007c8abb6a127d6b7e04f796238bccf5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59
 Stroke in Developing Countries: Issues and Challenges Jeyaraj D Pandian MD DM FRACP Professor and Head, Department of Neurology Head of Research, Betty Cowan Research and Innovation Centre Christian Medical College, Ludhiana, Punjab, India
Stroke in Developing Countries: Issues and Challenges Jeyaraj D Pandian MD DM FRACP Professor and Head, Department of Neurology Head of Research, Betty Cowan Research and Innovation Centre Christian Medical College, Ludhiana, Punjab, India
 Ludhiana
Ludhiana
 Global Burden of Stroke Project 2010
Global Burden of Stroke Project 2010

 Summary GBD 2010 Stroke Project • Incidence: From 1990 to 2010 age standardised incidence of stroke has decreased by 12% in high income countries and has increased by 12% in low and middle income countries • Mortality: decreased significantly in high income (37%), middle and low income countries (20%)
Summary GBD 2010 Stroke Project • Incidence: From 1990 to 2010 age standardised incidence of stroke has decreased by 12% in high income countries and has increased by 12% in low and middle income countries • Mortality: decreased significantly in high income (37%), middle and low income countries (20%)
 Summary GBD 2010 Stroke Project (absolute numbers of stroke worldwide 2010) • First ever stroke: 16. 9 million • Stroke survivors: 33 million • Stroke related deaths: 5. 9 million • Disability adjusted life years lost: 102 million • All the above indicators have increased since 1990
Summary GBD 2010 Stroke Project (absolute numbers of stroke worldwide 2010) • First ever stroke: 16. 9 million • Stroke survivors: 33 million • Stroke related deaths: 5. 9 million • Disability adjusted life years lost: 102 million • All the above indicators have increased since 1990
 Summary GBD 2010 Stroke Project (absolute numbers) • Most of the burden (68. 6% incident (new cases) strokes, 52. 2% prevalent strokes, 70. 9% stroke related deaths and 77. 7% DALYs lost are in low and middle income countries • In 2010, 5. 2 million (31%) strokes were in children below 20 years of age • Children 74, 000 low and middle income countries • Young and middle aged adults (20 -64 years of age) 4 million (78%) from low and middle income countries
