2e2294922c1405d8f76de599c8083911.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Structured Query Language Agenda: - SQL commands for DB definition - SQL DML commands - VIEWS and security control using SQL
Structured Query Language Agenda: - SQL commands for DB definition - SQL DML commands - VIEWS and security control using SQL
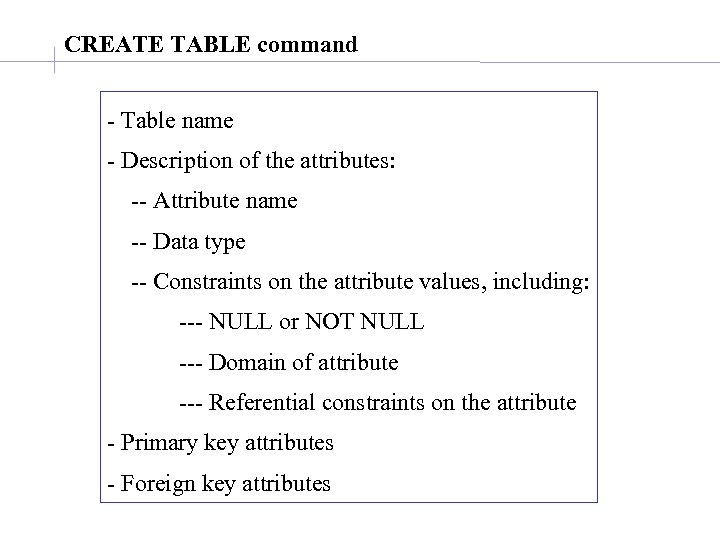 CREATE TABLE command - Table name - Description of the attributes: -- Attribute name -- Data type -- Constraints on the attribute values, including: --- NULL or NOT NULL --- Domain of attribute --- Referential constraints on the attribute - Primary key attributes - Foreign key attributes
CREATE TABLE command - Table name - Description of the attributes: -- Attribute name -- Data type -- Constraints on the attribute values, including: --- NULL or NOT NULL --- Domain of attribute --- Referential constraints on the attribute - Primary key attributes - Foreign key attributes
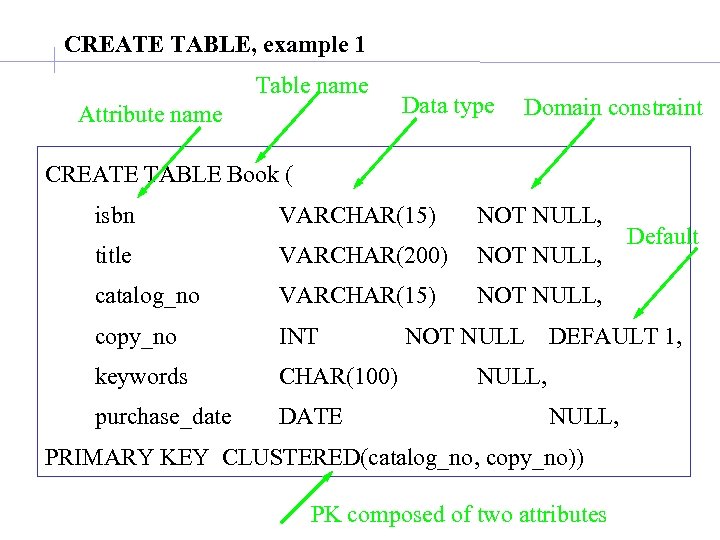 CREATE TABLE, example 1 Table name Attribute name Data type Domain constraint CREATE TABLE Book ( isbn VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL, title VARCHAR(200) NOT NULL, catalog_no VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL, copy_no INT keywords CHAR(100) purchase_date DATE NOT NULL Default DEFAULT 1, NULL, PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED(catalog_no, copy_no)) PK composed of two attributes
CREATE TABLE, example 1 Table name Attribute name Data type Domain constraint CREATE TABLE Book ( isbn VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL, title VARCHAR(200) NOT NULL, catalog_no VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL, copy_no INT keywords CHAR(100) purchase_date DATE NOT NULL Default DEFAULT 1, NULL, PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED(catalog_no, copy_no)) PK composed of two attributes
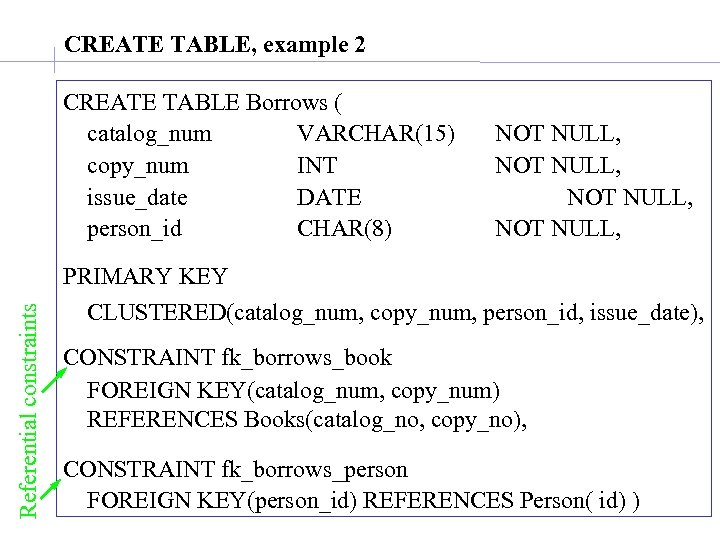 CREATE TABLE, example 2 Referential constraints CREATE TABLE Borrows ( catalog_num VARCHAR(15) copy_num INT issue_date DATE person_id CHAR(8) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED(catalog_num, copy_num, person_id, issue_date), CONSTRAINT fk_borrows_book FOREIGN KEY(catalog_num, copy_num) REFERENCES Books(catalog_no, copy_no), CONSTRAINT fk_borrows_person FOREIGN KEY(person_id) REFERENCES Person( id) )
CREATE TABLE, example 2 Referential constraints CREATE TABLE Borrows ( catalog_num VARCHAR(15) copy_num INT issue_date DATE person_id CHAR(8) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED(catalog_num, copy_num, person_id, issue_date), CONSTRAINT fk_borrows_book FOREIGN KEY(catalog_num, copy_num) REFERENCES Books(catalog_no, copy_no), CONSTRAINT fk_borrows_person FOREIGN KEY(person_id) REFERENCES Person( id) )
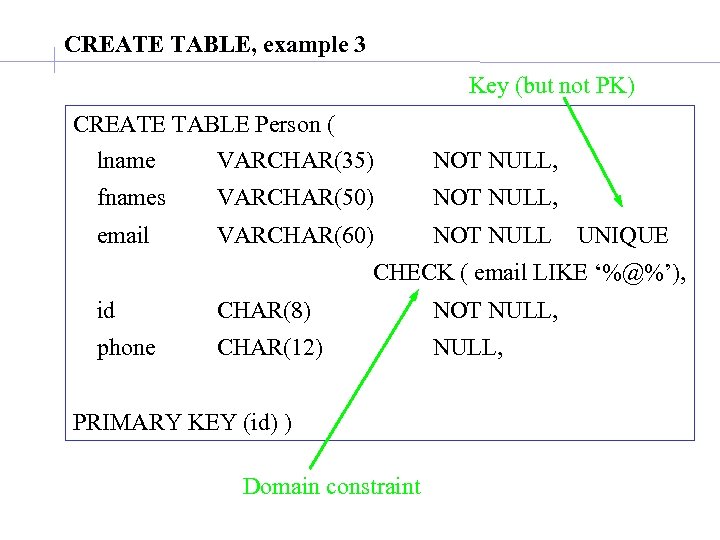 CREATE TABLE, example 3 Key (but not PK) CREATE TABLE Person ( lname VARCHAR(35) NOT NULL, fnames VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, email VARCHAR(60) NOT NULL UNIQUE CHECK ( email LIKE ‘%@%’), id CHAR(8) NOT NULL, phone CHAR(12) NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id) ) Domain constraint
CREATE TABLE, example 3 Key (but not PK) CREATE TABLE Person ( lname VARCHAR(35) NOT NULL, fnames VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, email VARCHAR(60) NOT NULL UNIQUE CHECK ( email LIKE ‘%@%’), id CHAR(8) NOT NULL, phone CHAR(12) NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id) ) Domain constraint
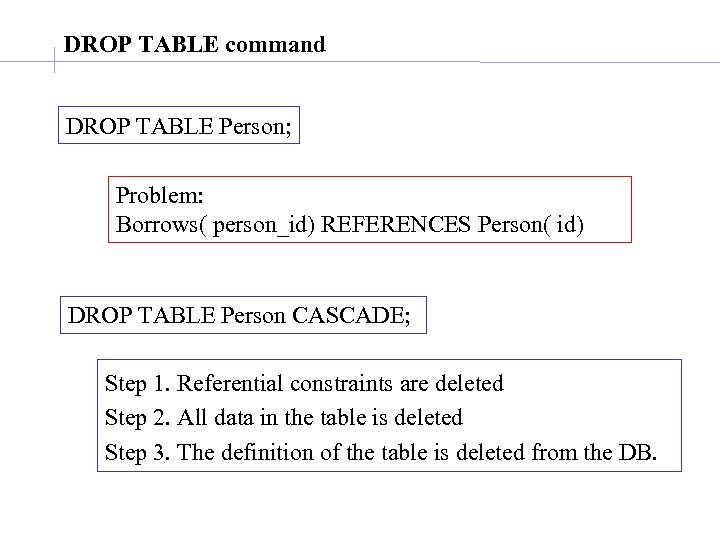 DROP TABLE command DROP TABLE Person; Problem: Borrows( person_id) REFERENCES Person( id) DROP TABLE Person CASCADE; Step 1. Referential constraints are deleted Step 2. All data in the table is deleted Step 3. The definition of the table is deleted from the DB.
