f10ab4cc8ffa408b341dcf04036b568c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT - Basanta Raj Sigdel - Suwarn Kumar Singh - Pratibha Dhungana

Agenda of the Session 2 Strategy in an organizational context Strategic thinking Strategic planning process

“If you don’t have a strategy, you will be …. part of somebody - else's strategy. - Alvin Toffler

Mind Reading 4 What comes to your mind while talking about Strategy? Please create a PICTURE within 5 minutes that expresses the term- ‘Strategy’. o Each participant will draw a concept first o Succeeding officers will build on the concept already drawn o You are requested NOT TO communicate while drawing o Circulate your drawing to other groups o Share learning in plenary in 5 minutes

5
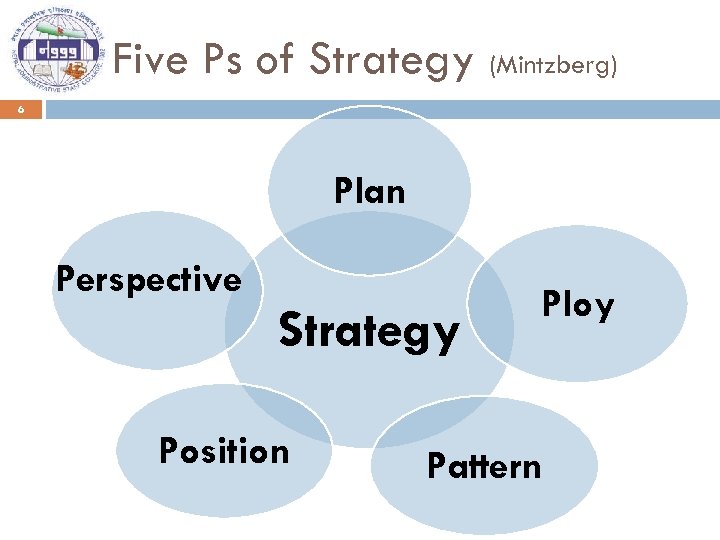
Five Ps of Strategy (Mintzberg) 6 Plan Perspective Strategy Position Ploy Pattern

Five Ps of Strategy 7 PLAN o Consciously intended course of action, a set of guidelines to deal with the situation PLOY o Specific maneuver intended to outwit an opponent or competitor PATTERN o In a stream of actions…consistency in behavior whether or not intended POSITION o Means of locating an organization in an environment PERSPECTIVE o An engrained way of perceiving the world

Strategic Thinking 8
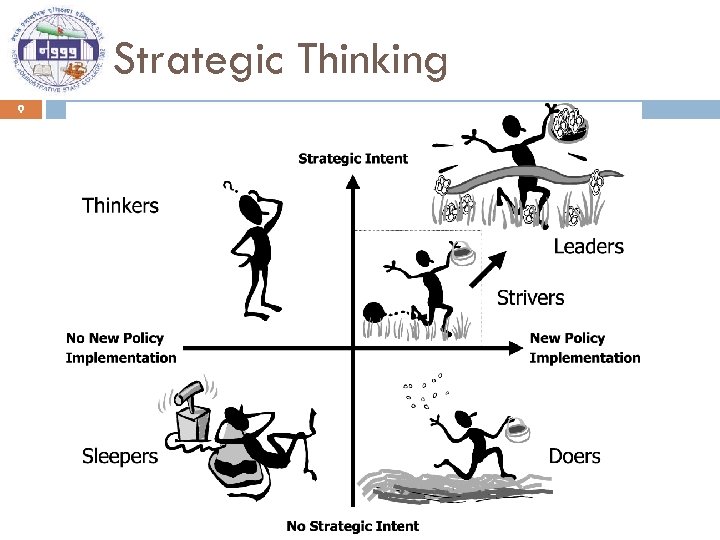
Strategic Thinking 9

Strategic Management 10 … is the application of strategic thinking to the job of leading an organisation. q “Managing strategically”, in other words: o ‘Diagnosing situation strategically’, and o ‘Applying knowledge strategically’ “… is continuous, iterative process aimed at keeping an organization as a whole appropriately matched to its environment. ” q - Certo and Peter