Summary GBD 2010 Stroke Project (absolute numbers) • Most of the burden (68. 6% incident (new cases) strokes, 52. 2% prevalent strokes, 70. 9% stroke related deaths and 77. 7% DALYs lost are in low and middle income countries • In 2010, 5. 2 million (31%) strokes were in children below 20 years of age • Children 74, 000 low and middle income countries • Young and middle aged adults (20 -64 years of age) 4 million (78%) from low and middle income countries
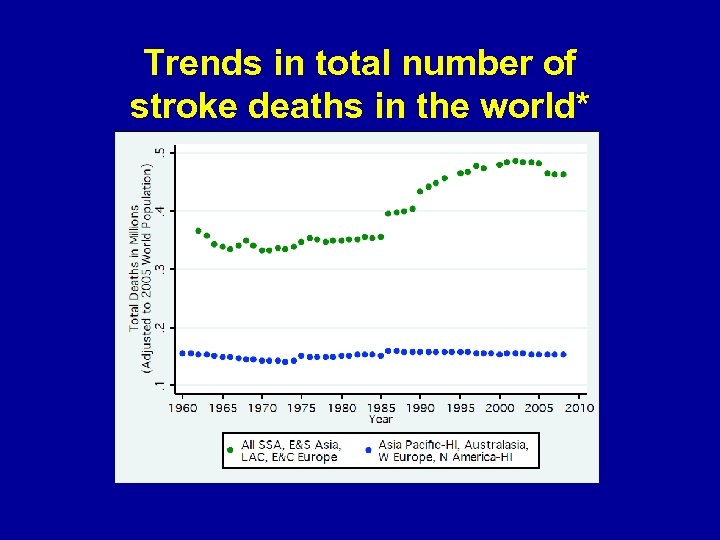 Trends in total number of stroke deaths in the world*
Trends in total number of stroke deaths in the world*
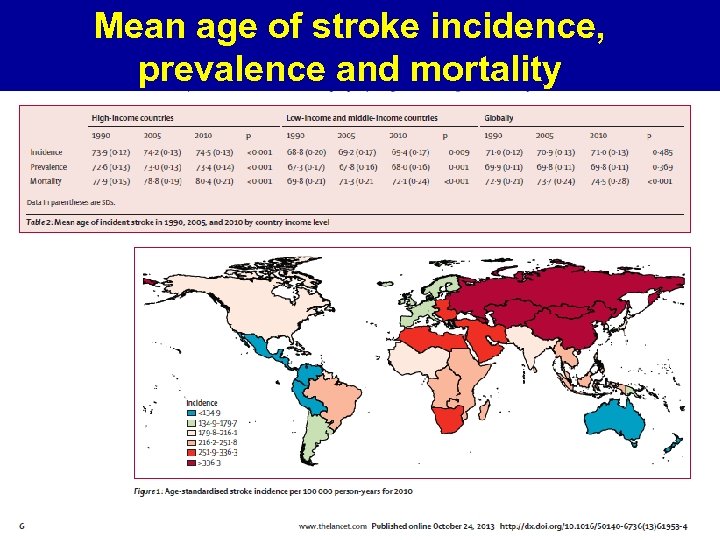 Mean age of stroke incidence, prevalence and mortality
Mean age of stroke incidence, prevalence and mortality
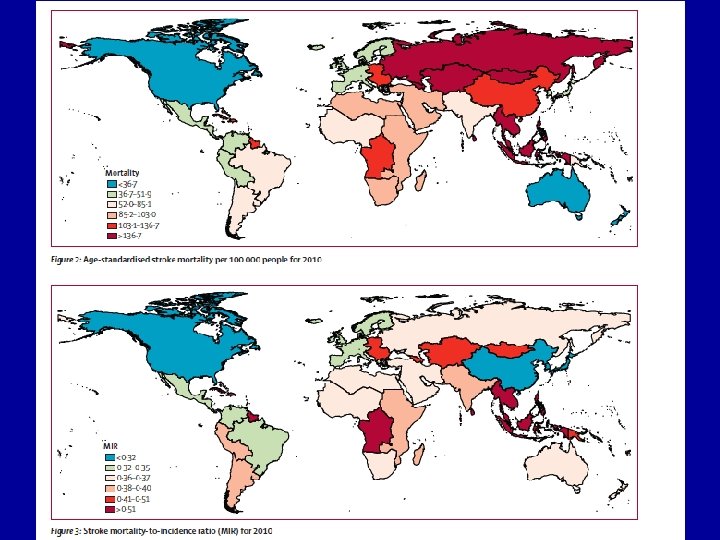
 GBD Project 2010 • Stroke incidence and mortality in low to middle income countries have now exceeded those in high income countries We are facing worldwide epidemic of stroke
GBD Project 2010 • Stroke incidence and mortality in low to middle income countries have now exceeded those in high income countries We are facing worldwide epidemic of stroke
 Why there is Rise in Burden of Stroke in Developing Countries? • Health and Demographic transition • Life style habits • Sedentary life • Rise in obesity • Rise in hypertension, diabetes
Why there is Rise in Burden of Stroke in Developing Countries? • Health and Demographic transition • Life style habits • Sedentary life • Rise in obesity • Rise in hypertension, diabetes
 Challenges
Challenges
 Patient 1 • 50 year old wealthy business man presents to a teaching hospital with sudden right face, arm and leg weakness of 20 mts duration • Arrives by a personal car • Evaluation by the stroke team • Receives rt. PA • Good improvement, discharged after 7 days • Total cost Rs 100, 000 ($US 2083), rt. PA alone $US 1562 (Expenses paid by the patient) Affordable
