9729f164ea51b0119212aab5283c83f6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

Strategies for Thrombus and No Reflow Management in the Cath Lab Gabriel Maluenda, MD Clinica Alemana, Santiago, Chile

Gabriel Maluenda, MD I/we have no real or apparent conflicts of interest to report.
IC thrombus and no-reflow implications The presence of thrombus and/or no-reflow during PCI it are associated with poor outcomes, including: • reduced procedural success • increased rates of abrupt vessel closure • adverse ventricular remodeling • major complications [death-MI-emergent CABG]
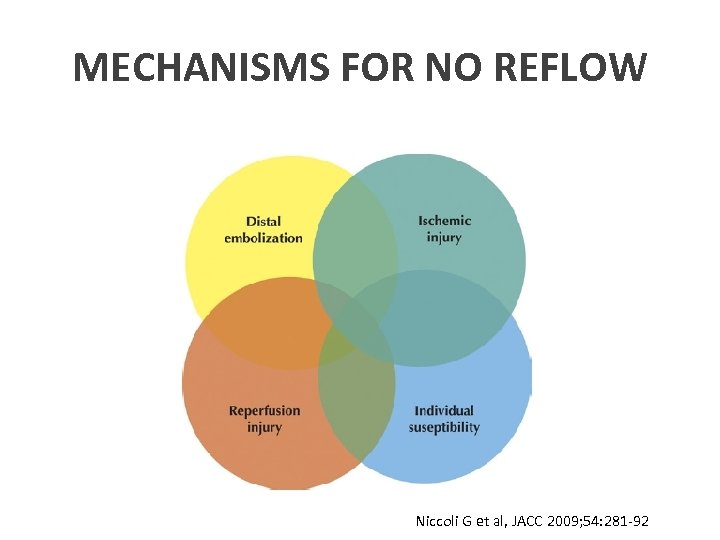
MECHANISMS FOR NO REFLOW Niccoli G et al, JACC 2009; 54: 281 -92
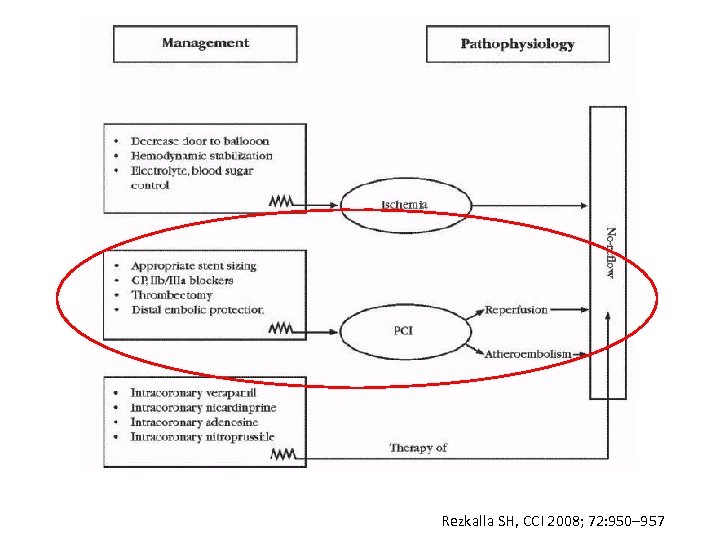
Rezkalla SH, CCI 2008; 72: 950– 957

Aspiration Thrombectomy and distal protection devices
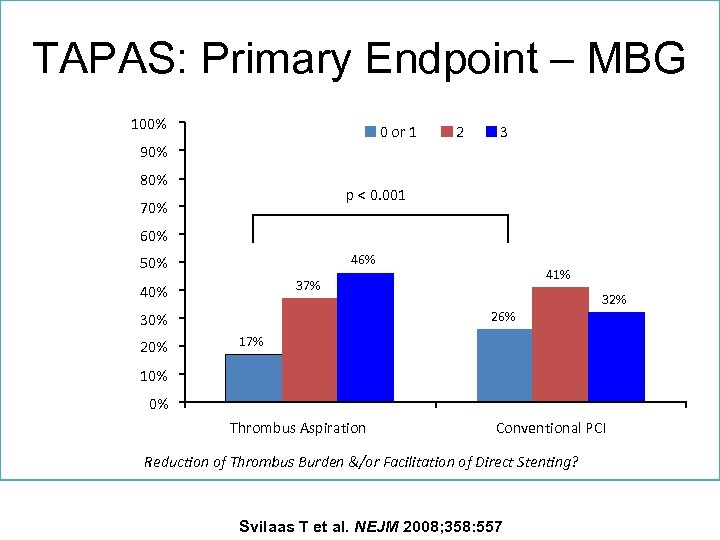
