f231a1c6d64509b3531c49da94210d22.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56

Strategic Management Final Case Study Andrea Baril Ashley Cleary Sylvia La. Brie Marie-Michele Lachance 05/03/2012

Company Overview • The Founder • Growth • Location Map • Walt Disney’s Division Existing Mission Proposed Mission and Vision SWOT Analysis External Audit • CPM • Positioning Map • EFE Internal Audit • Organizational Chart • Financial Trends • Balance Sheet • Financial Ratios • IFE Overview Strategic Plan • SWOT Matrix • Space Matrix • IE Matrix • Grand Strategy Matrix • BCG • Matrix Analysis • QSPM Implementation • Assumptions • Projected Income Statement • Projected Balance Sheet • Projected Ratios Evaluation • Stock Price • Balance Scored Card • Strategies • Recommendations • Objectives

Walt, after the Studio had won 4 Academy Awards The founder Walt Disney 1901 -1966 • Walt Disney was born on December 5, 1901 in Chicago • During the fall of 1918, Walt Disney attempted to enlist for military service but he got rejected. • He started a small company called Laugh-O-Grams, which eventually fell bankrupt. • With his suitcase, and $20 Walt headed to Hollywood to start anew. • After making a success of his "Alice Comedies, " Walt became a recognized Hollywood figure. • Disney took a deep interest in the establishment of California Institute of the Arts, a college-level professional school of all the creative and performing arts. • Walt Disney passed away on December 15, 1966. • Urban legend maintains his corpse would be frozen and stored beneath the Pirates of the Caribbean ride at Disneyland. . .

History October 16, 1923: This date is considered the start of the Disney Company first known as The Disney Brothers Studio. 1928: First Mickey Mouse cartoon, and the first appearance by Minnie Mouse. 1932: Flowers and Trees, first full-color cartoon and first Academy Award winner. 1939: The Disney Studio begins its move to Burbank, California. 1940: Walt Disney Productions issues its first stock.

Growth 1955: Mickey Mouse Club debuts on television. 1971: Walt Disney World Resort opens with the Magic Kingdom and two hotels near Orlando, Florida. 1982: EPCOT Center opens at Walt-Disney World Resort. 1983: Tokyo Disneyland, the first international Disney theme park, opens in Japan. 1987: The first Disney Store opens, in Glendale, California.

Growth cont. 1989: Disney-MGM Studios opens at Walt Disney World Resort. 1992: Disneyland Paris opens. 1995: Disney agrees to purchase 25 percent of the California Angels baseball team, Disney agrees to purchase Capital Cities/ABC for $19 billion. The Disney Channel begins operation in the UK. 1996: Disney Online launches Disney. com. Radio Disney, a live 24 -hour music-intensive radio network, debuts. 1998: ESPN Magazine debuts, Disney’s Animal Kingdom opens at Walt Disney World Resort, Disney Magic cruise ship departs on its inaugural cruise.

2009 Disney purchased Marvel Entertainment Gave a $0. 35 dividend per share Roy Disney died at age 79 He was a key person in Disney’s animation legacy Received approval to build a theme park in Shanghai Released the movie Up

LOCATION MAP Disney Resorts: 1. California 2. Florida 3. Tokyo 4. Hong Kong 5. Paris
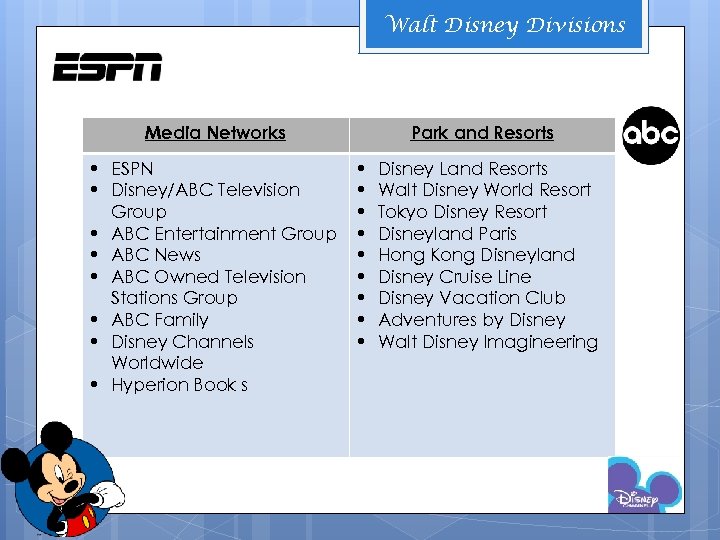
Walt Disney Divisions Media Networks • ESPN • Disney/ABC Television Group • ABC Entertainment Group • ABC News • ABC Owned Television Stations Group • ABC Family • Disney Channels Worldwide • Hyperion Book s Park and Resorts • • • Disney Land Resorts Walt Disney World Resort Tokyo Disney Resort Disneyland Paris Hong Kong Disneyland Disney Cruise Line Disney Vacation Club Adventures by Disney Walt Disney Imagineering

Walt Disney Divisions Cont. The Walt-Disney Studios Disney Consumer Products • Walt-Disney Studios Motion Pictures • Marvel Studios • Touchstone Pictures • Disneynature • Walt Disney Animation Studios • Pixar Animation Studios • Disney Music Groups • Disney Theatrical Group • Disney Licensing • Disney Publishing Worldwide • Disney Store Disney Interactive Media Group • Disney Online • Disney Games

Mission Statement "The mission of The Walt Disney Company is to be one of the world's leading producers and providers of entertainment and information. Using our portfolio of brands to differentiate our content, services and consumer products, we seek to develop the most creative, innovative and profitable entertainment experiences and related products in the world. "

Proposed Vision Walt Disney strives to be the world’s most famous entertainment company by creating an amazing experience for individual of all ages.

Proposed Mission Our Mission is to be one of the world’s leading producer and provider of entertainment and information, from parks to network media, and website for all ages. We seek to provide a great experience for our customers, as well as for our employees. By using our unique portfolio to differentiate our content, services and consumer products, we seek to develop the most creative, HISTORY innovative and profitable entertainment experiences, which would produce financial rewards to our shareholders. In everything we do, we try to contribute to our communities by giving them the best experience.

