a2b2346ec880e9e9d07bf8abb7143011.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Strategies for Implementing Reviews of Student Learning in a Decentralized Environment Sharon A. La Voy Office of Institutional Research, Planning and Assessment
Strategies for Implementing Reviews of Student Learning in a Decentralized Environment Sharon A. La Voy Office of Institutional Research, Planning and Assessment
 What We’ll Cover Today History of assessment at UM UM challenges Structure UM put in place Resources made available Development of process New campus context Successes and lessons learned
What We’ll Cover Today History of assessment at UM UM challenges Structure UM put in place Resources made available Development of process New campus context Successes and lessons learned
 Previous Assessment at UM Specialized Accreditation Engineering – ABET Education – NCATE Business – AACSB Campus Assessment Working Group (CAWG) Student satisfaction Describing student experiences
Previous Assessment at UM Specialized Accreditation Engineering – ABET Education – NCATE Business – AACSB Campus Assessment Working Group (CAWG) Student satisfaction Describing student experiences
 Data-Supported Decisions Program reviews Budget planning cycle Task forces Course evaluations
Data-Supported Decisions Program reviews Budget planning cycle Task forces Course evaluations
 Middle States Developments PRR highlighted CAWG’s efforts Team’s evaluation encouraged UM to make progress on learning outcomes General lack of awareness of scope of this recommendation Middle States numbers: Previous to new standard, 20 -30% further review; post new standard, 70 -80%
Middle States Developments PRR highlighted CAWG’s efforts Team’s evaluation encouraged UM to make progress on learning outcomes General lack of awareness of scope of this recommendation Middle States numbers: Previous to new standard, 20 -30% further review; post new standard, 70 -80%
 What is the New Expectation? Standard 14: Assessment of Student Learning Assessment of student learning demonstrates that the institution’s students have knowledge, skills, and competencies consistent with institutional goals and that students at graduation have achieved appropriate higher education goals. An accredited institution is…
What is the New Expectation? Standard 14: Assessment of Student Learning Assessment of student learning demonstrates that the institution’s students have knowledge, skills, and competencies consistent with institutional goals and that students at graduation have achieved appropriate higher education goals. An accredited institution is…
 Characterized by… Articulated expectations of student learning at various levels (institution, degree/program, course) that are consonant with the institution’s mission A plan that describes student learning assessment activities being undertaken at the institution Evidence that assessment information is used to improve teaching and learning
Characterized by… Articulated expectations of student learning at various levels (institution, degree/program, course) that are consonant with the institution’s mission A plan that describes student learning assessment activities being undertaken at the institution Evidence that assessment information is used to improve teaching and learning
 Others Following Suit State pressures to conform to common standards Modifications of professional school standards Some at the University interested in telling our story in language other than input factors
Others Following Suit State pressures to conform to common standards Modifications of professional school standards Some at the University interested in telling our story in language other than input factors
 Challenges to Overcome Few strong research university examples, for understandable reasons Threat of failed reaccreditation suspicious Size of the institution Common outcomes for Theater and Electrical Engineering? Decentralized culture
Challenges to Overcome Few strong research university examples, for understandable reasons Threat of failed reaccreditation suspicious Size of the institution Common outcomes for Theater and Electrical Engineering? Decentralized culture
 Many Tasks Institution-wide common outcomes And are these the same as our CORE general education program? Program-specific outcomes Course outcomes Assessment of all We began with what we could control…
Many Tasks Institution-wide common outcomes And are these the same as our CORE general education program? Program-specific outcomes Course outcomes Assessment of all We began with what we could control…
 A Centrally Validated Structure… The Provost’s Commission on Learning Outcomes Assessment: The Planning Team (two IR staff and four faculty administrators) The Deans Steering Committee The Faculty Working Group The College Coordinator Committee
A Centrally Validated Structure… The Provost’s Commission on Learning Outcomes Assessment: The Planning Team (two IR staff and four faculty administrators) The Deans Steering Committee The Faculty Working Group The College Coordinator Committee