TAPAS: Primary Endpoint – MBG 100% 0 or 1 90% 80% 2 3 p < 0. 001 70% 60% 46% 50% 40% 26% 30% 20% 41% 37% 32% 17% 10% 0% Thrombus Aspiration Conventional PCI Reduction of Thrombus Burden &/or Facilitation of Direct Stenting? Svilaas T et al. NEJM 2008; 358: 557
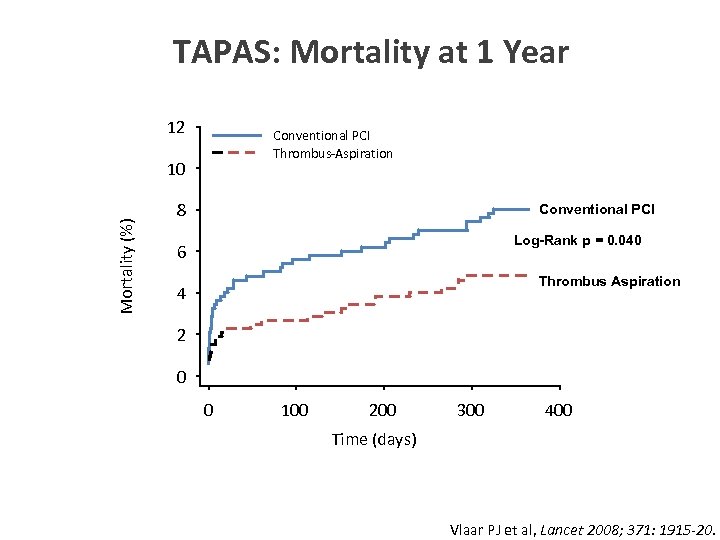
TAPAS: Mortality at 1 Year 12 Conventional PCI Thrombus-Aspiration Mortality (%) 10 8 Conventional PCI Log-Rank p = 0. 040 6 Thrombus Aspiration 4 2 0 0 100 200 300 400 Time (days) Vlaar PJ et al, Lancet 2008; 371: 1915 -20.
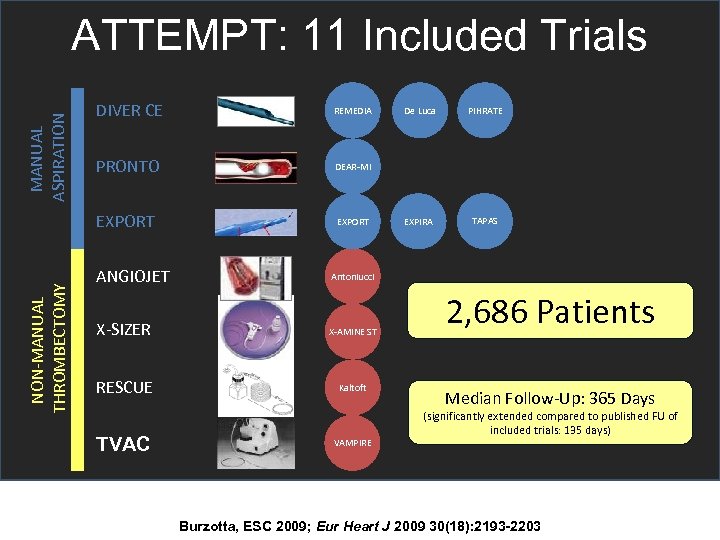
ATTEMPT: 11 Included Trials MANUAL ASPIRATION REMEDIA PRONTO DEAR-MI EXPORT NON-MANUAL THROMBECTOMY DIVER CE EXPORT ANGIOJET X-AMINE ST RESCUE Kaltoft PIHRATE EXPIRA TAPAS Antoniucci X-SIZER De Luca TVAC VAMPIRE 2, 686 Patients Median Follow-Up: 365 Days (significantly extended compared to published FU of included trials: 135 days) Burzotta, ESC 2009; Eur Heart J 2009 30(18): 2193 -2203
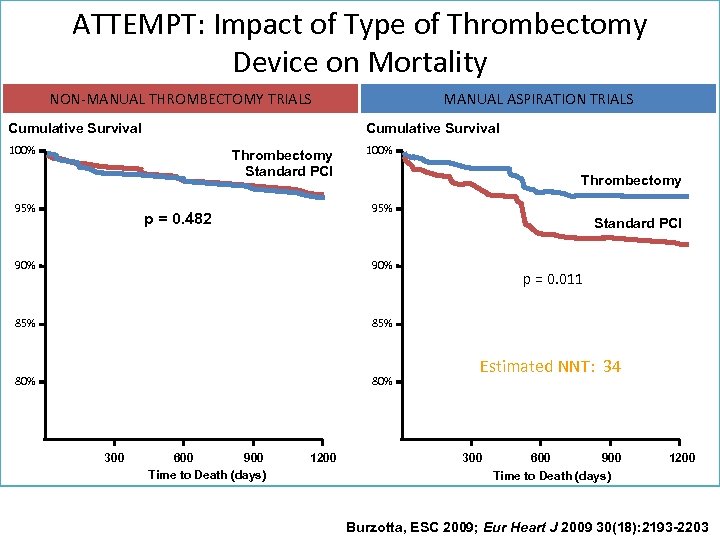
