6f74373109bd3ab033651fe7e9eb505e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 STRATEGIES FOR PERMANENT ACCESS TO SCIENTIFIC INFORMATION IN SOUTHERN AFRICA: FOCUS ON HEALTH AND ENVIRONMENTAL INFORMATION FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT AN INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP 5 -7 SEPTEMBER 2005 CSIR CONVENTIONCENTRE, PRETORIA, SOUTH AFRICA
STRATEGIES FOR PERMANENT ACCESS TO SCIENTIFIC INFORMATION IN SOUTHERN AFRICA: FOCUS ON HEALTH AND ENVIRONMENTAL INFORMATION FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT AN INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP 5 -7 SEPTEMBER 2005 CSIR CONVENTIONCENTRE, PRETORIA, SOUTH AFRICA
 UTILIZATION OF HEALTH INFORMATION IN NAMIBIA FOCUS ON CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES FACED BY HEALTH CARE DELIVERY SYSTEM DR. L. HAOSES-GORASES Ph. D, M Cur, Hon Cur, BA Cur, Adv. Univ. Dipl. in CHN & Education
UTILIZATION OF HEALTH INFORMATION IN NAMIBIA FOCUS ON CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES FACED BY HEALTH CARE DELIVERY SYSTEM DR. L. HAOSES-GORASES Ph. D, M Cur, Hon Cur, BA Cur, Adv. Univ. Dipl. in CHN & Education
 INTRODUCTION • • 2001 Population Census – 1. 830, 330 Population 1. 830, 330 -2001 Housing Census Annual growth rate 2. 6% Surface area 824, 116 km 2 Average 2 persons per km 2 People spread unevenly across the country Urban 33% Rural 67% (SSS 2004)
INTRODUCTION • • 2001 Population Census – 1. 830, 330 Population 1. 830, 330 -2001 Housing Census Annual growth rate 2. 6% Surface area 824, 116 km 2 Average 2 persons per km 2 People spread unevenly across the country Urban 33% Rural 67% (SSS 2004)
 NAMIBIA BY REGION
NAMIBIA BY REGION
 BACKGROUND HIS under Epidemiology Division n Collect routine data – all health facilities (clinics, health centres & hospitals) Aim: n Analyze n Documentation n Disseminate – planning n Direct changes in policies n Improve monitoring performance n Identify support needs n
BACKGROUND HIS under Epidemiology Division n Collect routine data – all health facilities (clinics, health centres & hospitals) Aim: n Analyze n Documentation n Disseminate – planning n Direct changes in policies n Improve monitoring performance n Identify support needs n
 KEY PLAYERS n n n n Mo. HSS & Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) Major surveys & census Data duplications occurring With new developments new programmes on board Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission (PMTCT) Anti Retroviral Treatment (ART) Voluntary Counseling & Testing (VCT)
KEY PLAYERS n n n n Mo. HSS & Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) Major surveys & census Data duplications occurring With new developments new programmes on board Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission (PMTCT) Anti Retroviral Treatment (ART) Voluntary Counseling & Testing (VCT)
 CONTINUE n n n Health Information System developed in 1990 after independence Many challenges –improvement in the past years In 2004 and 2005 situation analysis and comprehensive assessment of the system
CONTINUE n n n Health Information System developed in 1990 after independence Many challenges –improvement in the past years In 2004 and 2005 situation analysis and comprehensive assessment of the system
 OBJECTIVES To improve individual and institutional performance n To measure quality and efficiency of the strategies in place n To compare performance over time in relation to national targets n To provide support to regions, districts & health facilities To monitor trends in: n n n Coverage Quality Effectiveness of the services Guide policy-makers for resource allocation
