030ffc0017754a6d9062ff24e8a170c2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 86
 Strategic Management 1. Why is strategic management important? 2. What is strategic management? 3. Who is involved with strategic management? 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 1
Strategic Management 1. Why is strategic management important? 2. What is strategic management? 3. Who is involved with strategic management? 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 1
 Learning Outcome • Explain Why Strategic Management Is Important – Everyone in the organization has a role in strategic management – It enables understanding how strategic decisions are made – Establishes an understanding of how work is valued and rewarded – It makes a difference in how well an organization performs 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 2
Learning Outcome • Explain Why Strategic Management Is Important – Everyone in the organization has a role in strategic management – It enables understanding how strategic decisions are made – Establishes an understanding of how work is valued and rewarded – It makes a difference in how well an organization performs 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 2
 Learning Outcome • Studies show relationship between effective organizations and their use of strategic management – Impact on bottom line – Adapting to changing situations, internal & external – Coping with uncertainties – Effectively guides organizational decision makers 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 3
Learning Outcome • Studies show relationship between effective organizations and their use of strategic management – Impact on bottom line – Adapting to changing situations, internal & external – Coping with uncertainties – Effectively guides organizational decision makers 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 3
 Studies on Relationship Between Strategic Management & Performance • Studies of decision making process suggest the way strategy is developed can have an affect on performance – Decision makers that collected information and used analytical techniques make more effective strategic decisions than those that do not 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 4
Studies on Relationship Between Strategic Management & Performance • Studies of decision making process suggest the way strategy is developed can have an affect on performance – Decision makers that collected information and used analytical techniques make more effective strategic decisions than those that do not 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 4
 Studies on Relationship Between Strategic Management & Performance • Another study found organizations that used several approaches to develop strategy outperform those that use a single approach – Structured, systematic approach can positively affect organizational performance • Strategic management helps achieve the organization’s goals by – Coordinating and focusing the various divisions, departments, and work activities 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 5
Studies on Relationship Between Strategic Management & Performance • Another study found organizations that used several approaches to develop strategy outperform those that use a single approach – Structured, systematic approach can positively affect organizational performance • Strategic management helps achieve the organization’s goals by – Coordinating and focusing the various divisions, departments, and work activities 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 5
 Corporate Reputations • A good corporate reputation is critical and surveys support its importance and influence – On financial performance – Executing strategy – Transparency and disclosure of information – Strong corporate governance • Check Companies with the Best Reputations 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 6
Corporate Reputations • A good corporate reputation is critical and surveys support its importance and influence – On financial performance – Executing strategy – Transparency and disclosure of information – Strong corporate governance • Check Companies with the Best Reputations 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 6
 Learning Outcome • Explain what strategic management is • Explain who’s involved with strategic management • Discuss the three important factors impacting strategic management today 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 7
Learning Outcome • Explain what strategic management is • Explain who’s involved with strategic management • Discuss the three important factors impacting strategic management today 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 7
 Explain What Strategic Management Is • No matter what the business or industry, strategic management is involved in such varied areas as – Market expansion – Product development – Decision making 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 8
Explain What Strategic Management Is • No matter what the business or industry, strategic management is involved in such varied areas as – Market expansion – Product development – Decision making 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 8
 The Basics of Strategy and Strategic Management • Definition of Strategy – Strategy is a series of goal-directed plans and actions that align an organization’s skills and resources with the opportunities and threats in its environment • Definition of Strategic Management – This is a process for situation analysis and strategy formulation, implementation, and evaluation 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 9
The Basics of Strategy and Strategic Management • Definition of Strategy – Strategy is a series of goal-directed plans and actions that align an organization’s skills and resources with the opportunities and threats in its environment • Definition of Strategic Management – This is a process for situation analysis and strategy formulation, implementation, and evaluation 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 9
 The Definition of Strategy • Strategy: – Involves an organization’s goals – Engages goal directed action – Includes a series of related decisions and actions throughout the various levels and divisions of an organization – Takes into account organizational internal strengths (resources and capabilities) and external opportunities and threats 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 10
The Definition of Strategy • Strategy: – Involves an organization’s goals – Engages goal directed action – Includes a series of related decisions and actions throughout the various levels and divisions of an organization – Takes into account organizational internal strengths (resources and capabilities) and external opportunities and threats 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 10
 The Definition of Strategic Management • Strategic management involves those decisions and actions of organizational members that includes: – Analysis of the current situation – Development of appropriate strategies – Putting the strategies into action – Evaluating, modifying, changing strategies as needed 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 11
The Definition of Strategic Management • Strategic management involves those decisions and actions of organizational members that includes: – Analysis of the current situation – Development of appropriate strategies – Putting the strategies into action – Evaluating, modifying, changing strategies as needed 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 11
 Strategic Management in Action • IDEO is a design firm known for a range of innovative product designs that have won global design awards • The strategic management challenge for IDEO is keeping the ideas flowing – How can companies in today’s globally competitive environment generate creative ideas? 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 12