DROP TABLE command DROP TABLE Person; Problem: Borrows( person_id) REFERENCES Person( id) DROP TABLE Person CASCADE; Step 1. Referential constraints are deleted Step 2. All data in the table is deleted Step 3. The definition of the table is deleted from the DB.
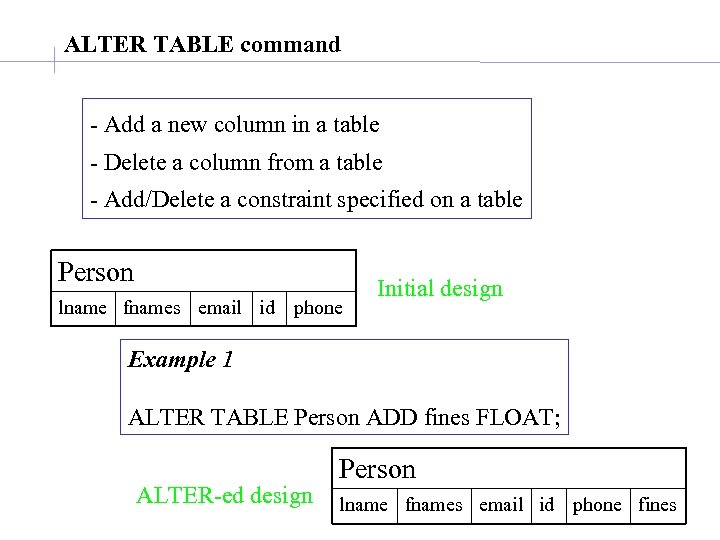 ALTER TABLE command - Add a new column in a table - Delete a column from a table - Add/Delete a constraint specified on a table Person lname fnames email id phone Initial design Example 1 ALTER TABLE Person ADD fines FLOAT; ALTER-ed design Person lname fnames email id phone fines
ALTER TABLE command - Add a new column in a table - Delete a column from a table - Add/Delete a constraint specified on a table Person lname fnames email id phone Initial design Example 1 ALTER TABLE Person ADD fines FLOAT; ALTER-ed design Person lname fnames email id phone fines
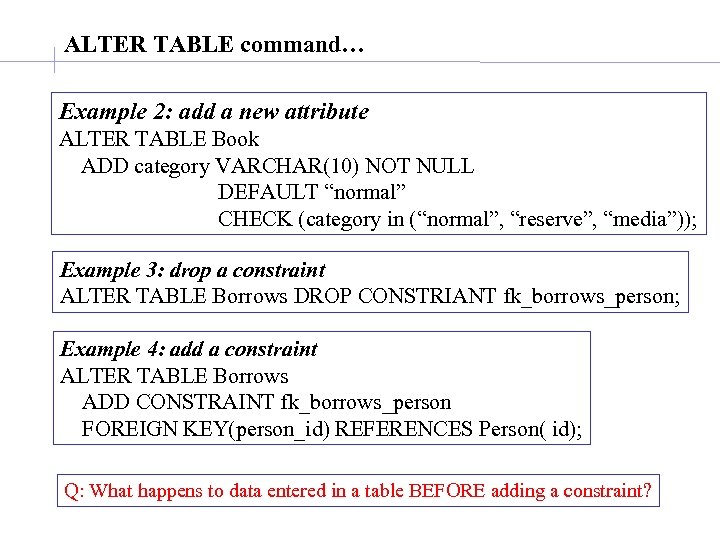 ALTER TABLE command… Example 2: add a new attribute ALTER TABLE Book ADD category VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT “normal” CHECK (category in (“normal”, “reserve”, “media”)); Example 3: drop a constraint ALTER TABLE Borrows DROP CONSTRIANT fk_borrows_person; Example 4: add a constraint ALTER TABLE Borrows ADD CONSTRAINT fk_borrows_person FOREIGN KEY(person_id) REFERENCES Person( id); Q: What happens to data entered in a table BEFORE adding a constraint?
ALTER TABLE command… Example 2: add a new attribute ALTER TABLE Book ADD category VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT “normal” CHECK (category in (“normal”, “reserve”, “media”)); Example 3: drop a constraint ALTER TABLE Borrows DROP CONSTRIANT fk_borrows_person; Example 4: add a constraint ALTER TABLE Borrows ADD CONSTRAINT fk_borrows_person FOREIGN KEY(person_id) REFERENCES Person( id); Q: What happens to data entered in a table BEFORE adding a constraint?
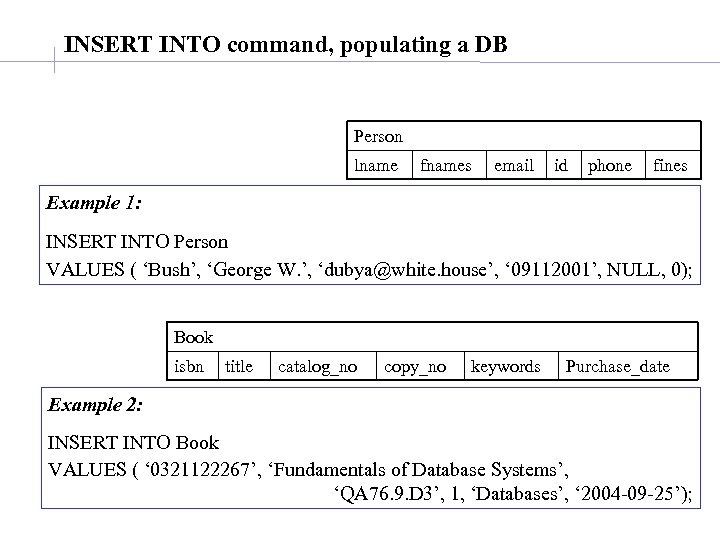 INSERT INTO command, populating a DB Person lname fnames email id phone fines Example 1: INSERT INTO Person VALUES ( ‘Bush’, ‘George W. ’, ‘dubya@white. house’, ‘ 09112001’, NULL, 0); Book isbn title catalog_no copy_no keywords Purchase_date Example 2: INSERT INTO Book VALUES ( ‘ 0321122267’, ‘Fundamentals of Database Systems’, ‘QA 76. 9. D 3’, 1, ‘Databases’, ‘ 2004 -09 -25’);
INSERT INTO command, populating a DB Person lname fnames email id phone fines Example 1: INSERT INTO Person VALUES ( ‘Bush’, ‘George W. ’, ‘dubya@white. house’, ‘ 09112001’, NULL, 0); Book isbn title catalog_no copy_no keywords Purchase_date Example 2: INSERT INTO Book VALUES ( ‘ 0321122267’, ‘Fundamentals of Database Systems’, ‘QA 76. 9. D 3’, 1, ‘Databases’, ‘ 2004 -09 -25’);
 DELETE FROM command - to delete one or more rows of data from a table Example 1: DELETE FROM Person WHERE id= ‘ 09112001’; Example 2: DELETE FROM Person WHERE lname=’Bush’; Example 3: DELETE FROM Borrows WHERE 1
DELETE FROM command - to delete one or more rows of data from a table Example 1: DELETE FROM Person WHERE id= ‘ 09112001’; Example 2: DELETE FROM Person WHERE lname=’Bush’; Example 3: DELETE FROM Borrows WHERE 1
 DELETE FROM command … Example 4: DELETE FROM Borrows WHERE person_id IN (“ 09112001”, “ 55554444”, “ 12345678”); Example 5: DELETE FROM Borrows WHERE person_id IN ( SELECT id FROM Person WHERE lname= ‘Bush’);
DELETE FROM command … Example 4: DELETE FROM Borrows WHERE person_id IN (“ 09112001”, “ 55554444”, “ 12345678”); Example 5: DELETE FROM Borrows WHERE person_id IN ( SELECT id FROM Person WHERE lname= ‘Bush’);
