2f76273f8ba67463f9753d8caea3c4c6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Strategies For Sustainable Rx Savings November 29, 2005 Scott Streator, Director of Health Care Ohio PERS

“Few aspects of the drug industry are more confused –or more confusing- that its pricing structure. ” “We recommend that the Department of Health should conduct a continuing survey of drug costs, average prescription prices, and drug use. ” Final Report. Task Force on Prescription Drugs. U. S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare: Washington, 1969


Mission: Fund and provide quality pension, disability, survivor, health care benefits and services to Ohio state, county, city and miscellaneous government employees – OPERS covers three quarters of a million Ohioans who are state, county, city, university and township employees: • 370, 000 contributing employees • 300, 000 inactive employees with accounts • 148, 000 benefit recipients • 3, 700 contributing employers – Annual benefit payments $3. 4 billion – $68 billion in assets – 9 th Largest State Pension System in U. S. , 16 th Largest in world
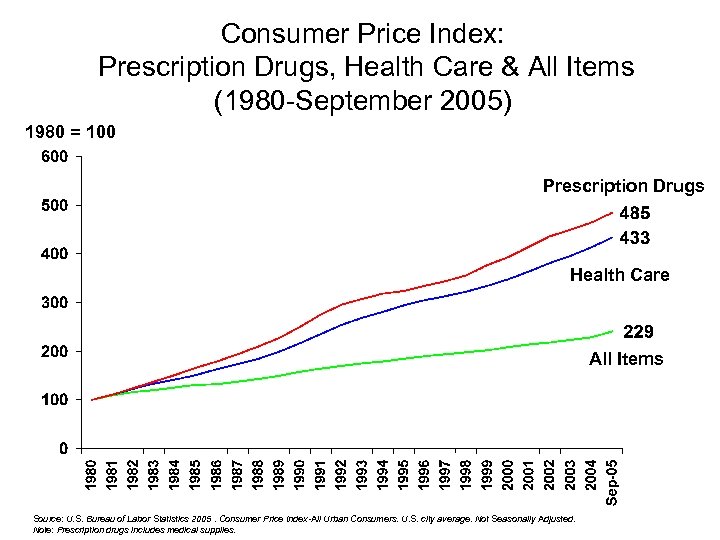
Consumer Price Index: Prescription Drugs, Health Care & All Items (1980 -September 2005) 1980 = 100 Prescription Drugs Health Care All Items Source: U. S. Bureau of Labor Statistics 2005. Consumer Price Index-All Urban Consumers. U. S. city average. Not Seasonally Adjusted. Note: Prescription drugs includes medical supplies.
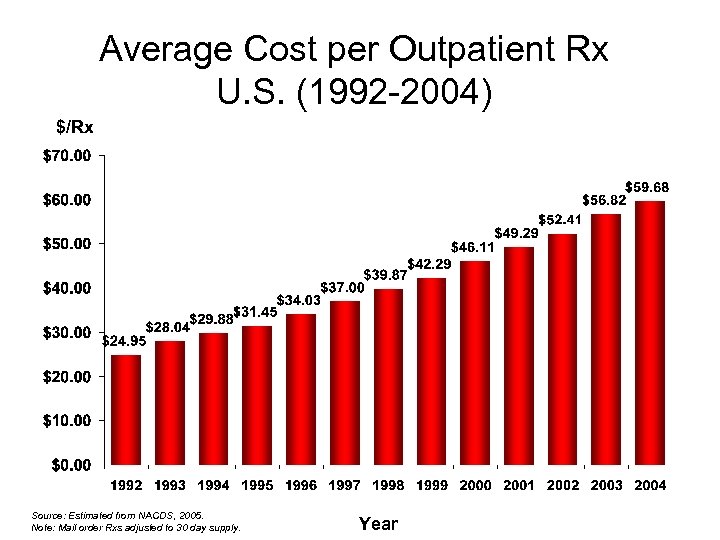
Average Cost per Outpatient Rx U. S. (1992 -2004) $/Rx Source: Estimated from NACDS, 2005. Note: Mail order Rxs adjusted to 30 day supply. Year
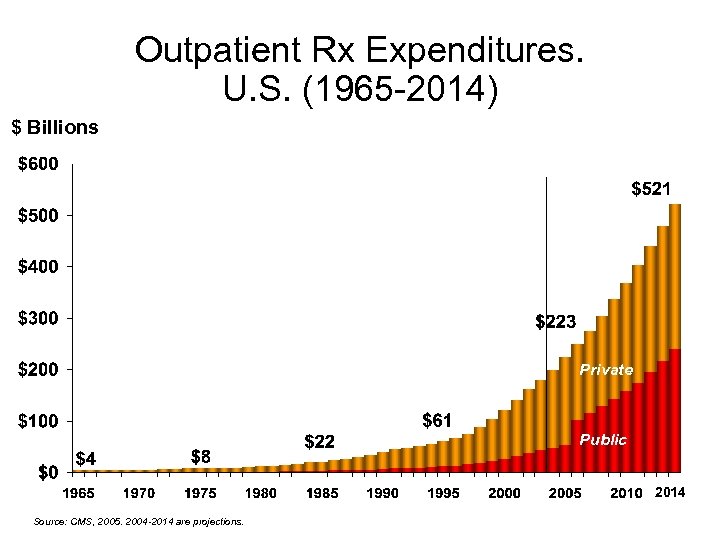
Outpatient Rx Expenditures. U. S. (1965 -2014) $ Billions Private Public 2014 Source: CMS, 2005. 2004 -2014 are projections.