Patient 1 • 50 year old wealthy business man presents to a teaching hospital with sudden right face, arm and leg weakness of 20 mts duration • Arrives by a personal car • Evaluation by the stroke team • Receives rt. PA • Good improvement, discharged after 7 days • Total cost Rs 100, 000 ($US 2083), rt. PA alone $US 1562 (Expenses paid by the patient) Affordable
 Patient 2 • 45 year old shopkeeper living in a village develops hemiataxia and hemiparesis, reaches a government hospital using a hired car • Patient goes out of the hospital to do a CT scan • Comes back and gets treated • After 1 month he is left disabled • Wife becomes the caregiver and the high school going son takes care of the shop Affordability and infrastructure
Patient 2 • 45 year old shopkeeper living in a village develops hemiataxia and hemiparesis, reaches a government hospital using a hired car • Patient goes out of the hospital to do a CT scan • Comes back and gets treated • After 1 month he is left disabled • Wife becomes the caregiver and the high school going son takes care of the shop Affordability and infrastructure
 Patient 3 • 35 year old truck driver develops left side weakness • Reaches the stroke centre within 1 hr • Eligible for rt. PA, but couldn’t afford the DRUG • 1 month follow-up dependent on ADL • House wife, 2 children, no social support and job Disability and Social Support
Patient 3 • 35 year old truck driver develops left side weakness • Reaches the stroke centre within 1 hr • Eligible for rt. PA, but couldn’t afford the DRUG • 1 month follow-up dependent on ADL • House wife, 2 children, no social support and job Disability and Social Support
 Challenges • • Availability of infrastructure Access to stroke services Personnel Cost of treatment Rehabilitation Community support Alternative medicines
Challenges • • Availability of infrastructure Access to stroke services Personnel Cost of treatment Rehabilitation Community support Alternative medicines
 Access to Stroke Services • 80% of the population in low and middle income countries live in rural areas • Transportation from rural to urban stroke centers is a major problem • Poor road connectivity, non-existent of ambulance services, irregular public transport • Alternative medicines