SWOT Analysis

Strengths One of the most recognizable entertainment company in the world Strong advertising Wide and unique portfolio Innovative entertainment business Strong customer service Strong Media Networks and Broadcasting division Disney owns a variety of companies, which allows them to generate more profits from different industry such as Media Networks and Broadcasting, Park and Resorts, Studio Entertainment and Disney Consumer Products Disney is the largest worldwide licensor of character-based merchandise and producer of children’s film-related products based on retail sales

Weaknesses Disney sends a corrupted influence to children Jasmine was in a forbidden relationship with Aladdin Snow White lived alone with 7 men Pinocchio was a liar Robin Hood was a thief Tarzan walked without clothes on A stranger kissed sleeping beauty and she married him Cinderella lied and sneaked out at night to attend a party Coyote runs off cliffs and blows himself up

Weaknesses Studio Entertainment and Disney Consumer Products divisions have been experiencing declining revenue for the last 3 years Disney as a narrow target market Disney as such a diversify product range that it can reduce efficiency and lead to a lack of strategic focus High cost of entertainment production High employee turnover Poor working conditions in factories Walt Disney’s Park and Resorts are not easily accessible which leads people to associate Disney World with a costly trip

Opportunities Opportunity to renovate attractions in Park and Resorts Division due to increase in profit Growth from cable and satellite operators creating even more potential for Disney to make money with their network Prospect to build more theme park and resorts worldwide Openings in other areas of the travel business Opportunity to invest in building theme parks to satisfy the increase in guest spending, theme park attendance, and hotel occupancy Target new costumers group

Threats Lasting economic recession leading to slow growth rate High unemployment rate Park and Resorts Divisions’ success is unpredictable because of exchange rate fluctuations; travel industry trends; amount of available leisure time; oil and transportation prices; and weather patterns and seasonality. Changes in technology leads customers to stream online instead of buying DVD. Online streaming makes Disney vulnerable to piracy and violation of its intellectual property. Retail distribution business are influenced by seasonal consumer purchasing behavior and by the timing and performance of animated theatrical release Increase in labor cost which will have a noticed impact in Walt. Disney expenses due to their large amount of employee.

External Audit
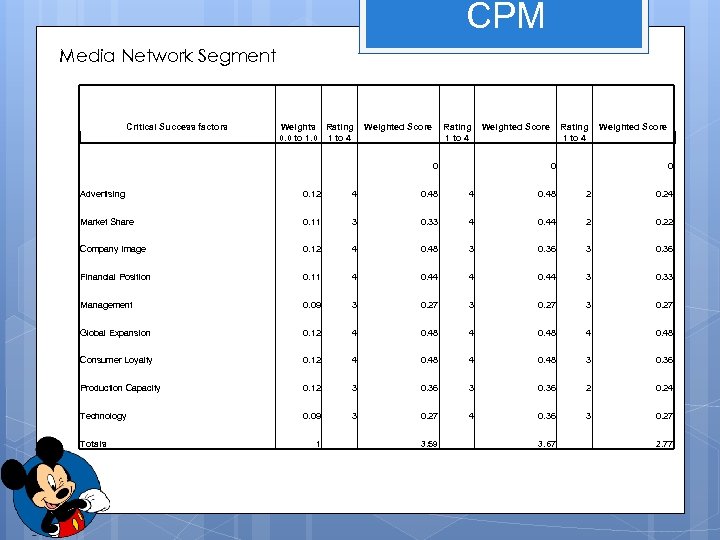
CPM Media Network Segment Critical Success factors Weights Rating 0. 0 to 1. 0 1 to 4 Weighted Score Rating 1 to 4 0 Weighted Score 0 Advertising 0. 12 4 0. 48 2 0. 24 Market Share 0. 11 3 0. 33 4 0. 44 2 0. 22 Company Image 0. 12 4 0. 48 3 0. 36 Financial Position 0. 11 4 0. 44 3 0. 33 Management 0. 09 3 0. 27 Global Expansion 0. 12 4 0. 48 Consumer Loyalty 0. 12 4 0. 48 3 0. 36 Production Capacity 0. 12 3 0. 36 2 0. 24 Technology 0. 09 3 0. 27 4 0. 36 3 0. 27 Totals 1 3. 59 3. 67 2. 77
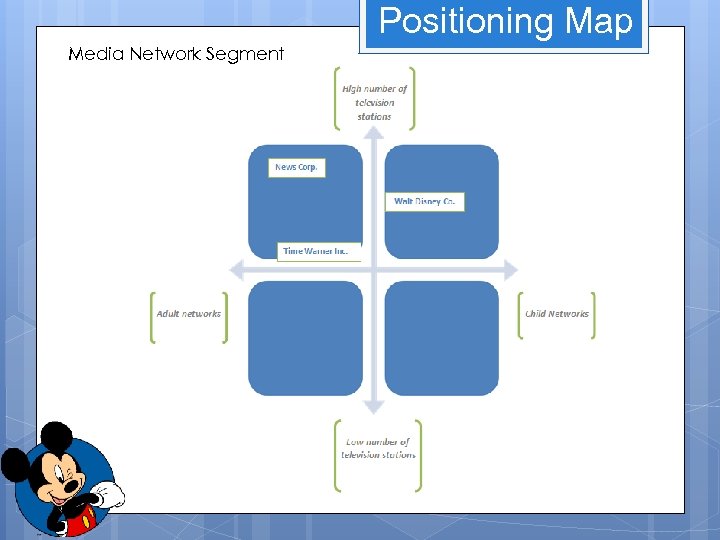
Positioning Map Media Network Segment
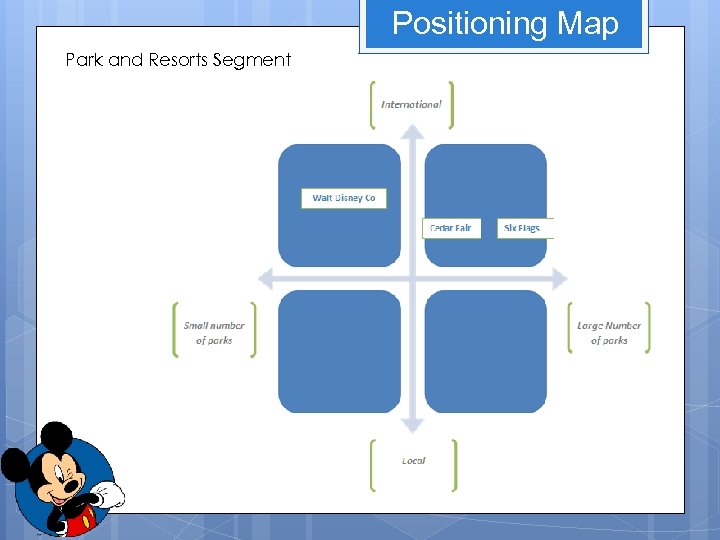
Positioning Map Park and Resorts Segment
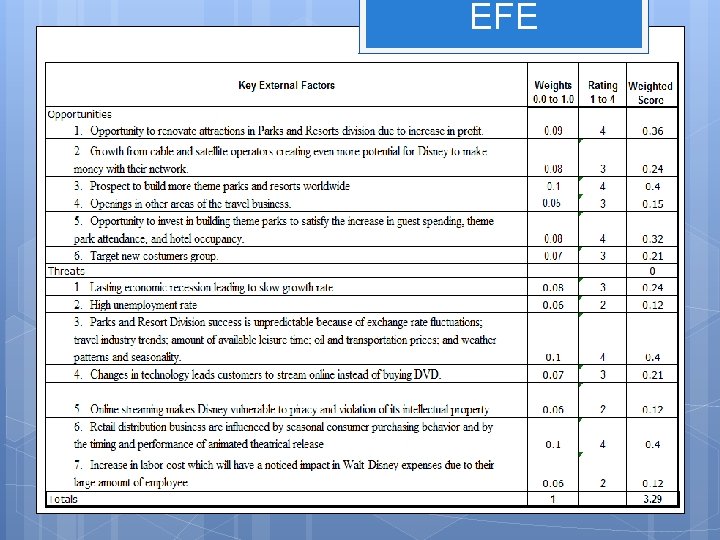
EFE