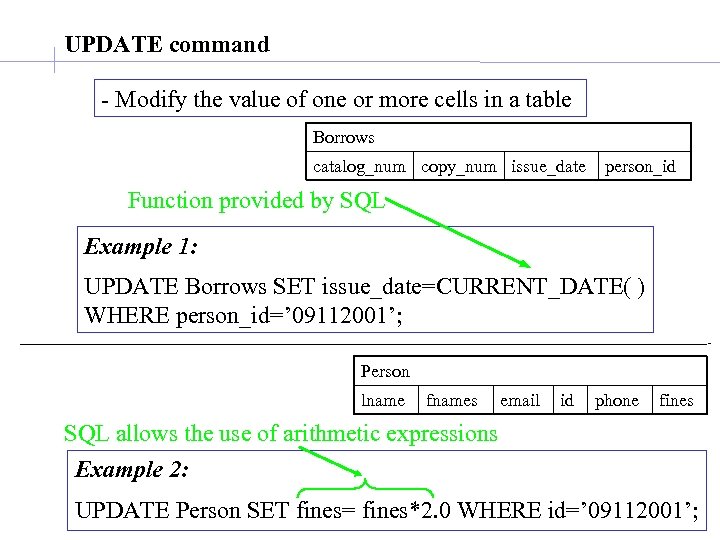 UPDATE command - Modify the value of one or more cells in a table Borrows catalog_num copy_num issue_date person_id Function provided by SQL Example 1: UPDATE Borrows SET issue_date=CURRENT_DATE( ) WHERE person_id=’ 09112001’; Person lname fnames email id phone fines SQL allows the use of arithmetic expressions Example 2: UPDATE Person SET fines= fines*2. 0 WHERE id=’ 09112001’;
UPDATE command - Modify the value of one or more cells in a table Borrows catalog_num copy_num issue_date person_id Function provided by SQL Example 1: UPDATE Borrows SET issue_date=CURRENT_DATE( ) WHERE person_id=’ 09112001’; Person lname fnames email id phone fines SQL allows the use of arithmetic expressions Example 2: UPDATE Person SET fines= fines*2. 0 WHERE id=’ 09112001’;
 SELECT command - Output required information from one or more tables For the following examples (unless stated otherwise): - Use the EMPLOYEE-DEPARTMENT-PROJECTS database - Assume the initial data in the tables as provided earlier
SELECT command - Output required information from one or more tables For the following examples (unless stated otherwise): - Use the EMPLOYEE-DEPARTMENT-PROJECTS database - Assume the initial data in the tables as provided earlier
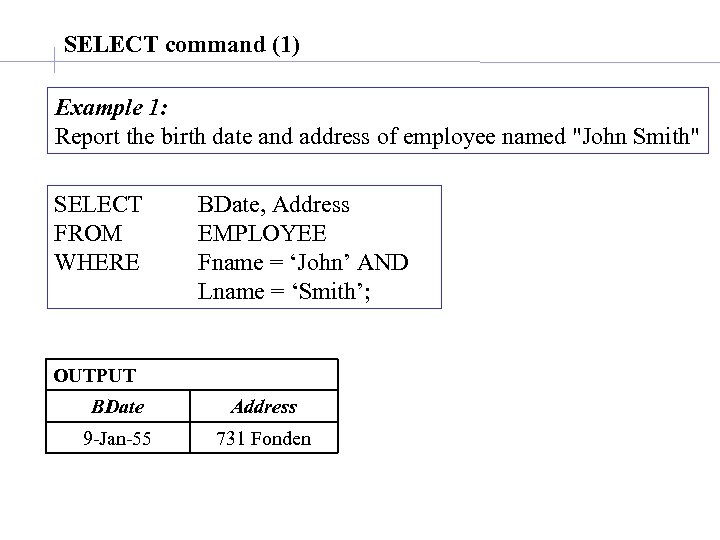 SELECT command (1) Example 1: Report the birth date and address of employee named "John Smith" SELECT FROM WHERE BDate, Address EMPLOYEE Fname = ‘John’ AND Lname = ‘Smith’; OUTPUT BDate Address 9 -Jan-55 731 Fonden
SELECT command (1) Example 1: Report the birth date and address of employee named "John Smith" SELECT FROM WHERE BDate, Address EMPLOYEE Fname = ‘John’ AND Lname = ‘Smith’; OUTPUT BDate Address 9 -Jan-55 731 Fonden
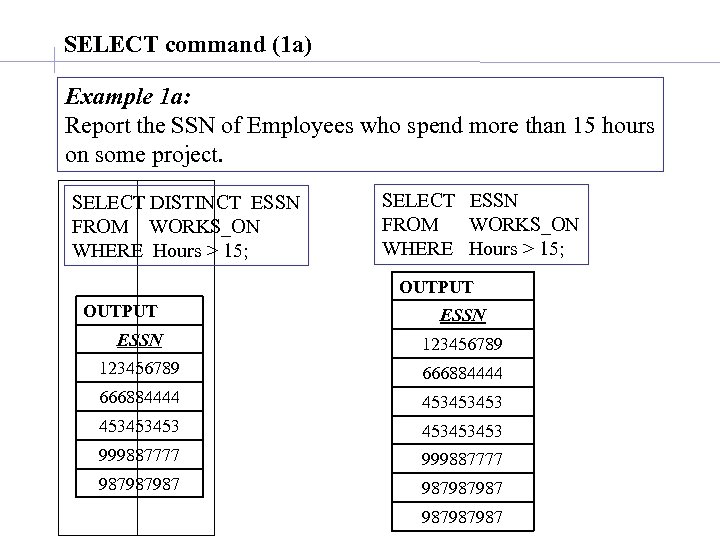 SELECT command (1 a) Example 1 a: Report the SSN of Employees who spend more than 15 hours on some project. SELECT DISTINCT ESSN FROM WORKS_ON WHERE Hours > 15; SELECT ESSN FROM WORKS_ON WHERE Hours > 15; OUTPUT ESSN 123456789 666884444 453453453 999887777 987987987
SELECT command (1 a) Example 1 a: Report the SSN of Employees who spend more than 15 hours on some project. SELECT DISTINCT ESSN FROM WORKS_ON WHERE Hours > 15; SELECT ESSN FROM WORKS_ON WHERE Hours > 15; OUTPUT ESSN 123456789 666884444 453453453 999887777 987987987
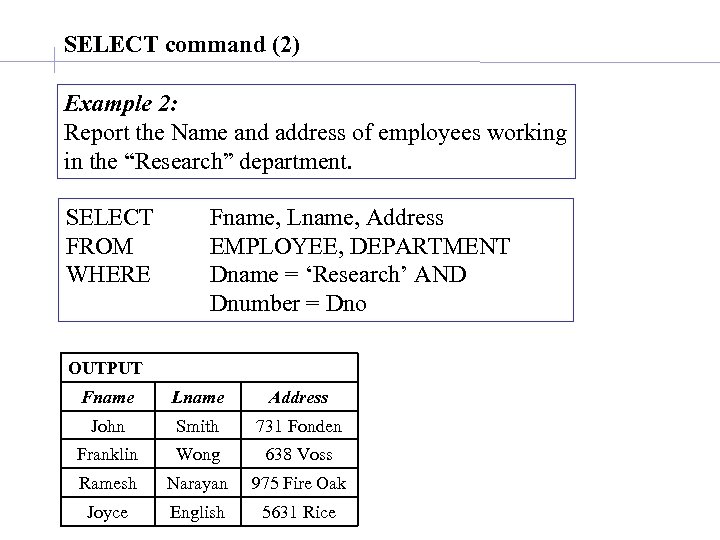 SELECT command (2) Example 2: Report the Name and address of employees working in the “Research” department. SELECT FROM WHERE Fname, Lname, Address EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT Dname = ‘Research’ AND Dnumber = Dno OUTPUT Fname Lname Address John Smith 731 Fonden Franklin Wong 638 Voss Ramesh Narayan 975 Fire Oak Joyce English 5631 Rice
SELECT command (2) Example 2: Report the Name and address of employees working in the “Research” department. SELECT FROM WHERE Fname, Lname, Address EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT Dname = ‘Research’ AND Dnumber = Dno OUTPUT Fname Lname Address John Smith 731 Fonden Franklin Wong 638 Voss Ramesh Narayan 975 Fire Oak Joyce English 5631 Rice
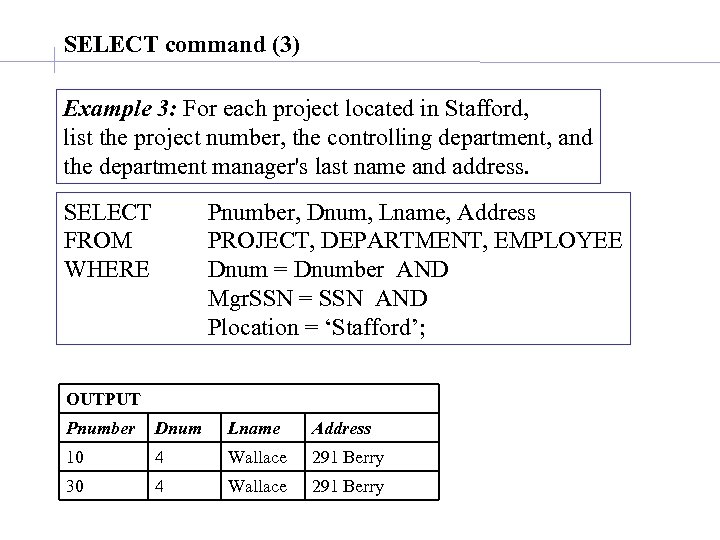 SELECT command (3) Example 3: For each project located in Stafford, list the project number, the controlling department, and the department manager's last name and address. SELECT FROM WHERE Pnumber, Dnum, Lname, Address PROJECT, DEPARTMENT, EMPLOYEE Dnum = Dnumber AND Mgr. SSN = SSN AND Plocation = ‘Stafford’; OUTPUT Pnumber Dnum Lname Address 10 4 Wallace 291 Berry 30 4 Wallace 291 Berry
