cbab3a089e32a878a1b8d2658f7ccde0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

Structural Context of Public Policy POS/PUB 140 Lecture 1/31/08

Sex Education: Should there be national standards?

The context of American policy making The Constitution Features of the System Policy in a historical context

Support for the U. S. Constitution Philosophical Background Influence of David Hume and John Locke Arguments in the Federalist Papers
![The Federalist Papers http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/List_of_Federalist_Papers http: //www. constitution. org/federa 00. htm ] The Federalist Papers http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/List_of_Federalist_Papers http: //www. constitution. org/federa 00. htm ]](https://present5.com/presentation/cbab3a089e32a878a1b8d2658f7ccde0/image-5.jpg)
The Federalist Papers http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/List_of_Federalist_Papers http: //www. constitution. org/federa 00. htm ] Madison (1787): human nature of individuals to form groups on common interests Proposed a “fragmented system”: horizontally and vertically Jefferson: more power to the States

Government before the Constitution: The Articles of Confederation The early concern/debate on what type of government we should have How might this strong vs. weak central government debate influence public policy? "The government which governs least, governs best” Thomas Jefferson Issues/problems with the Articles of Confederation?

The Constitution: Structure Three branches of government Supposedly co-equal Create what we know as “checks and balances” via a “separation of powers”
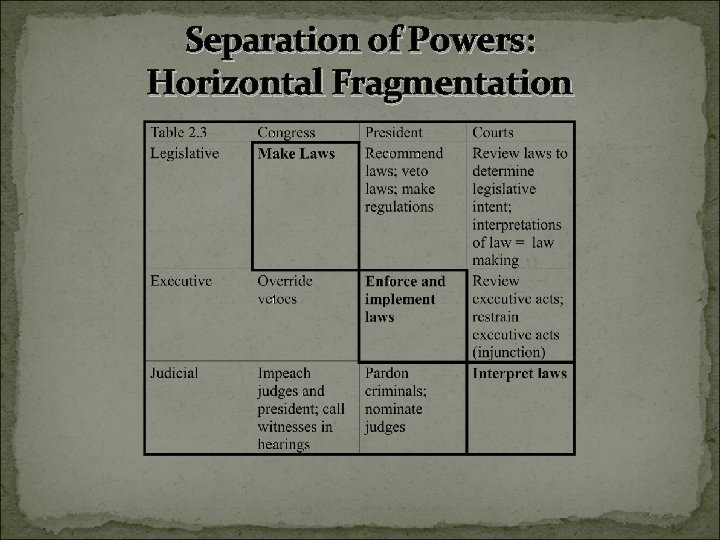
Separation of Powers: Horizontal Fragmentation

Article 1, Section 8: A key to public policy Collect Taxes, Duties, Imposts and Excises, to pay the Debts and provide for the common Defence and general Welfare of the United States; To borrow money on the credit of the United States To regulate Commerce To provide and maintain a Navy To make all Laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into Execution the foregoing Powers, and all other Powers vested by this Constitution in the Government of the United States, or in any Department or Officer thereof.

Checks and Balances Example #1: Congress power to impeach A judicial activity How often does this happen? Why? Example #2: Presidential Veto A legislative activity Which presidents have the most vetoes? What can Congress do in response? Example #3: Supreme Court reviews legislative intent What was a famous case for judicial review? http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Marbury_v. _Madison

Federalism: Vertical Fragmentation In terms of the structure of our government, what does federalism mean? What do the states do that the feds don’t? What do the feds do that the states don’t? What do both do?

Federalism: State and Federal Responsibilities State Federal Corrections Defense Elementary education Environment Postal Service Liquor / drinking Space Police (L) Air Traffic / Port Welfare Sanitation (L) Speed Limits Elections Authority Health Care – elderly and young Intelligence Citizenship / INS

Sex Education Intergovernmental Grants NYS Health Department did not reapply for federal funding under Title V, due to “rigid federal standards. ” The state would receive $3. 2 million under the program “You can’t teach contraception other than to talk about its failure rates, you must assert … the only acceptable sexual union is between a husband wife in monogamy and sex outside of that is harmful, psychologically and physically. ” Joann Smith, Family Planning Advocates

Does federalism really create "laboratories for democracy"? Different Types of Intergovernmental Grants Categorical Grants Matching Grants Block Grants http: //www. census. gov/govs/estimate/03 sl 00 us. html Example of a failed experiment in NY State Automated Child Welfare Information System (SACWIS) http: //www. gcn. com/state/vol 7_no 6/news/1073 -1. html Are all states the same? Political Commitment Administrative Capacity

Stability in American Politics and Policy Making (Anderson 2000) Ideological stability Political stability Policy stability Stability in power
cbab3a089e32a878a1b8d2658f7ccde0.ppt