Strategic Management in Action • IDEO is a design firm known for a range of innovative product designs that have won global design awards • The strategic management challenge for IDEO is keeping the ideas flowing – How can companies in today’s globally competitive environment generate creative ideas? 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 12
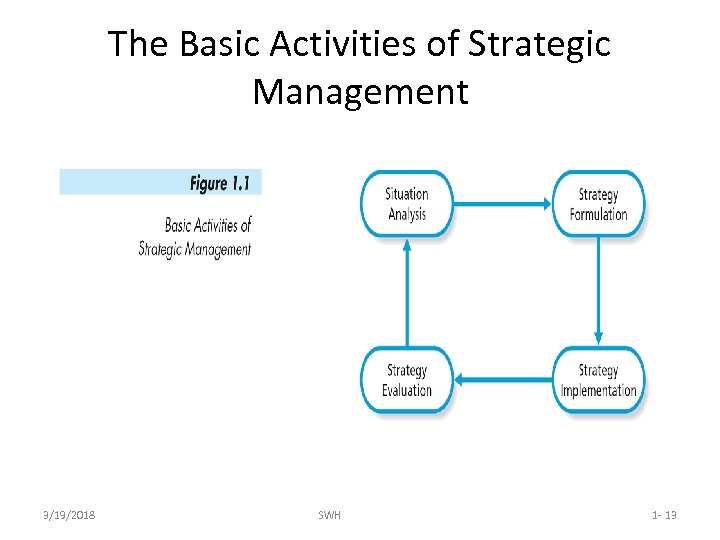 The Basic Activities of Strategic Management 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 13
The Basic Activities of Strategic Management 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 13
 The Four Characteristics of Strategic Management • Interdisciplinary – It focuses on the whole organization, rather than any functional part • External Focus – interaction of organization with external environment – Economy – Competitors – Market demographics 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 14
The Four Characteristics of Strategic Management • Interdisciplinary – It focuses on the whole organization, rather than any functional part • External Focus – interaction of organization with external environment – Economy – Competitors – Market demographics 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 14
 The Four Characteristics of Strategic Management – cont’d • Internal Focus – Understands the resources and capabilities the organization does or does not have • Future Direction of the Organization, includes – Decisions – Planning – Shifts or changes in products or markets 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 15
The Four Characteristics of Strategic Management – cont’d • Internal Focus – Understands the resources and capabilities the organization does or does not have • Future Direction of the Organization, includes – Decisions – Planning – Shifts or changes in products or markets 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 15
 Strategic Management in Action • IHOP – What strategic changes did the new IHOP CEO employ to turnaround a struggling company? – What challenges did it face with the acquisition of Applebee's in 2007? – What was different? What did Applebee's possess that could be used to build on? 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 16
Strategic Management in Action • IHOP – What strategic changes did the new IHOP CEO employ to turnaround a struggling company? – What challenges did it face with the acquisition of Applebee's in 2007? – What was different? What did Applebee's possess that could be used to build on? 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 16
 The Strategic Management Process • A process is a series of interrelated and continuous steps that lead to an outcome • The Strategic Management Process employs its four characteristics to create a set of strategies used to conduct its business 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 17
The Strategic Management Process • A process is a series of interrelated and continuous steps that lead to an outcome • The Strategic Management Process employs its four characteristics to create a set of strategies used to conduct its business 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 17
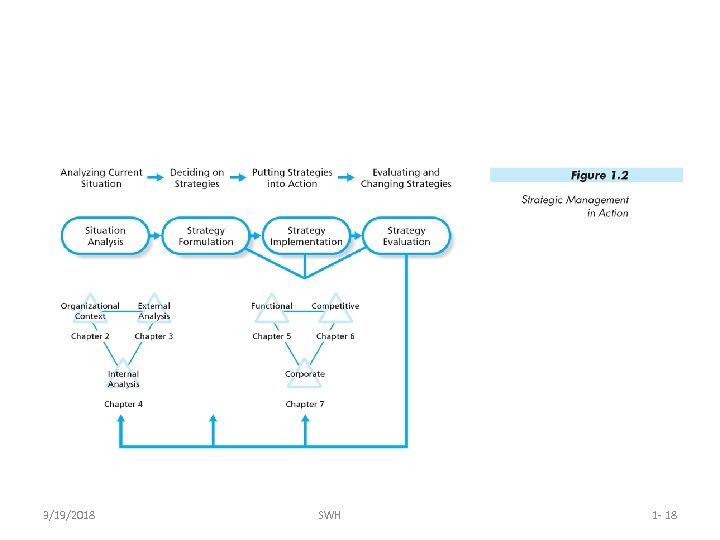 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 18
3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 18
 Situation Analysis • Situation analysis is required before deciding upon a strategic direction or response and it involves scanning and evaluating – The current organizational context – The external environment – The organizational environment 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 19
Situation Analysis • Situation analysis is required before deciding upon a strategic direction or response and it involves scanning and evaluating – The current organizational context – The external environment – The organizational environment 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 19
 Strategy Formulation • Strategy formulation is developing and choosing appropriate strategies, as guided by the situation analysis, and includes three main types of strategies – Functional Strategies (also called operational strategies) – Competitive Strategies (also called business strategies) – Corporate Strategies (these are guiding strategies by which all efforts are aligned) 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 20
Strategy Formulation • Strategy formulation is developing and choosing appropriate strategies, as guided by the situation analysis, and includes three main types of strategies – Functional Strategies (also called operational strategies) – Competitive Strategies (also called business strategies) – Corporate Strategies (these are guiding strategies by which all efforts are aligned) 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 20
 Functional Strategies • Functional strategies or operational strategies are goal oriented plans and actions of the functional areas of an organization, they include: – Production-Operations – Marketing – Research & Development – Human Resources – Financial-Accounting – Information Technology & Support 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 21
Functional Strategies • Functional strategies or operational strategies are goal oriented plans and actions of the functional areas of an organization, they include: – Production-Operations – Marketing – Research & Development – Human Resources – Financial-Accounting – Information Technology & Support 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 21
 Competitive Strategies • Competitive strategies or business strategies are goal directed plans and actions concerned with how an organization competes in a specific business or industry – Looks at all aspects of strategies and actions – Seeks to determine what the company currently can do and what it wants to do – Focus is on how it might more effectively compete 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 22
Competitive Strategies • Competitive strategies or business strategies are goal directed plans and actions concerned with how an organization competes in a specific business or industry – Looks at all aspects of strategies and actions – Seeks to determine what the company currently can do and what it wants to do – Focus is on how it might more effectively compete 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 22
 Corporate Strategy • Corporate strategies are goal directed plans and actions that are concerned with what business or businesses a firm wants to be in and what to do with those businesses; for example – Fed. Ex’s decision to acquire Kinko's – Pepsi. Co’s decision to spin off their fast-food division 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 23
Corporate Strategy • Corporate strategies are goal directed plans and actions that are concerned with what business or businesses a firm wants to be in and what to do with those businesses; for example – Fed. Ex’s decision to acquire Kinko's – Pepsi. Co’s decision to spin off their fast-food division 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 23
 Strategy Implementation • It is not enough to formulate great strategies, they must be implemented – Strategy implementation is putting the various stages of strategies into action – How a strategy is implemented must be considered 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 24
Strategy Implementation • It is not enough to formulate great strategies, they must be implemented – Strategy implementation is putting the various stages of strategies into action – How a strategy is implemented must be considered 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 24
 Strategy Evaluation • Strategy evaluation involves evaluating both the outcomes of the strategies and how they have been implemented – Determine if they produced the expected strategic goals – Helps with the evaluation of results and, if necessary, any modification of strategies 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 25
Strategy Evaluation • Strategy evaluation involves evaluating both the outcomes of the strategies and how they have been implemented – Determine if they produced the expected strategic goals – Helps with the evaluation of results and, if necessary, any modification of strategies 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 25