“Get Comfortable with Complexity” AW P V AIL C AD M IN IS TR A RE “HMG” HA S T SSRI KE AR M MULTI-SOURCE P& T CO DAYS SUPPLY M M IT TE E S C S HT IG G R N ITI D AU FORMULARY VS NON-FORMULARY EE MA S W A F ET R BRAND DISCOUNT VE P TI req re e sit ui ZE IL A RO B M AL AN COX II’s PDP CE B IL LI MEDICARE B, D NG REFERENCE PRICING “PPI”
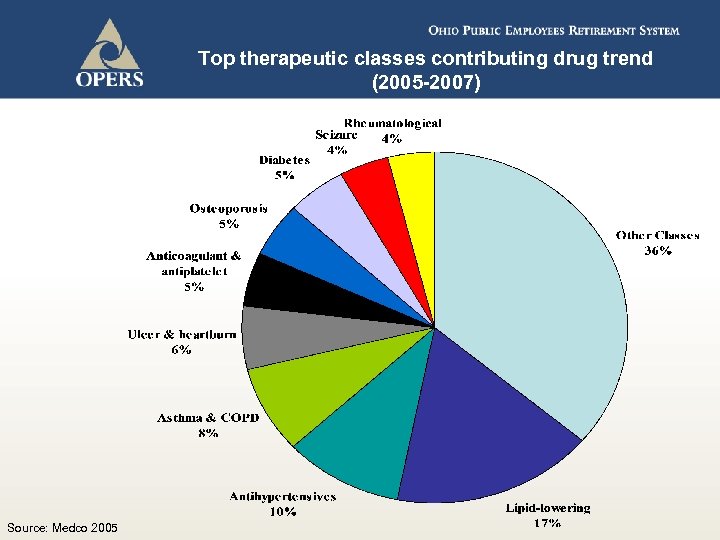
Top therapeutic classes contributing drug trend (2005 -2007) Source: Medco 2005
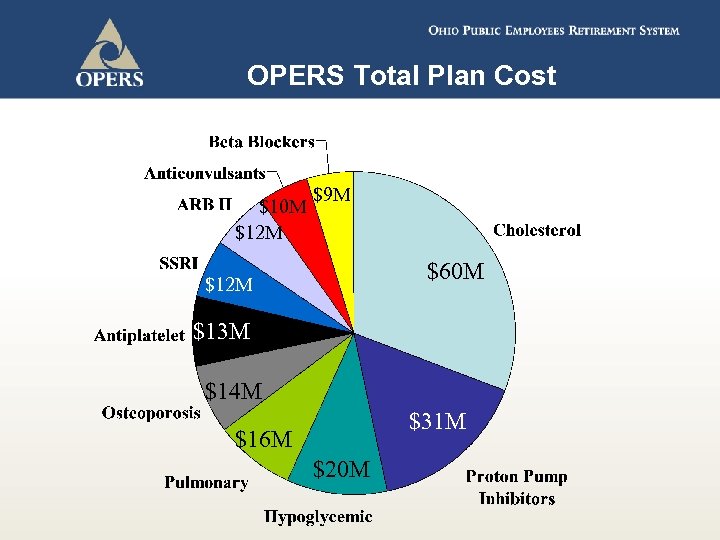
OPERS Total Plan Cost $10 M $12 M $9 M $60 M $12 M $13 M $14 M $31 M $16 M $20 M

Obtain Best Discounts & Rebates as a Foundation #1 gy te tra • Leverage size with Pharmacy Benefit Administrator S (PBM) or TPA • Reduce Administrative Complexity • Evaluate Network Access, Formulary Options Rx Cost = Members X Cost Product = Cost AWP-Discount+Fees. Rebates Product Selection # Units Unit Cost
