fa892522054a078be9a093967ca070df.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63

Strategicorp Value Based Reliability Accountability Productivity

RCM definitions Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) is a methodology used to determine The right maintenance tasks to ensure that any physical asset or system continues whatever its Users want it to do, in its present operating context
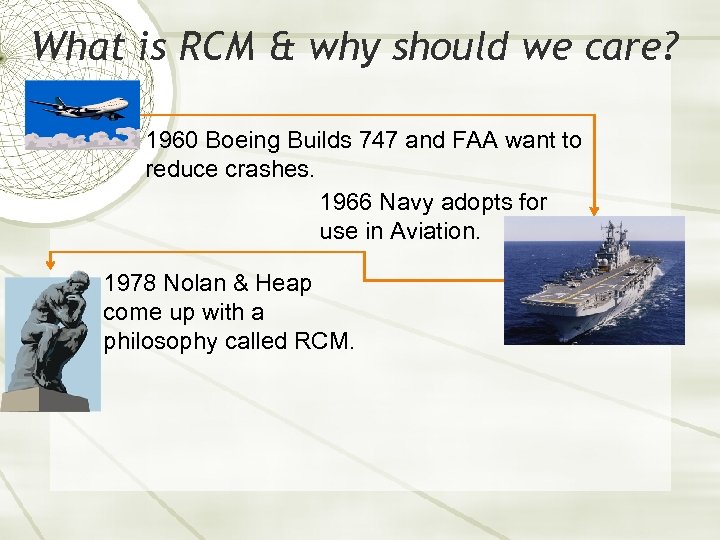
What is RCM & why should we care? 1960 Boeing Builds 747 and FAA want to reduce crashes. 1966 Navy adopts for use in Aviation. 1978 Nolan & Heap come up with a philosophy called RCM.
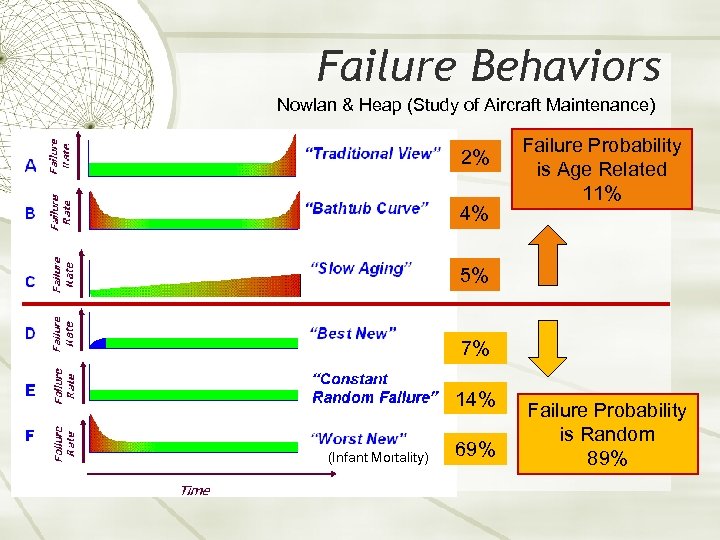
Failure Behaviors Nowlan & Heap (Study of Aircraft Maintenance) 2% 4% Failure Probability is Age Related 11% 5% 7% 14% (Infant Mortality) 69% Failure Probability is Random 89%

RCM Objectives The seven Basic Questions (John Moubray, RCM II, page 7) 1. What are the functions and associated 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. performance standards of the assets in its present operating context? In what ways can it fail to fulfill its function? What causes each functional failure? What happens when each failure occurs? In what way does each failure matter What proactive task can be done to prevent, or diminish the consequences of the failure? What should be done if a suitable proactive task cannot be found?

RCM Principles RCM is Function Oriented System Focused RCM investigates how Equipment Fails RCM defines the Maintenance Strategy based on the consequences of failures RCM acknowledges Design Limits RCM is an Ongoing Task

RCM Principles: Function oriented RCM focuses on preserving the functions of equipment, not on preserving the equipment itself, keep the process running! Equipment function: what its users want it to do 2 function categories primary functions: speed, output, product quality secondary functions: safety, comfort, environmental integrity RCM is more concerned with maintaining the system function, than individual component function
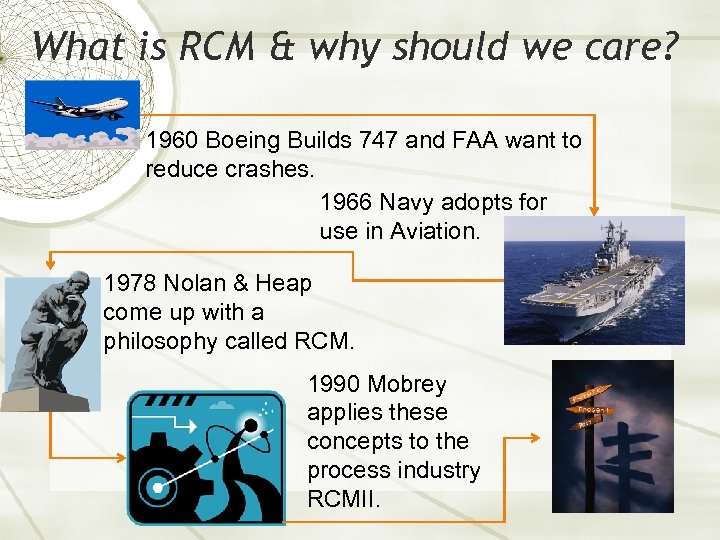
What is RCM & why should we care? 1960 Boeing Builds 747 and FAA want to reduce crashes. 1966 Navy adopts for use in Aviation. 1978 Nolan & Heap come up with a philosophy called RCM. 1990 Mobrey applies these concepts to the process industry RCMII.

Value Driven Maintenance Objectives Business-Oriented Working toward the most favourable maintenance program in support of operations. Optimize your maintenance efforts Focus on the most important functions of the systems Avoid maintenance actions that are not strictly necessary Strive for the required reliability At the lowest cost (without sacrificing safety and environment) Establish maintenance practices which focus more on The operational importance of a piece of equipment than on it’s failure/repair history and LESS on Vendor PM recommendations (Conservative – Often Generic) Traditional time-directed or overhaul tasks (Unreliable)

RCM-Turbo Origins Australian Company (BHP) • • 50, 000+ Employees World Force in Steel, Minerals and Petroleum $2 B Maintenance Budget Major Focus On Improving Steel Division’s Maintenance Costs. BHP Team Tasked To Find Better Maintenance Tools: • After a World-Wide Study Concluded • That They Were Already Using Among The Best Practices, Tools & Technology Available • Therefore They Began Development Of The SOS and RCMTurbo methodologies to further improve their performance

BHP Billiton Results. Original Issues that drove them to RCM and Spares Optimization. • In one site alone: • • Despite A Fully Functioning, State-Of-The. Art, Computerized Supply Management System Maintenance Spares Inventory Levels Were At $110 Million • • . . . And Increasing Yearly By 10%. . . And Were Clearly Out Of Control

