The Rationale for EMECA Level Playing Field OECD Exporters & EM Exporters ECA Counter- Party Risk: A Comparison of two ECAs United Kingdom: AAA Argentina: SD Exporter Bank Sovereign Buyer / Borrower ECGD Bank CASC Philippines: BB+ Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Level Playing Field OECD Exporters & EM Exporters ECA Counter- Party Risk: A Comparison of two ECAs United Kingdom: AAA Argentina: SD Exporter Bank Sovereign Buyer / Borrower ECGD Bank CASC Philippines: BB+ Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
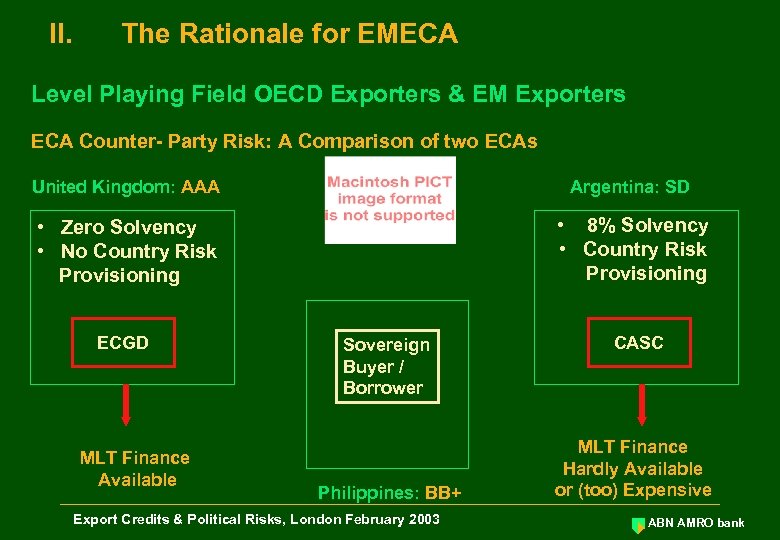 II. The Rationale for EMECA Level Playing Field OECD Exporters & EM Exporters ECA Counter- Party Risk: A Comparison of two ECAs United Kingdom: AAA Argentina: SD • Zero Solvency • No Country Risk Provisioning • 8% Solvency • Country Risk Provisioning ECGD MLT Finance Available Sovereign Buyer / Borrower Philippines: BB+ Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 CASC MLT Finance Hardly Available or (too) Expensive ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Level Playing Field OECD Exporters & EM Exporters ECA Counter- Party Risk: A Comparison of two ECAs United Kingdom: AAA Argentina: SD • Zero Solvency • No Country Risk Provisioning • 8% Solvency • Country Risk Provisioning ECGD MLT Finance Available Sovereign Buyer / Borrower Philippines: BB+ Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 CASC MLT Finance Hardly Available or (too) Expensive ABN AMRO bank
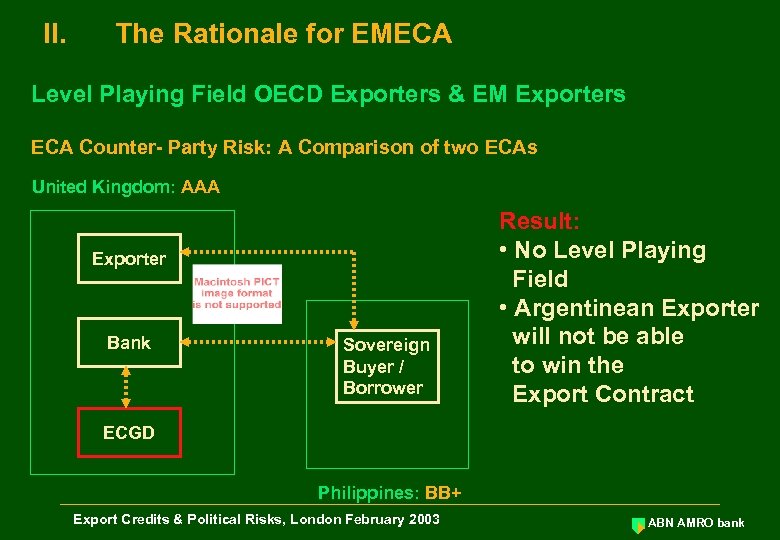 II. The Rationale for EMECA Level Playing Field OECD Exporters & EM Exporters ECA Counter- Party Risk: A Comparison of two ECAs United Kingdom: AAA Exporter Bank Sovereign Buyer / Borrower Result: • No Level Playing Field • Argentinean Exporter will not be able to win the Export Contract ECGD Philippines: BB+ Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA Level Playing Field OECD Exporters & EM Exporters ECA Counter- Party Risk: A Comparison of two ECAs United Kingdom: AAA Exporter Bank Sovereign Buyer / Borrower Result: • No Level Playing Field • Argentinean Exporter will not be able to win the Export Contract ECGD Philippines: BB+ Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
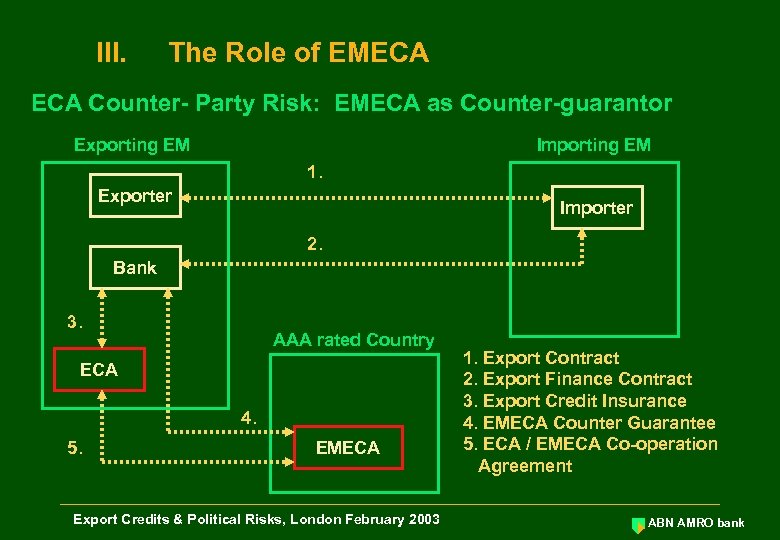 III. The Role of EMECA Counter- Party Risk: EMECA as Counter-guarantor Exporting EM Importing EM 1. Exporter Importer 2. Bank 3. AAA rated Country ECA 4. 5. EMECA Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 1. Export Contract 2. Export Finance Contract 3. Export Credit Insurance 4. EMECA Counter Guarantee 5. ECA / EMECA Co-operation Agreement ABN AMRO bank
III. The Role of EMECA Counter- Party Risk: EMECA as Counter-guarantor Exporting EM Importing EM 1. Exporter Importer 2. Bank 3. AAA rated Country ECA 4. 5. EMECA Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 1. Export Contract 2. Export Finance Contract 3. Export Credit Insurance 4. EMECA Counter Guarantee 5. ECA / EMECA Co-operation Agreement ABN AMRO bank