OBJECTIVES To improve individual and institutional performance n To measure quality and efficiency of the strategies in place n To compare performance over time in relation to national targets n To provide support to regions, districts & health facilities To monitor trends in: n n n Coverage Quality Effectiveness of the services Guide policy-makers for resource allocation
 RECORDING PROCEDURES n n n Tally sheets Daily ward census Monthly summary forms E-mail Floppy diskettes from regional to national level
RECORDING PROCEDURES n n n Tally sheets Daily ward census Monthly summary forms E-mail Floppy diskettes from regional to national level
 CONTINUE n n n n Information covers indicators on: Human resources Population Health facilities Financing Directive in terms of MDG’s Information only from: Public and mission health facilities
CONTINUE n n n n Information covers indicators on: Human resources Population Health facilities Financing Directive in terms of MDG’s Information only from: Public and mission health facilities
 QUALITY OF THE DATA n n Training of staff Computerized system E-mail functioning (80%) Floppy diskettes also introduced
QUALITY OF THE DATA n n Training of staff Computerized system E-mail functioning (80%) Floppy diskettes also introduced
 SOURCES OF DATA n n n Located in different directorates Directorate Planning & Human Resources (MIS) Central Bureau of statistics in National Planning Commission (Census, vital events) Ministry of Home Affairs (registration birth, deaths, immigrants etc. ) Discussions for 3 rd national statistic plan
SOURCES OF DATA n n n Located in different directorates Directorate Planning & Human Resources (MIS) Central Bureau of statistics in National Planning Commission (Census, vital events) Ministry of Home Affairs (registration birth, deaths, immigrants etc. ) Discussions for 3 rd national statistic plan
 STRENTHENING OF HIS n n n Revision in 1994 New forms introduced in 1995 Revised again after five years International standards ICD-10 included
STRENTHENING OF HIS n n n Revision in 1994 New forms introduced in 1995 Revised again after five years International standards ICD-10 included
 DECENTRALIZATION/ COMPUTERIZATION n n n All 13 regions 33 districts (computerized) To improve channels of processing of the data: Health facilities to district, regional and national level Telephoning instant training ICD-10 for coding purposes (IP)
DECENTRALIZATION/ COMPUTERIZATION n n n All 13 regions 33 districts (computerized) To improve channels of processing of the data: Health facilities to district, regional and national level Telephoning instant training ICD-10 for coding purposes (IP)
 INTRODUCTION OF STANDARD REGISTERS n n n Outpatient Department (OPD) Inpatient Department (IPD) Antenatal Care (ANC) Expanded Programme on Immunization (EPI) Legal records Reference manuals are available
INTRODUCTION OF STANDARD REGISTERS n n n Outpatient Department (OPD) Inpatient Department (IPD) Antenatal Care (ANC) Expanded Programme on Immunization (EPI) Legal records Reference manuals are available
 INTERNATIONAL PARTNERS ROLE n n Investing in specific programmes GF, USAID, FHI, CDC, PEPFAR UN AGENCIES (Malaria, TB, HIV/AIDS) Reporting circles UN agencies support the health service e. g. Country Response Information System (CRIS)
INTERNATIONAL PARTNERS ROLE n n Investing in specific programmes GF, USAID, FHI, CDC, PEPFAR UN AGENCIES (Malaria, TB, HIV/AIDS) Reporting circles UN agencies support the health service e. g. Country Response Information System (CRIS)
 REGULARLY & LEGAL FRAME WORK n n n Facility Act – draft Health Act –draft Consolidate information from private health facilities & other stakeholders