 Strategic Management Process in Action • The Strategic Management Process is a continual cycle – It is not a sequential process – It allows for analysis of the current situation – Enables adjustments to current strategies as necessary, to pursue and achieve goals 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 26
Strategic Management Process in Action • The Strategic Management Process is a continual cycle – It is not a sequential process – It allows for analysis of the current situation – Enables adjustments to current strategies as necessary, to pursue and achieve goals 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 26
 Making It Last • Characteristics of companies that endure – Continual focus on value and profitability – Keeping strategy simple by understanding key priorities – Committing to effective communication – Creating a performance oriented culture – Sharing decision making – Obtaining and filtering information – Rapidly adapting to change 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 27
Making It Last • Characteristics of companies that endure – Continual focus on value and profitability – Keeping strategy simple by understanding key priorities – Committing to effective communication – Creating a performance oriented culture – Sharing decision making – Obtaining and filtering information – Rapidly adapting to change 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 27
 Looking at Strategic Management’s Past • Strategy’s military roots – Origin of the word is Greek referring to military commander – Historical references to the design of plans and actions to gain an edge on the enemy – The concept involves analyzing the situation and effecting an appropriate response 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 28
Looking at Strategic Management’s Past • Strategy’s military roots – Origin of the word is Greek referring to military commander – Historical references to the design of plans and actions to gain an edge on the enemy – The concept involves analyzing the situation and effecting an appropriate response 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 28
 Principles of War • Nine principles taught by leading US military academies that can be used in business to develop strategies – Objective: every operation should be directed to a clearly defined, decisive, and attainable objective – Offensive: seize, retain, and exploit the initiative – Unity of command: forces must be under one commander with full authority and responsibility – Mass: concentrate combat power at the decisive place and time 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 29
Principles of War • Nine principles taught by leading US military academies that can be used in business to develop strategies – Objective: every operation should be directed to a clearly defined, decisive, and attainable objective – Offensive: seize, retain, and exploit the initiative – Unity of command: forces must be under one commander with full authority and responsibility – Mass: concentrate combat power at the decisive place and time 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 29
 Principles of War – cont’d • Economy of force: allocate on the essential minimum of forces to secondary efforts • Maneuver: place the enemy in a position of disadvantage through the flexible application of combat power • Surprise: strike at the enemy at a time or place that is unexpected • Security: never allow an enemy to acquire an unexpected advantage • Simplicity: need clear plans and concise orders 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 30
Principles of War – cont’d • Economy of force: allocate on the essential minimum of forces to secondary efforts • Maneuver: place the enemy in a position of disadvantage through the flexible application of combat power • Surprise: strike at the enemy at a time or place that is unexpected • Security: never allow an enemy to acquire an unexpected advantage • Simplicity: need clear plans and concise orders 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 30
 Academic Origins of Strategic Management • Strategic management is a relatively young field. The theoretical foundation is from economics and organization studies; with emphasis on – Rationality – Predictability – Similarity 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 31
Academic Origins of Strategic Management • Strategic management is a relatively young field. The theoretical foundation is from economics and organization studies; with emphasis on – Rationality – Predictability – Similarity 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 31
 Academic Origins of Strategic Management – cont’d • Key writers and their areas of interest – Frederick Taylor: Scientific Management – Max Weber: Bureaucratic organizations – Chester Barnard: Administrative functions & the organization as open systems • Focus by academics on – Role of managers – Efficiency and effectiveness 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 32
Academic Origins of Strategic Management – cont’d • Key writers and their areas of interest – Frederick Taylor: Scientific Management – Max Weber: Bureaucratic organizations – Chester Barnard: Administrative functions & the organization as open systems • Focus by academics on – Role of managers – Efficiency and effectiveness 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 32
 Strategic Planning and Strategic Management Emerge • During the 1960 s, organization theorists searched for explanations of organizational differences in functioning and performance – Attempts made to determine if there was one best way to manage in all situations – Contingency approaches emerged when it was determined that each organization was different and the best way to manage depended on the situation 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 33
Strategic Planning and Strategic Management Emerge • During the 1960 s, organization theorists searched for explanations of organizational differences in functioning and performance – Attempts made to determine if there was one best way to manage in all situations – Contingency approaches emerged when it was determined that each organization was different and the best way to manage depended on the situation 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 33
 Strategic Planning and Strategic Management Emerge – cont’d • Three classic strategy textbooks established many of basic precepts of strategic management and distinguishing it as a separate field of study • During 1970 s-1980 s, dichotomous view of strategy emerged – Process focus = “how” strategy is formed – Content focus = the “what” of strategy decisions 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 34
Strategic Planning and Strategic Management Emerge – cont’d • Three classic strategy textbooks established many of basic precepts of strategic management and distinguishing it as a separate field of study • During 1970 s-1980 s, dichotomous view of strategy emerged – Process focus = “how” strategy is formed – Content focus = the “what” of strategy decisions 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 34
 Learning Review: Learning Outcome 1. 2 • Define strategy and strategic management • Describe the strategic management process • Describe three types of organizational strategies • Explain the historical evolution of strategic management 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 35
Learning Review: Learning Outcome 1. 2 • Define strategy and strategic management • Describe the strategic management process • Describe three types of organizational strategies • Explain the historical evolution of strategic management 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 35
 Learning Outcome 1. 3 • Explain Who’s Involved with Strategic Management • The Board of Directors • The Role of Top Management • Other Managers and Organizational Employees 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 36
