4fa19ff7523e1ad04161002686b0cdc2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Strong Cryptographic Infrastructure and its Applications Dr Lucas Hui Center for Information Security & Cryptography Department of Computer Science & Information Systems The University of Hong Kong Tel: 2859 -2190 Fax: 2559 -8447 hui@csis. hku. hk Workshop on Strong Cryptographic Infrastructure December 17, 1998
Strong Cryptographic Infrastructure and its Applications Dr Lucas Hui Center for Information Security & Cryptography Department of Computer Science & Information Systems The University of Hong Kong Tel: 2859 -2190 Fax: 2559 -8447 hui@csis. hku. hk Workshop on Strong Cryptographic Infrastructure December 17, 1998
 Content 1. Use of Cryptography (in electronic commerce activities, Internet services) 2. Cryptographic Library 3. Public Key Infrastructure 4. Applications 5. Cryptographic Infrastructure 6. Relations of 2, 3, 4, 5 7. The SCI project in HKUCSIS
Content 1. Use of Cryptography (in electronic commerce activities, Internet services) 2. Cryptographic Library 3. Public Key Infrastructure 4. Applications 5. Cryptographic Infrastructure 6. Relations of 2, 3, 4, 5 7. The SCI project in HKUCSIS
 Use of Cryptography (in E. C. etc) • Hash functions (SHA, MD 5) • Symmetric key crypto-system (DES, DES 3) • Public Key Crypto-system – Digital signature – Data Encryption – Advanced usage : double hashing, group signature • In real usage, techniques are combined
Use of Cryptography (in E. C. etc) • Hash functions (SHA, MD 5) • Symmetric key crypto-system (DES, DES 3) • Public Key Crypto-system – Digital signature – Data Encryption – Advanced usage : double hashing, group signature • In real usage, techniques are combined
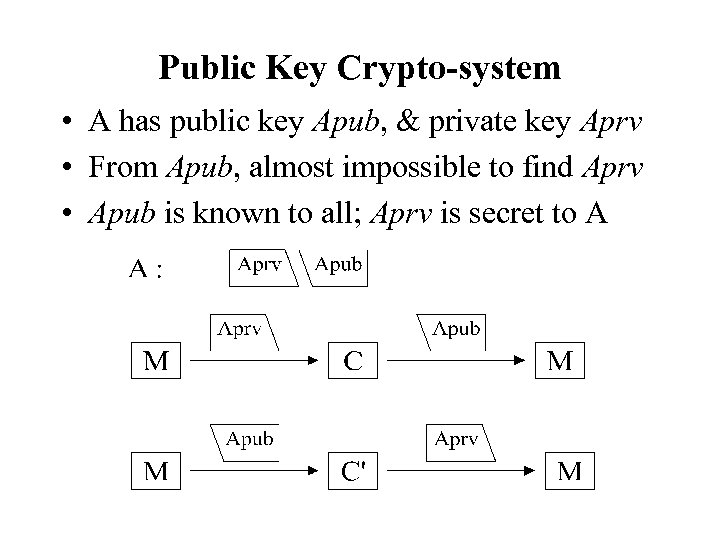 Public Key Crypto-system • A has public key Apub, & private key Aprv • From Apub, almost impossible to find Aprv • Apub is known to all; Aprv is secret to A