Access to Stroke Services • 80% of the population in low and middle income countries live in rural areas • Transportation from rural to urban stroke centers is a major problem • Poor road connectivity, non-existent of ambulance services, irregular public transport • Alternative medicines
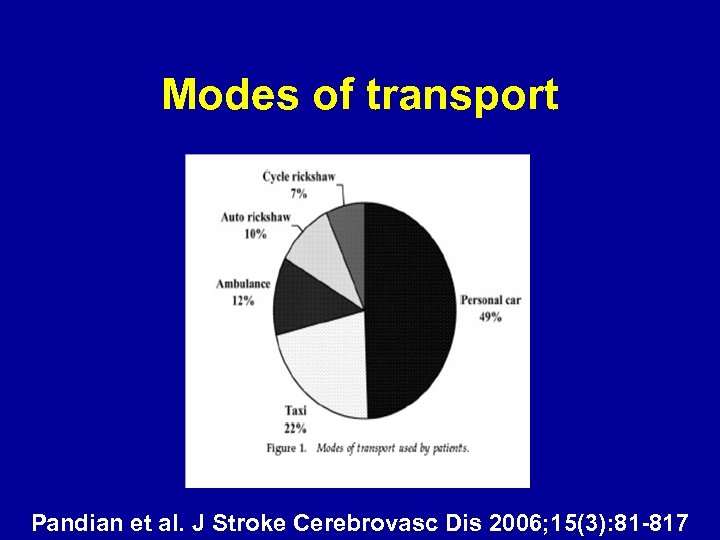 Modes of transport Pandian et al. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2006; 15(3): 81 -817
Modes of transport Pandian et al. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2006; 15(3): 81 -817
 Ambulance and Mobike Accident Rescue Services (AMARS)
Ambulance and Mobike Accident Rescue Services (AMARS)
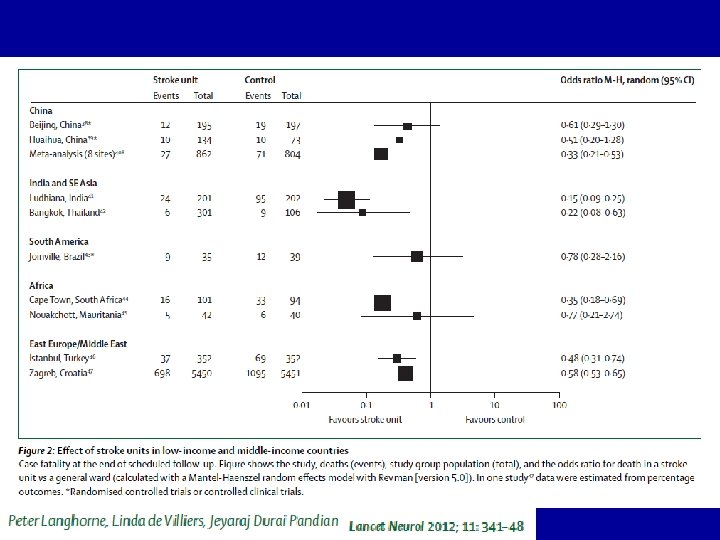
 Stroke Units
Stroke Units
 Stroke Unit Improved outcomes
Stroke Unit Improved outcomes

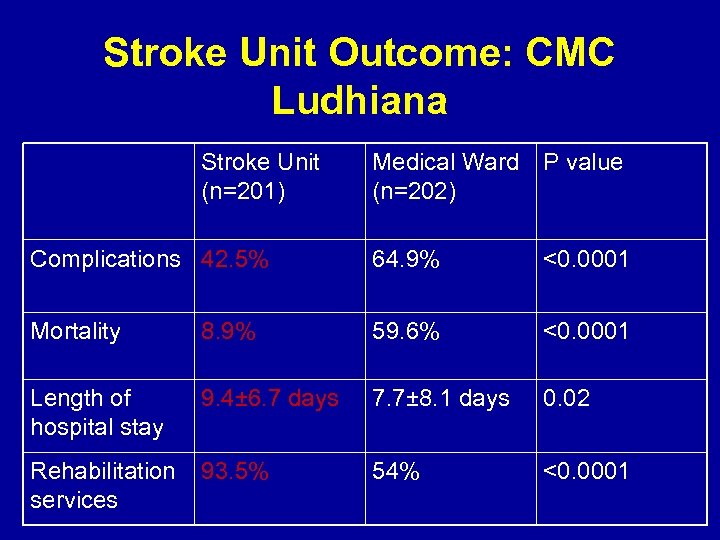 Stroke Unit Outcome: CMC Ludhiana Stroke Unit (n=201) Medical Ward (n=202) P value Complications 42. 5% 64. 9% <0. 0001 Mortality 8. 9% 59. 6% <0. 0001 Length of hospital stay 9. 4± 6. 7 days 7. 7± 8. 1 days 0. 02 Rehabilitation services 93. 5% 54% <0. 0001
Stroke Unit Outcome: CMC Ludhiana Stroke Unit (n=201) Medical Ward (n=202) P value Complications 42. 5% 64. 9% <0. 0001 Mortality 8. 9% 59. 6% <0. 0001 Length of hospital stay 9. 4± 6. 7 days 7. 7± 8. 1 days 0. 02 Rehabilitation services 93. 5% 54% <0. 0001
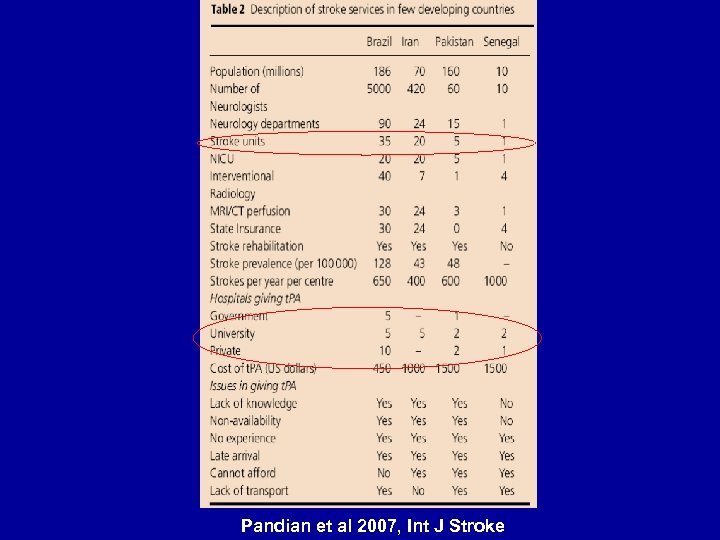 Pandian et al 2007, Int J Stroke
Pandian et al 2007, Int J Stroke
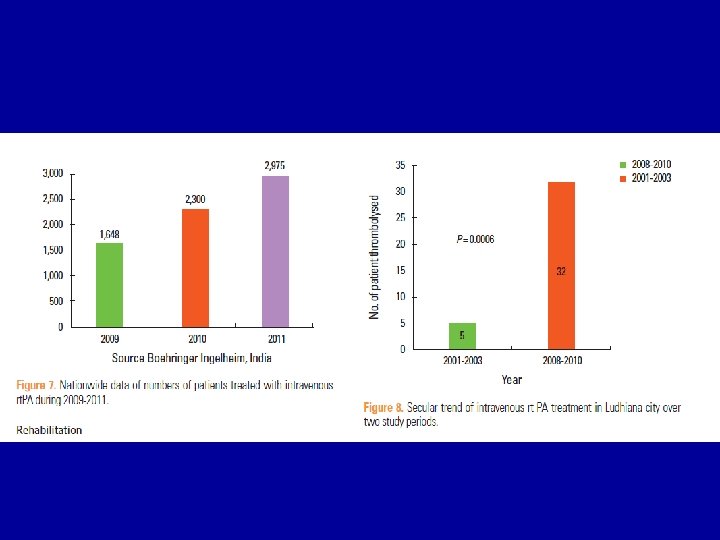
 Thrombolysis
Thrombolysis
 Pandian et al 2007, Int J Stroke
Pandian et al 2007, Int J Stroke
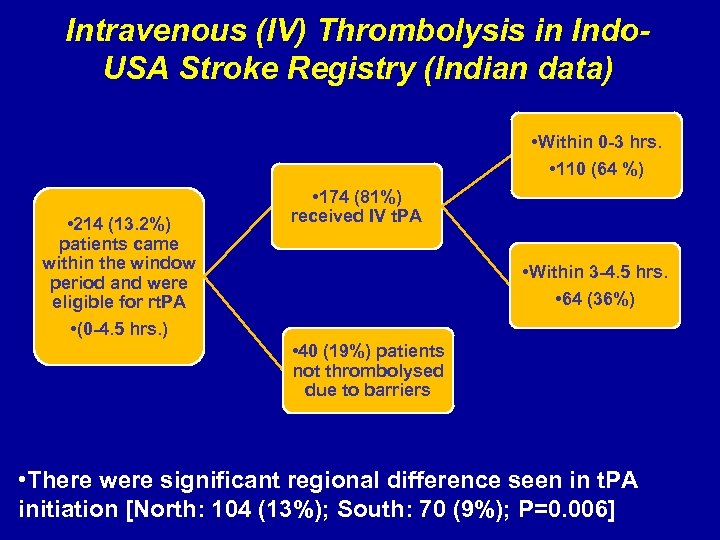 Intravenous (IV) Thrombolysis in Indo. USA Stroke Registry (Indian data) • Within 0 -3 hrs. • 110 (64 %) • 214 (13. 2%) patients came within the window period and were eligible for rt. PA • (0 -4. 5 hrs. ) • 174 (81%) received IV t. PA • Within 3 -4. 5 hrs. • 64 (36%) • 40 (19%) patients not thrombolysed due to barriers • There were significant regional difference seen in t. PA initiation [North: 104 (13%); South: 70 (9%); P=0. 006]
Intravenous (IV) Thrombolysis in Indo. USA Stroke Registry (Indian data) • Within 0 -3 hrs. • 110 (64 %) • 214 (13. 2%) patients came within the window period and were eligible for rt. PA • (0 -4. 5 hrs. ) • 174 (81%) received IV t. PA • Within 3 -4. 5 hrs. • 64 (36%) • 40 (19%) patients not thrombolysed due to barriers • There were significant regional difference seen in t. PA initiation [North: 104 (13%); South: 70 (9%); P=0. 006]