Learning Outcome 1. 3 • Explain Who’s Involved with Strategic Management • The Board of Directors • The Role of Top Management • Other Managers and Organizational Employees 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 36
 Explain Who’s Involved with Strategic Management • Strategic management is more than the responsibility of an organization’s top managers • People at all levels of the organization play a role in strategy – Developing it – Implementing it – Changing it 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 37
Explain Who’s Involved with Strategic Management • Strategic management is more than the responsibility of an organization’s top managers • People at all levels of the organization play a role in strategy – Developing it – Implementing it – Changing it 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 37
 The Board of Directors • Usually an elected group that represents a company’s shareholders – They have a legal obligation to represent and protect the interests of shareholders through corporate governance – In the past, board participation was viewed as approving strategies designed by management – With increasing shareholder activism, boards are more involved in the strategic process 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 38
The Board of Directors • Usually an elected group that represents a company’s shareholders – They have a legal obligation to represent and protect the interests of shareholders through corporate governance – In the past, board participation was viewed as approving strategies designed by management – With increasing shareholder activism, boards are more involved in the strategic process 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 38
 Typical Board Responsibilities • Review and approve strategic goals and plans • Review and approve organization’s financial standards and policies • Ensure the integrity of organization’s financial controls and reporting system • Approve an organizational philosophy • Monitor organizational performance and regularly review performance results 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 39
Typical Board Responsibilities • Review and approve strategic goals and plans • Review and approve organization’s financial standards and policies • Ensure the integrity of organization’s financial controls and reporting system • Approve an organizational philosophy • Monitor organizational performance and regularly review performance results 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 39
 Typical Board Responsibilities – cont’d • Select, and compensate top level managers • Develop management succession plans • Review and approve capital allocations and expenditures • Monitor relations with shareholders and other key stakeholders 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 40
Typical Board Responsibilities – cont’d • Select, and compensate top level managers • Develop management succession plans • Review and approve capital allocations and expenditures • Monitor relations with shareholders and other key stakeholders 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 40
 The Role of Top Management • Responsible for every decision and outcome, top management plays a most significant role in strategic management process • Top management includes C-Suite level officers, including – CEO, Chief Executive Officer – COO, Chief Operating Officer – CFO, Chief Finance Officer – CIO, Chief Information Officer 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 41
The Role of Top Management • Responsible for every decision and outcome, top management plays a most significant role in strategic management process • Top management includes C-Suite level officers, including – CEO, Chief Executive Officer – COO, Chief Operating Officer – CFO, Chief Finance Officer – CIO, Chief Information Officer 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 41
 The Role of Top Management – cont’d • Top management provides strategic leadership, which involves: – Determining organizational purpose – Exploiting and maintaining core competencies – Developing human capital – Creating and sustaining strong organizational culture – Emphasizing ethical decisions and practices – Establishing balanced controls 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 42
The Role of Top Management – cont’d • Top management provides strategic leadership, which involves: – Determining organizational purpose – Exploiting and maintaining core competencies – Developing human capital – Creating and sustaining strong organizational culture – Emphasizing ethical decisions and practices – Establishing balanced controls 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 42
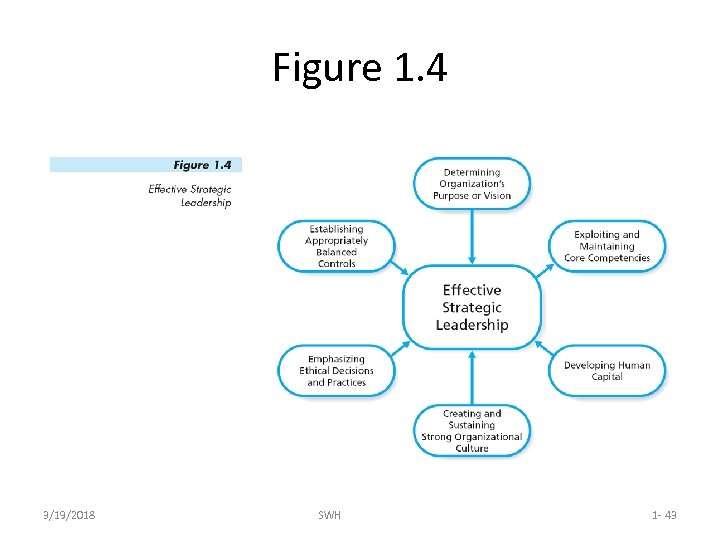 Figure 1. 4 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 43
Figure 1. 4 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 43
 Other Managers and Organizational Employees • Managers and employees at all levels have strategic responsibilities that include: – Strategy implementation, putting strategies into action – Strategy evaluation, determining if the strategies are working – Adjust the strategies to achieve desired ends 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 44
Other Managers and Organizational Employees • Managers and employees at all levels have strategic responsibilities that include: – Strategy implementation, putting strategies into action – Strategy evaluation, determining if the strategies are working – Adjust the strategies to achieve desired ends 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 44
 Learning Outcome 1. 3 • Explain the role of the board of directors in strategic management • Discuss how top managers can be effective strategic leaders • Describe the role of other managers and organizational employees 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 45
Learning Outcome 1. 3 • Explain the role of the board of directors in strategic management • Discuss how top managers can be effective strategic leaders • Describe the role of other managers and organizational employees 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 45
 Learning Outcome 1. 4 • Discuss the three important factors impacting strategic management today – The Global Economy and Globalization – Corporate Governance – Strategic Management in an E-Business World 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 46
Learning Outcome 1. 4 • Discuss the three important factors impacting strategic management today – The Global Economy and Globalization – Corporate Governance – Strategic Management in an E-Business World 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 46
 The Global Economy and Globalization • In past twenty-five years, globalization has become a leading focus of company strategies • Increasing number of companies have revenues coming from outside their country of origin • Global recession creates strategic challenges – Reduced consumer demand – Restricted access to capital – Pressures to reduce costs 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 47
The Global Economy and Globalization • In past twenty-five years, globalization has become a leading focus of company strategies • Increasing number of companies have revenues coming from outside their country of origin • Global recession creates strategic challenges – Reduced consumer demand – Restricted access to capital – Pressures to reduce costs 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 47
 The Global Economy and Globalization – cont’d • Globalization has created a greater sense of openness • Benefits from global expansion are economic (profits, market opportunities) and social (political and cultural) – Open up trade – Break down geographic barriers – Creates economic interdependence 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 48