BHP Action Plan Understand Problem
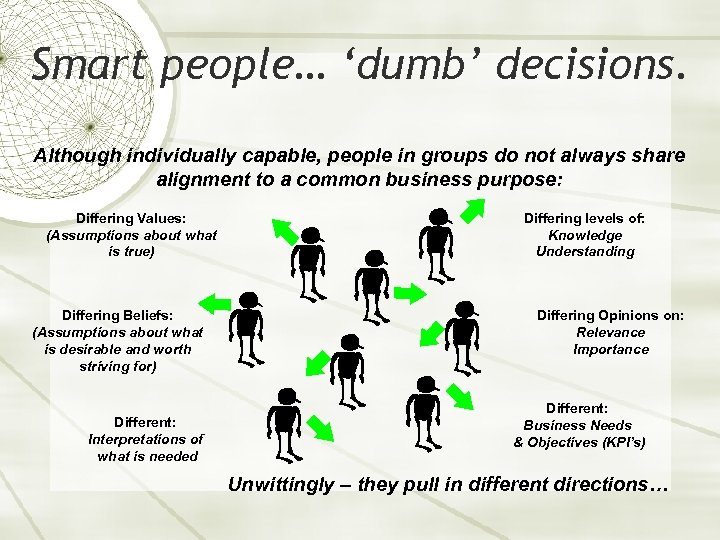
Smart people… ‘dumb’ decisions. Although individually capable, people in groups do not always share alignment to a common business purpose: Differing Values: (Assumptions about what is true) Differing Beliefs: (Assumptions about what is desirable and worth striving for) Different: Interpretations of what is needed Differing levels of: Knowledge Understanding Differing Opinions on: Relevance Importance Different: Business Needs & Objectives (KPI’s) Unwittingly – they pull in different directions…

BHP Action Plan Understand Problem Develop Approach for Solution 7 Step Plan

7 Step Plan for Holistic Asset Management 1. Re-Education 2. Re-Define Roles & Responsibilities 3. Re-Develop Measurements 4. Provide Processes and Systems 5. Apply Strategy Based Maintenance 6. Formalise Continuous Improvement 7. Focus on Waste Reduction

BHP Action Plan Understand Problem Develop Approach for Solution 7 Step Plan Set Overall Target 40% Reduce in Maintenance Cost Per Tonne in 5 years
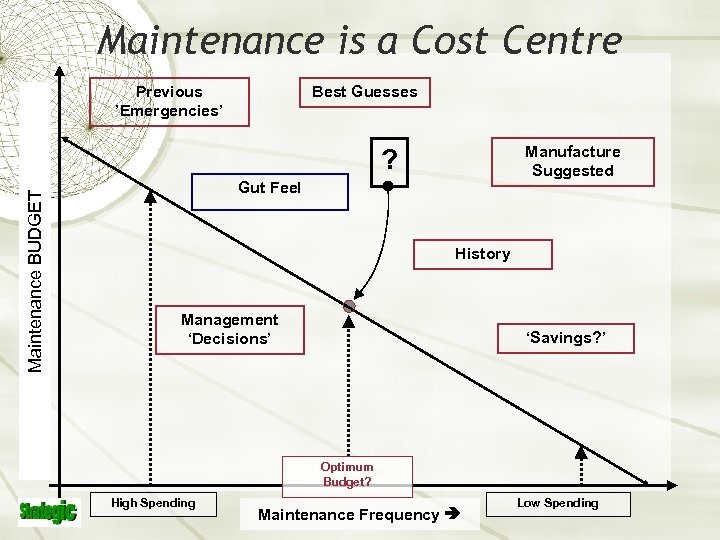
Maintenance is a Cost Centre Previous ’Emergencies’ Best Guesses Manufacture Suggested Maintenance BUDGET ? Gut Feel History Management ‘Decisions’ ‘Savings? ’ Optimum Budget? High Spending Maintenance Frequency Low Spending
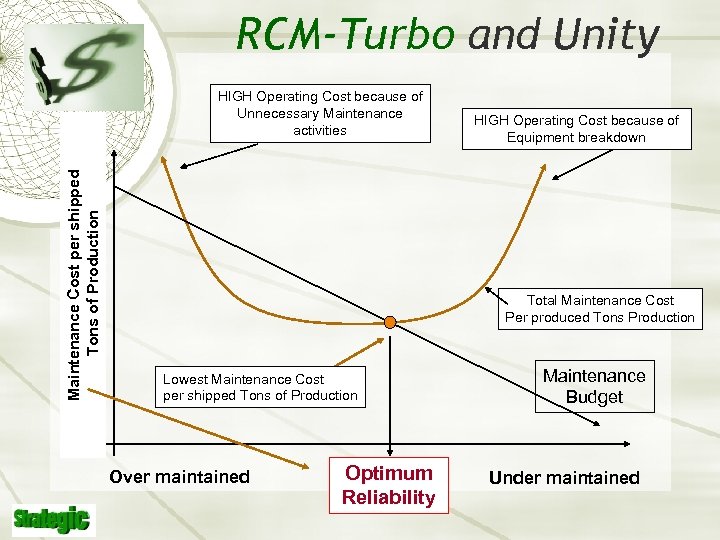
RCM-Turbo and Unity Maintenance Cost per shipped (Cost Center) Tons of Production HIGH Operating Cost because of Unnecessary Maintenance activities HIGH Operating Cost because of Equipment breakdown Total Maintenance Cost Per produced Tons Production Lowest Maintenance Cost per shipped Tons of Production Over maintained Optimum Budget Reliability Maintenance Budget Under maintained
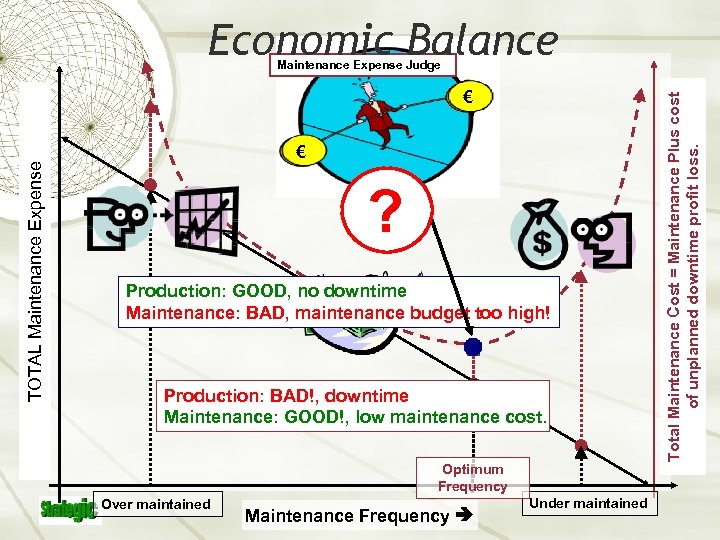
Economic Balance TOTAL Maintenance Expense € € ? Production: GOOD, no downtime Maintenance: BAD, maintenance budget too high! Production: BAD!, downtime Maintenance: GOOD!, low maintenance cost. Optimum Frequency Over maintained Maintenance Frequency Under maintained Total Maintenance Cost = Maintenance Plus cost of unplanned downtime profit loss. Maintenance Expense Judge