ATTEMPT: Impact of Type of Thrombectomy Device on Mortality NON-MANUAL THROMBECTOMY TRIALS Cumulative Survival 100% Thrombectomy Standard PCI 95% MANUAL ASPIRATION TRIALS 100% Thrombectomy 95% p = 0. 482 Standard PCI 90% 85% 80% 300 600 900 Time to Death (days) 1200 p = 0. 011 Estimated NNT: 34 300 600 900 Time to Death (days) 1200 Burzotta, ESC 2009; Eur Heart J 2009 30(18): 2193 -2203
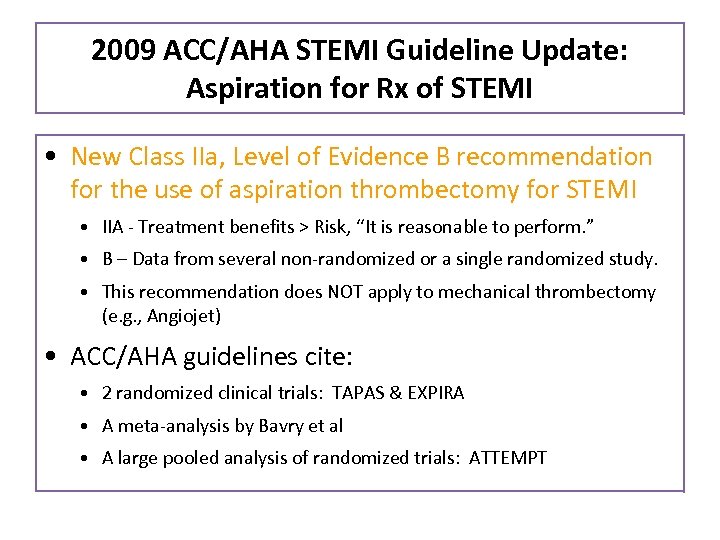
2009 ACC/AHA STEMI Guideline Update: Aspiration for Rx of STEMI • New Class IIa, Level of Evidence B recommendation for the use of aspiration thrombectomy for STEMI • IIA - Treatment benefits > Risk, “It is reasonable to perform. ” • B – Data from several non-randomized or a single randomized study. • This recommendation does NOT apply to mechanical thrombectomy (e. g. , Angiojet) • ACC/AHA guidelines cite: • 2 randomized clinical trials: TAPAS & EXPIRA • A meta-analysis by Bavry et al • A large pooled analysis of randomized trials: ATTEMPT

To catch the thrombus – mesh covered stent strategy