The Global Economy and Globalization – cont’d • Globalization has created a greater sense of openness • Benefits from global expansion are economic (profits, market opportunities) and social (political and cultural) – Open up trade – Break down geographic barriers – Creates economic interdependence 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 48
 The Global Economy and Globalization – cont’d • Problems with globalization – Economic interdependence means when one country’s economy falters, it can have a domino effect on others it does business with – Economic crises may result • Mechanisms to deal with economic crises – World Trade Organization – World Bank Group – International Monetary Fund 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 49
The Global Economy and Globalization – cont’d • Problems with globalization – Economic interdependence means when one country’s economy falters, it can have a domino effect on others it does business with – Economic crises may result • Mechanisms to deal with economic crises – World Trade Organization – World Bank Group – International Monetary Fund 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 49
 Global Economy: Key Mechanisms • World Trade Organization (WTO) – Helps 153 member countries conduct business • World Bank Group – Cooperative of 185 member countries that provides financial and technical assistance, to promote economic development and poverty reduction • International Monetary Fund (IMF) – Loans and assistance to establish financial stability 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 50
Global Economy: Key Mechanisms • World Trade Organization (WTO) – Helps 153 member countries conduct business • World Bank Group – Cooperative of 185 member countries that provides financial and technical assistance, to promote economic development and poverty reduction • International Monetary Fund (IMF) – Loans and assistance to establish financial stability 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 50
 Globalization: Challenges • Beyond openness and interdependence – Cultural differences – Degree of acceptance of capitalism varies among countries, as it is viewed as “Americanization” – Misunderstandings and disagreements between countries born of resentment, distrust – Need for greater understanding and awareness by strategic decision makers 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 51
Globalization: Challenges • Beyond openness and interdependence – Cultural differences – Degree of acceptance of capitalism varies among countries, as it is viewed as “Americanization” – Misunderstandings and disagreements between countries born of resentment, distrust – Need for greater understanding and awareness by strategic decision makers 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 51
 Corporate Governance • Greater awareness of the value of corporate governance driven by the financial scandals of the past decade – Destroyed billions of dollars in shareholder value – Directors of boards failed to find or address organizational problems 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 52
Corporate Governance • Greater awareness of the value of corporate governance driven by the financial scandals of the past decade – Destroyed billions of dollars in shareholder value – Directors of boards failed to find or address organizational problems 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 52
 Corporate Governance – cont’d • Scandals have led to legislative reform – Government views business as unwilling or unable to regulate itself to protect investors – Laws and regulations created to protect investors by improving accuracy and reliability of corporate disclosures 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 53
Corporate Governance – cont’d • Scandals have led to legislative reform – Government views business as unwilling or unable to regulate itself to protect investors – Laws and regulations created to protect investors by improving accuracy and reliability of corporate disclosures 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 53
 Corporate Governance – cont’d • What is corporate governance? – The way the a corporation is governed – The way the board uses organizational resources – The manner in which conflicts are resolved among multiple participants in the organization – The sum of how a corporation uses its resources to protect the interests of shareholders 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 54
Corporate Governance – cont’d • What is corporate governance? – The way the a corporation is governed – The way the board uses organizational resources – The manner in which conflicts are resolved among multiple participants in the organization – The sum of how a corporation uses its resources to protect the interests of shareholders 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 54
 Corporate Governance – cont’d • Sarbanes-Oxley, a US law, was designed to protect investors by improving accuracy and reliability of corporate disclosures • The law mandates two areas of corporate governance reform – The role of the board of directors – The type and scope of financial reporting 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 55
Corporate Governance – cont’d • Sarbanes-Oxley, a US law, was designed to protect investors by improving accuracy and reliability of corporate disclosures • The law mandates two areas of corporate governance reform – The role of the board of directors – The type and scope of financial reporting 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 55
 The Role of Boards of Directors • The original role of the board of directors was to ensure a group, independent from management, would look out for investors who were not involved in the daily operations of the corporation • In practice, the boards developed a “cozy” relationship with the CEO and management – It resulted in reciprocal “care taking” 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 56
The Role of Boards of Directors • The original role of the board of directors was to ensure a group, independent from management, would look out for investors who were not involved in the daily operations of the corporation • In practice, the boards developed a “cozy” relationship with the CEO and management – It resulted in reciprocal “care taking” 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 56
 The Role of Boards of Directors – cont’d • Sarbanes-Oxley changed the relationship – Demanding board members of publicly traded companies be responsible for strategic and financial decisions – The Business Roundtable, an association of CEOs of leading companies outlined a set of governance principles for boards and top managers that are critical to the effective functioning of corporations and the integrity of public markets 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 57
The Role of Boards of Directors – cont’d • Sarbanes-Oxley changed the relationship – Demanding board members of publicly traded companies be responsible for strategic and financial decisions – The Business Roundtable, an association of CEOs of leading companies outlined a set of governance principles for boards and top managers that are critical to the effective functioning of corporations and the integrity of public markets 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 57
 Corporate Governance: The Global Perspective • Corporate governance is a global issue • Governance Metrics International, a research and rating agency, using six broad categories of analysis to create their rating metric rates countries on their governance structures and procedures 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 58
Corporate Governance: The Global Perspective • Corporate governance is a global issue • Governance Metrics International, a research and rating agency, using six broad categories of analysis to create their rating metric rates countries on their governance structures and procedures 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 58
 Corporate Governance: The Global Perspective – cont’d • GMI Index for analysis – Board accountability – Financial disclosure and internal controls – Executive compensation – Shareholder rights – Ownership base – Takeover provisions 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 59