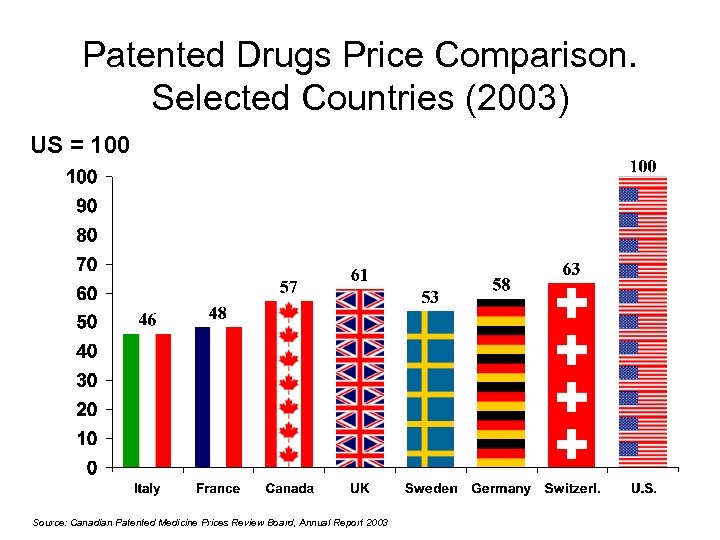
Patented Drugs Price Comparison. Selected Countries (2003) US = 100 Source: Canadian Patented Medicine Prices Review Board, Annual Report 2003
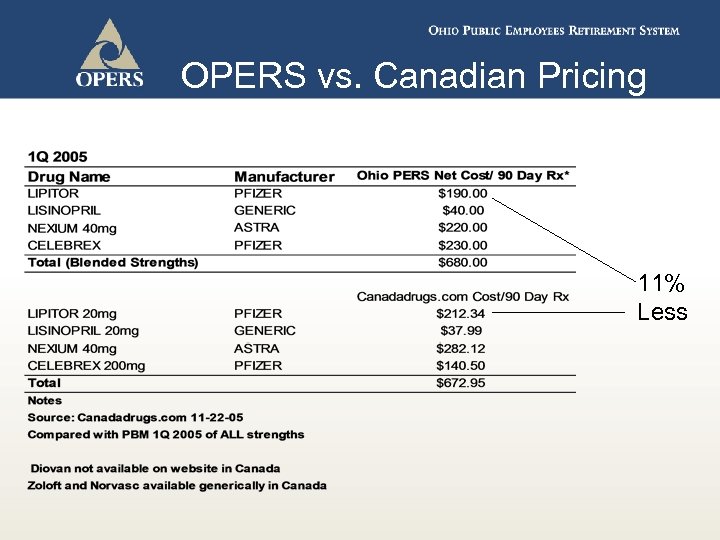
OPERS vs. Canadian Pricing 11% Less

Structure a “Transparent” Agreement #2 gy te tra S • • Define all Revenue Streams Leverage Auditing Rights No Retail Markup & CAP Mail Markup on Generics Administrative fee for specific services (fee or PMPM) “Shared Savings” Methodology Agreement Pricing terms of Brand, Generic, and Source Beware of Biotech Pricing
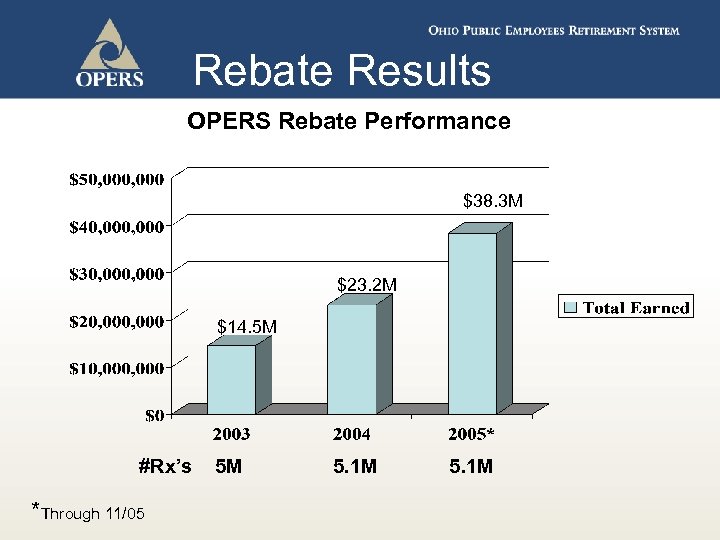
Rebate Results OPERS Rebate Performance $38. 3 M $23. 2 M $14. 5 M #Rx’s *Through 11/05 5 M 5. 1 M
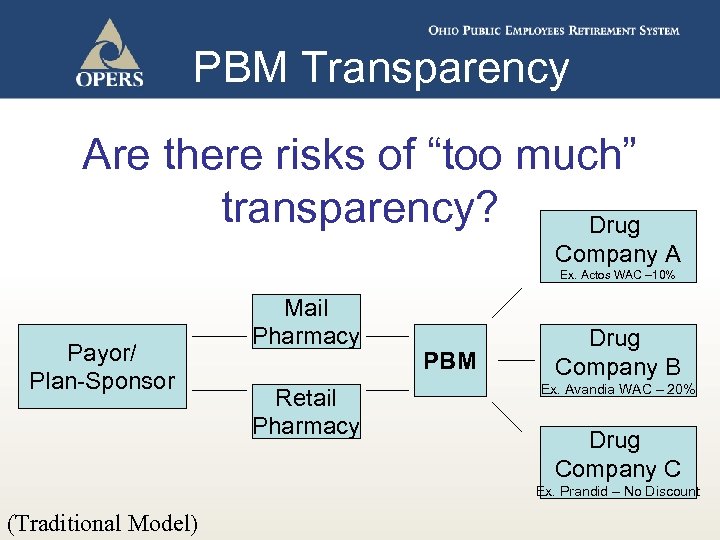