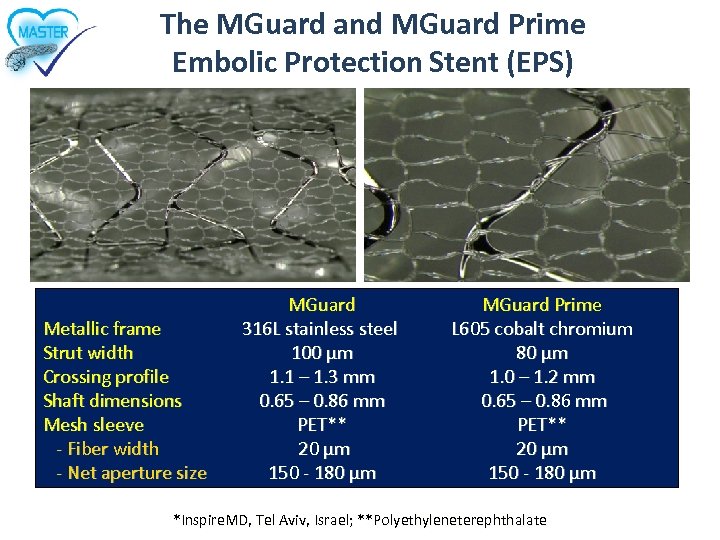
The MGuard and MGuard Prime Embolic Protection Stent (EPS) Metallic frame Strut width Crossing profile Shaft dimensions Mesh sleeve - Fiber width - Net aperture size MGuard 316 L stainless steel 100 µm 1. 1 – 1. 3 mm 0. 65 – 0. 86 mm PET** 20 µm 150 - 180 µm MGuard Prime L 605 cobalt chromium 80 µm 1. 0 – 1. 2 mm 0. 65 – 0. 86 mm PET** 20 µm 150 - 180 µm *Inspire. MD, Tel Aviv, Israel; **Polyethyleneterephthalate
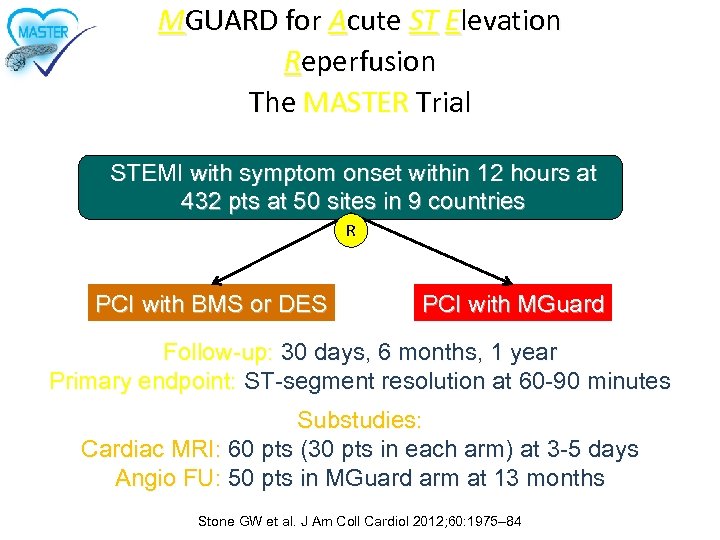
MGUARD for Acute ST Elevation Reperfusion The MASTER Trial STEMI with symptom onset within 12 hours at 432 pts at 50 sites in 9 countries R Stratified by infarct vessel and thrombus aspiration PCI with BMS or DES PCI with MGuard Follow-up: 30 days, 6 months, 1 year Primary endpoint: ST-segment resolution at 60 -90 minutes Substudies: Cardiac MRI: 60 pts (30 pts in each arm) at 3 -5 days Angio FU: 50 pts in MGuard arm at 13 months Stone GW et al. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012; 60: 1975– 84