SELECT command (3) Example 3: For each project located in Stafford, list the project number, the controlling department, and the department manager's last name and address. SELECT FROM WHERE Pnumber, Dnum, Lname, Address PROJECT, DEPARTMENT, EMPLOYEE Dnum = Dnumber AND Mgr. SSN = SSN AND Plocation = ‘Stafford’; OUTPUT Pnumber Dnum Lname Address 10 4 Wallace 291 Berry 30 4 Wallace 291 Berry
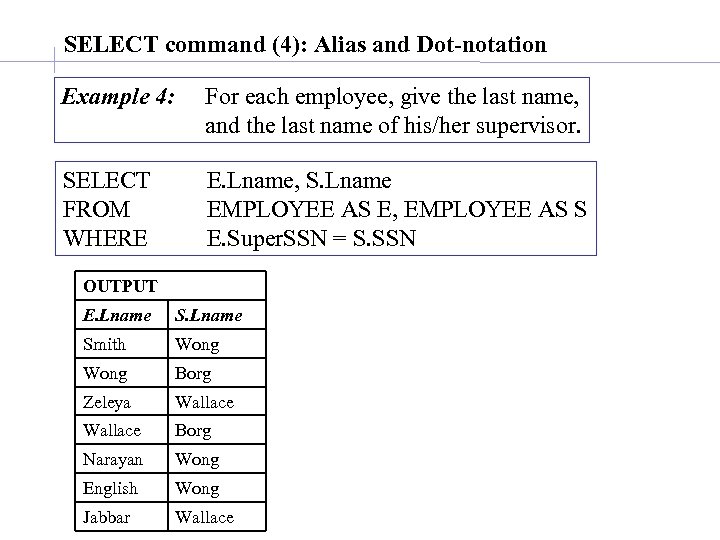 SELECT command (4): Alias and Dot-notation Example 4: For each employee, give the last name, and the last name of his/her supervisor. SELECT FROM WHERE E. Lname, S. Lname EMPLOYEE AS E, EMPLOYEE AS S E. Super. SSN = S. SSN OUTPUT E. Lname Smith Wong Borg Zeleya Wallace Borg Narayan Wong English Wong Jabbar Wallace
SELECT command (4): Alias and Dot-notation Example 4: For each employee, give the last name, and the last name of his/her supervisor. SELECT FROM WHERE E. Lname, S. Lname EMPLOYEE AS E, EMPLOYEE AS S E. Super. SSN = S. SSN OUTPUT E. Lname Smith Wong Borg Zeleya Wallace Borg Narayan Wong English Wong Jabbar Wallace
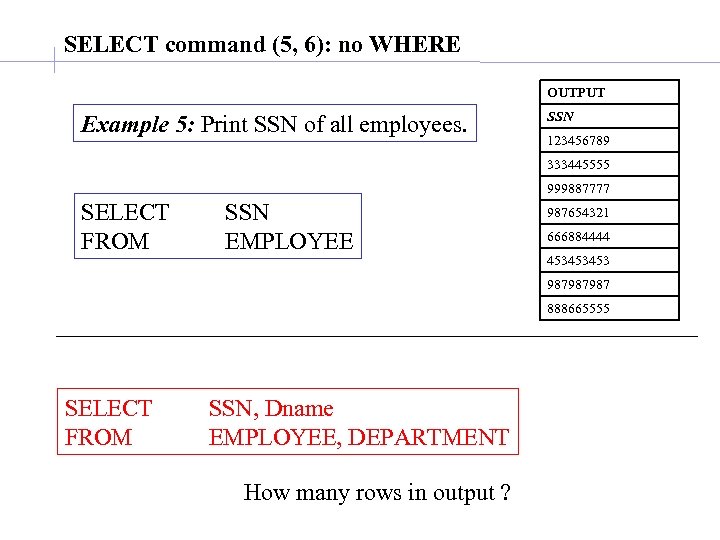 SELECT command (5, 6): no WHERE OUTPUT Example 5: Print SSN of all employees. SSN 123456789 333445555 999887777 SELECT FROM SSN EMPLOYEE 987654321 666884444 453453453 987987987 888665555 SELECT FROM SSN, Dname EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT How many rows in output ?
SELECT command (5, 6): no WHERE OUTPUT Example 5: Print SSN of all employees. SSN 123456789 333445555 999887777 SELECT FROM SSN EMPLOYEE 987654321 666884444 453453453 987987987 888665555 SELECT FROM SSN, Dname EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT How many rows in output ?
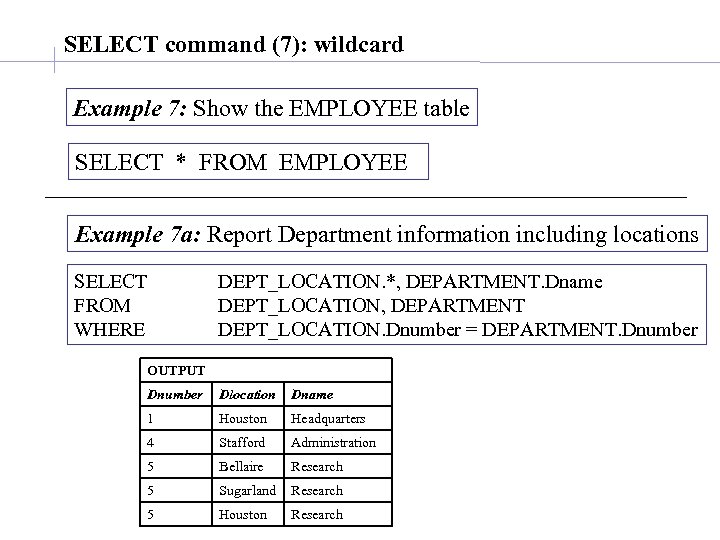 SELECT command (7): wildcard Example 7: Show the EMPLOYEE table SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE Example 7 a: Report Department information including locations SELECT FROM WHERE DEPT_LOCATION. *, DEPARTMENT. Dname DEPT_LOCATION, DEPARTMENT DEPT_LOCATION. Dnumber = DEPARTMENT. Dnumber OUTPUT Dnumber Dlocation Dname 1 Houston Headquarters 4 Stafford Administration 5 Bellaire Research 5 Sugarland Research 5 Houston Research
SELECT command (7): wildcard Example 7: Show the EMPLOYEE table SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE Example 7 a: Report Department information including locations SELECT FROM WHERE DEPT_LOCATION. *, DEPARTMENT. Dname DEPT_LOCATION, DEPARTMENT DEPT_LOCATION. Dnumber = DEPARTMENT. Dnumber OUTPUT Dnumber Dlocation Dname 1 Houston Headquarters 4 Stafford Administration 5 Bellaire Research 5 Sugarland Research 5 Houston Research
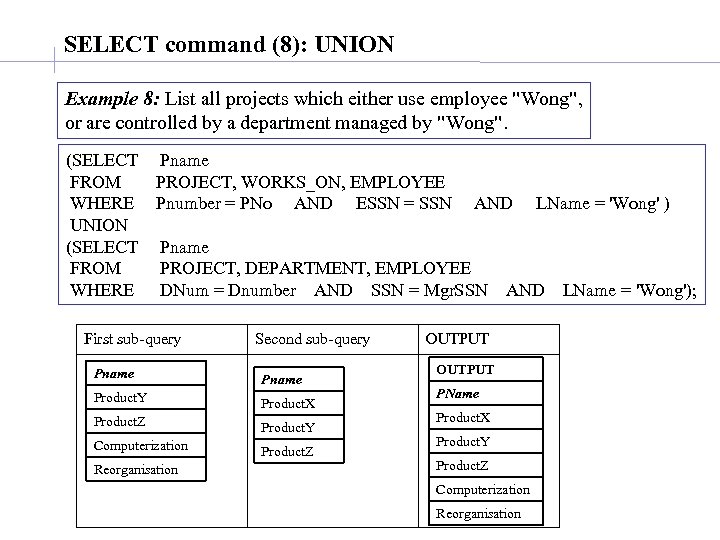 SELECT command (8): UNION Example 8: List all projects which either use employee "Wong", or are controlled by a department managed by "Wong". (SELECT FROM WHERE UNION (SELECT FROM WHERE Pname PROJECT, WORKS_ON, EMPLOYEE Pnumber = PNo AND ESSN = SSN AND Pname PROJECT, DEPARTMENT, EMPLOYEE DNum = Dnumber AND SSN = Mgr. SSN First sub-query Second sub-query Pname Product. Y Product. X Product. Z Product. Y Computerization Product. Z Reorganisation LName = 'Wong' ) AND OUTPUT PName Product. X Product. Y Product. Z Computerization Reorganisation LName = 'Wong');
SELECT command (8): UNION Example 8: List all projects which either use employee "Wong", or are controlled by a department managed by "Wong". (SELECT FROM WHERE UNION (SELECT FROM WHERE Pname PROJECT, WORKS_ON, EMPLOYEE Pnumber = PNo AND ESSN = SSN AND Pname PROJECT, DEPARTMENT, EMPLOYEE DNum = Dnumber AND SSN = Mgr. SSN First sub-query Second sub-query Pname Product. Y Product. X Product. Z Product. Y Computerization Product. Z Reorganisation LName = 'Wong' ) AND OUTPUT PName Product. X Product. Y Product. Z Computerization Reorganisation LName = 'Wong');