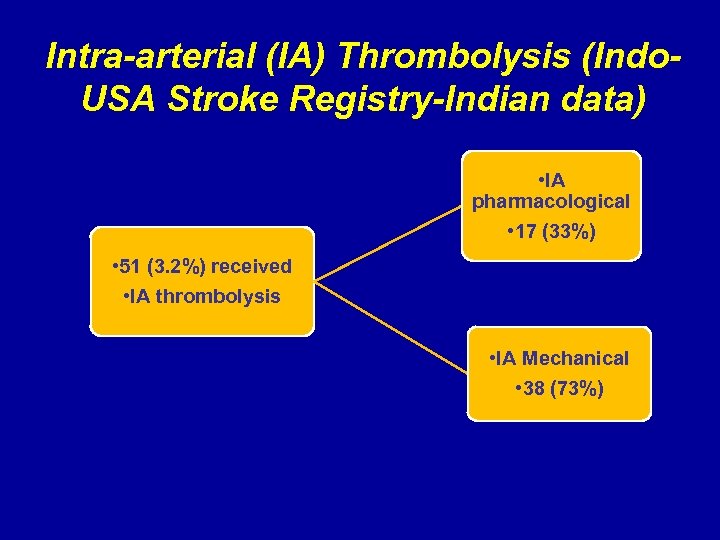 Intra-arterial (IA) Thrombolysis (Indo. USA Stroke Registry-Indian data) • IA pharmacological • 17 (33%) • 51 (3. 2%) received • IA thrombolysis • IA Mechanical • 38 (73%)
Intra-arterial (IA) Thrombolysis (Indo. USA Stroke Registry-Indian data) • IA pharmacological • 17 (33%) • 51 (3. 2%) received • IA thrombolysis • IA Mechanical • 38 (73%)
 Pandian et al 2007, Int J Stroke
Pandian et al 2007, Int J Stroke
 Thrombolysis in Developing Countries • Reduction of the cost • Cheaper drugs: Urokinase, newer streptokinase trials?
Thrombolysis in Developing Countries • Reduction of the cost • Cheaper drugs: Urokinase, newer streptokinase trials?
 Primary and Secondary Prevention of Stroke
Primary and Secondary Prevention of Stroke
 Modifiable Risk Factors • Blood pressure • Tobacco smoking • Salt intake (particularly the one hidden in the food) • Cholesterol level • Obesity (Amarenco 2006)
Modifiable Risk Factors • Blood pressure • Tobacco smoking • Salt intake (particularly the one hidden in the food) • Cholesterol level • Obesity (Amarenco 2006)
 Issues in Secondary Prevention of Stroke in Developing Countries • Developing countries spend only 2% to 15% of gross domestic product on health • The out-of-pocket expenditure varies from 20% to 80% of the total health expenditure (Pandian et al, 2007)
Issues in Secondary Prevention of Stroke in Developing Countries • Developing countries spend only 2% to 15% of gross domestic product on health • The out-of-pocket expenditure varies from 20% to 80% of the total health expenditure (Pandian et al, 2007)
 Issues in Secondary Prevention of Stroke in Developing Countries • The approximate cost of the secondary prevention of stroke in India is Rs 500 (US $10) per month (using 2 antihypertensive agents, one antiplatelet agent, and a statin) (Stroke 2007; 38: 3063 -3069)
Issues in Secondary Prevention of Stroke in Developing Countries • The approximate cost of the secondary prevention of stroke in India is Rs 500 (US $10) per month (using 2 antihypertensive agents, one antiplatelet agent, and a statin) (Stroke 2007; 38: 3063 -3069)