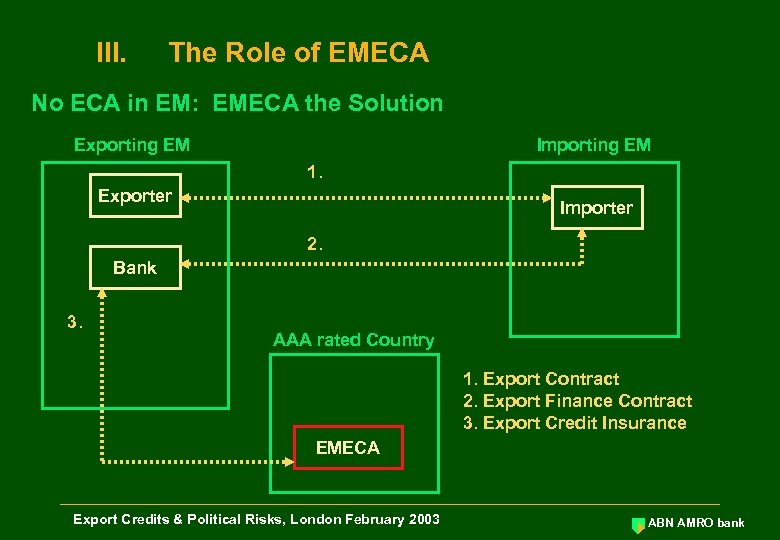 III. The Role of EMECA No ECA in EM: EMECA the Solution Exporting EM Importing EM 1. Exporter Importer 2. Bank 3. AAA rated Country 1. Export Contract 2. Export Finance Contract 3. Export Credit Insurance EMECA Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
III. The Role of EMECA No ECA in EM: EMECA the Solution Exporting EM Importing EM 1. Exporter Importer 2. Bank 3. AAA rated Country 1. Export Contract 2. Export Finance Contract 3. Export Credit Insurance EMECA Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 II. The Rationale for EMECA No Dedicated Program to support Exports from Developing Countries Main Characteristics of the Official Financial Support to Developing Countries: • Bilateral & MLA Support is mainly provided to Public Sector in Developing Countries • Limited Support for Private Sector Development (Mainly IFC, MIGA) Some MLAs are explicitly not allowed to be involved in ECA Exports Business Examples: EBRD & MIGA Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
II. The Rationale for EMECA No Dedicated Program to support Exports from Developing Countries Main Characteristics of the Official Financial Support to Developing Countries: • Bilateral & MLA Support is mainly provided to Public Sector in Developing Countries • Limited Support for Private Sector Development (Mainly IFC, MIGA) Some MLAs are explicitly not allowed to be involved in ECA Exports Business Examples: EBRD & MIGA Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 III. The Role of EMECA Mandate: Act as ECA & provide insurance / guarantees to Banks, EM exporters, Capital Market Financiers to support Trade between EM Location: EMECA should be located in AAA rated country Main Business Principles: • Support within framework International Rules (OECD Consensus, WTO Break even) • No Competition, but active Co-operation with the Market (Banks, EM Exporters, PRIs, Capital Market Investors) • Active Co-operation with other Official Agencies (MLAs, OECD ECAs & ECAs in EM, DAC Donor Agencies, Governments) Main Business Area: • Non Marketable risks (MLT): Main Role act as Insurer / Guarantor • Marketable risks (ST < 2 Year): Main Role act as intermediary for PRIs Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
III. The Role of EMECA Mandate: Act as ECA & provide insurance / guarantees to Banks, EM exporters, Capital Market Financiers to support Trade between EM Location: EMECA should be located in AAA rated country Main Business Principles: • Support within framework International Rules (OECD Consensus, WTO Break even) • No Competition, but active Co-operation with the Market (Banks, EM Exporters, PRIs, Capital Market Investors) • Active