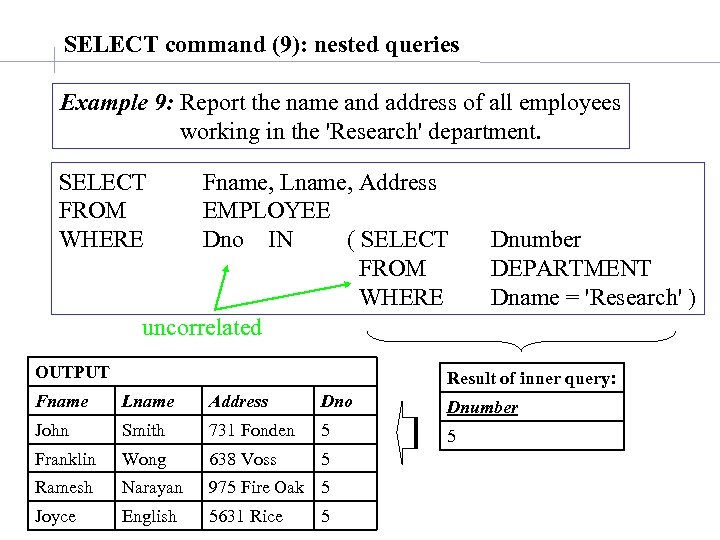 SELECT command (9): nested queries Example 9: Report the name and address of all employees working in the 'Research' department. SELECT FROM WHERE Fname, Lname, Address EMPLOYEE Dno IN ( SELECT FROM WHERE uncorrelated OUTPUT Dnumber DEPARTMENT Dname = 'Research' ) Result of inner query: Fname Lname Address Dno Dnumber John Smith 731 Fonden 5 5 Franklin Wong 638 Voss 5 Ramesh Narayan 975 Fire Oak 5 Joyce English 5631 Rice 5
SELECT command (9): nested queries Example 9: Report the name and address of all employees working in the 'Research' department. SELECT FROM WHERE Fname, Lname, Address EMPLOYEE Dno IN ( SELECT FROM WHERE uncorrelated OUTPUT Dnumber DEPARTMENT Dname = 'Research' ) Result of inner query: Fname Lname Address Dno Dnumber John Smith 731 Fonden 5 5 Franklin Wong 638 Voss 5 Ramesh Narayan 975 Fire Oak 5 Joyce English 5631 Rice 5
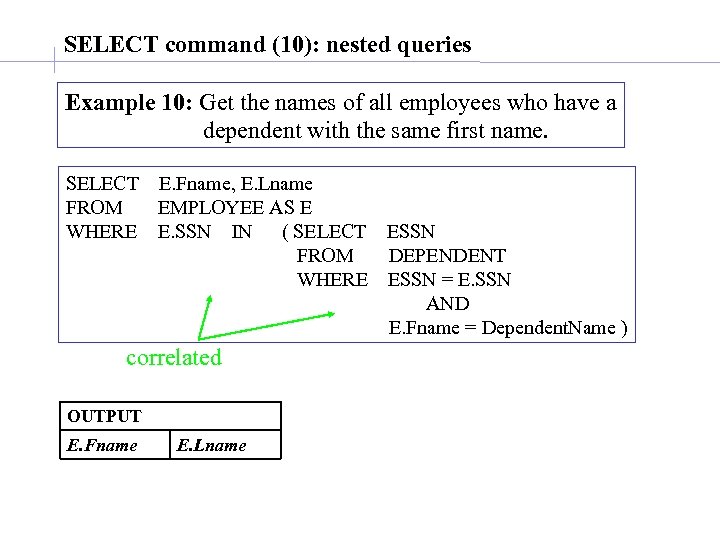 SELECT command (10): nested queries Example 10: Get the names of all employees who have a dependent with the same first name. SELECT E. Fname, E. Lname FROM EMPLOYEE AS E WHERE E. SSN IN ( SELECT ESSN FROM DEPENDENT WHERE ESSN = E. SSN AND E. Fname = Dependent. Name ) correlated OUTPUT E. Fname E. Lname
SELECT command (10): nested queries Example 10: Get the names of all employees who have a dependent with the same first name. SELECT E. Fname, E. Lname FROM EMPLOYEE AS E WHERE E. SSN IN ( SELECT ESSN FROM DEPENDENT WHERE ESSN = E. SSN AND E. Fname = Dependent. Name ) correlated OUTPUT E. Fname E. Lname
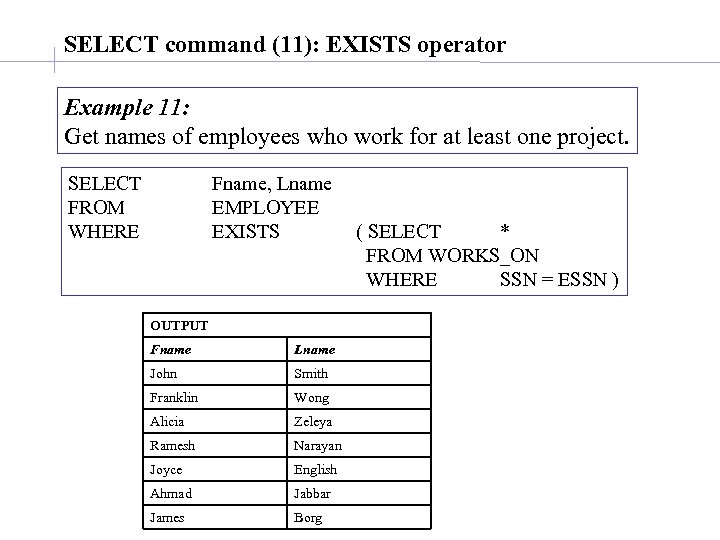 SELECT command (11): EXISTS operator Example 11: Get names of employees who work for at least one project. SELECT FROM WHERE Fname, Lname EMPLOYEE EXISTS OUTPUT Fname Lname John Smith Franklin Wong Alicia Zeleya Ramesh Narayan Joyce English Ahmad Jabbar James Borg ( SELECT * FROM WORKS_ON WHERE SSN = ESSN )
SELECT command (11): EXISTS operator Example 11: Get names of employees who work for at least one project. SELECT FROM WHERE Fname, Lname EMPLOYEE EXISTS OUTPUT Fname Lname John Smith Franklin Wong Alicia Zeleya Ramesh Narayan Joyce English Ahmad Jabbar James Borg ( SELECT * FROM WORKS_ON WHERE SSN = ESSN )
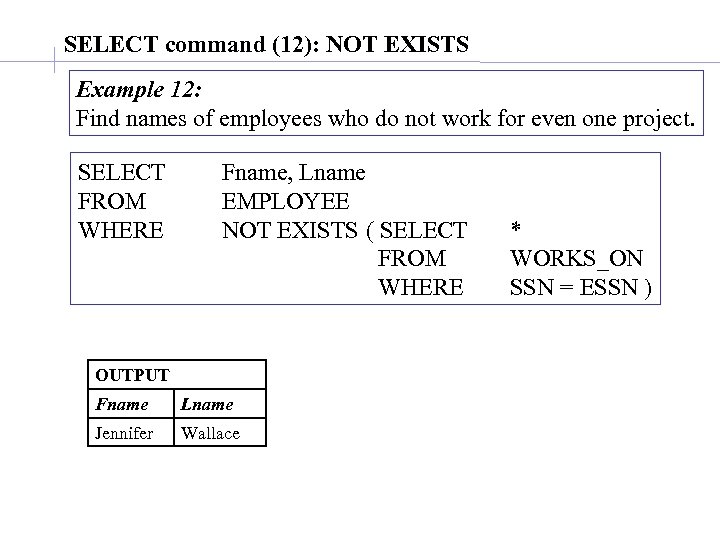 SELECT command (12): NOT EXISTS Example 12: Find names of employees who do not work for even one project. SELECT FROM WHERE Fname, Lname EMPLOYEE NOT EXISTS ( SELECT FROM WHERE OUTPUT Fname Lname Jennifer Wallace * WORKS_ON SSN = ESSN )
SELECT command (12): NOT EXISTS Example 12: Find names of employees who do not work for even one project. SELECT FROM WHERE Fname, Lname EMPLOYEE NOT EXISTS ( SELECT FROM WHERE OUTPUT Fname Lname Jennifer Wallace * WORKS_ON SSN = ESSN )
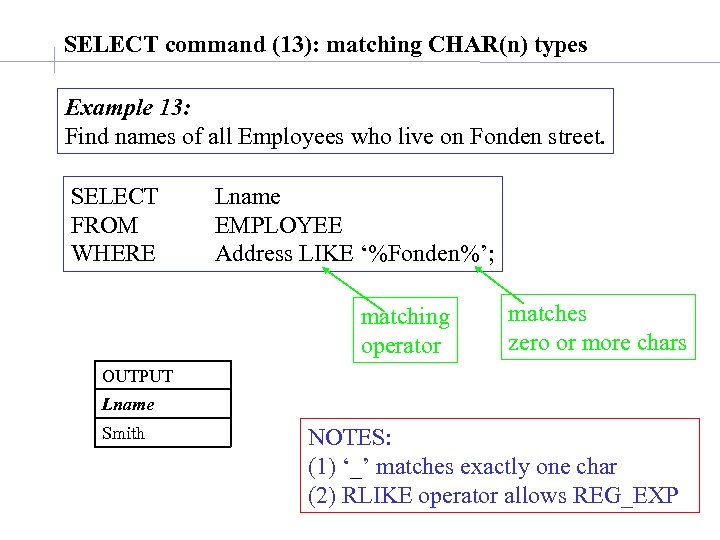 SELECT command (13): matching CHAR(n) types Example 13: Find names of all Employees who live on Fonden street. SELECT FROM WHERE Lname EMPLOYEE Address LIKE ‘%Fonden%’; matching operator matches zero or more chars OUTPUT Lname Smith NOTES: (1) ‘_’ matches exactly one char (2) RLIKE operator allows REG_EXP
SELECT command (13): matching CHAR(n) types Example 13: Find names of all Employees who live on Fonden street. SELECT FROM WHERE Lname EMPLOYEE Address LIKE ‘%Fonden%’; matching operator matches zero or more chars OUTPUT Lname Smith NOTES: (1) ‘_’ matches exactly one char (2) RLIKE operator allows REG_EXP