 • Rheumatic heart disease • AF • Prosthetic Valve
• Rheumatic heart disease • AF • Prosthetic Valve
 Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation
 India Number of Physiotherapists Number of Occupational therapists Number of Speech therapists 32800 registered in Indian Association of Physiotherapists till 2011 3000 registered in Indian Association of Occupational Therapists till 2011 Currently, 1700 registered in Indian Association of speech therapists 500 registered in Rehabilitation Council of India
India Number of Physiotherapists Number of Occupational therapists Number of Speech therapists 32800 registered in Indian Association of Physiotherapists till 2011 3000 registered in Indian Association of Occupational Therapists till 2011 Currently, 1700 registered in Indian Association of speech therapists 500 registered in Rehabilitation Council of India
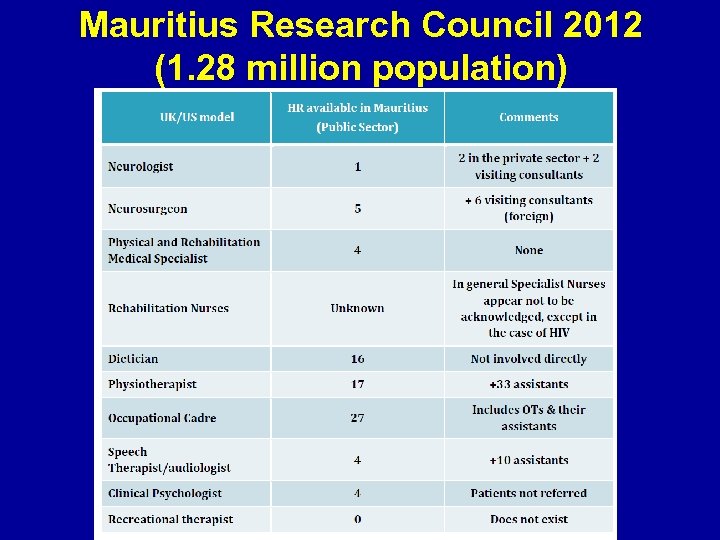 Mauritius Research Council 2012 (1. 28 million population)
Mauritius Research Council 2012 (1. 28 million population)
 China • China has few professionals trained in western methods of rehabilitative therapy • Urban > rural • Combination of Traditional Chinese Medicines and Western treatments for rehab (Zhao et al, 2009) • Acupuncture, acupressure, herbal remedies, massage therapy, and meditation
China • China has few professionals trained in western methods of rehabilitative therapy • Urban > rural • Combination of Traditional Chinese Medicines and Western treatments for rehab (Zhao et al, 2009) • Acupuncture, acupressure, herbal remedies, massage therapy, and meditation
 Pakistan • Lack of awareness among neurologists and physicians • Five stroke units, very few physiotherapists • Less than 20 Rehab physicians (Hashmia and Wasay 2012)
Pakistan • Lack of awareness among neurologists and physicians • Five stroke units, very few physiotherapists • Less than 20 Rehab physicians (Hashmia and Wasay 2012)
 Thailand • 12 public hospitals with in-patient rehabilitation • Thailand Stroke Rehab Registry • Average length of stay 1 month • Discharged home to care givers (relatives) (Kuptniratsaikul et al. J Rehabil Med 2009; 41: 684– 686)