REGULARLY & LEGAL FRAME WORK n n n Facility Act – draft Health Act –draft Consolidate information from private health facilities & other stakeholders
 STRATEGIES n n n n CBS conducts surveys & household census Ministry of Home Affairs generates info on births, death and immigration Integrated disease surveillance system collects info on notifiable diseases such as: Measles Neonatal Tetanus Polio (AFP) etc NDHS scheduled for 2006 (every five years)
STRATEGIES n n n n CBS conducts surveys & household census Ministry of Home Affairs generates info on births, death and immigration Integrated disease surveillance system collects info on notifiable diseases such as: Measles Neonatal Tetanus Polio (AFP) etc NDHS scheduled for 2006 (every five years)
 INFORMATION MANAGEMENT Several sets: n Health indicators used for: Planning Resources allocation Monitoring & evaluation n Compiled at district to regional and national n Data cleaned at all levels & actions taken n Several data bases coming up n Development partners choice n MOHSS is constantly updating it’s website – new version to be release this year n SPSS, EPI-INFO & Microsoft Access in used
INFORMATION MANAGEMENT Several sets: n Health indicators used for: Planning Resources allocation Monitoring & evaluation n Compiled at district to regional and national n Data cleaned at all levels & actions taken n Several data bases coming up n Development partners choice n MOHSS is constantly updating it’s website – new version to be release this year n SPSS, EPI-INFO & Microsoft Access in used
 AVAILABILITY OF SOUND HEALTH STATISTICS n n Strength (quality) of the data assessed Statistical techniques examined Major elements (domains) n n n Health profile of the population Risk factors Service coverage Factors influencing data n n n Timeliness Representativeness Periocity Consistency 65% info readily available
AVAILABILITY OF SOUND HEALTH STATISTICS n n Strength (quality) of the data assessed Statistical techniques examined Major elements (domains) n n n Health profile of the population Risk factors Service coverage Factors influencing data n n n Timeliness Representativeness Periocity Consistency 65% info readily available
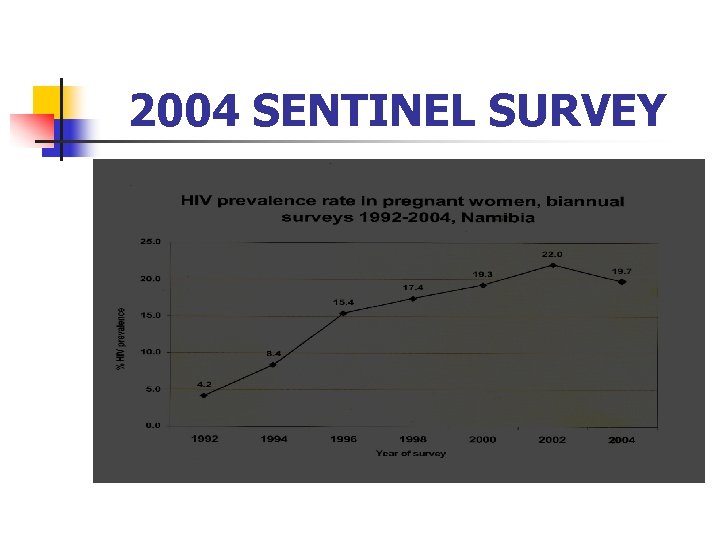 2004 SENTINEL SURVEY
2004 SENTINEL SURVEY
 UTILIZATION n n n Vital vehicle – M & E Reprogramming Planning Development of policies/guidelines Setting of priorities
UTILIZATION n n n Vital vehicle – M & E Reprogramming Planning Development of policies/guidelines Setting of priorities
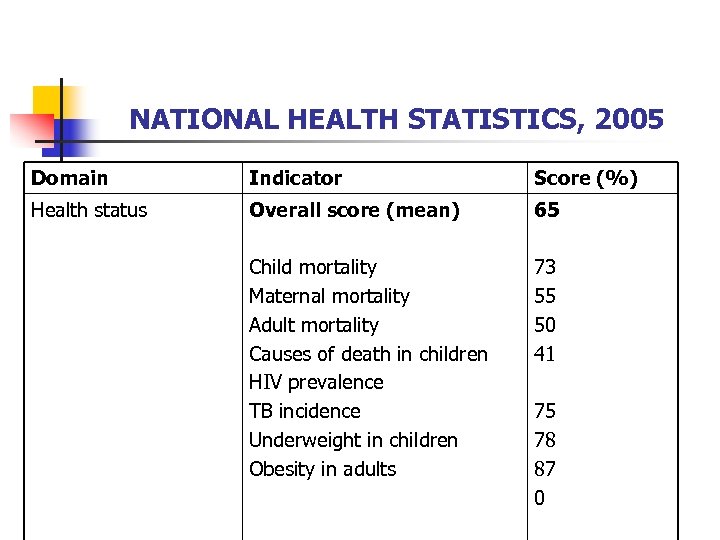 NATIONAL HEALTH STATISTICS, 2005 Domain Indicator Score (%) Health status Overall score (mean) 65 Child mortality Maternal mortality Adult mortality Causes of death in children HIV prevalence TB incidence Underweight in children Obesity in adults 73 55 50 41 75 78 87 0
NATIONAL HEALTH STATISTICS, 2005 Domain Indicator Score (%) Health status Overall score (mean) 65 Child mortality Maternal mortality Adult mortality Causes of death in children HIV prevalence TB incidence Underweight in children Obesity in adults 73 55 50 41 75 78 87 0
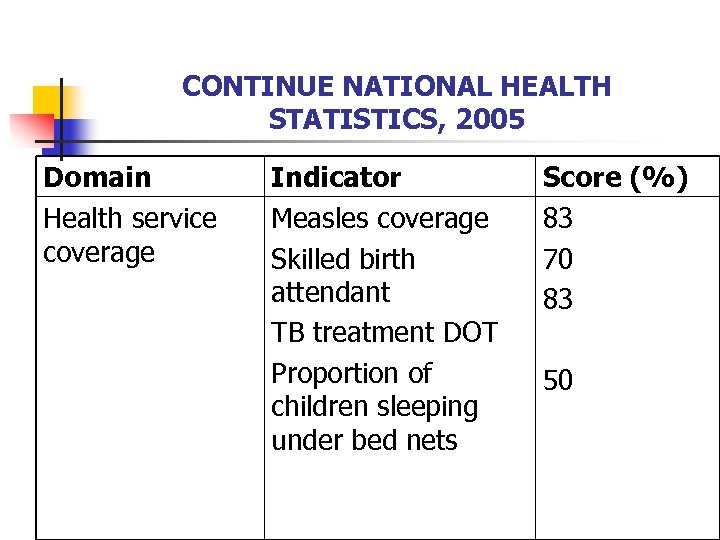 CONTINUE NATIONAL HEALTH STATISTICS, 2005 Domain Health service coverage Indicator Measles coverage Skilled birth attendant TB treatment DOT Proportion of children sleeping under bed nets Score (%) 83 70 83 50
CONTINUE NATIONAL HEALTH STATISTICS, 2005 Domain Health service coverage Indicator Measles coverage Skilled birth attendant TB treatment DOT Proportion of children sleeping under bed nets Score (%) 83 70 83 50
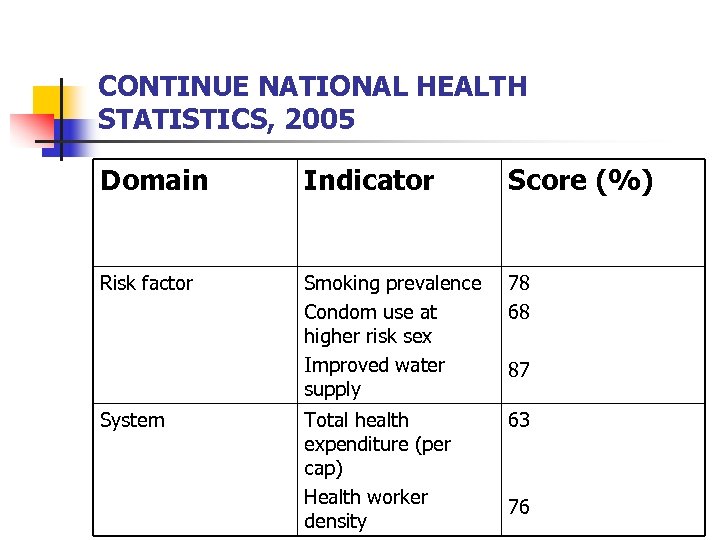 CONTINUE NATIONAL HEALTH STATISTICS, 2005 Domain Indicator Score (%) Risk factor Smoking prevalence Condom use at higher risk sex Improved water supply 78 68 Total health expenditure (per cap) Health worker density 63 System 87 76