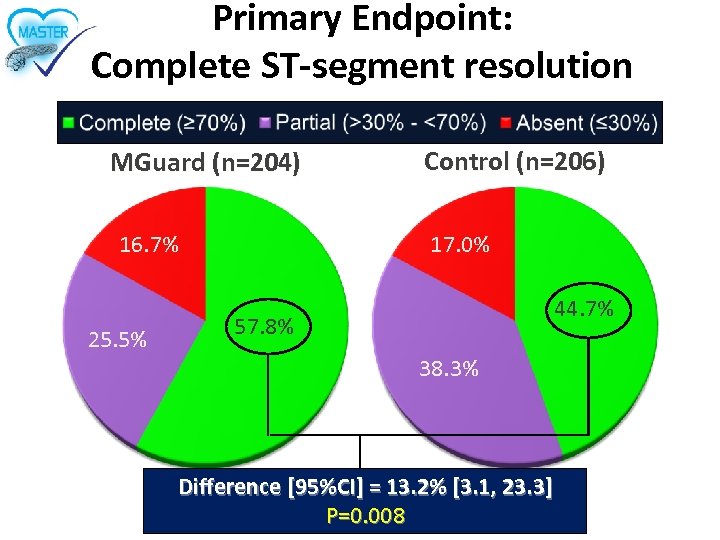
Primary Endpoint: Complete ST-segment resolution MGuard (n=204) 16. 7% 25. 5% Control (n=206) 17. 0% 44. 7% 57. 8% 38. 3% Difference [95%CI] = 13. 2% [3. 1, 23. 3] P=0. 008
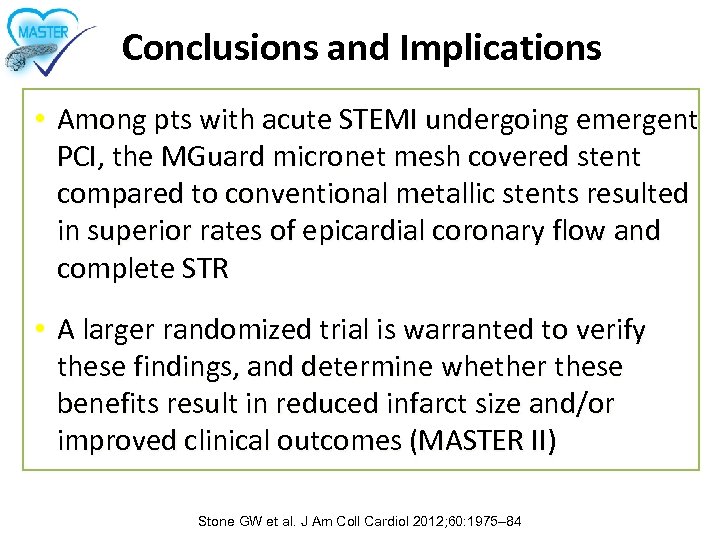
Conclusions and Implications • Among pts with acute STEMI undergoing emergent PCI, the MGuard micronet mesh covered stent compared to conventional metallic stents resulted in superior rates of epicardial coronary flow and complete STR • A larger randomized trial is warranted to verify these findings, and determine whether these benefits result in reduced infarct size and/or improved clinical outcomes (MASTER II) Stone GW et al. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012; 60: 1975– 84

Intracoronary infusion of IIb-IIIa inhibitors
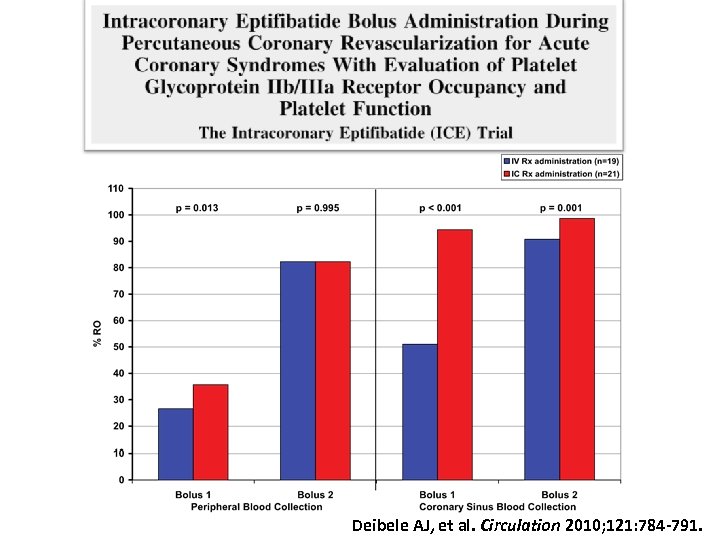
Deibele AJ, et al. Circulation 2010; 121: 784 -791.