Internal Audit Disneyland will never be completed. It will continue to grow as long as there is imagination left in the world. - Walt Disney

Organizational Chart
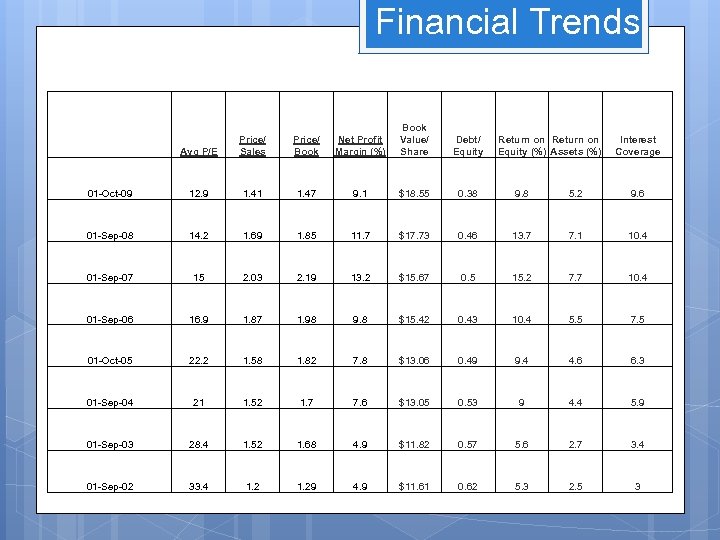
Financial Trends Price/ Book Net Profit Margin (%) Book Value/ Share Debt/ Equity Avg P/E Price/ Sales Return on Equity (%) Assets (%) Interest Coverage 01 -Oct-09 12. 9 1. 41 1. 47 9. 1 $18. 55 0. 38 9. 8 5. 2 9. 6 01 -Sep-08 14. 2 1. 69 1. 85 11. 7 $17. 73 0. 46 13. 7 7. 1 10. 4 01 -Sep-07 15 2. 03 2. 19 13. 2 $15. 67 0. 5 15. 2 7. 7 10. 4 01 -Sep-06 16. 9 1. 87 1. 98 9. 8 $15. 42 0. 43 10. 4 5. 5 7. 5 01 -Oct-05 22. 2 1. 58 1. 82 7. 8 $13. 06 0. 49 9. 4 4. 6 6. 3 01 -Sep-04 21 1. 52 1. 7 7. 6 $13. 05 0. 53 9 4. 4 5. 9 01 -Sep-03 28. 4 1. 52 1. 68 4. 9 $11. 82 0. 57 5. 6 2. 7 3. 4 01 -Sep-02 33. 4 1. 29 4. 9 $11. 61 0. 62 5. 3 2. 5 3
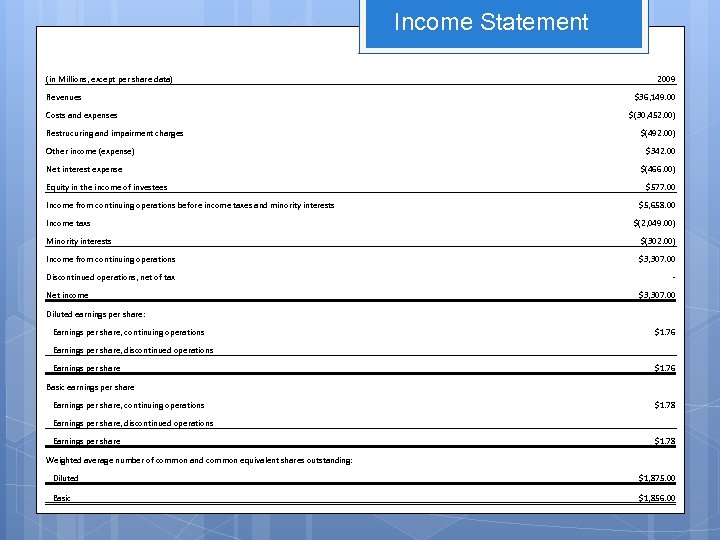
Income Statement (in Millions, except per share data) 2009 Revenues $36, 149. 00 Costs and expenses $(30, 452. 00) Restrucuring and impairment charges $(492. 00) Other income (expense) $342. 00 Net interest expense $(466. 00) Equity in the income of investees $577. 00 Income from continuing operations before income taxes and minority interests $5, 658. 00 Income taxs $(2, 049. 00) Minority interests $(302. 00) Income from continuing operations $3, 307. 