Public Key Crypto-system • A has public key Apub, & private key Aprv • From Apub, almost impossible to find Aprv • Apub is known to all; Aprv is secret to A
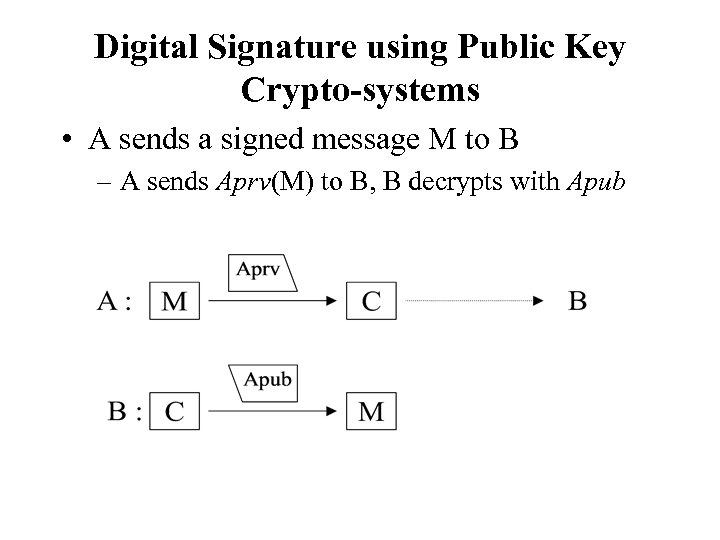 Digital Signature using Public Key Crypto-systems • A sends a signed message M to B – A sends Aprv(M) to B, B decrypts with Apub
Digital Signature using Public Key Crypto-systems • A sends a signed message M to B – A sends Aprv(M) to B, B decrypts with Apub
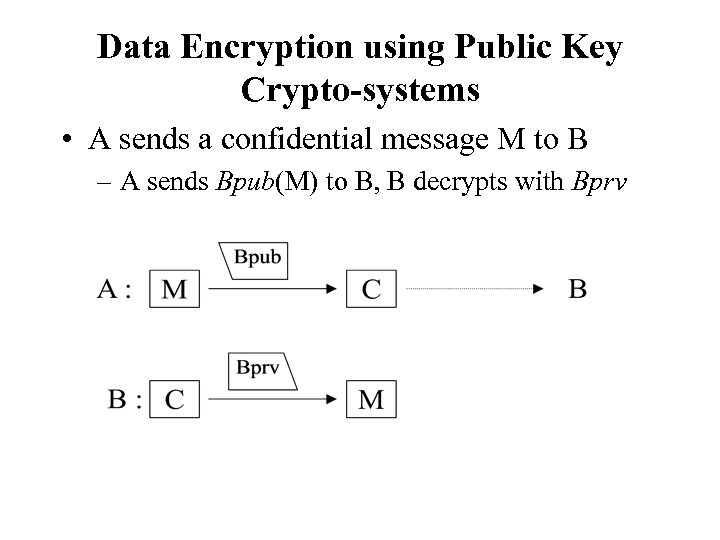 Data Encryption using Public Key Crypto-systems • A sends a confidential message M to B – A sends Bpub(M) to B, B decrypts with Bprv
Data Encryption using Public Key Crypto-systems • A sends a confidential message M to B – A sends Bpub(M) to B, B decrypts with Bprv
 Cryptographic Library • Provide cryptographic algorithms such as RSA • Provide interface to add new cryptographic algorithms easily • Provide other functions • Q : How to set up/manage the private/public keys? • A : Using a Public Key Infrastructure
Cryptographic Library • Provide cryptographic algorithms such as RSA • Provide interface to add new cryptographic algorithms easily • Provide other functions • Q : How to set up/manage the private/public keys? • A : Using a Public Key Infrastructure
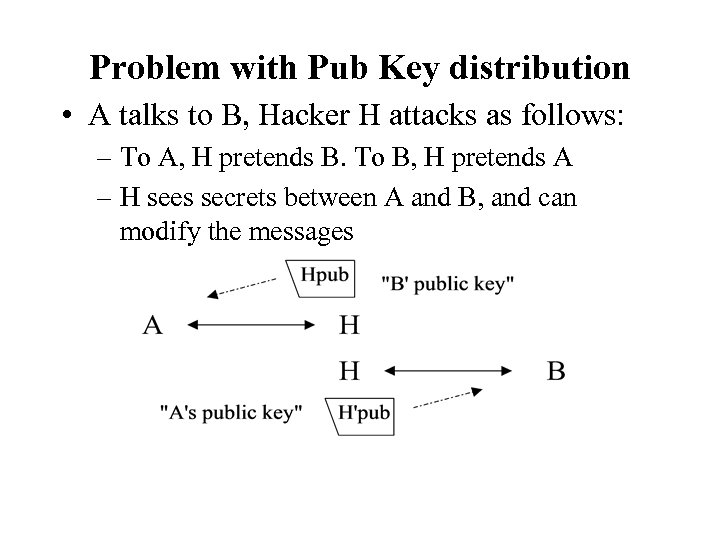 Problem with Pub Key distribution • A talks to B, Hacker H attacks as follows: – To A, H pretends B. To B, H pretends A – H sees secrets between A and B, and can modify the messages
Problem with Pub Key distribution • A talks to B, Hacker H attacks as follows: – To A, H pretends B. To B, H pretends A – H sees secrets between A and B, and can modify the messages
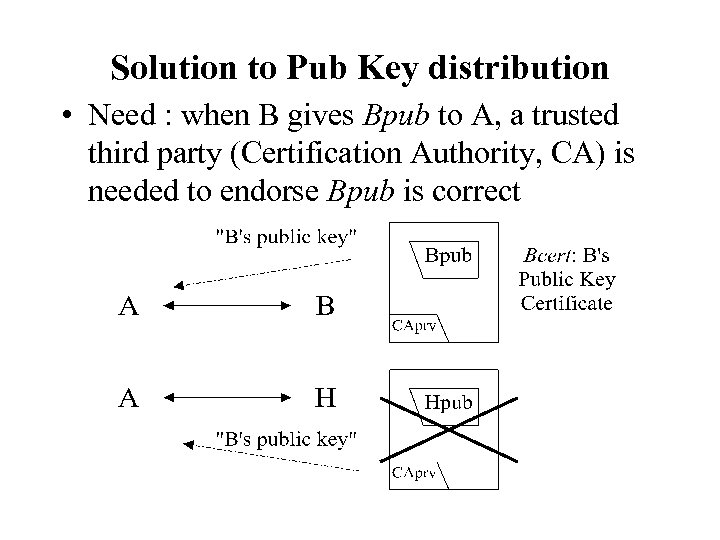 Solution to Pub Key distribution • Need : when B gives Bpub to A, a trusted third party (Certification Authority, CA) is needed to endorse Bpub is correct
Solution to Pub Key distribution • Need : when B gives Bpub to A, a trusted third party (Certification Authority, CA) is needed to endorse Bpub is correct