RCM-Turbo The Expense Maintenance Judge RCM-Turbo Is: A Tool Which Effectively Combines Both Maintenance AND Business / Financial Objectives An Effective Way To Bring Multiple Disciplines Together To Make Better Decisions: § Maintenance § Reliability Engineering § Business Economics
Can this work? The desired outcome of education is to align everyone’s understanding of required maintenance plan: Operational Improvement Net change for effort expended can be greatly improved…
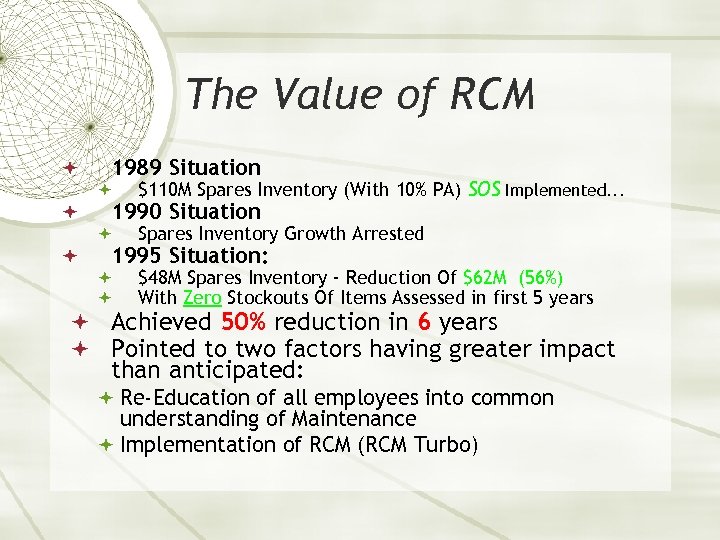
The Value of RCM 1989 Situation $110 M Spares Inventory (With 10% PA) SOS Implemented. . . Spares Inventory Growth Arrested $48 M Spares Inventory - Reduction Of $62 M (56%) With Zero Stockouts Of Items Assessed in first 5 years 1990 Situation 1995 Situation: Achieved 50% reduction in 6 years Pointed to two factors having greater impact than anticipated: Re-Education of all employees into common understanding of Maintenance Implementation of RCM (RCM Turbo)

How do the pieces fit?
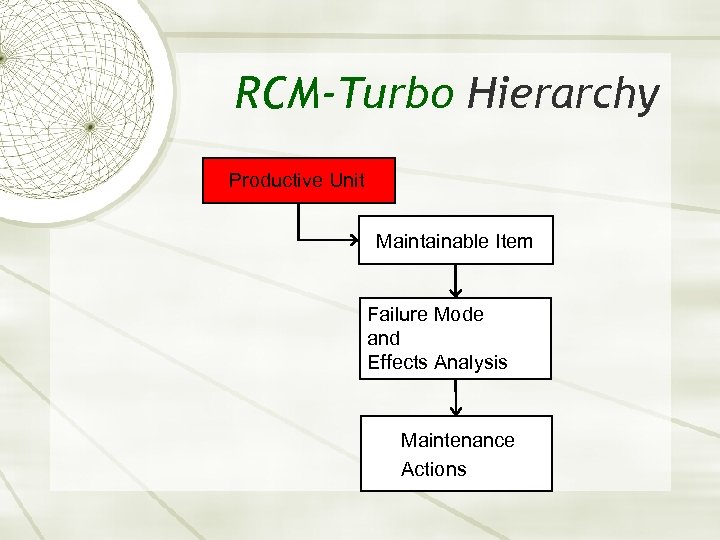
RCM-Turbo Hierarchy Productive Unit Maintainable Item Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Maintenance Actions
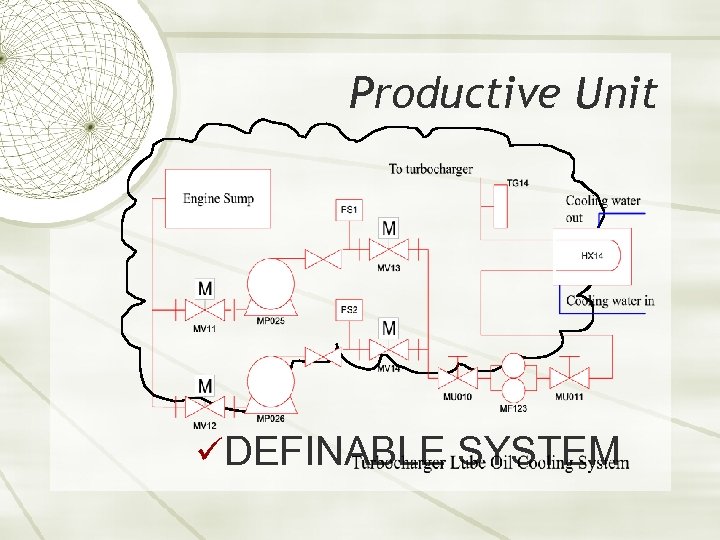
Productive Unit üDEFINABLE SYSTEM