00 Discontinued operations, net of tax - Net income $3, 307. 00 Diluted earnings per share: Earnings per share, continuing operations Earnings per share, discontinued operations $1. 76 Earnings per share $1. 76 Basic earnings per share Earnings per share, continuing operations Earnings per share, discontinued operations Earnings per share $1. 78 Weighted average number of common and common equivalent shares outstanding: Diluted $1, 875. 00 Basic $1, 856. 00
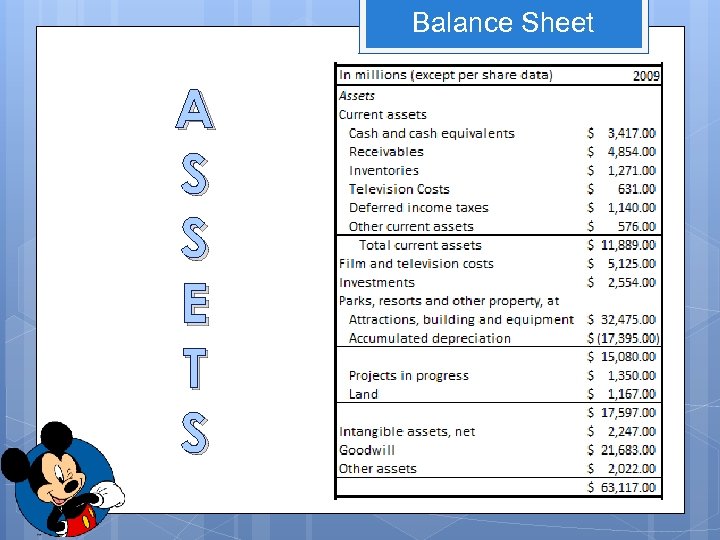
Balance Sheet A S S E T S
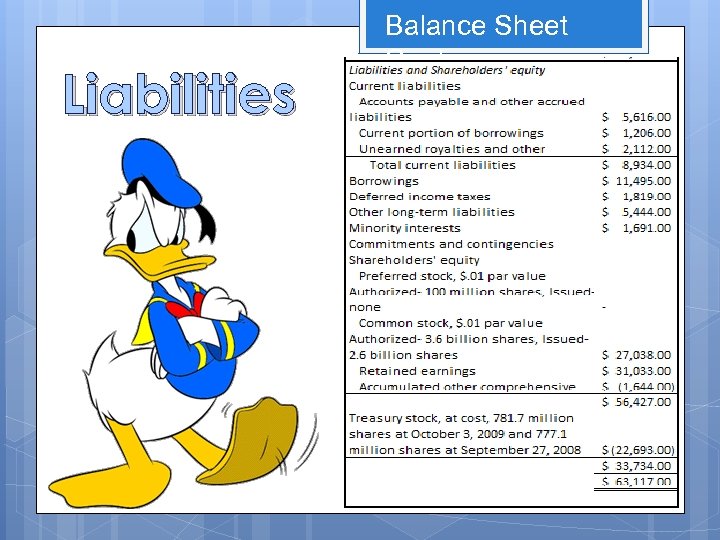
Liabilities Balance Sheet Cont.
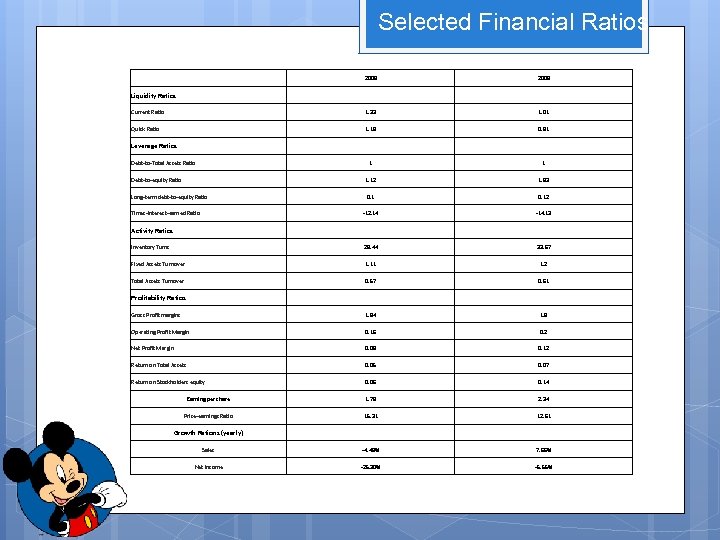
Selected Financial Ratios 2009 2008 Current Ratio 1. 33 1. 01 Quick Ratio 1. 19 0. 91 Leverage Ratios Debt-to-Total Assets Ratio 1 1 Debt-to-equity Ratio 1. 12 1. 93 Long-term debt-to-equity Ratio 0. 12 -12. 14 -14. 13 Activity Ratios Inventory Turns 28. 44 33. 67 Fixed Assets Turnover 1. 11 1. 2 Total Assets Turnover 0. 57 0. 61 Profitability Ratios Gross Profit margins 1. 84 1. 8 Operating Profit Margin 0. 16 0. 2 Net Profit Margin 0. 09 0. 12 Return on Total Assets 0. 05 0. 07 Return on Stockholders equity 0. 06 0. 14 Earning per share 1. 78 2. 34 Price-earnings Ratio 15. 31 12. 61 Growth Rations (yearly) Sales -4. 48% 7. 66% Net Income -25. 30% -5. 55% Liquidity Ratios Times-Interest-earned Ratio
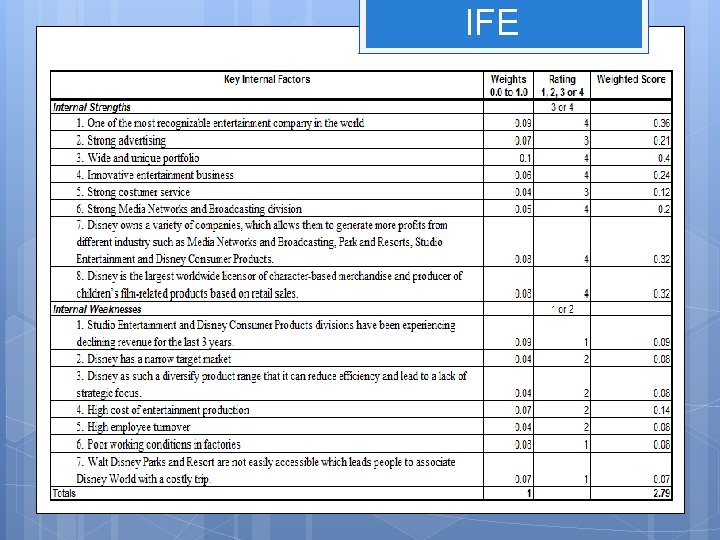
IFE