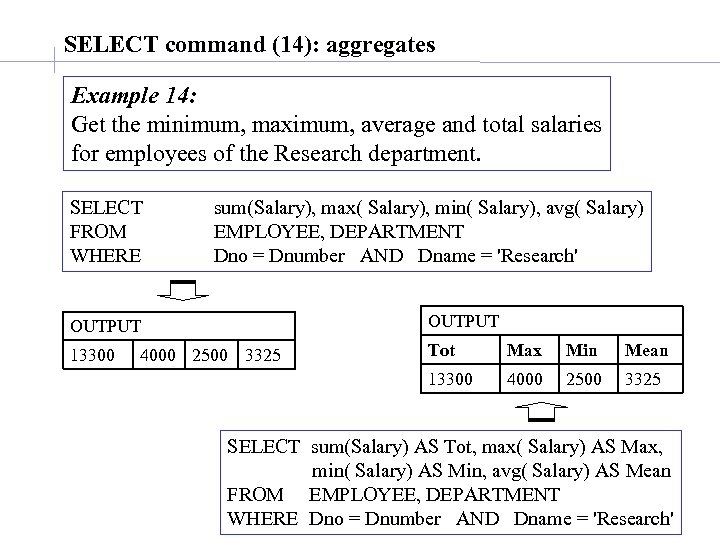 SELECT command (14): aggregates Example 14: Get the minimum, maximum, average and total salaries for employees of the Research department. SELECT FROM WHERE sum(Salary), max( Salary), min( Salary), avg( Salary) EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT Dno = Dnumber AND Dname = 'Research' OUTPUT 13300 Tot Max Min Mean 13300 4000 2500 3325 SELECT sum(Salary) AS Tot, max( Salary) AS Max, min( Salary) AS Min, avg( Salary) AS Mean FROM EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT WHERE Dno = Dnumber AND Dname = 'Research'
SELECT command (14): aggregates Example 14: Get the minimum, maximum, average and total salaries for employees of the Research department. SELECT FROM WHERE sum(Salary), max( Salary), min( Salary), avg( Salary) EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT Dno = Dnumber AND Dname = 'Research' OUTPUT 13300 Tot Max Min Mean 13300 4000 2500 3325 SELECT sum(Salary) AS Tot, max( Salary) AS Max, min( Salary) AS Min, avg( Salary) AS Mean FROM EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT WHERE Dno = Dnumber AND Dname = 'Research'
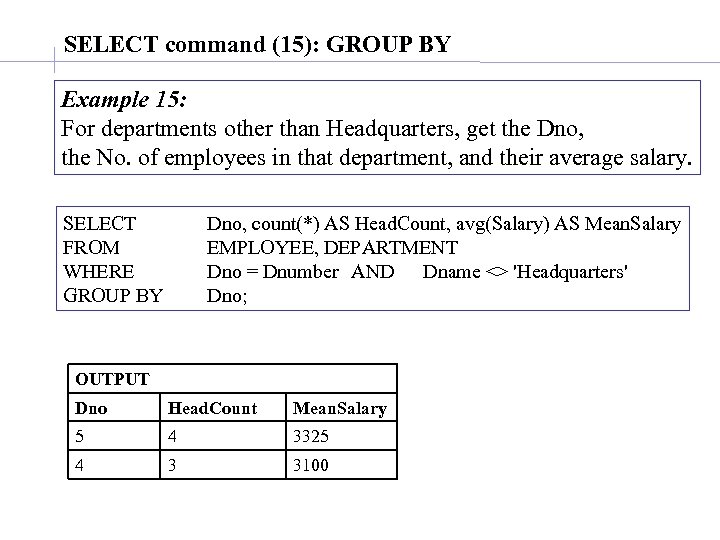 SELECT command (15): GROUP BY Example 15: For departments other than Headquarters, get the Dno, the No. of employees in that department, and their average salary. SELECT FROM WHERE GROUP BY Dno, count(*) AS Head. Count, avg(Salary) AS Mean. Salary EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT Dno = Dnumber AND Dname <> 'Headquarters' Dno; OUTPUT Dno Head. Count Mean. Salary 5 4 3325 4 3 3100
SELECT command (15): GROUP BY Example 15: For departments other than Headquarters, get the Dno, the No. of employees in that department, and their average salary. SELECT FROM WHERE GROUP BY Dno, count(*) AS Head. Count, avg(Salary) AS Mean. Salary EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT Dno = Dnumber AND Dname <> 'Headquarters' Dno; OUTPUT Dno Head. Count Mean. Salary 5 4 3325 4 3 3100
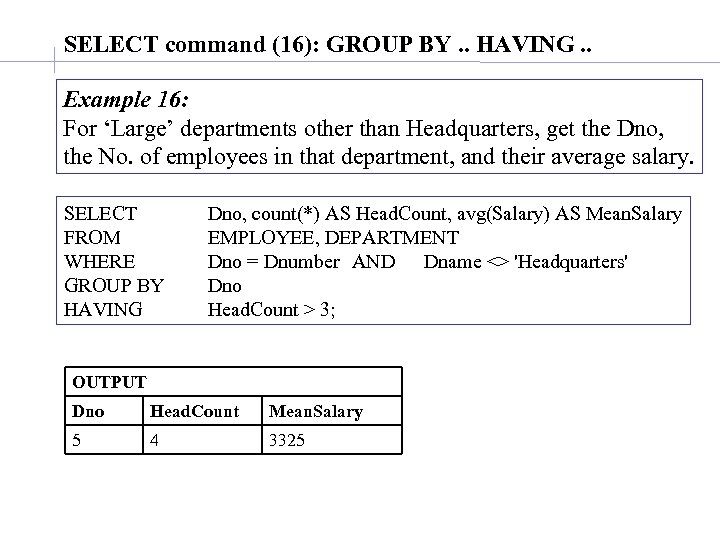 SELECT command (16): GROUP BY. . HAVING. . Example 16: For ‘Large’ departments other than Headquarters, get the Dno, the No. of employees in that department, and their average salary. SELECT FROM WHERE GROUP BY HAVING Dno, count(*) AS Head. Count, avg(Salary) AS Mean. Salary EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT Dno = Dnumber AND Dname <> 'Headquarters' Dno Head. Count > 3; OUTPUT Dno Head. Count Mean. Salary 5 4 3325
SELECT command (16): GROUP BY. . HAVING. . Example 16: For ‘Large’ departments other than Headquarters, get the Dno, the No. of employees in that department, and their average salary. SELECT FROM WHERE GROUP BY HAVING Dno, count(*) AS Head. Count, avg(Salary) AS Mean. Salary EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT Dno = Dnumber AND Dname <> 'Headquarters' Dno Head. Count > 3; OUTPUT Dno Head. Count Mean. Salary 5 4 3325
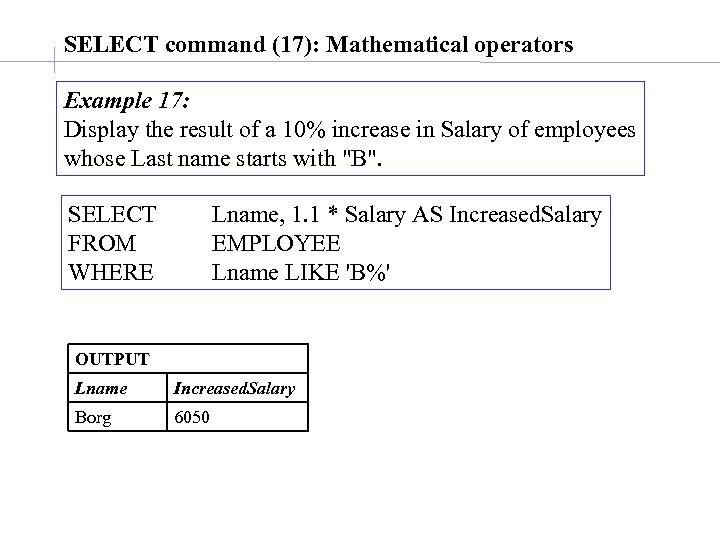 SELECT command (17): Mathematical operators Example 17: Display the result of a 10% increase in Salary of employees whose Last name starts with "B". SELECT FROM WHERE Lname, 1. 1 * Salary AS Increased. Salary EMPLOYEE Lname LIKE 'B%' OUTPUT Lname Increased. Salary Borg 6050
SELECT command (17): Mathematical operators Example 17: Display the result of a 10% increase in Salary of employees whose Last name starts with "B". SELECT FROM WHERE Lname, 1. 1 * Salary AS Increased. Salary EMPLOYEE Lname LIKE 'B%' OUTPUT Lname Increased. Salary Borg 6050
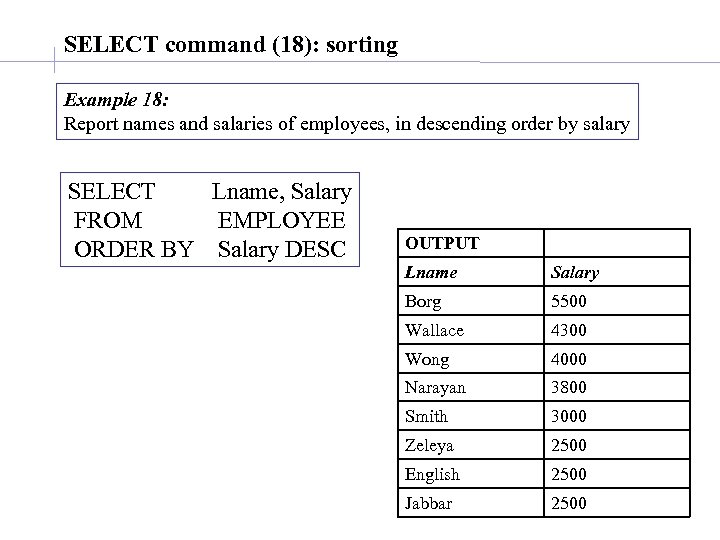 SELECT command (18): sorting Example 18: Report names and salaries of employees, in descending order by salary SELECT Lname, Salary FROM EMPLOYEE ORDER BY Salary DESC OUTPUT Lname Salary Borg 5500 Wallace 4300 Wong 4000 Narayan 3800 Smith 3000 Zeleya 2500 English 2500 Jabbar 2500