CONTINUE NATIONAL HEALTH STATISTICS, 2005 Domain Indicator Score (%) Risk factor Smoking prevalence Condom use at higher risk sex Improved water supply 78 68 Total health expenditure (per cap) Health worker density 63 System 87 76
 CHALLENGES n n n n Turn-over of staff/training Timeliness – info – national level No designated staff at district level Computer – literacy lacking Info – private sector not available Development partners agenda Coordination of the systems Involvement of top level management
CHALLENGES n n n n Turn-over of staff/training Timeliness – info – national level No designated staff at district level Computer – literacy lacking Info – private sector not available Development partners agenda Coordination of the systems Involvement of top level management
 OPPORTUNITIES n n n n Strengthening/coordination of system Capacity development Completion of facility & Health Act Capitalize on development partners’ support to strengthen lower levels Regional collaboration/expertise (SADC, WHO etc). Development of critical mass in the region e. g. WHO, SADC etc. Availability of expertise in the SADC region
OPPORTUNITIES n n n n Strengthening/coordination of system Capacity development Completion of facility & Health Act Capitalize on development partners’ support to strengthen lower levels Regional collaboration/expertise (SADC, WHO etc). Development of critical mass in the region e. g. WHO, SADC etc. Availability of expertise in the SADC region
 CONCLUSION n n n Key constituencies to form coordinating mechanism Designated staff at district level Mobilization of resources by all stakeholders Involve policy-makers (vital tool) Country needs driven system Indicators to match with National Development Plan
CONCLUSION n n n Key constituencies to form coordinating mechanism Designated staff at district level Mobilization of resources by all stakeholders Involve policy-makers (vital tool) Country needs driven system Indicators to match with National Development Plan
 CONTINUE n n n Train staff on computer literacy on HIS Involvement of policy makers and stakeholders for better understanding & support Computer back-up system at regional level Facility and Health Acts be finalized and implemented Sustainability of HIS address Horizontal learning (regional expertise)
CONTINUE n n n Train staff on computer literacy on HIS Involvement of policy makers and stakeholders for better understanding & support Computer back-up system at regional level Facility and Health Acts be finalized and implemented Sustainability of HIS address Horizontal learning (regional expertise)
 NB! n n n HIS is serving as a vital instrument in our health service delivering system It is directing the Mo. HSS in identification of shortcomings (revision of the system, adjusting of the indicators, software etc. Strengthening at all levels Make information available in a user-friendly manner Proper utilization of the system
NB! n n n HIS is serving as a vital instrument in our health service delivering system It is directing the Mo. HSS in identification of shortcomings (revision of the system, adjusting of the indicators, software etc. Strengthening at all levels Make information available in a user-friendly manner Proper utilization of the system
 CONTINUE n n HIS is reporting on diseases targeted for eradication and elimination (e. g. Polio (80% WHO) Measles and Neonatal Tetanus HIS is in high demand by sectors – positive move Thank you!!!
CONTINUE n n HIS is reporting on diseases targeted for eradication and elimination (e. g. Polio (80% WHO) Measles and Neonatal Tetanus HIS is in high demand by sectors – positive move Thank you!!!