PBM Transparency Are there risks of “too much” transparency? Drug Company A Ex. Actos WAC – 10% Payor/ Plan-Sponsor Mail Pharmacy Retail Pharmacy PBM Drug Company B Ex. Avandia WAC – 20% Drug Company C Ex. Prandid – No Discount (Traditional Model)
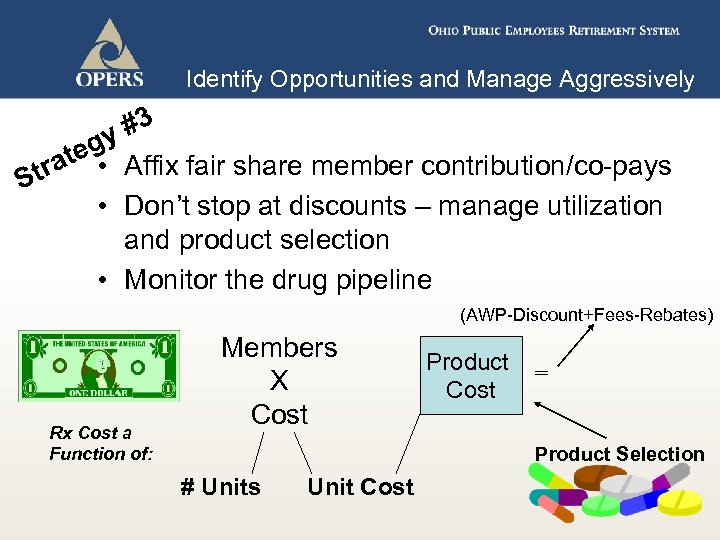
Identify Opportunities and Manage Aggressively #3 gy ate • Affix fair share member contribution/co-pays Str • Don’t stop at discounts – manage utilization and product selection • Monitor the drug pipeline (AWP-Discount+Fees-Rebates) Rx Cost a Function of: Members X Cost Product = Cost Product Selection # Units Unit Cost
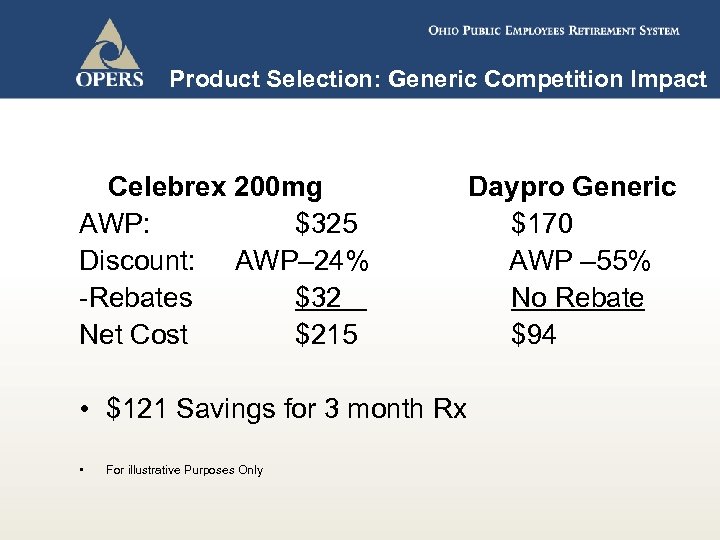
Product Selection: Generic Competition Impact Celebrex 200 mg AWP: $325 Discount: AWP– 24% -Rebates $32 Net Cost $215 Daypro Generic $170 AWP – 55% No Rebate $94 • $121 Savings for 3 month Rx • For illustrative Purposes Only
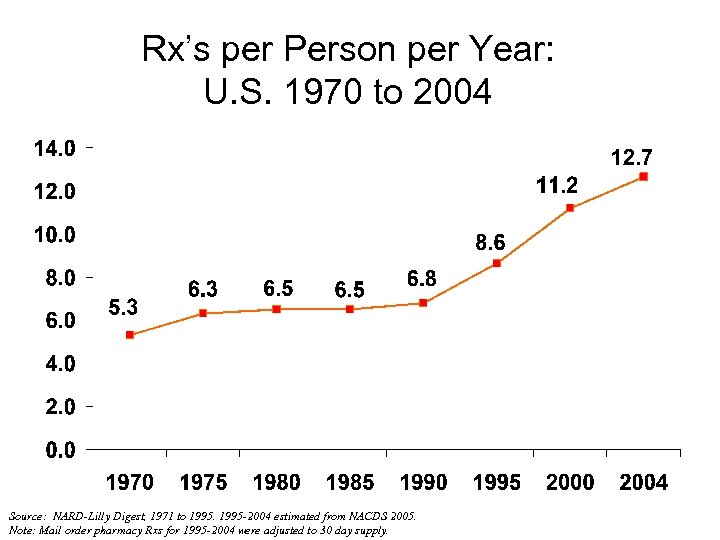