SELECT command (18): sorting Example 18: Report names and salaries of employees, in descending order by salary SELECT Lname, Salary FROM EMPLOYEE ORDER BY Salary DESC OUTPUT Lname Salary Borg 5500 Wallace 4300 Wong 4000 Narayan 3800 Smith 3000 Zeleya 2500 English 2500 Jabbar 2500
 VIEWS VIEW: A virtual table derived from a set of existing tables. Main uses of a view: - Security (selective display of information to different users) - Ease-of-use -- Explicit display of derived attributes -- Explicit display of related information from different tables -- Intermediate table can be used to simplify SQL query
VIEWS VIEW: A virtual table derived from a set of existing tables. Main uses of a view: - Security (selective display of information to different users) - Ease-of-use -- Explicit display of derived attributes -- Explicit display of related information from different tables -- Intermediate table can be used to simplify SQL query
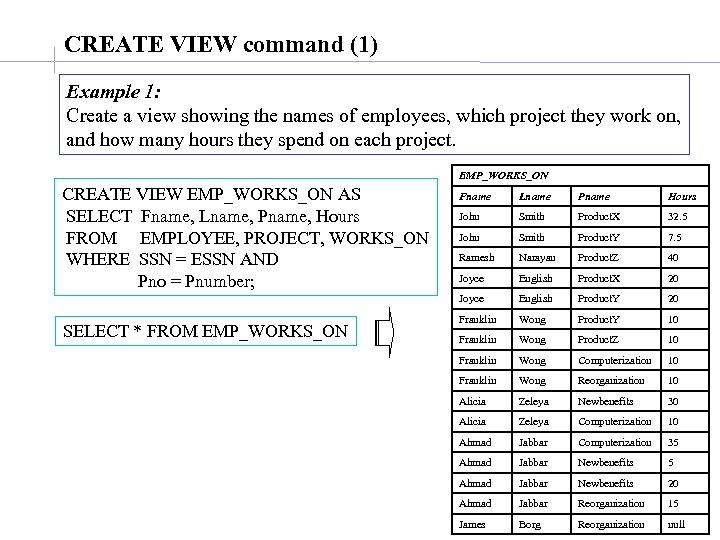 CREATE VIEW command (1) Example 1: Create a view showing the names of employees, which project they work on, and how many hours they spend on each project. EMP_WORKS_ON CREATE VIEW EMP_WORKS_ON AS SELECT Fname, Lname, Pname, Hours FROM EMPLOYEE, PROJECT, WORKS_ON WHERE SSN = ESSN AND Pno = Pnumber; Lname Pname Hours John Smith Product. X 32. 5 John Smith Product. Y 7. 5 Ramesh Narayan Product. Z 40 Joyce English Product. X 20 Joyce SELECT * FROM EMP_WORKS_ON Fname English Product. Y 20 Franklin Wong Product. Y 10 Franklin Wong Product. Z 10 Franklin Wong Computerization 10 Franklin Wong Reorganization 10 Alicia Zeleya Newbenefits 30 Alicia Zeleya Computerization 10 Ahmad Jabbar Computerization 35 Ahmad Jabbar Newbenefits 20 Ahmad Jabbar Reorganization 15 James Borg Reorganization null
CREATE VIEW command (1) Example 1: Create a view showing the names of employees, which project they work on, and how many hours they spend on each project. EMP_WORKS_ON CREATE VIEW EMP_WORKS_ON AS SELECT Fname, Lname, Pname, Hours FROM EMPLOYEE, PROJECT, WORKS_ON WHERE SSN = ESSN AND Pno = Pnumber; Lname Pname Hours John Smith Product. X 32. 5 John Smith Product. Y 7. 5 Ramesh Narayan Product. Z 40 Joyce English Product. X 20 Joyce SELECT * FROM EMP_WORKS_ON Fname English Product. Y 20 Franklin Wong Product. Y 10 Franklin Wong Product. Z 10 Franklin Wong Computerization 10 Franklin Wong Reorganization 10 Alicia Zeleya Newbenefits 30 Alicia Zeleya Computerization 10 Ahmad Jabbar Computerization 35 Ahmad Jabbar Newbenefits 20 Ahmad Jabbar Reorganization 15 James Borg Reorganization null
 VIEWS: mechanism of storage/updates 1. Only definition of view is stored in memory 2. Data for a view is only generated when the query is processed 3. Update a view attribute data in the underlying table is updated
VIEWS: mechanism of storage/updates 1. Only definition of view is stored in memory 2. Data for a view is only generated when the query is processed 3. Update a view attribute data in the underlying table is updated
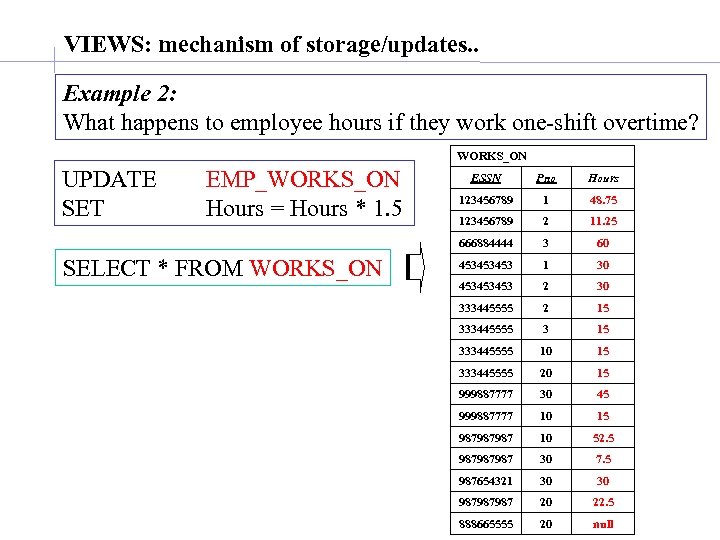 VIEWS: mechanism of storage/updates. . Example 2: What happens to employee hours if they work one-shift overtime? WORKS_ON UPDATE SET EMP_WORKS_ON Hours = Hours * 1. 5 Pno Hours 123456789 1 48. 75 123456789 2 11. 25 666884444 SELECT * FROM WORKS_ON ESSN 3 60 453453453 1 30 453453453 2 30 333445555 2 15 333445555 3 15 333445555 10 15 333445555 20 15 999887777 30 45 999887777 10 15 987987987 10 52. 5 987987987 30 7. 5 987654321 30 30 987987987 20 22. 5 888665555 20 null