Corporate Governance: The Global Perspective – cont’d • GMI Index for analysis – Board accountability – Financial disclosure and internal controls – Executive compensation – Shareholder rights – Ownership base – Takeover provisions 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 59
 Corporate Governance: The Global Perspective – cont’d • GMI also looks at corporate behavior and social responsibility – Among the highest ratings went to Ireland, Canada, UK, Australia, USA – Among the lowest were Indonesia, Mexico, China, Japan 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 60
Corporate Governance: The Global Perspective – cont’d • GMI also looks at corporate behavior and social responsibility – Among the highest ratings went to Ireland, Canada, UK, Australia, USA – Among the lowest were Indonesia, Mexico, China, Japan 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 60
 Financial Reporting • Sarbanes-Oxley also called for more disclosure and transparency of financial information, creating specific requirements for businesses – Certification of the accuracy of financial statements by requiring senior managers to sign off on them – Mandated publicly traded firms establish an auditing of internal financial controls through independent auditors – These mandates have created compliance costs 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 61
Financial Reporting • Sarbanes-Oxley also called for more disclosure and transparency of financial information, creating specific requirements for businesses – Certification of the accuracy of financial statements by requiring senior managers to sign off on them – Mandated publicly traded firms establish an auditing of internal financial controls through independent auditors – These mandates have created compliance costs 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 61
 Guiding Principles of Corporate Governance 1. The primary duty of the board is to select a CEO and oversee the CEO and senior management in an effort to achieve a competent and ethical operation of the business 2. It is the responsibility of management to operate in an effective and ethical manner to produce shareholder value 3. It is the responsibility of management to produce in a timely manner financial statements that fairly represent the financial condition and results of corporate operations 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 62
Guiding Principles of Corporate Governance 1. The primary duty of the board is to select a CEO and oversee the CEO and senior management in an effort to achieve a competent and ethical operation of the business 2. It is the responsibility of management to operate in an effective and ethical manner to produce shareholder value 3. It is the responsibility of management to produce in a timely manner financial statements that fairly represent the financial condition and results of corporate operations 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 62
 Guiding Principles of Corporate Governance – cont’d 4. It is the responsibility of the board to engage an independent accounting firm to audit the financial statements, issue an opinion that those statements are in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, and oversee the corporation’s relationship with the outside auditor 5. It is the responsibility of the board to play a leadership role in shaping corporate governance 6. It is the responsibility of the board to adopt and oversee implementation of compensation policies for management and CEO performance 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 63
Guiding Principles of Corporate Governance – cont’d 4. It is the responsibility of the board to engage an independent accounting firm to audit the financial statements, issue an opinion that those statements are in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, and oversee the corporation’s relationship with the outside auditor 5. It is the responsibility of the board to play a leadership role in shaping corporate governance 6. It is the responsibility of the board to adopt and oversee implementation of compensation policies for management and CEO performance 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 63
 Guiding Principles of Corporate Governance – cont’d 7. It is the responsibility of the board to respond appropriately to shareholder concerns 8. It is the responsibility of the corporation to deal with its employees, customers, suppliers, and other constituencies in a fair and equitable manner 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 64
Guiding Principles of Corporate Governance – cont’d 7. It is the responsibility of the board to respond appropriately to shareholder concerns 8. It is the responsibility of the corporation to deal with its employees, customers, suppliers, and other constituencies in a fair and equitable manner 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 64
 Strategic Management in an EBusiness World • E-business is using information and communication technologies to support all the activities of a business – It includes e-commerce, which is the retailing side of e-business – An increasing number of businesses conduct ecommerce, some sell exclusively over the Internet 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 65
Strategic Management in an EBusiness World • E-business is using information and communication technologies to support all the activities of a business – It includes e-commerce, which is the retailing side of e-business – An increasing number of businesses conduct ecommerce, some sell exclusively over the Internet 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 65
 E-Business Strategic Approaches • Strategic decision makers often choose from among three different strategic approaches to e-business • An e-business enhanced organization that maintains its traditional structure, while setting up e-commerce – Many large firms have evolved using this approach – These companies use information and communication technology to enhance business 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 66
E-Business Strategic Approaches • Strategic decision makers often choose from among three different strategic approaches to e-business • An e-business enhanced organization that maintains its traditional structure, while setting up e-commerce – Many large firms have evolved using this approach – These companies use information and communication technology to enhance business 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 66
 E-Business Strategic Approaches – cont’d • Another approach is an e-business enabled organization that uses information and communication technology to perform its traditional business functions better; but not sell through the internet – This technology enables the organization to do their work more efficiently and effectively – The effort often employs the means to more effectively interact with employees and customers 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 67
E-Business Strategic Approaches – cont’d • Another approach is an e-business enabled organization that uses information and communication technology to perform its traditional business functions better; but not sell through the internet – This technology enables the organization to do their work more efficiently and effectively – The effort often employs the means to more effectively interact with employees and customers 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 67
 E-Business Strategic Approaches – cont’d • The final strategic approach is when an organization is a total e-business – The focus is on completely transforming the way it does its work and sells its products – It is based entirely on the Internet – Examples of such companies include: Amazon, Google, Yahoo, and EBay 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 68