Productive Unit Ø Criticality Assessment Used for focusing priority Ø Functions and Standards Primary Function Secondary Functions Ø Functional Failures At what point is the Equipment no longer meeting the Functional Requirements?
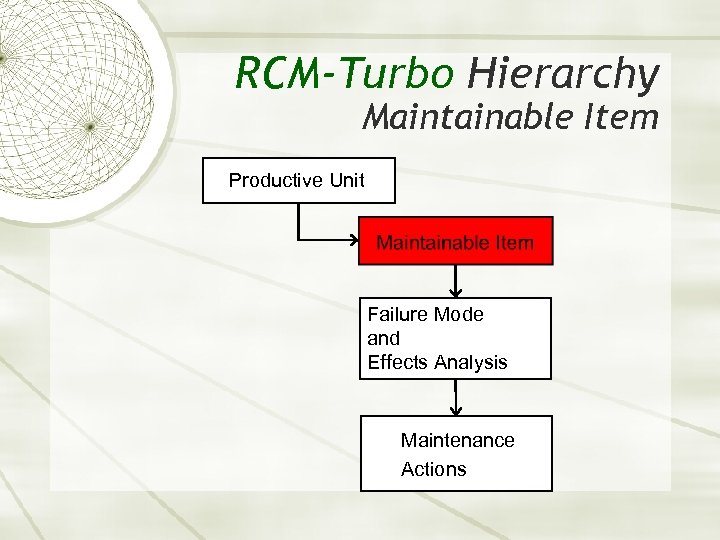
RCM-Turbo Hierarchy Maintainable Item Productive Unit Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Maintenance Actions
Maintainable Item üINDIVIDUAL EQUIPMENT ITEM e. g. Pump
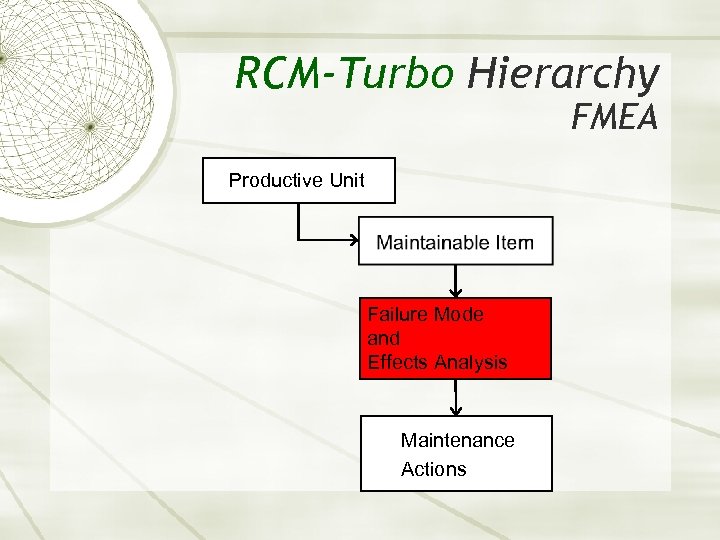
RCM-Turbo Hierarchy FMEA Productive Unit Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Maintenance Actions
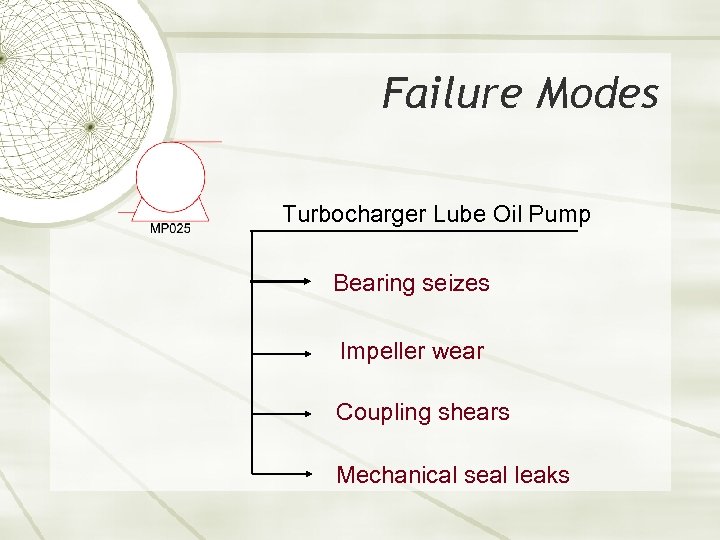
Failure Modes Turbocharger Lube Oil Pump Bearing seizes Impeller wear Coupling shears Mechanical seal leaks
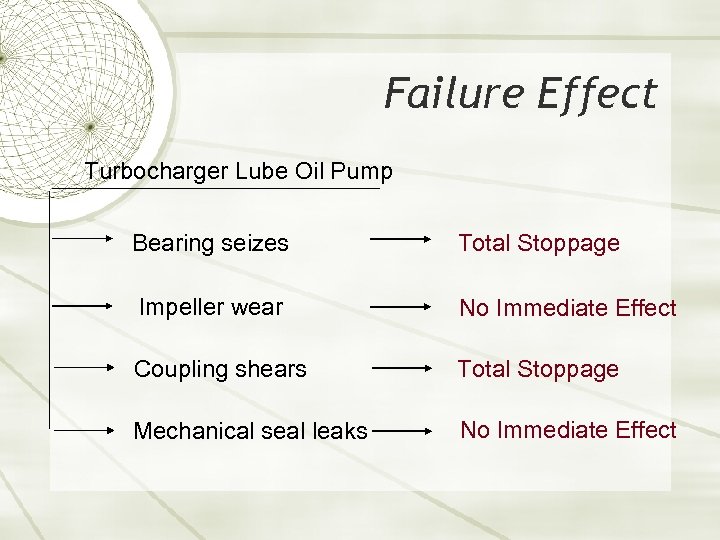
Failure Effect Turbocharger Lube Oil Pump Bearing seizes Total Stoppage Impeller wear No Immediate Effect Coupling shears Total Stoppage Mechanical seal leaks No Immediate Effect
RCM-Turbo Maintenance Actions Productive Unit Failure Mode and Effects Analysis

Maintenance Activities Turbocharger Lube Oil Pump Bearing seizes Impeller wear Lubrication, Vibration or Oil Analysis Monitor flow rate Coupling shears Check Lubrication & Inspect for wear Mechanical seal leaks Inspect for signs of oil leakage
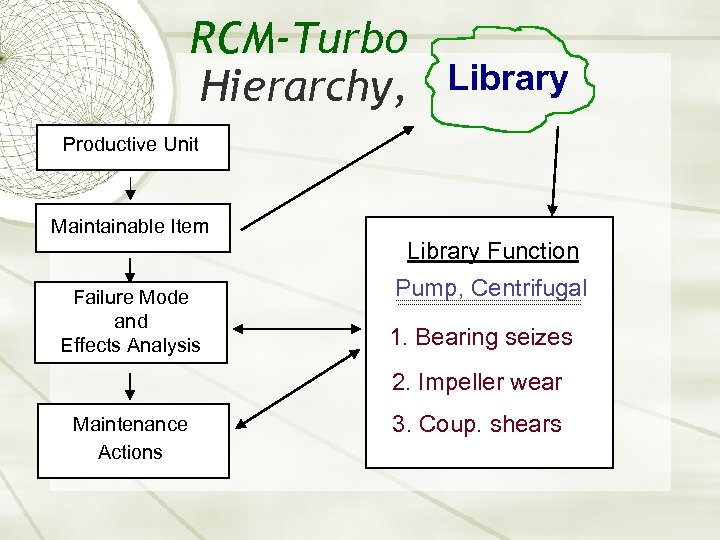
RCM-Turbo Hierarchy, Library Productive Unit Maintainable Item Library Function Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Pump, Centrifugal 1. Bearing seizes 2. Impeller wear Maintenance Actions 3. Coup. shears
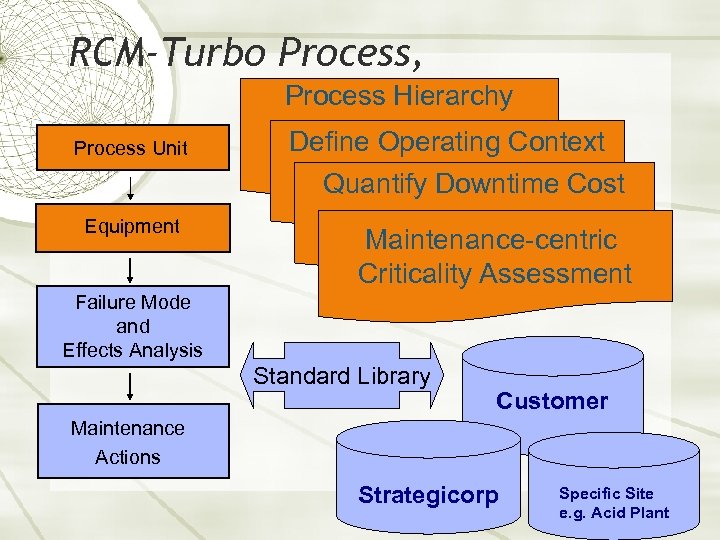
RCM-Turbo Process, Process Hierarchy Process Unit Define Operating Context Quantify Downtime Cost Equipment Maintenance-centric Criticality Assessment Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Standard Library Customer Maintenance Actions Strategicorp Specific Site e. g. Acid Plant
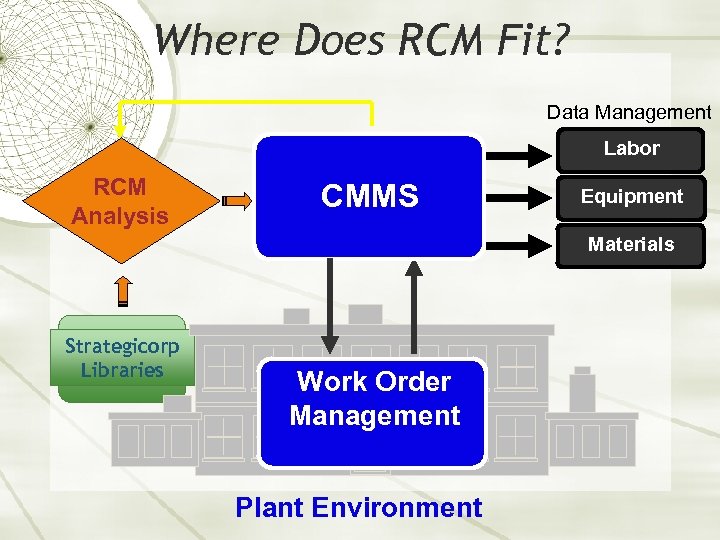
Where Does RCM Fit? Data Management Labor RCM Analysis CMMS Equipment Materials Strategicorp Libraries Work Order Management Plant Environment