Rx’s per Person per Year: U. S. 1970 to 2004 Source: NARD-Lilly Digest, 1971 to 1995 -2004 estimated from NACDS 2005. Note: Mail order pharmacy Rxs for 1995 -2004 were adjusted to 30 day supply.
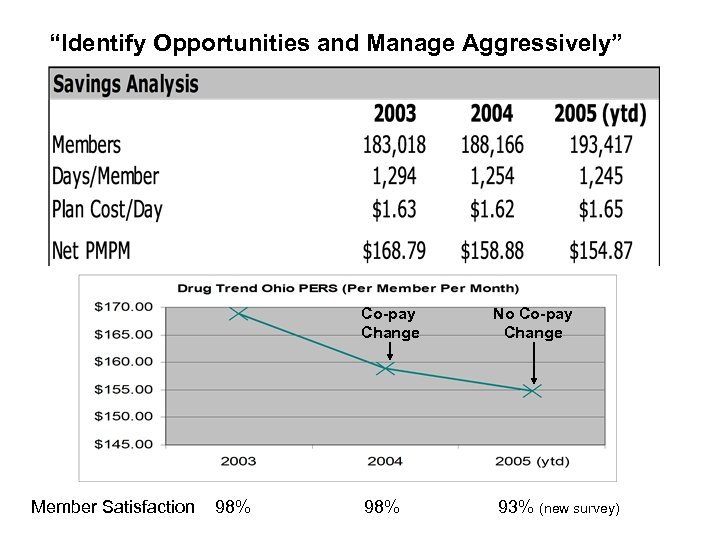
“Identify Opportunities and Manage Aggressively” Co-pay Change Member Satisfaction 98% No Co-pay Change 93% (new survey)
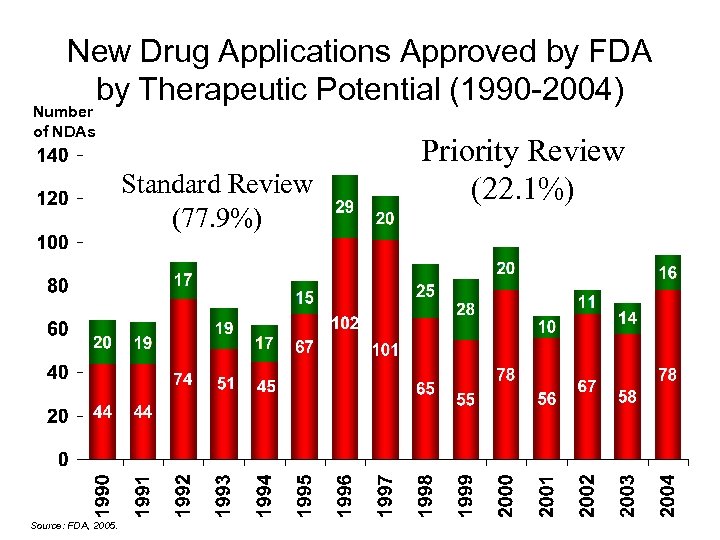
New Drug Applications Approved by FDA by Therapeutic Potential (1990 -2004) Number of NDAs Standard Review (77. 9%) Source: FDA, 2005. Priority Review (22. 1%)
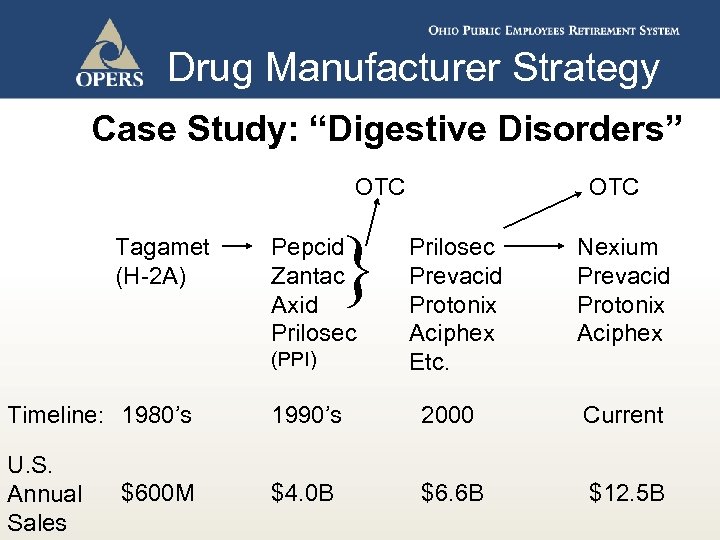
Drug Manufacturer Strategy Case Study: “Digestive Disorders” OTC Tagamet (H-2 A) } Pepcid Zantac Axid Prilosec (PPI) OTC Prilosec Prevacid Protonix Aciphex Etc. Nexium Prevacid Protonix Aciphex Timeline: 1980’s 1990’s 2000 Current U. S. Annual Sales $4. 0 B $6. 6 B $12. 5 B $600 M
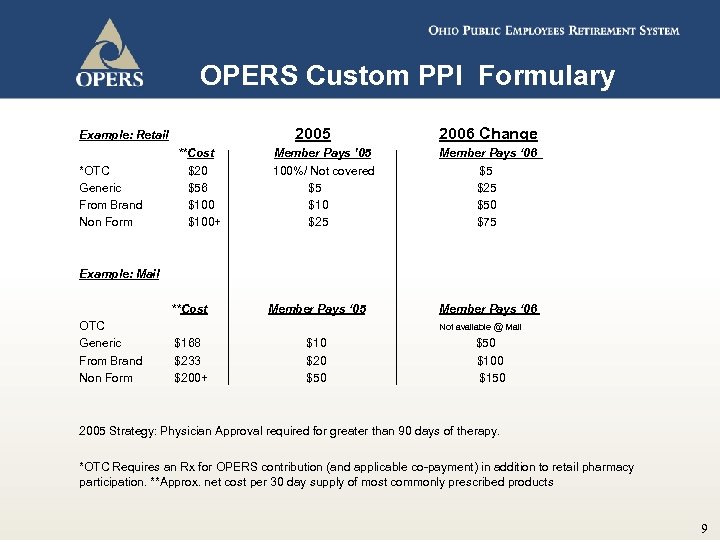
OPERS Custom PPI Formulary 2005 Example: Retail 2006 Change **Cost Member Pays ’ 05 Member Pays ‘ 06 *OTC $20 100%/ Not covered $5 Generic $56 $5 $25 From Brand $100 $10 $50 Non Form $100+ $25 $75 Example: Mail **Cost OTC Generic $168 From Brand $233 Non Form $200+ Member Pays ‘ 05 Member Pays ‘ 06 Not available @ Mail $10 $50 $20 $100 $50 $150 2005 Strategy: Physician Approval required for greater than 90 days of therapy. *OTC Requires an Rx for OPERS contribution (and applicable co-payment) in addition to retail pharmacy participation. **Approx. net cost per 30 day supply of most commonly prescribed products 9

Communication and Consumerism tra S #4 y eg t • Plan Design: 2, 3, 4 tiers, % on flat co-pays? Plan Sponsor vs. Member Responsibility • • • Prevention Quality & Safety-Physician Rx Surveillance Managing change Co-pay confusion Communicate early, using multiple channels to physician, pharmacy and member.