Strategic Formulation “I do not like to repeat successes, I like to go on to other things. ” Walt Disney
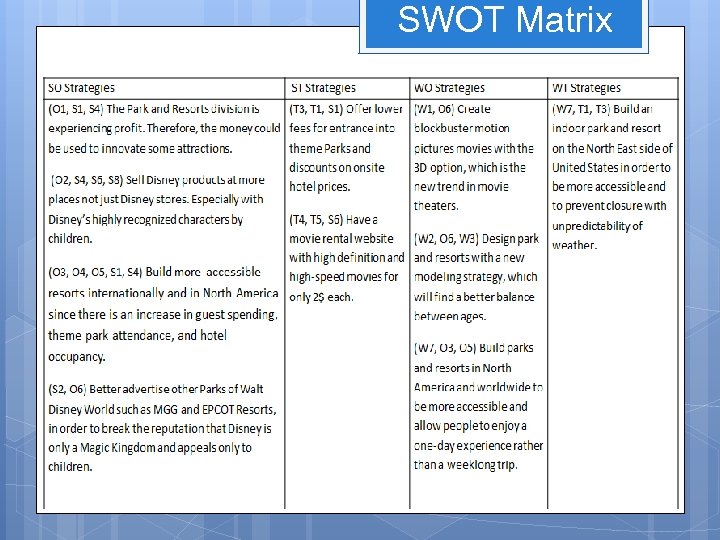
SWOT Matrix
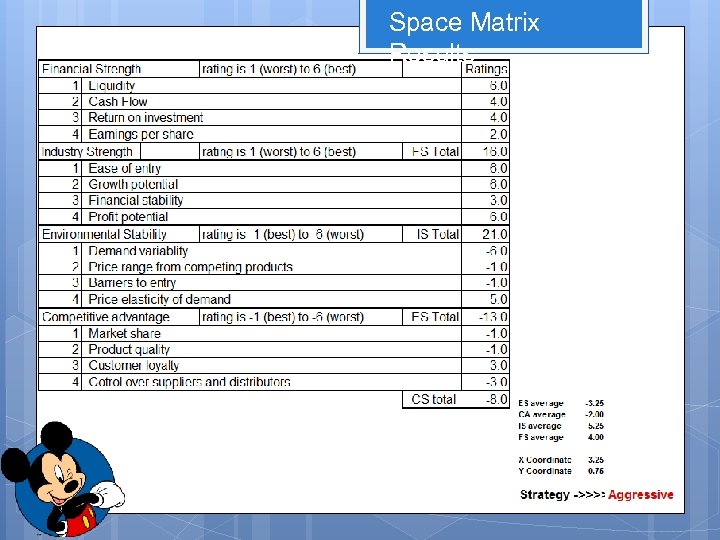
Space Matrix Results
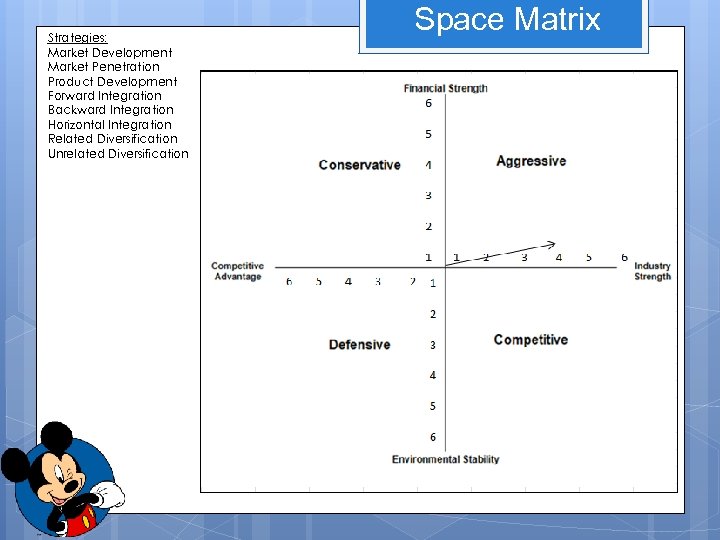
Strategies: Market Development Market Penetration Product Development Forward Integration Backward Integration Horizontal Integration Related Diversification Unrelated Diversification Space Matrix
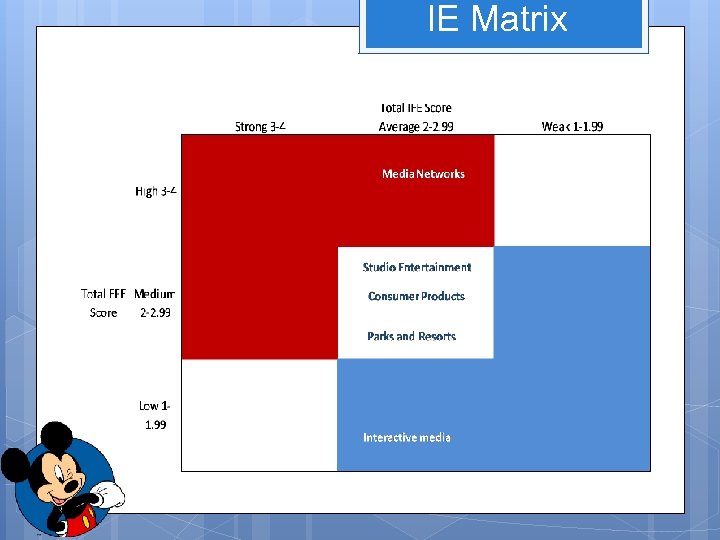