Strategic Planning 11 Strategic Planning is a disciplined effort to produce fundamental decisions and actions that shape and guide what an organisation is, what it does, and why it does it with a focus on the future (JM Bryson). It focuses on the best ‘fit’ between an organisation and its environment. It is defined as the process of addressing the following questions:
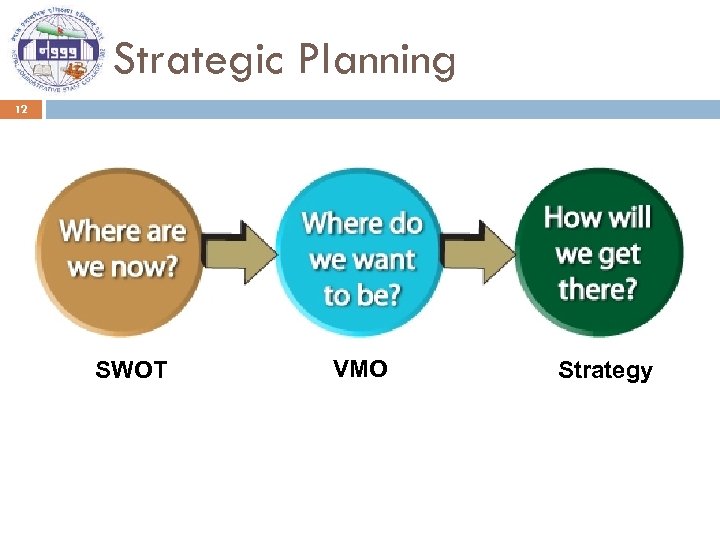
Strategic Planning 12 SWOT VMO Strategy

Strategic Planning Process 13 It is an ongoing process and involving a series of steps to be followed. 1. Getting Ready (Agreement) 2. Environmental Scanning (SWOT Analysis) 3. Strategy Formulation (Identification of Strategic Issues, Strategies) 4. Vision, Mission, Strategy Implementation Objectives, Roles, (Strategic Actions (Action Plan): Actions/Activities, By whom, By when, Resources, Indicators, Critical factors)
Environmental Analysis 14 Analysis and diagnosis of an organization, often referred to as an Organization Audit or SWOT analysis. It is undertaken to assess an organisation’s ability to deal with its environment by identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT).

Internal (Supply Side) Analysis 15 An analysis of internal organizational factors which reviews and investigates the prevailing resources, processes and performance of organization. The analysis identifies major strengths and weaknesses - of all the key functional elements (Structure, Functions, HR, Finance, IT, Rules, Procedures, etc. ). What are major internal Strengths and Weaknesses in terms of Structure, Resources, Processes, Performance, Culture, etc. ?

External (Demand Side) Analysis 16 The analysis indicates the opportunities and threats faced by the organization from its relationship with external stakeholders. Major categories of external environment: 1. Forces and trends – PEST 2. Clients, customers, or payers 3. Actual or potential competitors or collaborators What major external Opportunities and Threats (Political, Economic, Social, Technology, Legal, Stakeholders, etc. ) do the organization face?

Considerations 17 Use precise, verifiable statements ("Cost advantage of Rs……/unit in sourcing resources x", rather than "Good value for money")- be specific. Reduce long lists of factors, and prioritize them, so that you spend your time thinking about the most significant factors.