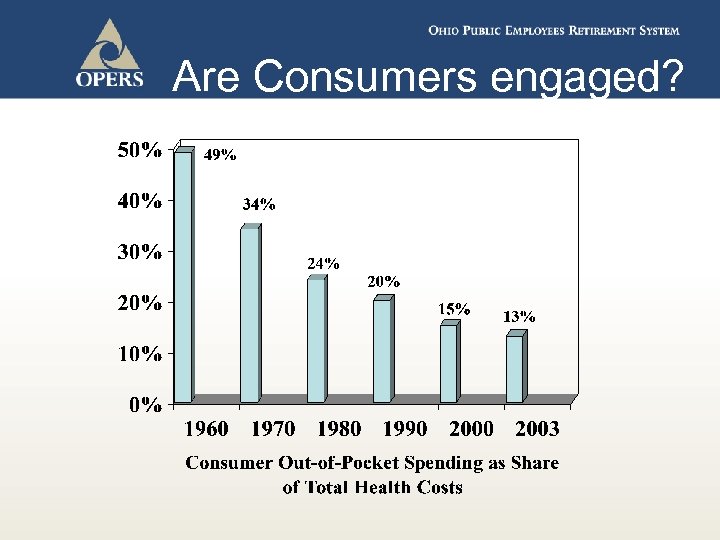
Are Consumers engaged?

Tale of Two Members Two Patients with Identical Diagnosis-different costs Member Costs/30 days Member A: Zyrtec Cozaar Pravachol $70. 00 (Not Covered) $53 -$81 (Covered if ACE I failed) $25 (Non-Formulary Co-pay) $176 Member B: Flonase Lisinopril Lipitor $10 (Co-pay) or Claritin OTC $5 (Generic Co-pay) $10 (Formulary Co-pay) $25 Savings: $151/Month! Source: Walgreens. com April 2005 of common strengths
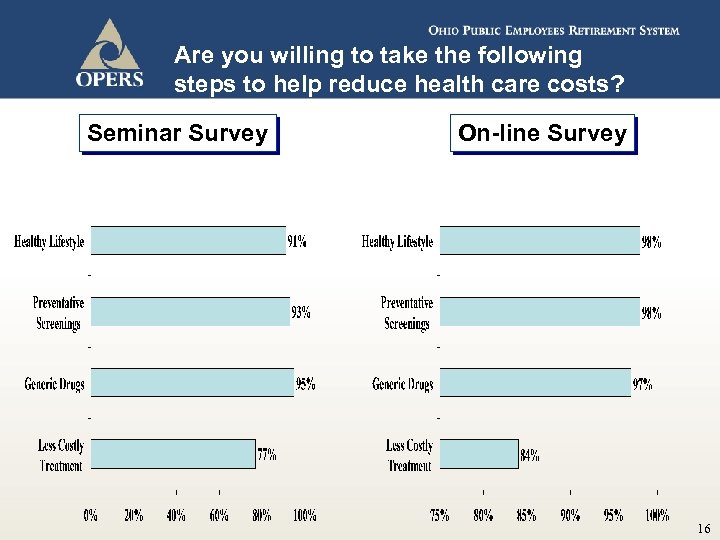
Are you willing to take the following steps to help reduce health care costs? Seminar Survey On-line Survey 16

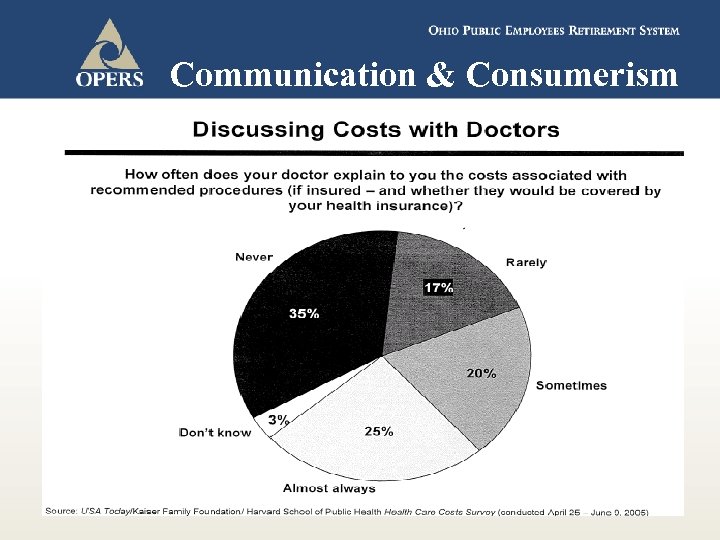
Communication & Consumerism

Alternatives to Traditional Rx Purchasing #5 y eg t tra S • Evaluate Traditional vs. Emerging Models

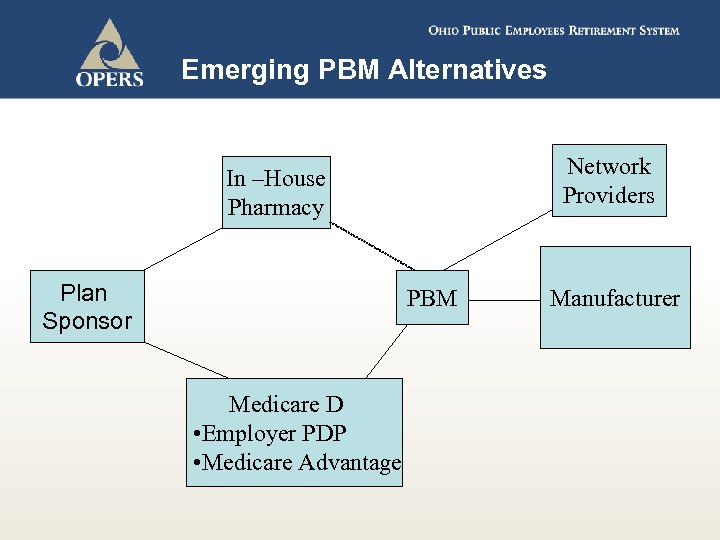