IE Matrix
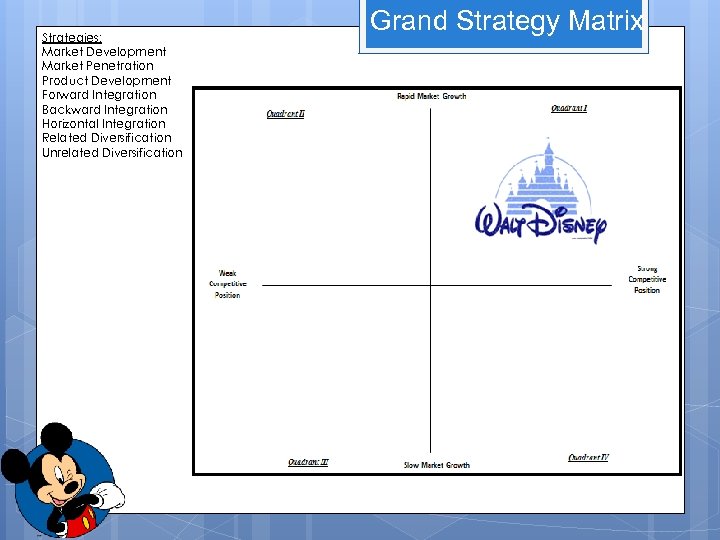
Strategies: Market Development Market Penetration Product Development Forward Integration Backward Integration Horizontal Integration Related Diversification Unrelated Diversification Grand Strategy Matrix
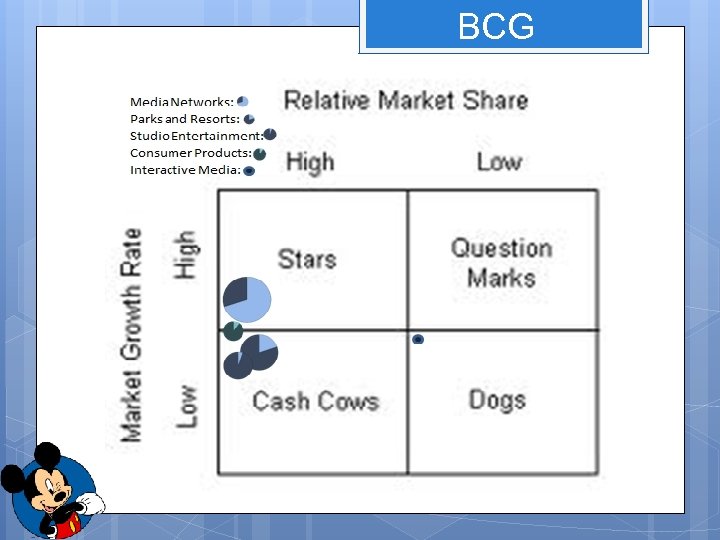
BCG
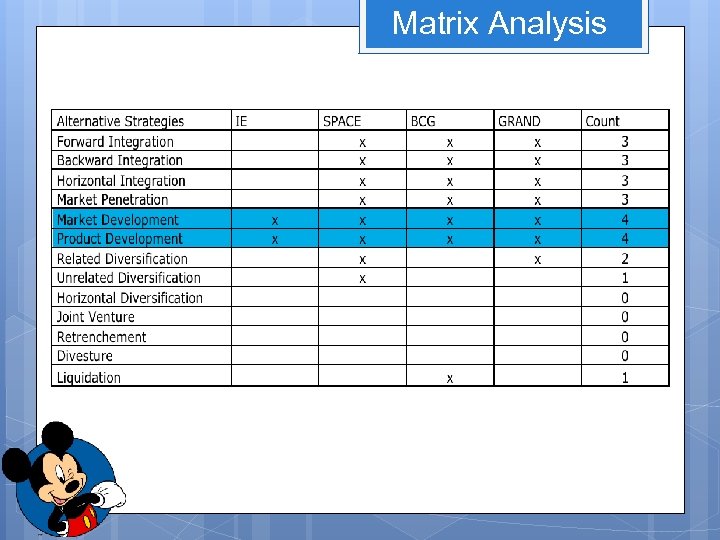
Matrix Analysis
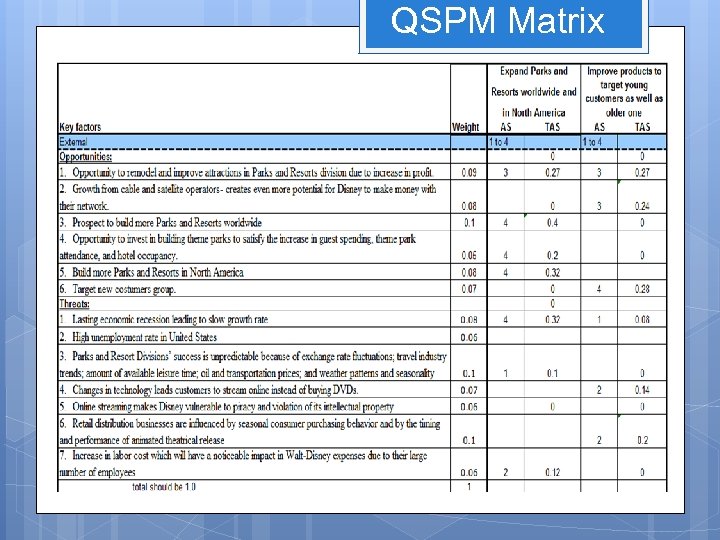
QSPM Matrix
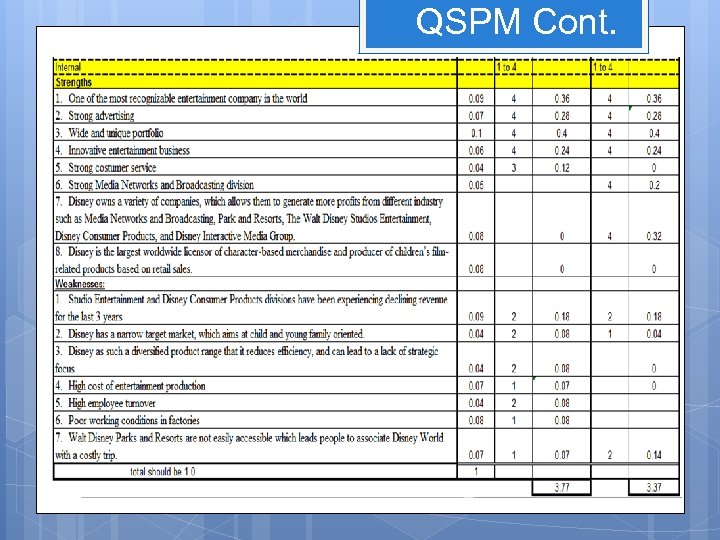
QSPM Cont.