Intracoronary Compared with Intravenous Bolus Abciximab Application During Primary PCI Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Substudy of the AIDA STEMI trial Holger Thiele, MD; Jochen Wöhrle, MD; Henning Suenkel, BSc; Josephine Meissner, MD; Sebastian Kerber, MD; Bernward Lauer, MD; Matthias Pauschinger, MD; Ralf Birkemeyer, MD; Christoph Axthelm, MD; Rainer Zimmermann, MD; Petra Neuhaus, Ph. D; Oana Brosteanu, Ph. D; Steffen Desch, MD; Matthias Gutberlet, MD; Gerhard Schuler, MD; Ingo Eitel, MD on behalf of the AIDA STEMI Investigators
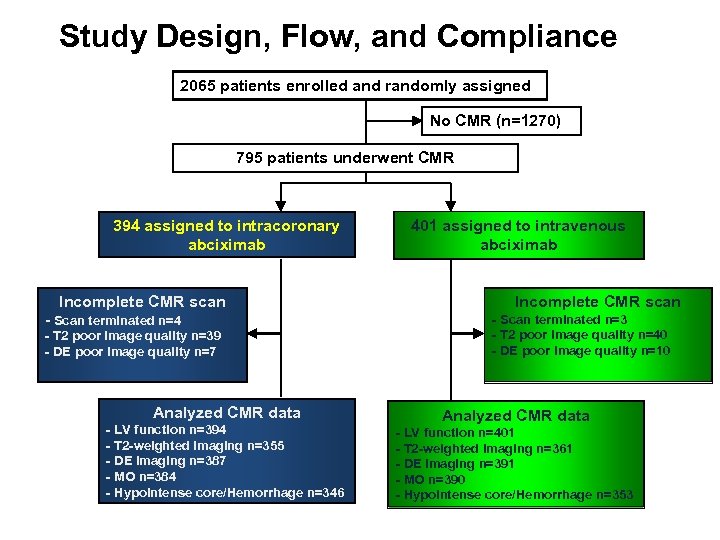
Study Design, Flow, and Compliance 2065 patients enrolled and randomly assigned No CMR (n=1270) 795 patients underwent CMR 394 assigned to intracoronary abciximab Incomplete CMR scan - Scan terminated n=4 - T 2 poor image quality n=39 - DE poor image quality n=7 Analyzed CMR data - LV function n=394 - T 2 -weighted imaging n=355 - DE imaging n=387 - MO n=384 - Hypointense core/Hemorrhage n=346 401 assigned to intravenous abciximab Incomplete CMR scan - Scan terminated n=3 - T 2 poor image quality n=40 - DE poor image quality n=10 Analyzed CMR data - LV function n=401 - T 2 -weighted imaging n=361 - DE imaging n=391 - MO n=390 - Hypointense core/Hemorrhage n=353
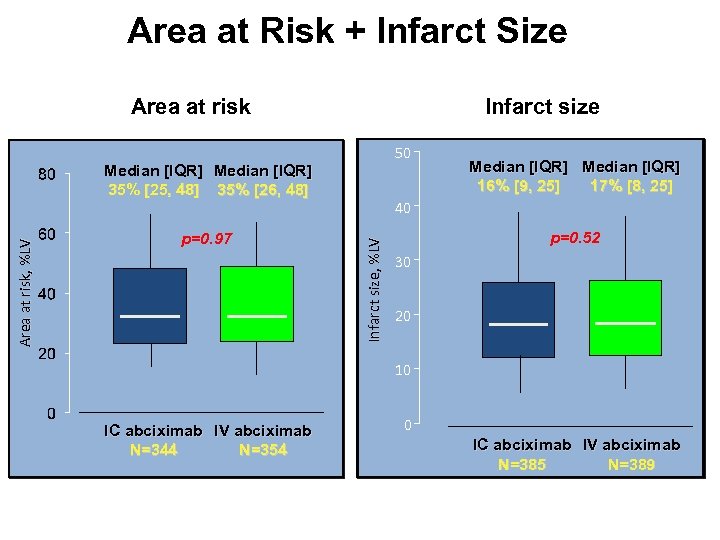