 Certification Authority • A wants to get B’s public key Bpub. How? • Method 1 : use a repository • Method 2 : B gives Bpub to A, which is endorsed by a trusted-third-party, the CA (Certification Authority). This is B’s public key certificate BCert, which is Bpub signed by CA’s private key CAprv • CA’s public key, CApub, is known to all • A use CApub to verify that BCert is correct
Certification Authority • A wants to get B’s public key Bpub. How? • Method 1 : use a repository • Method 2 : B gives Bpub to A, which is endorsed by a trusted-third-party, the CA (Certification Authority). This is B’s public key certificate BCert, which is Bpub signed by CA’s private key CAprv • CA’s public key, CApub, is known to all • A use CApub to verify that BCert is correct
 X. 509 Public Key Infrastructure (PKIX) • Set up, manage, and terminate usage of keys (private/public), & public key certificates – Registration & Initialization – Certification (signing of a certificate) – Key pair recovery – Key Generation, Update – Cross-certification – Key Revocation (managing CRLs) Note: Make use of Cryptographic functions
X. 509 Public Key Infrastructure (PKIX) • Set up, manage, and terminate usage of keys (private/public), & public key certificates – Registration & Initialization – Certification (signing of a certificate) – Key pair recovery – Key Generation, Update – Cross-certification – Key Revocation (managing CRLs) Note: Make use of Cryptographic functions
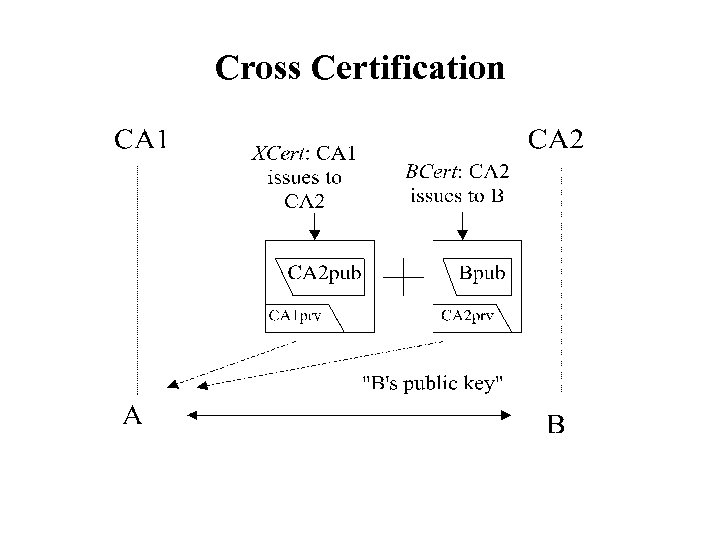 Cross Certification
Cross Certification
 Cross-Certification • 2 CAs: CA 1, CA 2, & 2 persons: A, B. • CA 2 issues a public key Cert BCert to B (Bpub signed by CA 2’s private key) • CA 1 issues a Cross-Cert, XCert, to CA 2 (CA 2’s public key signed by CA 1’s private key) • A trusts CA 1 (A knows CA 1’s public key) • B sends BCert and XCert to A • A can now verify B’s public key in 2 steps.
