 Structural Geology § Chapter 9 § Group 5 § Naufalov Ali 30 § Yussupov Yeskender 41 § Miranda Ray 27
Structural Geology § Chapter 9 § Group 5 § Naufalov Ali 30 § Yussupov Yeskender 41 § Miranda Ray 27
 Structural Geology § Attitudes of sedimentary rocks are important criteria in petroleum exploration, because folded rocks form structures that are fundamental to petroleum accumulations.
Structural Geology § Attitudes of sedimentary rocks are important criteria in petroleum exploration, because folded rocks form structures that are fundamental to petroleum accumulations.
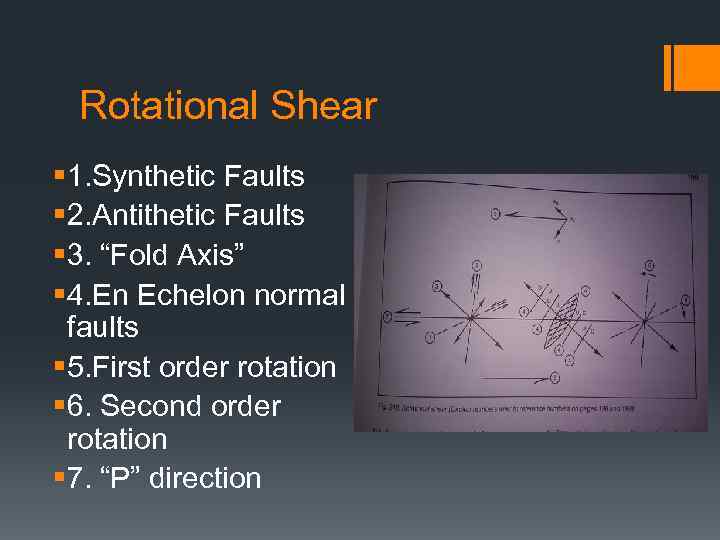 Rotational Shear § 1. Synthetic Faults § 2. Antithetic Faults § 3. “Fold Axis” § 4. En Echelon normal faults § 5. First order rotation § 6. Second order rotation § 7. “P” direction
Rotational Shear § 1. Synthetic Faults § 2. Antithetic Faults § 3. “Fold Axis” § 4. En Echelon normal faults § 5. First order rotation § 6. Second order rotation § 7. “P” direction
 Triaxial Stress §Three mutually perpendicular stress axes comprise a compressive nonrotational pure shear stress field.
Triaxial Stress §Three mutually perpendicular stress axes comprise a compressive nonrotational pure shear stress field.
 Superposition § Rocks are laid down in order of
Superposition § Rocks are laid down in order of
 Questions and Answers § 1. What are faults? § Answer: Faults are a break in the earth crust along which there is or has been discernible movement § 2. What is the term “fault terminology”? § Answer: A schematic diagram illustrating primary components observed in fault-related deformation. § 3 What are classifications of faults based on? § Answer: They are based on relative movements of fault blocks. § 4. Describe what is the meaning of strike and dip. § Answer: Strike is always at a right angle to the direction of dip and has a direction expressed as an azimuth or bearing, strike and dip are represented on geologic maps. § 5. Another way of using three dimensions in solving problems is by what method? § Answer: the use of stereographic projection and plotting of structural data on the stereo net.
Questions and Answers § 1. What are faults? § Answer: Faults are a break in the earth crust along which there is or has been discernible movement § 2. What is the term “fault terminology”? § Answer: A schematic diagram illustrating primary components observed in fault-related deformation. § 3 What are classifications of faults based on? § Answer: They are based on relative movements of fault blocks. § 4. Describe what is the meaning of strike and dip. § Answer: Strike is always at a right angle to the direction of dip and has a direction expressed as an azimuth or bearing, strike and dip are represented on geologic maps. § 5. Another way of using three dimensions in solving problems is by what method? § Answer: the use of stereographic projection and plotting of structural data on the stereo net.
 Summary §Structural geology is primarily a study in which a system in three dimensional distribution of rock units of deformation are studied and are very important to the petroleum industry as well in economic geology and the mining industry of geology. The importance in this system is to understand the structural evolution of areas or regions of patterns of rock deformation.
Summary §Structural geology is primarily a study in which a system in three dimensional distribution of rock units of deformation are studied and are very important to the petroleum industry as well in economic geology and the mining industry of geology. The importance in this system is to understand the structural evolution of areas or regions of patterns of rock deformation.