Area at Risk + Infarct Size Area at risk Infarct size 50 p=0. 97 Median [IQR] 16% [9, 25] 17% [8, 25] 40 Infarct size, %LV Area at risk, %LV Median [IQR] 35% [25, 48] 35% [26, 48] p=0. 52 30 20 10 IC abciximab IV abciximab N=344 N=354 0 IC abciximab IV abciximab N=385 N=389
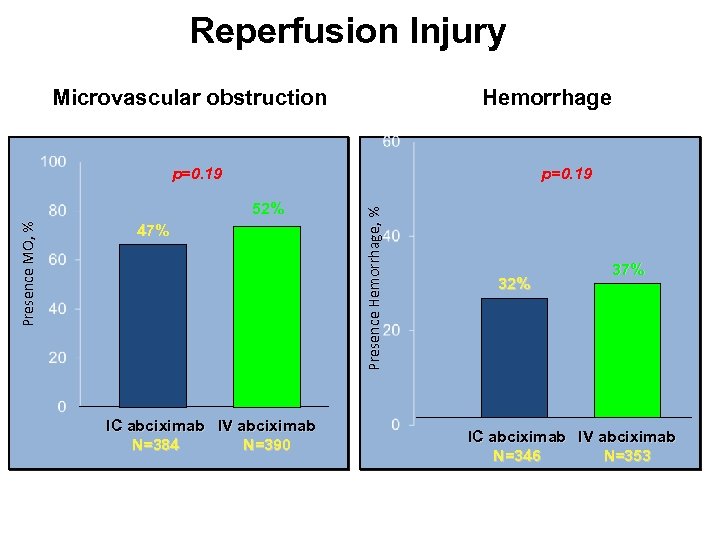
Reperfusion Injury Hemorrhage Microvascular obstruction p=0. 19 Presence MO, % 52% 47% IC abciximab IV abciximab N=384 N=390 Presence Hemorrhage, % p=0. 19 32% 37% IC abciximab IV abciximab N=346 N=353
AIDA STEMI Conclusions • This largest multicenter CMR study in STEMI patients to date demonstrates that IC as compared to IV abciximab did not result in a difference in myocardial damage and/or reperfusion injury. • The results of the AIDA STEMI CMR substudy therefore confirm the lack of difference in the combined endpoint of death, reinfarction or congestive heart failure of the AIDA STEMI trial.

IC infusion of Gp IIb-IIIa via dedicated perfusion catheter? • May reduce thrombus burden at site of lesion in a most efficient manner • May reduce no reflow phenomenon • May address residual thrombus to prevent SAT • May reduce cost with only bolus strategy
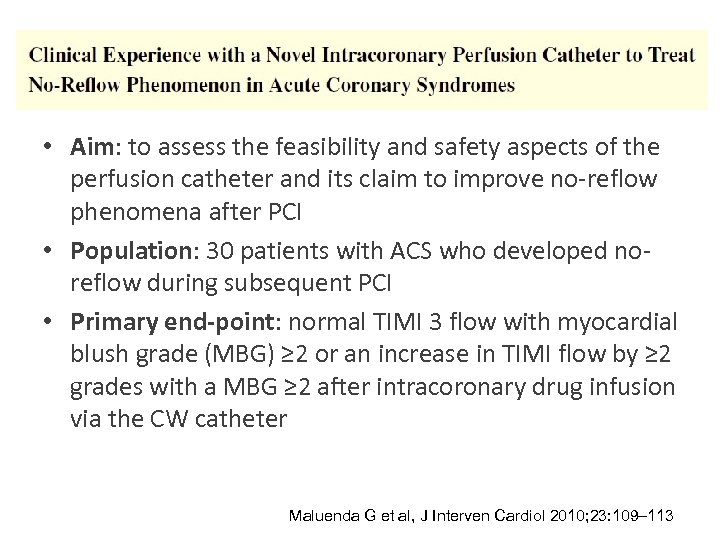
• Aim: to assess the feasibility and safety aspects of the perfusion catheter and its claim to improve no-reflow phenomena after PCI • Population: 30 patients with ACS who developed noreflow during subsequent PCI • Primary end-point: normal TIMI 