Cross-Certification • 2 CAs: CA 1, CA 2, & 2 persons: A, B. • CA 2 issues a public key Cert BCert to B (Bpub signed by CA 2’s private key) • CA 1 issues a Cross-Cert, XCert, to CA 2 (CA 2’s public key signed by CA 1’s private key) • A trusts CA 1 (A knows CA 1’s public key) • B sends BCert and XCert to A • A can now verify B’s public key in 2 steps.
 Applications • Examples: E. Commerce, E. Banking, Secure Email, Secure Workflow (in schools, etc) • Using a transaction protocol which makes use of cryptographic algorithms from a Cryptographic Library • Use PKIX for subject (customers, etc) identity and encryption key management
Applications • Examples: E. Commerce, E. Banking, Secure Email, Secure Workflow (in schools, etc) • Using a transaction protocol which makes use of cryptographic algorithms from a Cryptographic Library • Use PKIX for subject (customers, etc) identity and encryption key management
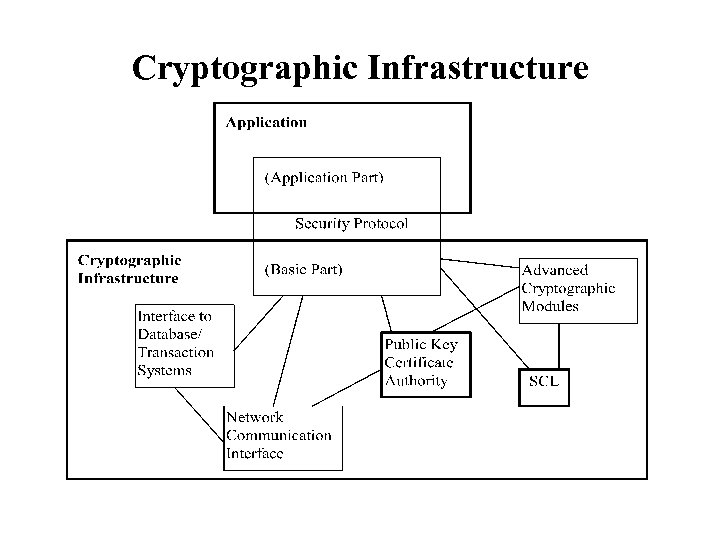 Cryptographic Infrastructure
Cryptographic Infrastructure
 Strong Cryptographic Infrastructure Project (SCI) in HKUCSIS • What does Strong mean? – Algorithms are “Strong” (e. g. RSA-1024) – “Strong” in implementation (e. g. Random No. ) – New encryption paradigm (elliptic curves) • supported by ISF • available to users in HK • Start with Strong Cryptographic Library (SCL) • Beta version expected in March 1999
Strong Cryptographic Infrastructure Project (SCI) in HKUCSIS • What does Strong mean? – Algorithms are “Strong” (e. g. RSA-1024) – “Strong” in implementation (e. g. Random No. ) – New encryption paradigm (elliptic curves) • supported by ISF • available to users in HK • Start with Strong Cryptographic Library (SCL) • Beta version expected in March 1999
 SCI project team • Dr Lucas Hui (Chief Designer) • Dr K. P. Chow (Project Manager) • Dr W. W. Tsang, Prof Francis Chin, Prof G. Marsaglia • Dr C. F. Chong, Dr H. W. Chan • Ms Vivien Chan, Mr Marcus Lee, Mr K. M. Chan • Mr Doug Kwan, Mr Luke Lam, Mr Henry Fung, Ms Taellus Lo
SCI project team • Dr Lucas Hui (Chief Designer) • Dr K. P. Chow (Project Manager) • Dr W. W. Tsang, Prof Francis Chin, Prof G. Marsaglia • Dr C. F. Chong, Dr H. W. Chan • Ms Vivien Chan, Mr Marcus Lee, Mr K. M. Chan • Mr Doug Kwan, Mr Luke Lam, Mr Henry Fung, Ms Taellus Lo