Thailand • 12 public hospitals with in-patient rehabilitation • Thailand Stroke Rehab Registry • Average length of stay 1 month • Discharged home to care givers (relatives) (Kuptniratsaikul et al. J Rehabil Med 2009; 41: 684– 686)
 What is the best model for stroke rehab in less wealthy areas?
What is the best model for stroke rehab in less wealthy areas?
 Home based Rehabilitation • The early hospital discharge and home-based rehabilitation scheme was less costly ($8040) than conventional hospital rehab with community care ($10, 054) for patients with stroke (Anderson et al, Stroke 2000; 31(5): 1032 -7)
Home based Rehabilitation • The early hospital discharge and home-based rehabilitation scheme was less costly ($8040) than conventional hospital rehab with community care ($10, 054) for patients with stroke (Anderson et al, Stroke 2000; 31(5): 1032 -7)
 The ATTEND- Trial FAmily-Led Rehabili. Ta. Tion aft. Er stroke in INDia (Ongoing) • Family-led caregiver-delivered homebased rehabilitation intervention versus usual care for those with disabling stroke in India • CMC Ludhiana, Indian Inst. of Public Health, Hyderabad, The George Inst. Sydney, University of Nottingham, University of Leeds, University of Glasgow
The ATTEND- Trial FAmily-Led Rehabili. Ta. Tion aft. Er stroke in INDia (Ongoing) • Family-led caregiver-delivered homebased rehabilitation intervention versus usual care for those with disabling stroke in India • CMC Ludhiana, Indian Inst. of Public Health, Hyderabad, The George Inst. Sydney, University of Nottingham, University of Leeds, University of Glasgow
 Alternative Medicine
Alternative Medicine


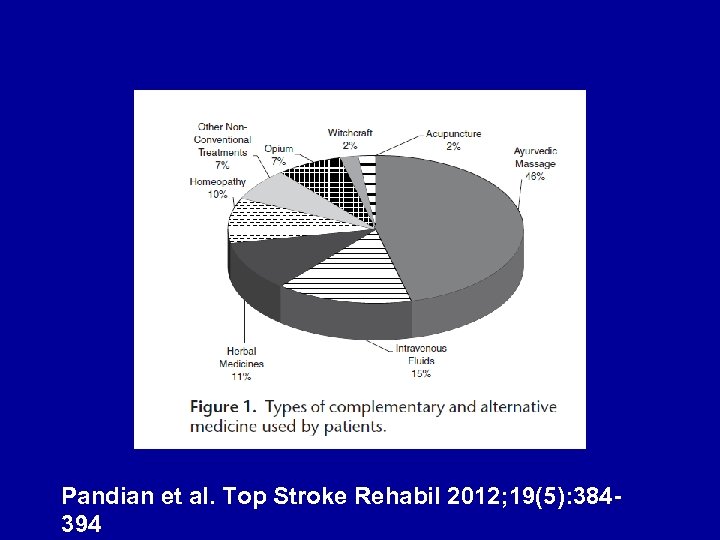 Pandian et al. Top Stroke Rehabil 2012; 19(5): 384394
Pandian et al. Top Stroke Rehabil 2012; 19(5): 384394
 CNS Infections and Stroke • • HIV Malaria Sub-arachnoid Neurocysticercosis Japanese B Encephalitis Dengue Invasive Fungal Infections Trypanosomiasis Tuberculous meningitis
CNS Infections and Stroke • • HIV Malaria Sub-arachnoid Neurocysticercosis Japanese B Encephalitis Dengue Invasive Fungal Infections Trypanosomiasis Tuberculous meningitis