E-Business Strategic Approaches – cont’d • The final strategic approach is when an organization is a total e-business – The focus is on completely transforming the way it does its work and sells its products – It is based entirely on the Internet – Examples of such companies include: Amazon, Google, Yahoo, and EBay 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 68
 Concluding Thought • Strategic management is a business reality – No matter where in an organization a person works or what their particular job may be, they will be involved with and affected in some way by strategic management 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 69
Concluding Thought • Strategic management is a business reality – No matter where in an organization a person works or what their particular job may be, they will be involved with and affected in some way by strategic management 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 69
 Learning Review: Learning Outcome 1. 4 • Discuss how the global economy and globalization affect strategic management • Explain the concept of corporate governance and how it impacts strategic management • Describe three approaches to e-business 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 70
Learning Review: Learning Outcome 1. 4 • Discuss how the global economy and globalization affect strategic management • Explain the concept of corporate governance and how it impacts strategic management • Describe three approaches to e-business 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 70
 Review of Learning Outcomes • Outcome 1. 1: Explain why strategic management is important – Individually: you will be evaluated on and rewarded for doing your job well, which means understanding how and why strategic decisions are made – Organizationally: it can make a difference in how well an organization performs; it also helps with adapting to changing situations and coordination of various divisions, functions, and work activities 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 71
Review of Learning Outcomes • Outcome 1. 1: Explain why strategic management is important – Individually: you will be evaluated on and rewarded for doing your job well, which means understanding how and why strategic decisions are made – Organizationally: it can make a difference in how well an organization performs; it also helps with adapting to changing situations and coordination of various divisions, functions, and work activities 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 71
 Review of Learning Outcomes – cont’d • Outcome 1. 2: Explain what strategic management is – Strategies: are an organization’s goal directed plans and actions that align its capabilities and resources with the opportunities and threats in its environment – Strategic management: is a process of analyzing the current situation; developing appropriate strategies; putting strategies into action; and evaluating , modifying, or changing strategies 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 72
Review of Learning Outcomes – cont’d • Outcome 1. 2: Explain what strategic management is – Strategies: are an organization’s goal directed plans and actions that align its capabilities and resources with the opportunities and threats in its environment – Strategic management: is a process of analyzing the current situation; developing appropriate strategies; putting strategies into action; and evaluating , modifying, or changing strategies 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 72
 Review of Learning Outcomes – cont’d • Outcome 1. 2: Explain what strategic management is – cont’d – Four characteristics: include interdisciplinary, external focus, internal focus, and future-oriented – Strategic management process: situation analysis, strategy formulation, strategy implementation, and strategy evaluation – Types of organizational strategies: function or operational, competitive or business, corporate or what to do with those businesses 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 73
Review of Learning Outcomes – cont’d • Outcome 1. 2: Explain what strategic management is – cont’d – Four characteristics: include interdisciplinary, external focus, internal focus, and future-oriented – Strategic management process: situation analysis, strategy formulation, strategy implementation, and strategy evaluation – Types of organizational strategies: function or operational, competitive or business, corporate or what to do with those businesses 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 73
 Review of Learning Outcomes – cont’d • Outcome 1. 2: Explain what strategic management is – cont’d – Reality: process may not always follow the sequence, but activities are still completed – Background: military strategies and academic origins (economics and organizational theory) – Emergence of strategic planning and strategic management: 1960 s, attempt to explain variances in performance; 1970 s-1980 s, focus on process and content 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 74
Review of Learning Outcomes – cont’d • Outcome 1. 2: Explain what strategic management is – cont’d – Reality: process may not always follow the sequence, but activities are still completed – Background: military strategies and academic origins (economics and organizational theory) – Emergence of strategic planning and strategic management: 1960 s, attempt to explain variances in performance; 1970 s-1980 s, focus on process and content 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 74
 Review of Learning Outcomes – cont’d • Outcome 1. 3: Explain who is involved with strategic management – Assumption: all employees have a role – Three main groups: boards of directors (representing shareholders), strategic leadership (senior management work to create viable future), other managers and employees (responsible for strategy implementation and evaluation) – Six key dimensions of strategic leadership (exploit resources, create culture, and make decisions) 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 75
Review of Learning Outcomes – cont’d • Outcome 1. 3: Explain who is involved with strategic management – Assumption: all employees have a role – Three main groups: boards of directors (representing shareholders), strategic leadership (senior management work to create viable future), other managers and employees (responsible for strategy implementation and evaluation) – Six key dimensions of strategic leadership (exploit resources, create culture, and make decisions) 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 75
 Review of Learning Outcomes – cont’d • Outcome 1. 4: Discuss the important factors impacting strategic management today – Global economy and globalization: provides economic and social benefits; challenges come from openness which makes countries vulnerable to political and cultural differences; as well as economic interdependence of trading nations – Challenges facing nations have been countered by the World Trade Organization, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 76
Review of Learning Outcomes – cont’d • Outcome 1. 4: Discuss the important factors impacting strategic management today – Global economy and globalization: provides economic and social benefits; challenges come from openness which makes countries vulnerable to political and cultural differences; as well as economic interdependence of trading nations – Challenges facing nations have been countered by the World Trade Organization, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 76
 Review of Learning Outcomes – cont’d • Outcome 1. 4: Discuss the important factors impacting strategic management todaycont’d – Challenges of cultural and political differences requires sensitivity to differences – Corporate governance: reform brought about by legislative action designed to protect investors and reform the role of boards and financial reporting – E-business (including e-commerce): these are businesses that are enhanced, enabled, or made 3/19/2018 totally e-business through the Internet SWH 1 - 77