Co-operation with other Official Agencies (MLAs, OECD ECAs & ECAs in EM, DAC Donor Agencies, Governments) Main Business Area: • Non Marketable risks (MLT): Main Role act as Insurer / Guarantor • Marketable risks (ST < 2 Year): Main Role act as intermediary for PRIs Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 III. The Role of EMECA The main Benefits of EMECA Benefits for Emerging Markets (EM): • Trade is Sustainable Aid • Support Private Sector Development (e. g. EM Exporters) • Support Private Capital Flows to EM Borrowers • Enhance Trade & Investments between Emerging Markets (e. g. Intra Regional Trade, South / South Trade) • Increased Access to Stable MLT Finance • Improvement of Financial Infrastructure in EM - Local ECA & Bank Business / Expertise - Implementation of sound commercial business practices • Increase Local Knowledge re. Export Finance / Insurance • Positive Developmental Impact in two EM Exporting EM: Increase Hard Currency Income, Sustainable Jobs, Additional Tax Income Importing EM: Decrease of Import Costs • Increase Independence & Decrease Aid Dependency Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
III. The Role of EMECA The main Benefits of EMECA Benefits for Emerging Markets (EM): • Trade is Sustainable Aid • Support Private Sector Development (e. g. EM Exporters) • Support Private Capital Flows to EM Borrowers • Enhance Trade & Investments between Emerging Markets (e. g. Intra Regional Trade, South / South Trade) • Increased Access to Stable MLT Finance • Improvement of Financial Infrastructure in EM - Local ECA & Bank Business / Expertise - Implementation of sound commercial business practices • Increase Local Knowledge re. Export Finance / Insurance • Positive Developmental Impact in two EM Exporting EM: Increase Hard Currency Income, Sustainable Jobs, Additional Tax Income Importing EM: Decrease of Import Costs • Increase Independence & Decrease Aid Dependency Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 III. The Role of EMECA The main Benefits of EMECA Benefits for EM Exporters: • Level Playing Field with OECD Exporters • Financial Stability (exports = Hard Currency Income) Benefits for Banks: • Allow Banks to Finance MLT Trade Transactions between EM • Incentive for Banks to Originate Export Business in EM • Improved RAROC for Business with EM clients Benefits for Private Risk Insurers: • Co / Re - insurance opportunities with EMECA (e. g. MIGA CUP) • “Umbrella”- Protection EMECA Benefits for OECD Donor Countries: • Instrument to achieve Sustainable Development & UN Millennium Goals • Increase Aid Efficiency Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