 The Deans Steering Committee Chaired by the Undergraduate Deans of prominent colleges asked to serve We work out details with them Introduce decisions to Council of Deans and community with them already on board They nominated faculty to Working Group (we asked for strong faculty with vibrant research agendas)
The Deans Steering Committee Chaired by the Undergraduate Deans of prominent colleges asked to serve We work out details with them Introduce decisions to Council of Deans and community with them already on board They nominated faculty to Working Group (we asked for strong faculty with vibrant research agendas)
 The Faculty Working Group Chaired by the Undergraduate Dean Tasked with writing outcomes for Middle States “Five Essential Elements” of an undergraduate education (in addition to Gen Ed and disciplines) Met for a semester, reviewed other institutions’ goals, worked out language
The Faculty Working Group Chaired by the Undergraduate Dean Tasked with writing outcomes for Middle States “Five Essential Elements” of an undergraduate education (in addition to Gen Ed and disciplines) Met for a semester, reviewed other institutions’ goals, worked out language
 Rolling Out to the Programs Could show progress at University level Provost distributed Faculty Working Group results, and said ALL programs must follow Back to Deans Steering Committee Process has to be owned in the Colleges I envisioned programs submitting centrally; but that would not honor College control They appoint College Coordinator for each
Rolling Out to the Programs Could show progress at University level Provost distributed Faculty Working Group results, and said ALL programs must follow Back to Deans Steering Committee Process has to be owned in the Colleges I envisioned programs submitting centrally; but that would not honor College control They appoint College Coordinator for each
 College Coordinators Sharing of experiences Honest critique of all work Peer review Seminar-type discussions on issues Ground rules for privacy and sharing work
College Coordinators Sharing of experiences Honest critique of all work Peer review Seminar-type discussions on issues Ground rules for privacy and sharing work
 College Process Organize learning outcomes assessment process internally (College Coordinators and Deans) Consider whethere are common Collegewide outcome goals Review department and program plans for consistency with College standards for quality Submit all assembled Assessment Plans under the signature of the Dean to the Provost
College Process Organize learning outcomes assessment process internally (College Coordinators and Deans) Consider whethere are common Collegewide outcome goals Review department and program plans for consistency with College standards for quality Submit all assembled Assessment Plans under the signature of the Dean to the Provost
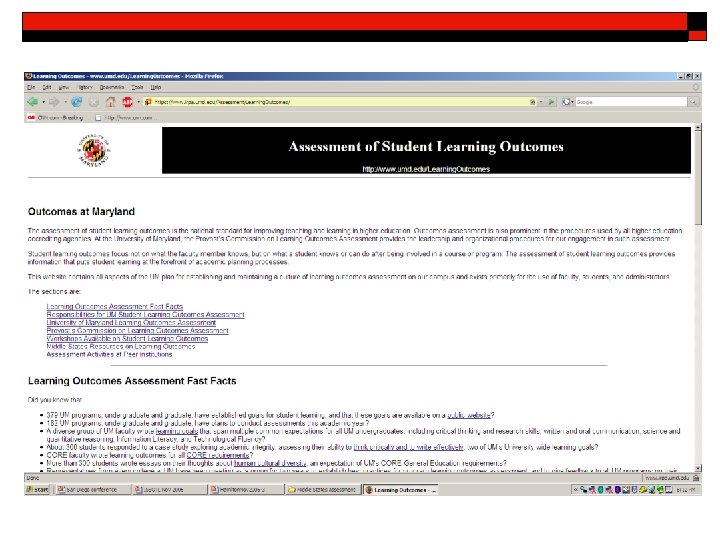
 Resources Made Available Planning Team always available for presentations and consultations Registration for local (thankfully) Middle States assessment conference funded Learning outcomes workshops with nationally renowned speakers for Coordinators; all faculty and staff invited to keynote addresses www. umd. edu/Learning. Outcomes
Resources Made Available Planning Team always available for presentations and consultations Registration for local (thankfully) Middle States assessment conference funded Learning outcomes workshops with nationally renowned speakers for Coordinators; all faculty and staff invited to keynote addresses www. umd. edu/Learning. Outcomes
 Developments Program Plans submitted in Spring 2006 400 plans split up among teams of Coordinators and reviewed using rubric Coordinators provide written feedback instead of rubric results, deleting ‘judgments’ Overall and program specific feedback sent to Deans from Provost
Developments Program Plans submitted in Spring 2006 400 plans split up among teams of Coordinators and reviewed using rubric Coordinators provide written feedback instead of rubric results, deleting ‘judgments’ Overall and program specific feedback sent to Deans from Provost
 Developments Revisions to plans submitted in Fall Plans for assessments this academic year Deans Steering Committee – Colleges decide how they do this within a 4 year cycle Results and projected curriculum changes submitted in March, after accreditation visit Reviewed by Coordinators, feedback given to colleges
Developments Revisions to plans submitted in Fall Plans for assessments this academic year Deans Steering Committee – Colleges decide how they do this within a 4 year cycle Results and projected curriculum changes submitted in March, after accreditation visit Reviewed by Coordinators, feedback given to colleges
 Survey of Coordinators What was the most important experience you had in working with your college? The language of evaluation has changed in my college. There is a larger sense of a shared commitment to our students. There is a shared sense of the value of articulating the learning outcome goals. Faculty have been very cooperative. I have shared good ideas from other disciplines with my college. We can meet our own needs and the needs of accrediting agencies at the same time.