Add the ‘Value’?
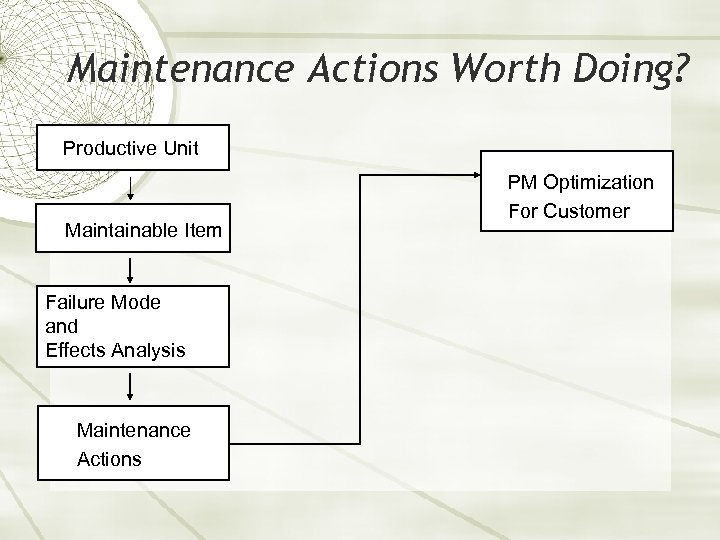
Maintenance Actions Worth Doing? Productive Unit Maintainable Item Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Maintenance Actions PM Optimization For Customer

“When should PM tasks be done? ” Anthony (Mac) Smith: "When" should these tasks be done? " 1. Ideally, we would like to …specify the level of risk that we wish to take verses dollars involved, and accurately define the desired frequency in an appropriate measurement (hours, cycles, days, etc. ). The problem here, of course, is that we almost never have enough data to use this approach. 2. Or Use “Best judgment“ 1. Age Exploration (Keep doing what you’re doing. )
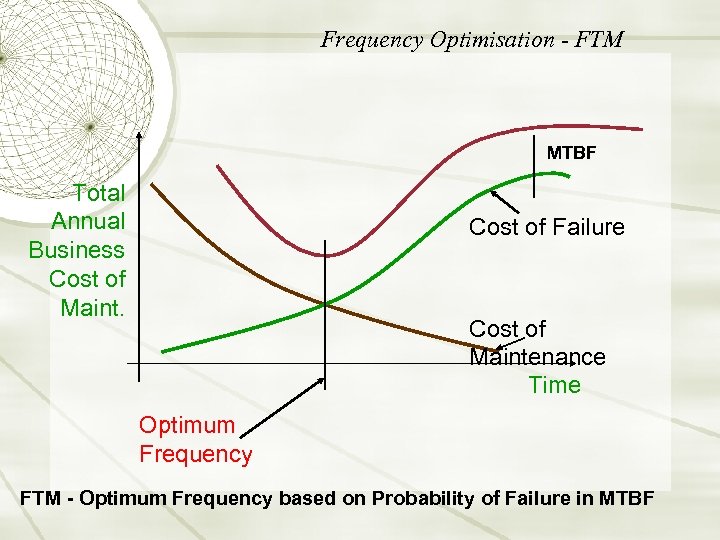
Frequency Optimisation - FTM MTBF Total Annual Business Cost of Maint. Cost of Failure Cost of Maintenance Time Optimum Frequency FTM - Optimum Frequency based on Probability of Failure in MTBF
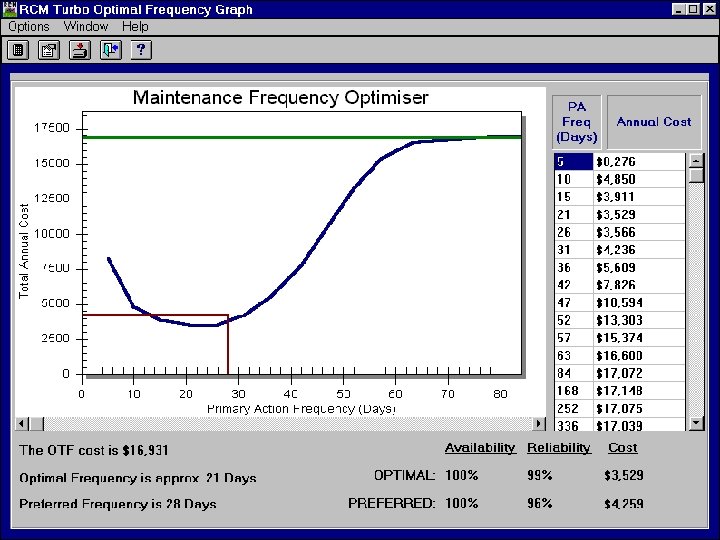
Frequency Optimisation Graph
Measuring the ‘benefits’! UPM Kymmene Case Study. üCaveats: üIncluded a two week audit of failures. üMultiple Analysis on a range of downtime costs. üTook Two weeks of RCM work.

Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Economically Centered Maintenance Tervasaari 25. 10. 2005 – 4. 11. 2005 PK 7 rollers and cylinder vibration analysis - Wire - Jenkipress - Pope-Roller - Drier Comparison: Current handheld measurement Optimized handheld measurement Automated vibration measurement
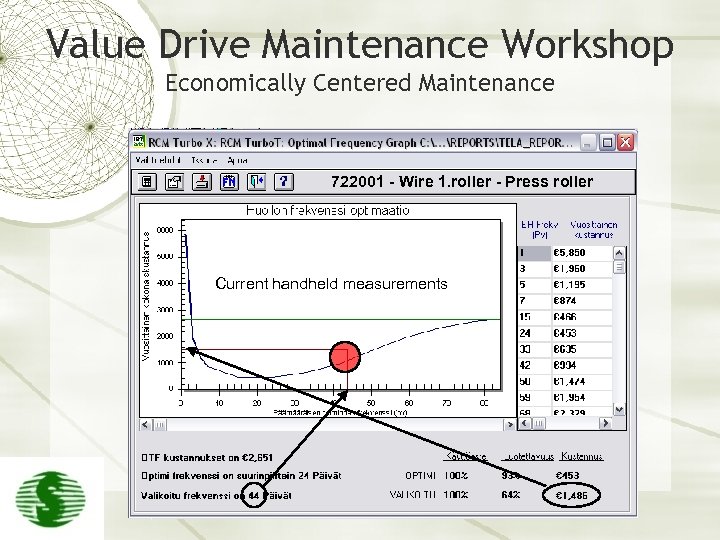
Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Economically Centered Maintenance 722001 - Wire 1. roller - Press roller Current handheld measurements
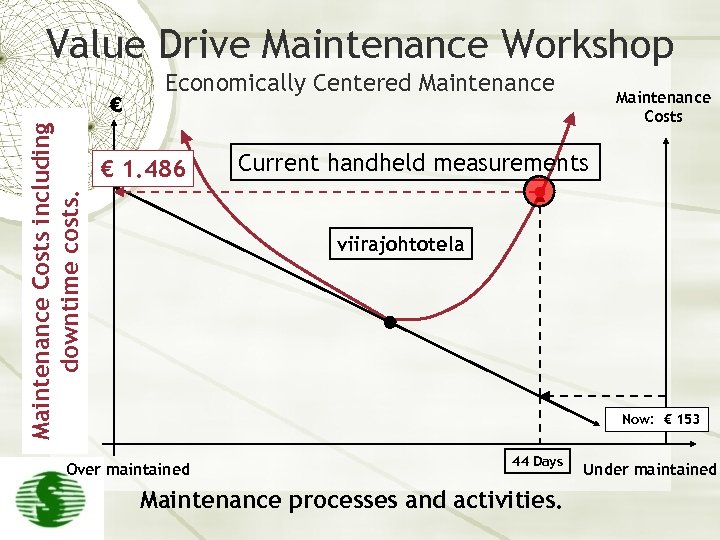
Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Maintenance Costs including downtime costs. € Economically Centered Maintenance € 1. 486 Maintenance Costs Current handheld measurements viirajohtotela Now: € 153 Over maintained 44 Days Maintenance processes and activities. Under maintained
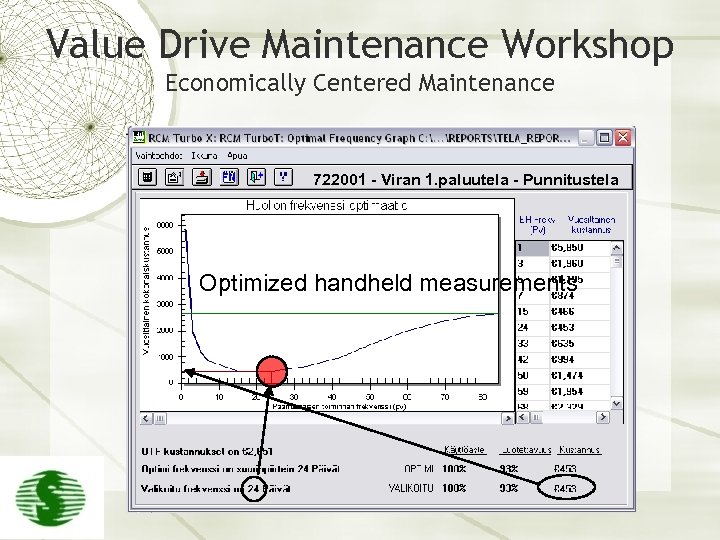
Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Economically Centered Maintenance 722001 - Viran 1. paluutela - Punnitustela Optimized handheld measurements
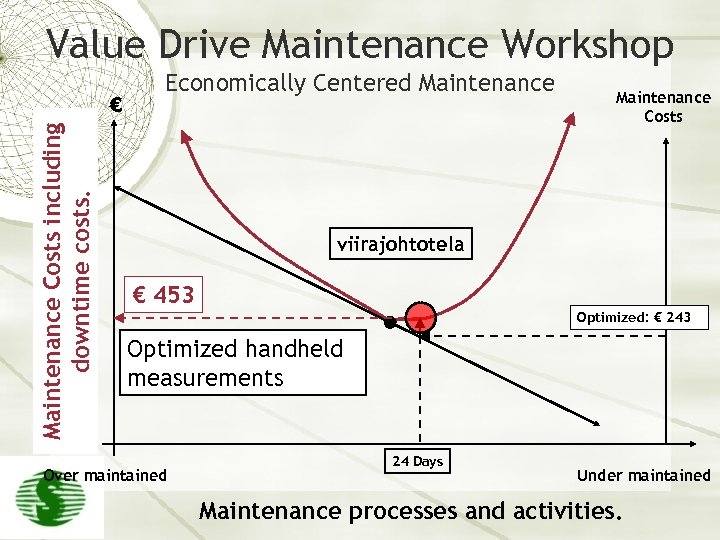
Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Maintenance Costs including downtime costs. € Economically Centered Maintenance Costs viirajohtotela € 453 Optimized: € 243 Optimized handheld measurements Over maintained 24 Days Under maintained Maintenance processes and activities.