III. The Role of EMECA The main Benefits of EMECA Benefits for EM Exporters: • Level Playing Field with OECD Exporters • Financial Stability (exports = Hard Currency Income) Benefits for Banks: • Allow Banks to Finance MLT Trade Transactions between EM • Incentive for Banks to Originate Export Business in EM • Improved RAROC for Business with EM clients Benefits for Private Risk Insurers: • Co / Re - insurance opportunities with EMECA (e. g. MIGA CUP) • “Umbrella”- Protection EMECA Benefits for OECD Donor Countries: • Instrument to achieve Sustainable Development & UN Millennium Goals • Increase Aid Efficiency Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 III. The Role of EMECA Ranking Emerging Markets & Capital Goods Exports No. 1 - 10 (Average Exports 1995 - 1999) Exports of Machinery and Transport Equipment in million US$ (SITC 7) Source: Unctad Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
III. The Role of EMECA Ranking Emerging Markets & Capital Goods Exports No. 1 - 10 (Average Exports 1995 - 1999) Exports of Machinery and Transport Equipment in million US$ (SITC 7) Source: Unctad Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 III. The Role of EMECA Ranking Emerging Markets & Capital Goods Exports No. 10 - 20 (Average Exports 1995 -1999) Exports of Machinery and Transport Equipment in million US$ (SITC 7) Source: Unctad Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
III. The Role of EMECA Ranking Emerging Markets & Capital Goods Exports No. 10 - 20 (Average Exports 1995 -1999) Exports of Machinery and Transport Equipment in million US$ (SITC 7) Source: Unctad Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 III. The Role of EMECA Ranking Emerging Markets & Capital Goods Exports No. 20 - 30 (Average Exports 1995 -1999) Exports of Machinery and Transport Equipment in million US$ (SITC 7) Source: Unctad Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
III. The Role of EMECA Ranking Emerging Markets & Capital Goods Exports No. 20 - 30 (Average Exports 1995 -1999) Exports of Machinery and Transport Equipment in million US$ (SITC 7) Source: Unctad Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 III. The Role of EMECA Source: OECD & IMF Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
III. The Role of EMECA Source: OECD & IMF Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 IV. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market Some examples of Public & Private Sector risk Participation: 1. Equity participation by public & private sector 2. Treaty Re-insurance 3. Partial Credit Insurance 4. Partial Risk Insurance 5. Country risk specific risk sharing Public / Private Sector 6. Risk participation by the Insured (private sector) These risk sharing arrangements do show the Huge leverage potential of EMECA Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