3 flow with myocardial blush grade (MBG) ≥ 2 or an increase in TIMI flow by ≥ 2 grades with a MBG ≥ 2 after intracoronary drug infusion via the CW catheter Maluenda G et al, J Interven Cardiol 2010; 23: 109– 113
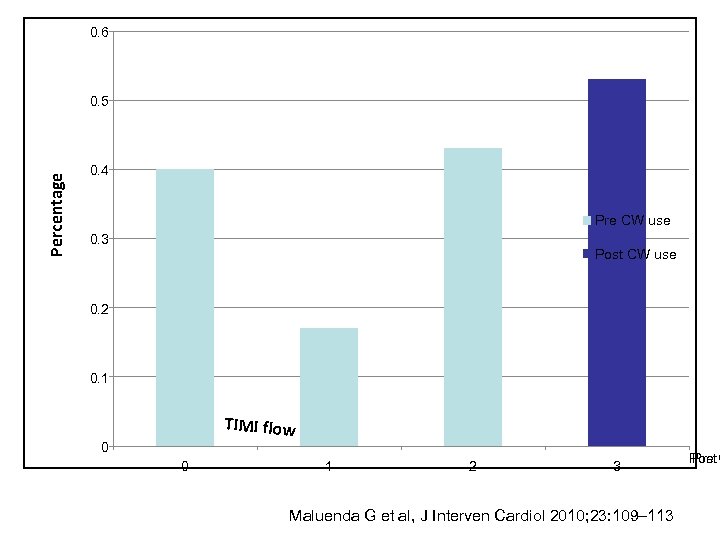
0. 6 Percentage 0. 5 0. 4 Pre CW use 0. 3 Post CW use 0. 2 0. 1 TIMI flow 0 0 1 2 3 Maluenda G et al, J Interven Cardiol 2010; 23: 109– 113 Post C Pre




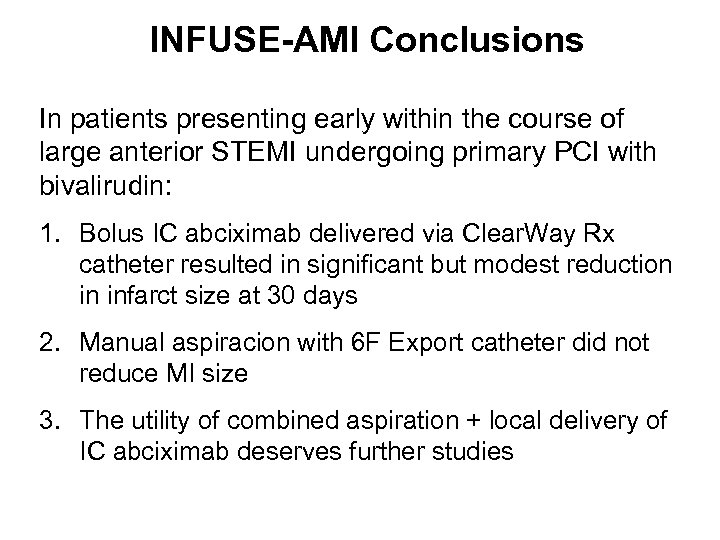
INFUSE-AMI Conclusions In patients presenting early within the course of large anterior STEMI undergoing primary PCI with bivalirudin: 1. Bolus IC abciximab delivered via Clear. Way Rx catheter resulted in significant but modest reduction in infarct size at 30 days 2. Manual aspiracion with 6 F Export catheter did not reduce MI size 3. The utility of combined aspiration + local delivery of IC abciximab deserves further studies
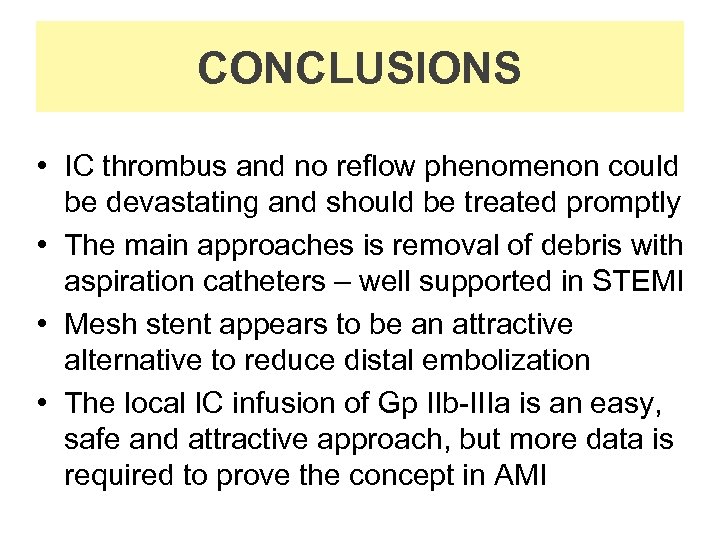
CONCLUSIONS • IC thrombus and no reflow phenomenon could be devastating and should be treated promptly • The main approaches is removal of debris with aspiration catheters – well supported in STEMI • Mesh stent appears to be an attractive alternative to reduce distal embolization • The local IC infusion of Gp IIb-IIIa is an easy, safe and attractive approach, but more data is required to prove the concept in AMI

Thank you!
9729f164ea51b0119212aab5283c83f6.ppt