Implementation “Disneyland will never be completed. It will continue to grow as long as there is imagination left in the world. ” Walt Disney “Pixar is the most technically advanced creative company; Apple is the most creatively advanced technical company. “ Steve Jobs 2005 -02 -21

Assumptions Eliminate 10 billion out of the borrowings from the retained earnings Finance 1 billion to buy a land in order to open indoor resort in New York in the next three years. Invest 10 million for advertisement Spend 1 billion in each of the five existing Park for renovation and new attractions. = Total of 5 billion Total Investment of 19. 01 billion
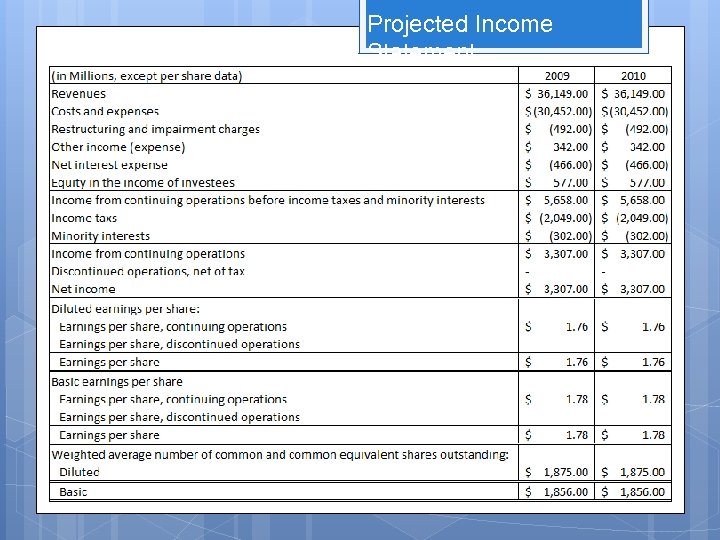
Projected Income Statement
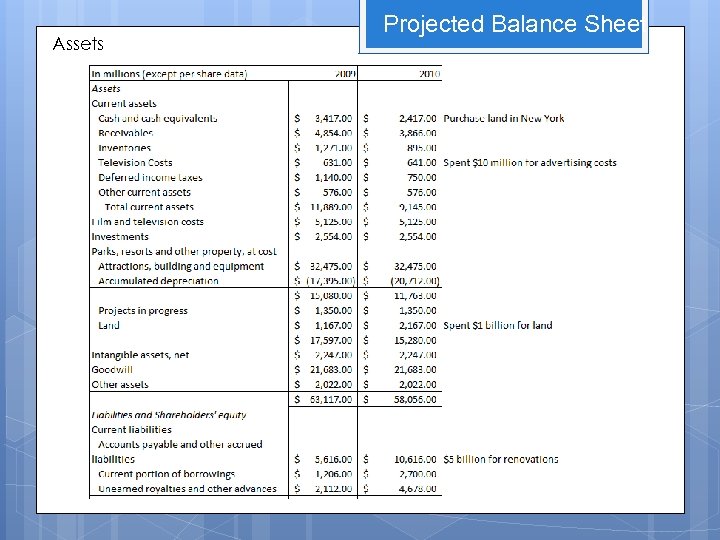
Assets Projected Balance Sheet
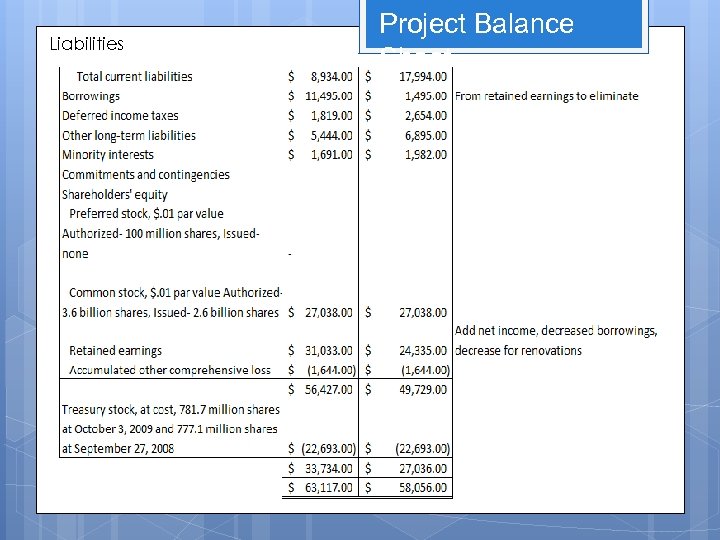
Liabilities Project Balance Sheet
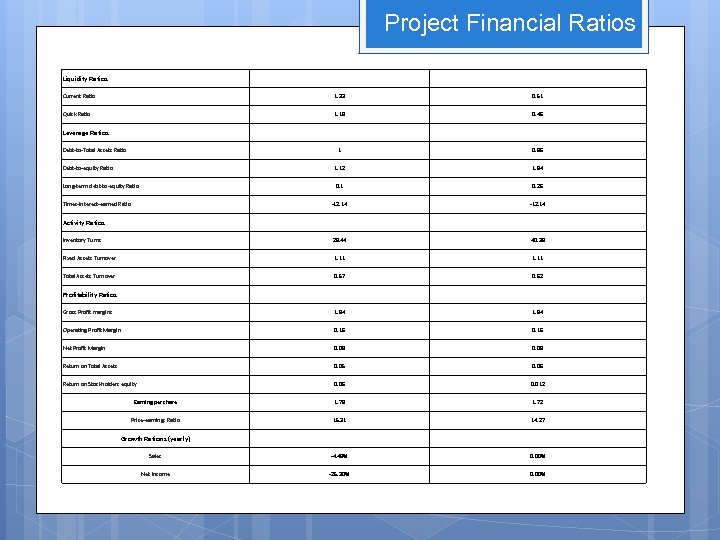
Project Financial Ratios Liquidity Ratios Current Ratio 1. 33 0. 51 Quick Ratio 1. 19 0. 46 Leverage Ratios Debt-to-Total Assets Ratio 1 0. 86 Debt-to-equity Ratio 1. 12 1. 84 Long-term debt-to-equity Ratio 0. 1 0. 26 -12. 14 Activity Ratios Inventory Turns 28. 44 40. 39 Fixed Assets Turnover 1. 11 Total Assets Turnover 0. 57 0. 62 Profitability Ratios Gross Profit margins 1. 84 Operating Profit Margin 0. 16 Net Profit Margin 0. 09 Return on Total Assets 0. 05 0. 06 Return on Stockholders equity 0. 06 0. 012 Earning per share 1. 78 1. 72 Price-earnings Ratio 15. 31 14. 27 Growth Rations (yearly) Sales -4. 48% 0. 00% Net Income -25. 30% 0. 00% Times-Interest-earned Ratio