IV. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market Some examples of Public & Private Sector risk Participation: 1. Equity participation by public & private sector 2. Treaty Re-insurance 3. Partial Credit Insurance 4. Partial Risk Insurance 5. Country risk specific risk sharing Public / Private Sector 6. Risk participation by the Insured (private sector) These risk sharing arrangements do show the Huge leverage potential of EMECA Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
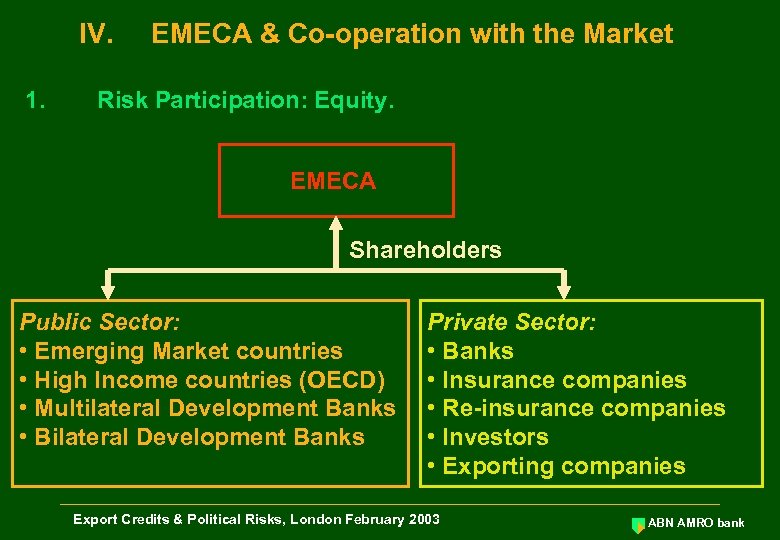 IV. 1. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market Risk Participation: Equity. EMECA Shareholders Public Sector: • Emerging Market countries • High Income countries (OECD) • Multilateral Development Banks • Bilateral Development Banks Private Sector: • Banks • Insurance companies • Re-insurance companies • Investors • Exporting companies Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
IV. 1. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market Risk Participation: Equity. EMECA Shareholders Public Sector: • Emerging Market countries • High Income countries (OECD) • Multilateral Development Banks • Bilateral Development Banks Private Sector: • Banks • Insurance companies • Re-insurance companies • Investors • Exporting companies Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
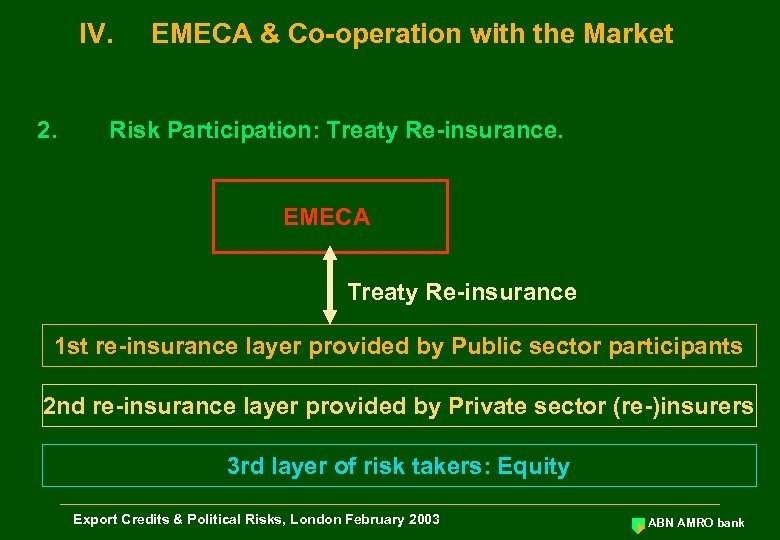 IV. 2. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market Risk Participation: Treaty Re-insurance. EMECA Treaty Re-insurance 1 st re-insurance layer provided by Public sector participants 2 nd re-insurance layer provided by Private sector (re-)insurers 3 rd layer of risk takers: Equity Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
IV. 2. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market Risk Participation: Treaty Re-insurance. EMECA Treaty Re-insurance 1 st re-insurance layer provided by Public sector participants 2 nd re-insurance layer provided by Private sector (re-)insurers 3 rd layer of risk takers: Equity Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
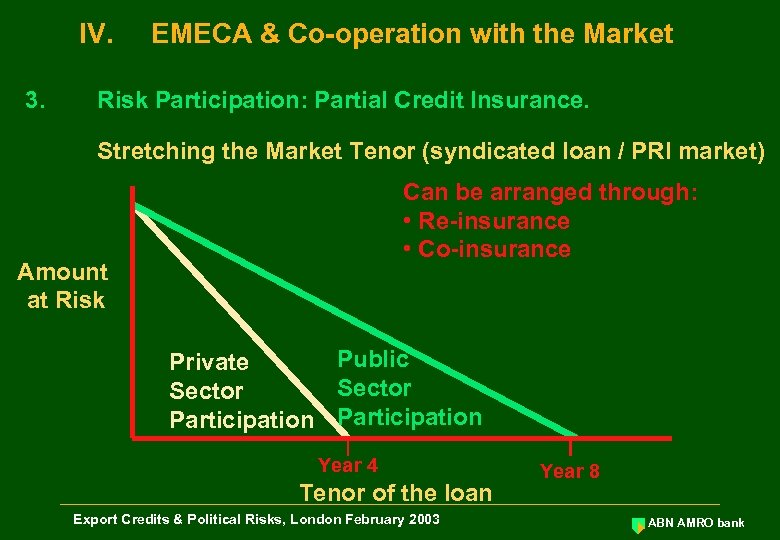 IV. 3. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market Risk Participation: Partial Credit Insurance. Stretching the Market Tenor (syndicated loan / PRI market) Can be arranged through: • Re-insurance • Co-insurance Amount at Risk Public Private Sector Participation Year 4 Tenor of the loan Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 Year 8 ABN AMRO bank
IV. 3. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market Risk Participation: Partial Credit Insurance. Stretching the Market Tenor (syndicated loan / PRI market) Can be arranged through: • Re-insurance • Co-insurance Amount at Risk Public Private Sector Participation Year 4 Tenor of the loan Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 Year 8 ABN AMRO bank