Information for SWOT Sources of Information Primary Secondary Methods of Information Collection Interview Focus group discussion / Workshop Questionnaire Survey Observation Reviewing documents, reports, etc.
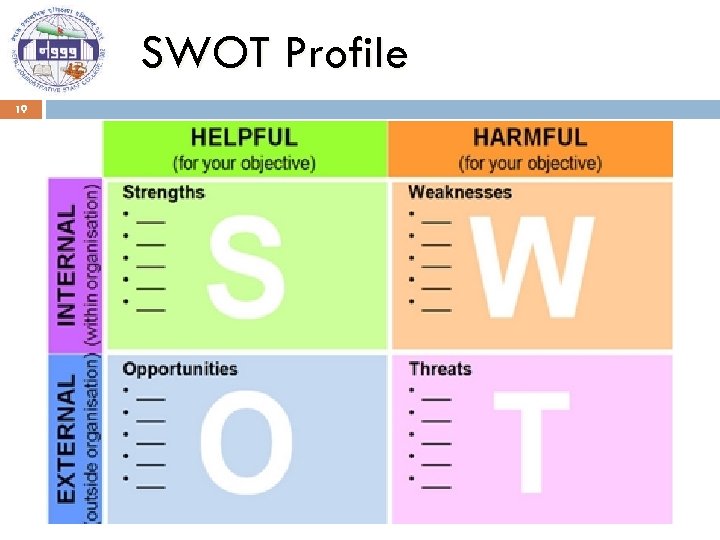
SWOT Profile 19
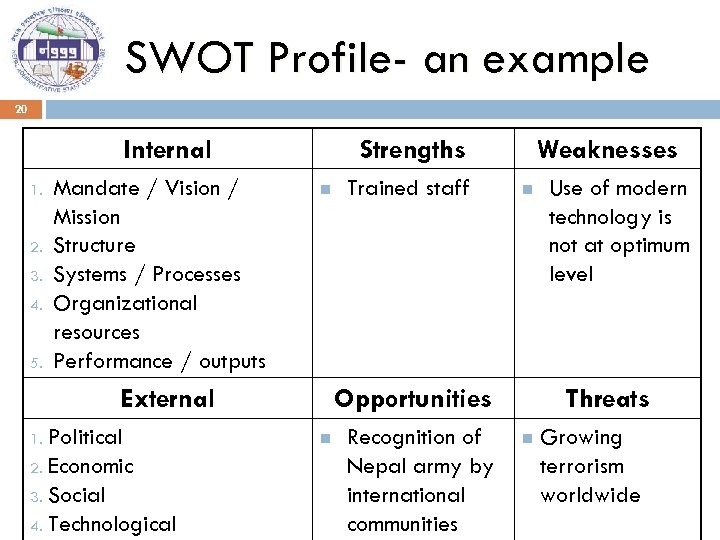
SWOT Profile- an example 20 Internal 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Mandate / Vision / Mission Structure Systems / Processes Organizational resources Performance / outputs Strengths n External Political 2. Economic 3. Social 4. Technological 1. Trained staff Weaknesses n Opportunities n Recognition of Nepal army by international communities Use of modern technology is not at optimum level Threats n Growing terrorism worldwide

21 Exercise: SWOT Analysis

Sample organizations for Exercise 22 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Army Command Staff College Army Hospital Welfare Fund Logistics Management Disaster Risk Management

Strategic Issues 23 Fundamental policy questions or critical challenges that affect An organization’s mandates, mission and values Organization/management Costs, financing Services Consumers, users…. About which something can be done. John M. Bryson, Strategic Planning for Public and Nonprofit Organizations: A Guide to Strengthening and Sustaining Organizational Achievement, rev. ed. (San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 1995), 30

Strategic Issues 24 Example 1. How to optimize technology in enhancing operational efficiency of the organization? Prioritizing Issues No action is needed at present, but needs monitoring Can be handled as regular planning Urgent, must be dealt with Actionable/feasible, Resources, Stakeholder readiness, Importance

Vision, Mission, Objectives, Roles Vision: …is a mental picture of a possible situation or state of affairs. …a statement about what your organization wants to become. How the organisation would like the world in which it operates to be? What it should look like? Where it wants to go in future? Example: “Center of Excellence in developing managerial 25 capabilities of public service organizations”

Mission 26 The fundamental purpose of an organisation, basically describing why it exists (reasons for existence – purpose) and what it does to achieve its Vision. Why it should be doing what it does? Example: “Develop managerial competencies and organizational capabilities of public sector through training, consulting and research services”

Objectives 27 What you are trying to achieve by a particular course of action. Stated in terms of the results it needs/wants to achieve in future. Objectives should relate to the expectations and requirements of all the major stakeholders. They should be SMART. Example: Ensure training programmes based on real learning need of officers.

Roles The position that an organisation has in a particular situation, which determines how much it is involved in the situation or how much responsibility it has. Roles are identified considering strategic strengths and opportunities. Example: 1. Policy advice 2. Implementation of policies 3. Research 4. HRD