Evaluation “You're dead if you aim only for kids. Adults are only kids grown up, anyway. ” Walt Disney
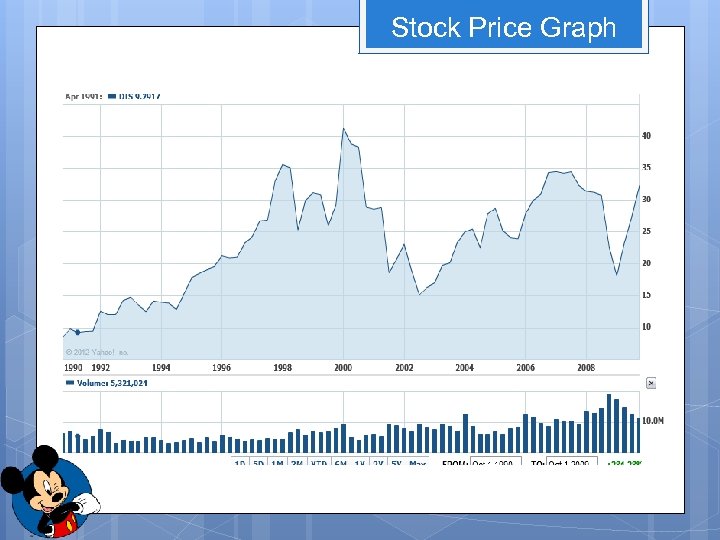
Stock Price Graph
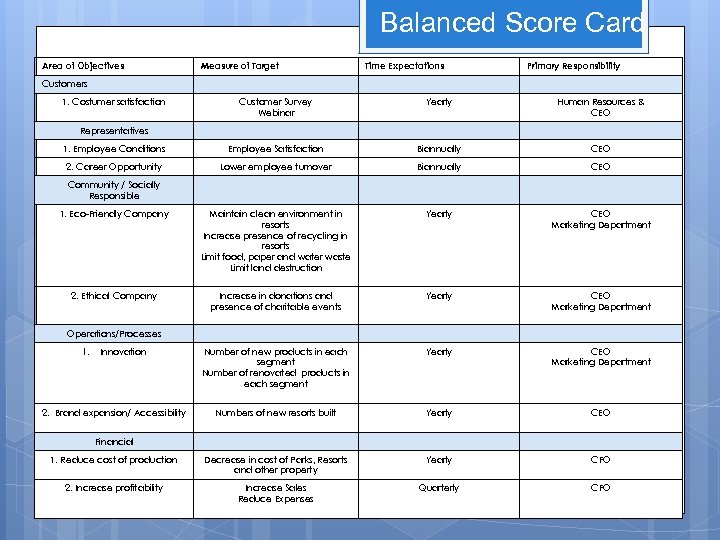
Balanced Score Card Area of Objectives Measure of Target Time Expectations Primary Responsibility Customers 1. Costumer satisfaction Customer Survey Webinar Yearly Human Resources & CEO 1. Employee Conditions Employee Satisfaction Biannually CEO 2. Career Opportunity Lower employee turnover Biannually CEO 1. Eco-Friendly Company Maintain clean environment in resorts Increase presence of recycling in resorts Limit food, paper and water waste Limit land destruction Yearly CEO Marketing Department 2. Ethical Company Increase in donations and presence of charitable events Yearly CEO Marketing Department Number of new products in each segment Number of renovated products in each segment Yearly CEO Marketing Department Numbers of new resorts built Yearly CEO 1. Reduce cost of production Decrease in cost of Parks, Resorts and other property Yearly CFO 2. Increase profitability Increase Sales Reduce Expenses Quarterly CFO Representatives Community / Socially Responsible Operations/Processes 1. Innovation 2. Brand expansion/ Accessibility Financial

Strategies Use product development to renovate and build new attractions in order to attract an older target market. Use market development to build a new theme park which will be more accessible to the North East area.

Recommendations In the next three years Walt Disney should. . Build an indoor theme Park and Resort in New York. Improve advertising to promote entertainment which target a more mature audience. Remove the Interactive Media Segment. Remodel and build new attractions in every Park and Resorts to stay appealing to our customers.

Objectives In the next year Walt Disney should… Improve advertising to promote entertainment Remove Buy the Interactive Media Segment a land in New York City

Questions
Sources ““Home, The Walt Disney Company”, < http: //thewaltdisneycompany. com/<ALDRIDGE, B. “Walt Disney”, Brad Aldridge Productions, Berkley, CA, August 2002, http: //www. justdisney. com/walt_disney/’> “ Annual Reports, The Walt Disney Company”, <http: //thewaltdisneycompany. com/investors/financial-information/annual-report > “ Who Owns the Media? Media Ownership Charts, Free Press”, Florence, MA, <http: //www. freepress. net/ownership/chart> “ Investor Relations, The Walt Disney Company”, <http: //thewaltdisneycompany. com/investors> “ Walt Disney Company (DIS) News – The New York Times” <http: //topics. nytimes. com/top/news/business/companies/disney_walt_company/index. html> “ Stock Quote for Walt Disney Co – MSN Money”, page generated 9: 55 PM, <http: //investing. money. msn. com/investments/stock-price? Symbol=dis&ocid=qbeb> “ DIS: Summary for Walt Disney Company (The) Common – Yahoo! Finance ” <http: //finance. yahoo. com/q? s=dis&ql=1> “ Organizational Chart The Walt Disney Company – The. Official. Board”, <http: //www. theofficialboard. com/org-chart/walt-disney> “ Disney Corporate Press Releases , The Walt Disney Company”, <http: //thewaltdisneycompany. com/disney-news/pressreleases? tid=All&field_press_release_date_value[value][year]=2009&title=&page=3>
f231a1c6d64509b3531c49da94210d22.ppt