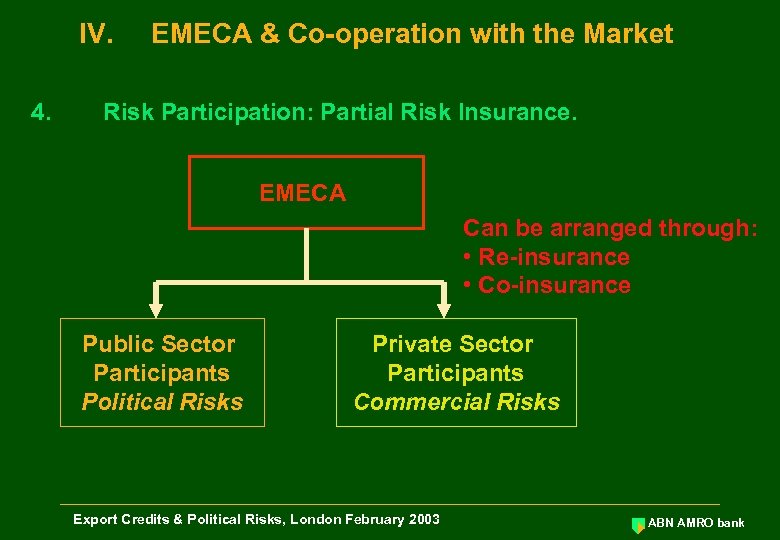 IV. 4. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market Risk Participation: Partial Risk Insurance. EMECA Can be arranged through: • Re-insurance • Co-insurance Public Sector Participants Political Risks Private Sector Participants Commercial Risks Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
IV. 4. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market Risk Participation: Partial Risk Insurance. EMECA Can be arranged through: • Re-insurance • Co-insurance Public Sector Participants Political Risks Private Sector Participants Commercial Risks Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 IV. 5. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market Country risk specific risk sharing Public / Private Sector. % Share in Risk OECD Country risk category Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
IV. 5. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market Country risk specific risk sharing Public / Private Sector. % Share in Risk OECD Country risk category Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
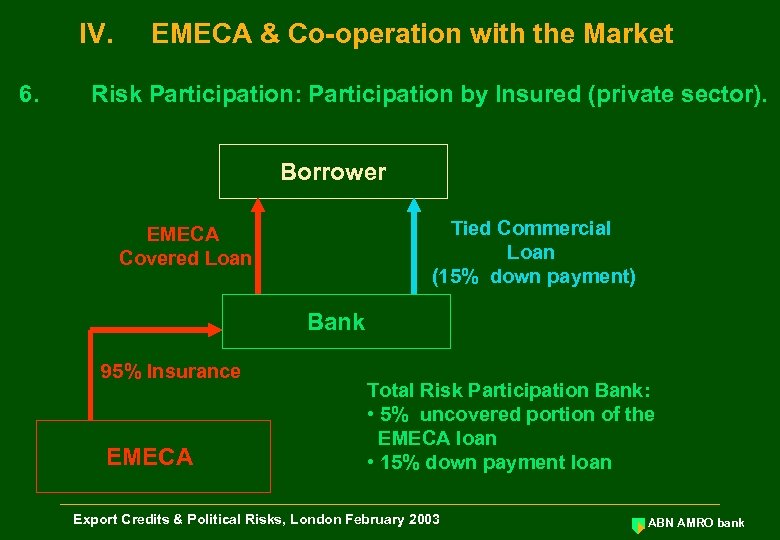 IV. 6. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market Risk Participation: Participation by Insured (private sector). Borrower Tied Commercial Loan (15% down payment) EMECA Covered Loan Bank 95% Insurance EMECA Total Risk Participation Bank: • 5% uncovered portion of the EMECA loan • 15% down payment loan Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
IV. 6. EMECA & Co-operation with the Market Risk Participation: Participation by Insured (private sector). Borrower Tied Commercial Loan (15% down payment) EMECA Covered Loan Bank 95% Insurance EMECA Total Risk Participation Bank: • 5% uncovered portion of the EMECA loan • 15% down payment loan Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 IV. Summary & Conclusions EMECA is Key for Sustainable Development of Emerging Markets Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
IV. Summary & Conclusions EMECA is Key for Sustainable Development of Emerging Markets Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 ABN AMRO Bank ABN AMRO bank
ABN AMRO Bank ABN AMRO bank
 Annex I Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
Annex I Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 Annex I Severely Indebted Low-Income Countries Debt in Billions US$m Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
Annex I Severely Indebted Low-Income Countries Debt in Billions US$m Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 Annex I Debt Indicators: Severely Indebted Low-Income Countries EDT /XGS: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Exports Goods & Services EDT/GNI: NPV External Debt as a% of annual Gross National Income Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
Annex I Debt Indicators: Severely Indebted Low-Income Countries EDT /XGS: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Exports Goods & Services EDT/GNI: NPV External Debt as a% of annual Gross National Income Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 Annex II Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