 Cerebral Venous Thrombosis • Peripartum • Cultural practices: restriction of water • Regular antinatal care • Men: dehydration in hot weather (manual labourers)
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis • Peripartum • Cultural practices: restriction of water • Regular antinatal care • Men: dehydration in hot weather (manual labourers)
 Sociocultural Factors • Smoking and women • Religion • Diet habits
Sociocultural Factors • Smoking and women • Religion • Diet habits
 Conclusions • Stroke epidemic in low and middle income countries • There is a lack of infrastructure, personnel, access to stroke care, thrombolysis, prevention and rehabilitation • National programs: Physicians, nurses and health care workers • Government, private sector, NGOs, industries
Conclusions • Stroke epidemic in low and middle income countries • There is a lack of infrastructure, personnel, access to stroke care, thrombolysis, prevention and rehabilitation • National programs: Physicians, nurses and health care workers • Government, private sector, NGOs, industries
 GBD Stroke Experts Group Acknowledgement • • • Valery Feigin (Chair) NZ Nate Nair USA Andrew Moran USA Ralph Sacco USA Hannah Gardener USA Myles Connor Scotland & S. Africa Derrick Bennett UK Martin O’Donnell UK NV Ramani Singapore Yukito Shinohara Japan • • • George Mensah USA Majid Ezzati USA Thomas Truelsen Denmark Laurie Anderson USA Rita Krishnamurthi NZ Suzanne Barker-Collo NZ Carlene Lawes NZ Varsha Parag NZ Jeyaraj Durai Pandian India
GBD Stroke Experts Group Acknowledgement • • • Valery Feigin (Chair) NZ Nate Nair USA Andrew Moran USA Ralph Sacco USA Hannah Gardener USA Myles Connor Scotland & S. Africa Derrick Bennett UK Martin O’Donnell UK NV Ramani Singapore Yukito Shinohara Japan • • • George Mensah USA Majid Ezzati USA Thomas Truelsen Denmark Laurie Anderson USA Rita Krishnamurthi NZ Suzanne Barker-Collo NZ Carlene Lawes NZ Varsha Parag NZ Jeyaraj Durai Pandian India

 Welcome to Hyderabad, World Stroke Congress 2016
Welcome to Hyderabad, World Stroke Congress 2016
 Christian Medical College Comprehensive Stroke Program
Christian Medical College Comprehensive Stroke Program