Emerging PBM Alternatives Network Providers In –House Pharmacy Plan Sponsor PBM Medicare D • Employer PDP • Medicare Advantage Manufacturer
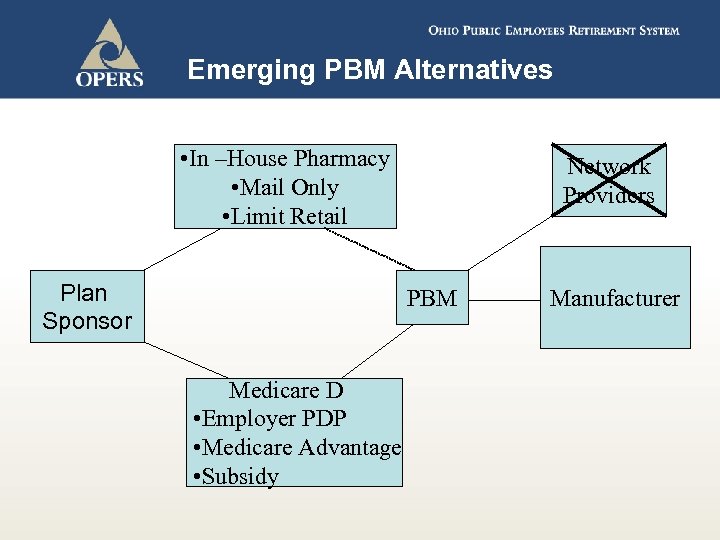
Emerging PBM Alternatives • In –House Pharmacy • Mail Only • Limit Retail Plan Sponsor Network Providers PBM Medicare D • Employer PDP • Medicare Advantage • Subsidy Manufacturer
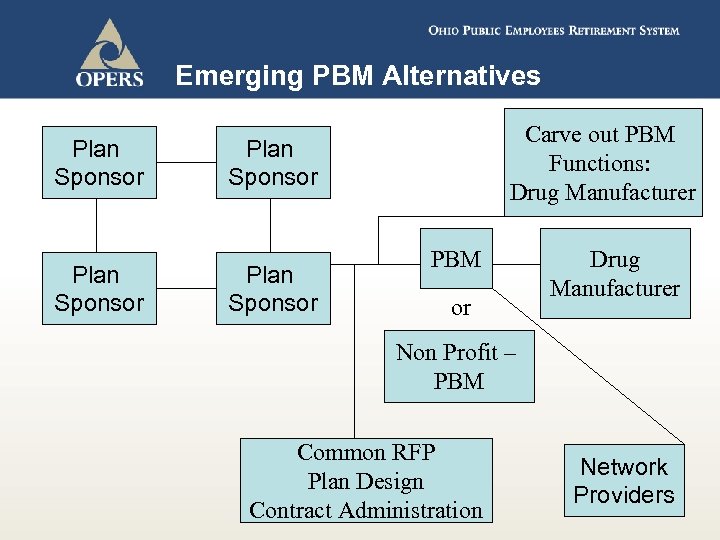
Emerging PBM Alternatives Plan Sponsor Carve out PBM Functions: Drug Manufacturer Plan Sponsor PBM or Drug Manufacturer Non Profit – PBM Common RFP Plan Design Contract Administration Network Providers

Future Topics • Managing the Biotech Beast or Inevitable Explosion? • Medicare D – Assimilation Results • FDA: Overhaul or Fine Tuning? • Pharma Marketing • Drug Safety and Post Marketing Surveilane • International Models • “Bio-shield” and Drug Patent Laws
2f76273f8ba67463f9753d8caea3c4c6.ppt