Annex II Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 Annex II Severely Indebted Middle-Income Countries Debt in Billion US$ Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
Annex II Severely Indebted Middle-Income Countries Debt in Billion US$ Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 Annex II Debt Indicators: Severely Indebted Middle-Income Countries EDT /XGS: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Exports Goods & Services EDT/GNI: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Gross National Income Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
Annex II Debt Indicators: Severely Indebted Middle-Income Countries EDT /XGS: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Exports Goods & Services EDT/GNI: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Gross National Income Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 Annex II Moderately Indebted Low-Income Countries Debt in Billion US$ Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
Annex II Moderately Indebted Low-Income Countries Debt in Billion US$ Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 Annex II Debt Indicators: Moderately Indebted Low-Income Countries EDT /XGS: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Exports Goods & Services EDT/GNI: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Gross National Income Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
Annex II Debt Indicators: Moderately Indebted Low-Income Countries EDT /XGS: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Exports Goods & Services EDT/GNI: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Gross National Income Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 Annex III Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
Annex III Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 Annex III Moderately Indebted Middle-Income Countries Debt in Billion US$ Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
Annex III Moderately Indebted Middle-Income Countries Debt in Billion US$ Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
 Annex III Debt Indicators: Moderately Indebted Middle-Income Countries EDT /XGS: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Exports Goods & Services EDT/GNI: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Gross National Income Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank
Annex III Debt Indicators: Moderately Indebted Middle-Income Countries EDT /XGS: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Exports Goods & Services EDT/GNI: NPV External Debt as a % of annual Gross National Income Export Credits & Political Risks, London February 2003 ABN AMRO bank