Strategy Formulation 29 Strategy is an action oriented plan of operation for achieving desired goals based on situation analysis, and emphasises what an organisation will be doing in future. An effective strategy must meet several criteria: Technically workable Politically acceptable to key stakeholders Accord with the organisation’s philosophy and values. Ethical, moral and legal, Deal with issues it was supposed to address
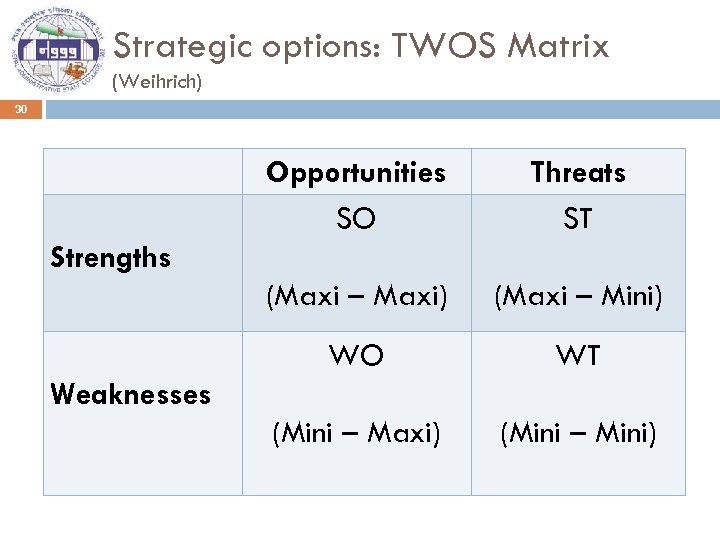
Strategic options: TWOS Matrix (Weihrich) 30 Opportunities SO Threats ST (Maxi – Maxi) (Maxi – Mini) WO WT (Mini – Maxi) (Mini – Mini) Strengths Weaknesses

Considerations in strategy formulation 31 Organisational competence and resources to capture opportunities Environmental threats to its long-term well being Personal values and aspirations of managers Societal obligations and ethical considerations Organisational culture

Strategy 32 Example: Foster institutional networking and coordination The Choice of Strategy depends upon organisation’s environment and mission and objectives.
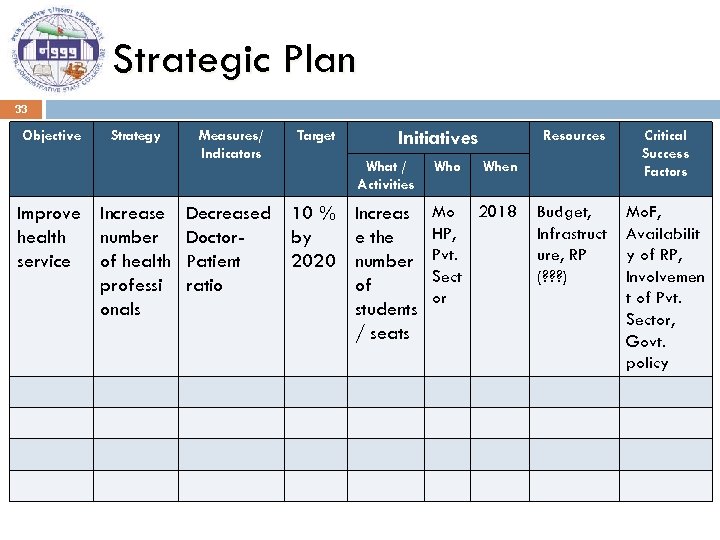
Strategic Plan 33 Objective Strategy Improve Increase health number service of health professi onals Measures/ Indicators Decreased Doctor. Patient ratio Target Resources Initiatives What / Activities 10 % Increas by e the 2020 number of students / seats Who Critical Success Factors Budget, Infrastruct ure, RP (? ? ? ) Mo. F, Availabilit y of RP, Involvemen t of Pvt. Sector, Govt. policy When Mo 2018 HP, Pvt. Sect or

Strategy Implementation 34 o o o Building an organisation structure to the requirements of the strategy Allocating resources and energies on accomplishment of the strategic goals Ensuring organisation-wide commitment Installing administrative support system Shaping the organisation culture to fit the strategy Exerting strategic leadership

Evaluation and Control 35 The implementation of the strategy must be monitored and adjustments made as needed. Evaluation and control consists: I. Parameters and target values for those parameters II. Performing measurements III. Comparing measured results to the predefined standard IV. Making necessary changes

WHY STRATEGIC INITIATIVES FAIL? 36 When one is STUPID: Sponsorship not forthcoming Team member do not function as agents of change Unclear vision and commitment Poorly planned change programme Inappropriate/ Insufficient Communication Don’t take account of culture

The SUCCESS Principle 37 Shared vision Understand the organization Cultural alignment Communication Experience help where necessary / Executive support Strong leadership Stakeholder buy-in / Systematic planning / Short-term wins

Conclusion Strategic Management originated as a discipline in 1950 s and 1960 s is “diagnosing situation strategically” and “applying knowledge strategically” to achieve objectives. It starts with getting ready for planning and moves on to addressing the questions: Where are we today? Where we want to go? How do we get there? Organisations to achieve their long term objectives successfully have to put strategic management into practice strategically involving key stakeholders in the planning process at some level. 38

The story continues… 39
f10ab4cc8ffa408b341dcf04036b568c.ppt