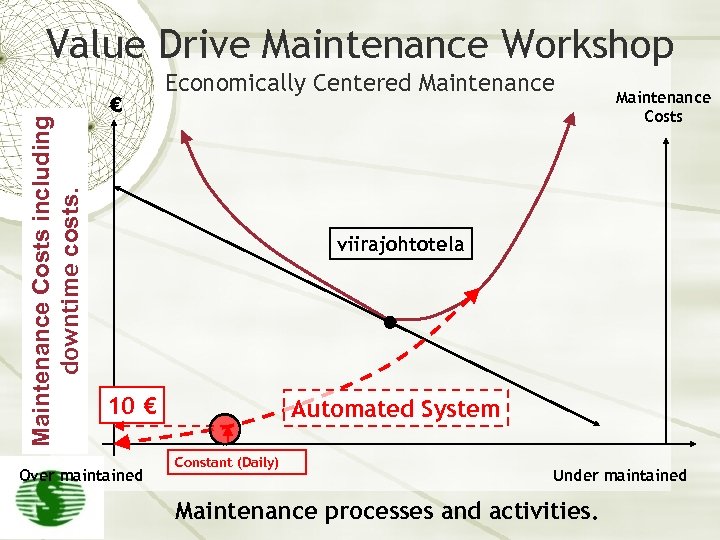
Maintenance Costs including downtime costs. Value Drive Maintenance Workshop € Economically Centered Maintenance Costs viirajohtotela 10 € X € Over maintained Automated System Constant (Daily) Under maintained Maintenance processes and activities.
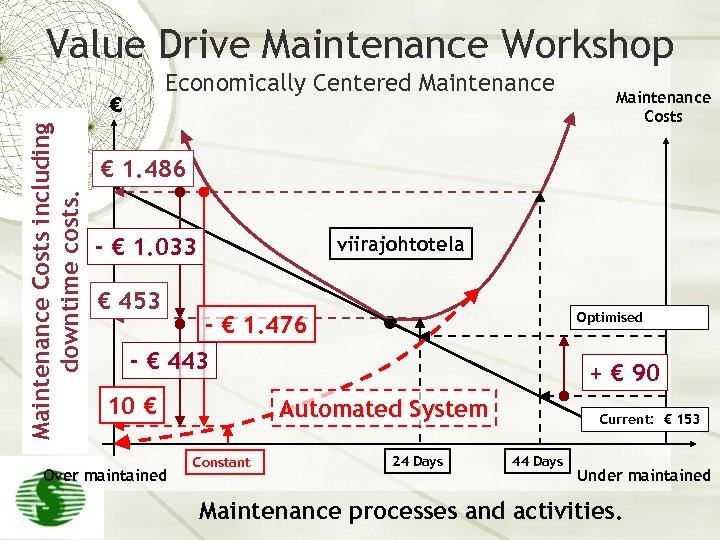
Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Economically Centered Maintenance Costs including downtime costs. € Maintenance Costs € 1. 486 viirajohtotela - € 1. 033 € 453 Optimised - € 1. 476 - € 443 10 € Over maintained + € 90 Automated System Constant 24 Days Current: € 153 44 Days Under maintained Maintenance processes and activities.
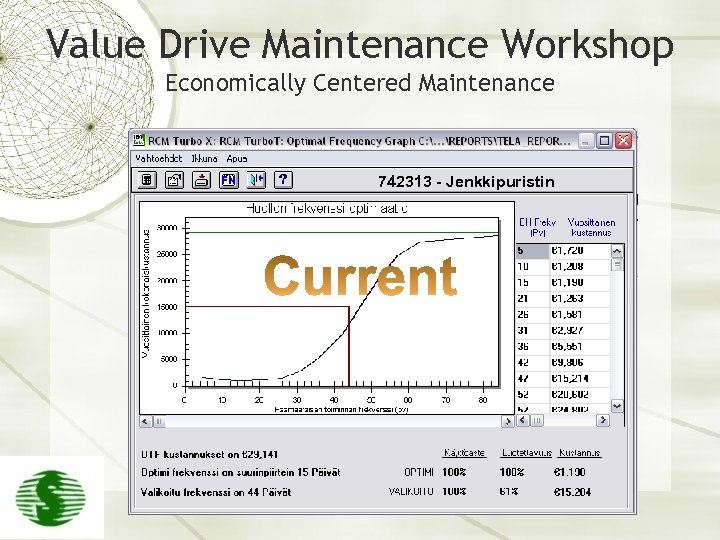
Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Economically Centered Maintenance 742313 - Jenkkipuristin
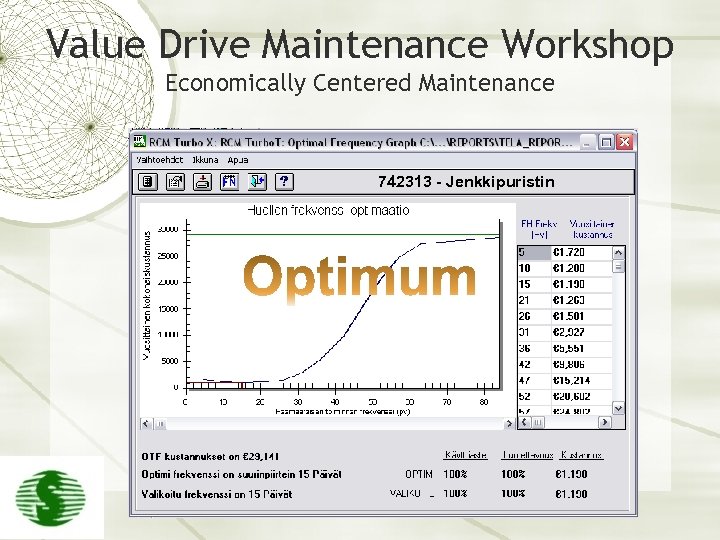
Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Economically Centered Maintenance 742313 - Jenkkipuristin
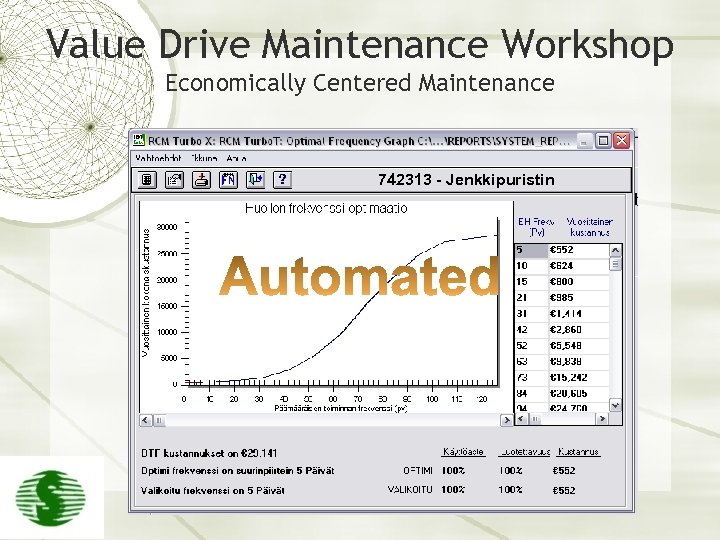
Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Economically Centered Maintenance 742313 - Jenkkipuristin

Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Economically Centered Maintenance

Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Economically Centered Maintenance
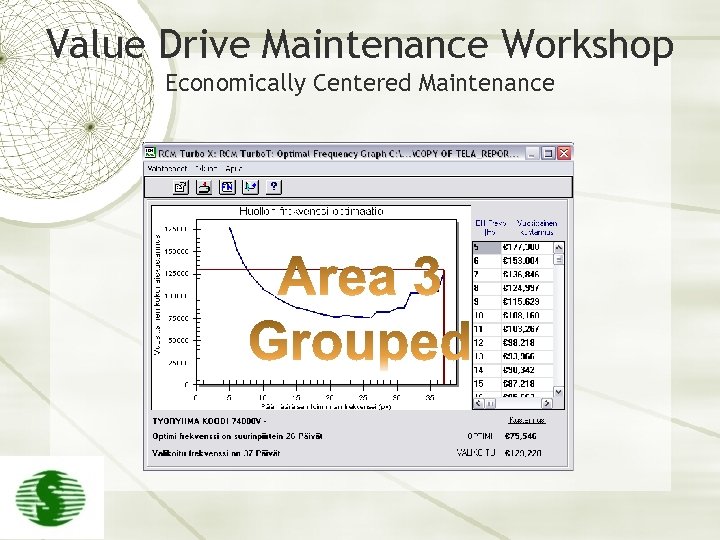
Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Economically Centered Maintenance
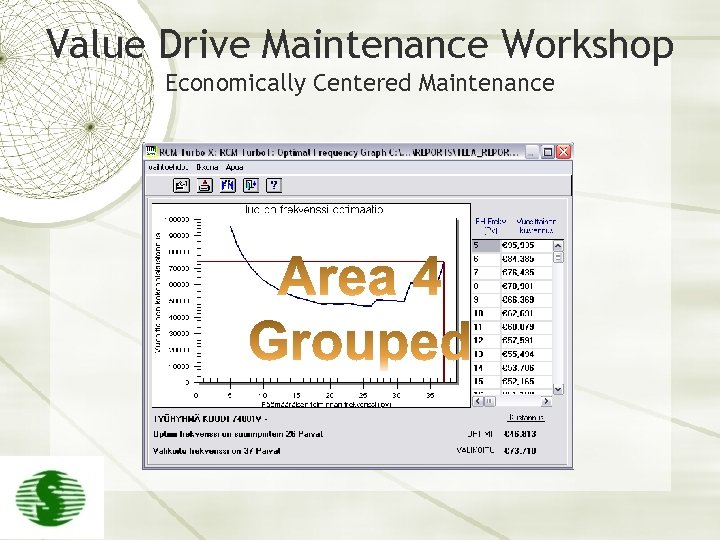
Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Economically Centered Maintenance
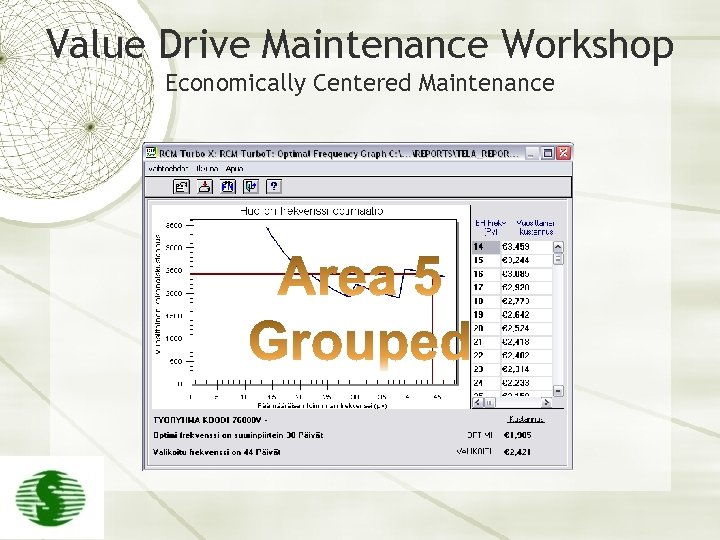
Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Economically Centered Maintenance
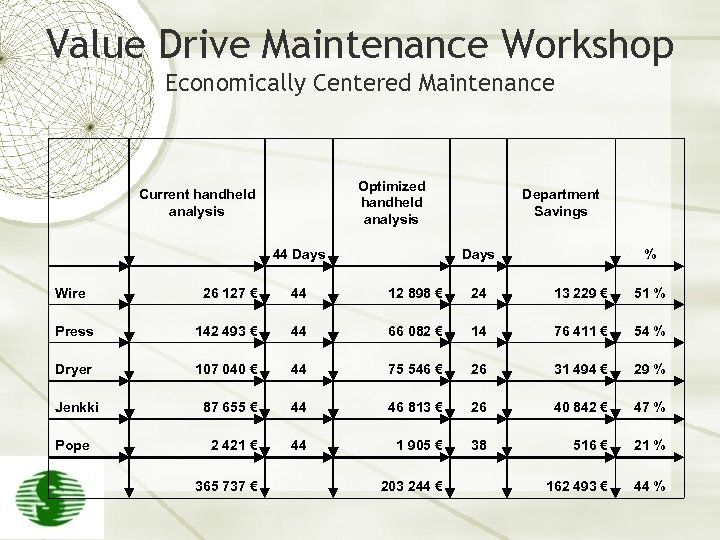
Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Economically Centered Maintenance Optimized handheld analysis Current handheld analysis Department Savings 44 Days % Wire 26 127 € 44 12 898 € 24 13 229 € 51 % Press 142 493 € 44 66 082 € 14 76 411 € 54 % Dryer 107 040 € 44 75 546 € 26 31 494 € 29 % Jenkki 87 655 € 44 46 813 € 26 40 842 € 47 % 2 421 € 44 1 905 € 38 516 € 21 % 162 493 € 44 % Pope 365 737 € 203 244 €
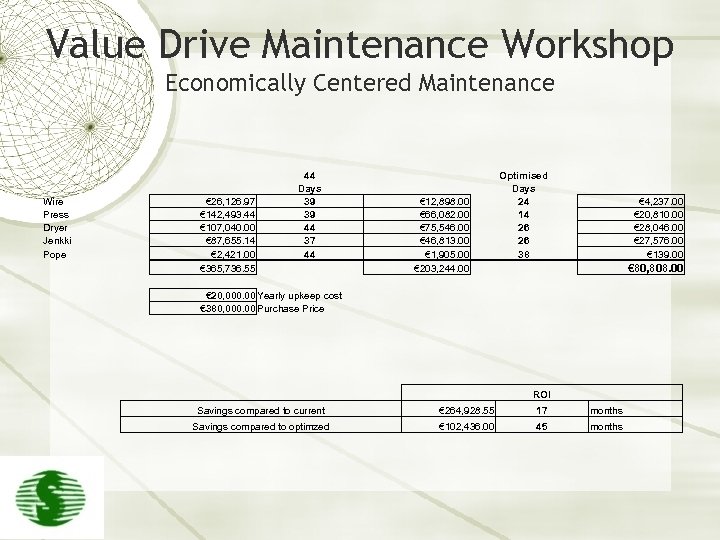
Value Drive Maintenance Workshop Economically Centered Maintenance Wire Press Dryer Jenkki Pope € 26, 126. 97 € 142, 493. 44 € 107, 040. 00 € 87, 655. 14 € 2, 421. 00 € 365, 736. 55 44 Days 39 39 44 37 44 € 12, 898. 00 € 66, 082. 00 € 75, 546. 00 € 46, 813. 00 € 1, 905. 00 € 203, 244. 00 Optimised Days 24 14 26 26 38 € 4, 237. 00 € 20, 810. 00 € 28, 046. 00 € 27, 576. 00 € 139. 00 € 80, 808. 00 € 20, 000. 00 Yearly upkeep cost € 380, 000. 00 Purchase Price ROI Savings compared to current € 264, 928. 55 17 months Savings compared to optimzed € 102, 436. 00 45 months

Which one are we… which ones?

Benefits Focus on “Correct” Maintenance Thereby helping the customer Reduce Total Operating Costs. Build knowledge for maintenance plans to improve customer availability to support their operational requirements. Help customer adopt pro-active repair solutions that support asset reliability. Encourage “What If” Scenarios Resulting In more Educated Maintenance Plans. Structure Data To Enhance Small Step Improvement And Total Quality Management Plan. Enforce consistent delivery of the RCM concept to support the maintenance program facilitator

Further Benefits Help customer to establish optimum plant shutdown dates based on: safety, reliability and economics. Determination of optimum task and shutdown frequency Alternate task comparison (“What-If Analyses”) Task frequency impact on reliability and cost To establish optimum work-flow and work-groups for the local maintenance crew. Help customers to recognize the need for valid spares. To assist integrating the results of System design and process experience with maintenance requirements for plant operation.

Thank You. Alexander Willems EMEA Regional Director, Strategicorp +358 40 532 2863 alex. willems@strategicorp. com
fa892522054a078be9a093967ca070df.ppt