Survey of Coordinators What was the most important experience you had in working with your college? The language of evaluation has changed in my college. There is a larger sense of a shared commitment to our students. There is a shared sense of the value of articulating the learning outcome goals. Faculty have been very cooperative. I have shared good ideas from other disciplines with my college. We can meet our own needs and the needs of accrediting agencies at the same time.
 Survey of Coordinators What was most important to you in participating in the College Coordinator group? A well-directed and focused committee can get a lot done. A committed group can take on a challenging project, work hard, and succeed. Communication across campus with different disciplines increased my understanding. The assessment rubric for graduate programs that was distributed helps us a lot.
Survey of Coordinators What was most important to you in participating in the College Coordinator group? A well-directed and focused committee can get a lot done. A committed group can take on a challenging project, work hard, and succeed. Communication across campus with different disciplines increased my understanding. The assessment rubric for graduate programs that was distributed helps us a lot.
 Survey of Coordinators What was most problematic for you in this process? Getting agreement on the assessment of graduate programs. Finding the time. Adding this to our workload.
Survey of Coordinators What was most problematic for you in this process? Getting agreement on the assessment of graduate programs. Finding the time. Adding this to our workload.
 Survey of Coordinators What is the overall result for you and your college? There have been significant new conversations about how to change teaching. Faculty have changed their syllabi. We wonder if the university will continue this process.
Survey of Coordinators What is the overall result for you and your college? There have been significant new conversations about how to change teaching. Faculty have changed their syllabi. We wonder if the university will continue this process.
 Successes and Milestones Utilizing groups to their utmost capacity College Coordinators act as community of scholars Reported “brainwashing” of some as they come to understand value of learning outcomes assessment CORE faculty committee saw benefits and established general education learning outcomes with little resistance
Successes and Milestones Utilizing groups to their utmost capacity College Coordinators act as community of scholars Reported “brainwashing” of some as they come to understand value of learning outcomes assessment CORE faculty committee saw benefits and established general education learning outcomes with little resistance
 Examples of CORE outcomes Demonstrate critical analysis of arguments and evaluation of an argument’s major assertions, its background assumptions, the evidence used to support its assertions, and its explanatory utility Understand articulate the importance and influence of diversity within and among cultures and societies
Examples of CORE outcomes Demonstrate critical analysis of arguments and evaluation of an argument’s major assertions, its background assumptions, the evidence used to support its assertions, and its explanatory utility Understand articulate the importance and influence of diversity within and among cultures and societies
 CORE Assessment Milestones In 2005, faculty groups articulated student learning outcomes for all CORE categories. In 2006, faculty who teach CORE courses mapped their courses to published CORE outcomes by using “checklists. ”
CORE Assessment Milestones In 2005, faculty groups articulated student learning outcomes for all CORE categories. In 2006, faculty who teach CORE courses mapped their courses to published CORE outcomes by using “checklists. ”
 New Campus Context New programs New CORE courses Program Review Focus on graduate programs College-based development of assessment instruments and measures
New Campus Context New programs New CORE courses Program Review Focus on graduate programs College-based development of assessment instruments and measures
 Lessons Learned In one instance, not utilizing established structures for buy-in and gentle roll-out caused relative uproar Successes in one venue will influence others Giving up control of process is necessary Utilizing existing structures essential
Lessons Learned In one instance, not utilizing established structures for buy-in and gentle roll-out caused relative uproar Successes in one venue will influence others Giving up control of process is necessary Utilizing existing structures essential
 Questions, comments, and discussion welcome!
Questions, comments, and discussion welcome!