VIEWS: mechanism of storage/updates. . Example 2: What happens to employee hours if they work one-shift overtime? WORKS_ON UPDATE SET EMP_WORKS_ON Hours = Hours * 1. 5 Pno Hours 123456789 1 48. 75 123456789 2 11. 25 666884444 SELECT * FROM WORKS_ON ESSN 3 60 453453453 1 30 453453453 2 30 333445555 2 15 333445555 3 15 333445555 10 15 333445555 20 15 999887777 30 45 999887777 10 15 987987987 10 52. 5 987987987 30 7. 5 987654321 30 30 987987987 20 22. 5 888665555 20 null
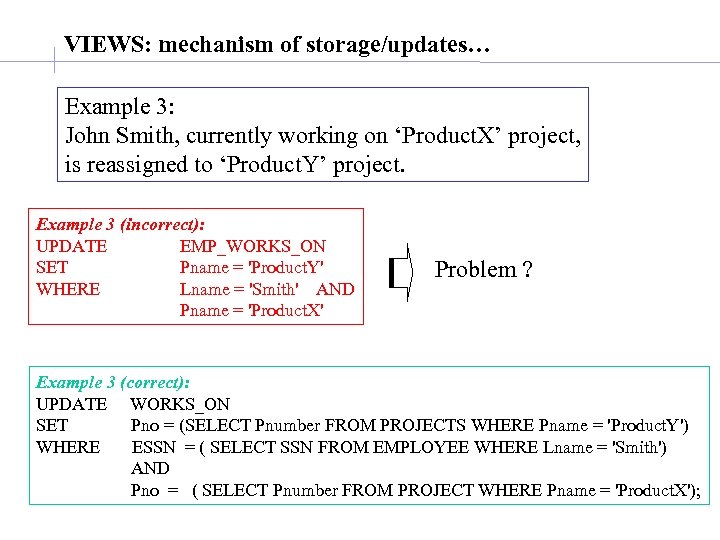 VIEWS: mechanism of storage/updates… Example 3: John Smith, currently working on ‘Product. X’ project, is reassigned to ‘Product. Y’ project. Example 3 (incorrect): UPDATE EMP_WORKS_ON SET Pname = 'Product. Y' WHERE Lname = 'Smith' AND Pname = 'Product. X' Problem ? Example 3 (correct): UPDATE WORKS_ON SET Pno = (SELECT Pnumber FROM PROJECTS WHERE Pname = 'Product. Y') WHERE ESSN = ( SELECT SSN FROM EMPLOYEE WHERE Lname = 'Smith') AND Pno = ( SELECT Pnumber FROM PROJECT WHERE Pname = 'Product. X');
VIEWS: mechanism of storage/updates… Example 3: John Smith, currently working on ‘Product. X’ project, is reassigned to ‘Product. Y’ project. Example 3 (incorrect): UPDATE EMP_WORKS_ON SET Pname = 'Product. Y' WHERE Lname = 'Smith' AND Pname = 'Product. X' Problem ? Example 3 (correct): UPDATE WORKS_ON SET Pno = (SELECT Pnumber FROM PROJECTS WHERE Pname = 'Product. Y') WHERE ESSN = ( SELECT SSN FROM EMPLOYEE WHERE Lname = 'Smith') AND Pno = ( SELECT Pnumber FROM PROJECT WHERE Pname = 'Product. X');
 VIEWS: using derived attributes CREATE VIEW DEPT_INFO AS SELECT DName, count(*) AS Num. Emps, sum( Salary) AS Total. Salary FROM DEPARTMENT, EMPLOYEE WHERE DNumber = DNo GROUP BY DName; NOTE: - you cannot UPDATE a computed attribute
VIEWS: using derived attributes CREATE VIEW DEPT_INFO AS SELECT DName, count(*) AS Num. Emps, sum( Salary) AS Total. Salary FROM DEPARTMENT, EMPLOYEE WHERE DNumber = DNo GROUP BY DName; NOTE: - you cannot UPDATE a computed attribute
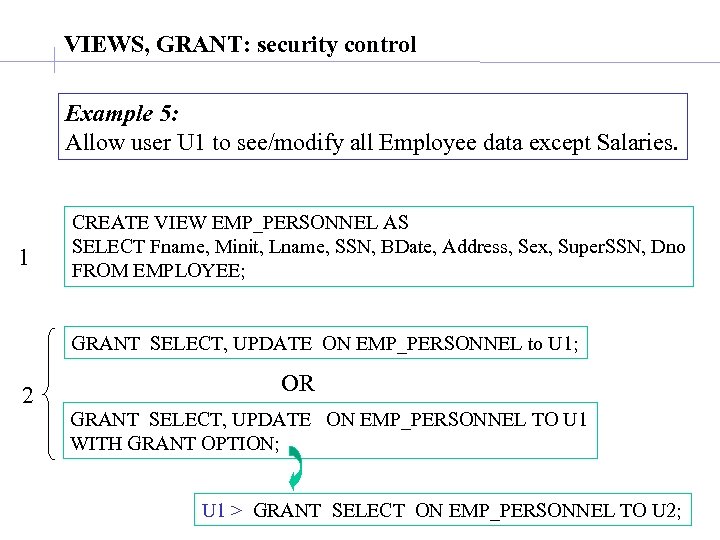 VIEWS, GRANT: security control Example 5: Allow user U 1 to see/modify all Employee data except Salaries. 1 CREATE VIEW EMP_PERSONNEL AS SELECT Fname, Minit, Lname, SSN, BDate, Address, Sex, Super. SSN, Dno FROM EMPLOYEE; GRANT SELECT, UPDATE ON EMP_PERSONNEL to U 1; 2 OR GRANT SELECT, UPDATE ON EMP_PERSONNEL TO U 1 WITH GRANT OPTION; U 1 > GRANT SELECT ON EMP_PERSONNEL TO U 2;
VIEWS, GRANT: security control Example 5: Allow user U 1 to see/modify all Employee data except Salaries. 1 CREATE VIEW EMP_PERSONNEL AS SELECT Fname, Minit, Lname, SSN, BDate, Address, Sex, Super. SSN, Dno FROM EMPLOYEE; GRANT SELECT, UPDATE ON EMP_PERSONNEL to U 1; 2 OR GRANT SELECT, UPDATE ON EMP_PERSONNEL TO U 1 WITH GRANT OPTION; U 1 > GRANT SELECT ON EMP_PERSONNEL TO U 2;
 GRANT, REVOKE commands Disallow U 2 from seeing anything in EMP_PERSONNEL: REVOKE SELECT ON EMP_PERSONNEL FROM U 2; GRANT , REVOKE can refer to individual attributes Allow U 3 to change Salary in EMPLOYEE table: GRANT UPDATE ON EMPLOYEE( Salary) TO U 3;
GRANT, REVOKE commands Disallow U 2 from seeing anything in EMP_PERSONNEL: REVOKE SELECT ON EMP_PERSONNEL FROM U 2; GRANT , REVOKE can refer to individual attributes Allow U 3 to change Salary in EMPLOYEE table: GRANT UPDATE ON EMPLOYEE( Salary) TO U 3;
 Concluding remarks GRANT on SELECT use VIEW or TABLE GRANT on INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE use TABLE Next topic: Indexes
Concluding remarks GRANT on SELECT use VIEW or TABLE GRANT on INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE use TABLE Next topic: Indexes