Review of Learning Outcomes – cont’d • Outcome 1. 4: Discuss the important factors impacting strategic management todaycont’d – Challenges of cultural and political differences requires sensitivity to differences – Corporate governance: reform brought about by legislative action designed to protect investors and reform the role of boards and financial reporting – E-business (including e-commerce): these are businesses that are enhanced, enabled, or made 3/19/2018 totally e-business through the Internet SWH 1 - 77
 Case Questions: Case 1 Making Magic Happen 1. What is the Disney Difference and how will it affect the company’s corporate, competitive, and functional strategies? 2. What challenges do you think Disney might face in doing business in Russia? How could Iger and his top management team best prepare for those challenges? 3. “The steward of the entire Disney brand. ” What do you think it means that Iger views himself as this? Is this a part of being a leader? How might it affect the company’s strategy formulation/implementation? 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 78
Case Questions: Case 1 Making Magic Happen 1. What is the Disney Difference and how will it affect the company’s corporate, competitive, and functional strategies? 2. What challenges do you think Disney might face in doing business in Russia? How could Iger and his top management team best prepare for those challenges? 3. “The steward of the entire Disney brand. ” What do you think it means that Iger views himself as this? Is this a part of being a leader? How might it affect the company’s strategy formulation/implementation? 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 78
 Case Questions: Case 1 Making Magic Happen – cont’d 4. How might Iger and his top management team use the strategic management process to “keep the magic coming” in the current economic climate? 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 79
Case Questions: Case 1 Making Magic Happen – cont’d 4. How might Iger and his top management team use the strategic management process to “keep the magic coming” in the current economic climate? 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 79
 Case Questions: Case 2: MTV’s New Reality 1. Explain how strategic management and its process are illustrated in the case. 2. What are some performance measures that MTV’s strategic decision makers might use as they evaluate the results of their digital and global strategies? 3. Look for information on MTV’s website that helps describe its strategic approach and that of its various entertainment brands. 4. Evaluate Judy Mc. Grath’s strategic leadership. 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 80
Case Questions: Case 2: MTV’s New Reality 1. Explain how strategic management and its process are illustrated in the case. 2. What are some performance measures that MTV’s strategic decision makers might use as they evaluate the results of their digital and global strategies? 3. Look for information on MTV’s website that helps describe its strategic approach and that of its various entertainment brands. 4. Evaluate Judy Mc. Grath’s strategic leadership. 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 80
 Case Questions: Case 3 Making Over Avon 1. Explain how strategic management and its process are illustrated in this case. 2. What are some performance measures that Avon’s strategic decision makers might use to evaluate the results of the restructuring initiatives? 3. Andrea Jung is Avon’s first female CEO, which might be surprising considering its target customer is female. Do some research on the number of female CEOs and board members there are in US companies. Have these numbers changed over time? What conclusions might be drawn? 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 81
Case Questions: Case 3 Making Over Avon 1. Explain how strategic management and its process are illustrated in this case. 2. What are some performance measures that Avon’s strategic decision makers might use to evaluate the results of the restructuring initiatives? 3. Andrea Jung is Avon’s first female CEO, which might be surprising considering its target customer is female. Do some research on the number of female CEOs and board members there are in US companies. Have these numbers changed over time? What conclusions might be drawn? 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 81
 Case Questions: Making Over Avon – cont’d 4. Go to Avon’s website and identify its vision and mission. How might these affect strategic decisions and actions? Check the companies senior management and select one manager other than Jung. Describe that person’s job responsibilities. Finally, select one of the firm’s brands and describe what strategies are being used for that brand. 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 82
Case Questions: Making Over Avon – cont’d 4. Go to Avon’s website and identify its vision and mission. How might these affect strategic decisions and actions? Check the companies senior management and select one manager other than Jung. Describe that person’s job responsibilities. Finally, select one of the firm’s brands and describe what strategies are being used for that brand. 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 82
 Case Questions: Case 4 Fighting Grime 1. Do you think strategic management has contributed to the Clorox company’s success? Why or why not? 2. Given the information included in the case, what step in the strategic management process do you think it excels? Explain your choice. 3. How might the CEO use strategic management to manage the company’s challenges? 4. Check the website and determine Clorox sales volume, number of employees, and current strategies. 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 83
Case Questions: Case 4 Fighting Grime 1. Do you think strategic management has contributed to the Clorox company’s success? Why or why not? 2. Given the information included in the case, what step in the strategic management process do you think it excels? Explain your choice. 3. How might the CEO use strategic management to manage the company’s challenges? 4. Check the website and determine Clorox sales volume, number of employees, and current strategies. 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 83
 Case Questions: Case 5 In the Zone 1. In the brief description of Auto. Zone, how is strategic management illustrated? 2. What examples of functional strategy do you see? What factor/s do you think it might use in its competitive strategy? 3. Auto. Zone is committed to ethical business. Check their website for corporate governance and describe and evaluate what the company has done to promote the concept. 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 84
Case Questions: Case 5 In the Zone 1. In the brief description of Auto. Zone, how is strategic management illustrated? 2. What examples of functional strategy do you see? What factor/s do you think it might use in its competitive strategy? 3. Auto. Zone is committed to ethical business. Check their website for corporate governance and describe and evaluate what the company has done to promote the concept. 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 84
 Case Questions: Case 5 In the Zone – cont’d 4. What types of strategic challenges might the CEO and the company face as it pursues its strategic initiatives? How might strategic management help them deal with these challenges? 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 85
Case Questions: Case 5 In the Zone – cont’d 4. What types of strategic challenges might the CEO and the company face as it pursues its strategic initiatives? How might strategic management help them deal with these challenges? 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 85
 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher. Printed in the United States of America. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 86
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher. Printed in the United States of America. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3/19/2018 SWH 1 - 86


