fd3875ca96d59dab9578cd353bbb1aa6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

Storage Resource Broker Data Grids and Data Management Reagan W. Moore moore@sdsc. edu http: //www. sdsc. edu/srb

Topics • Data management evolution • Shared collections • Digital Libraries • Persistent Archives • Building shared collections • Project level / National level / International • Demonstration of shared collections • Access to collections at SDSC

Shared Collections • Data grids support the creation of shared collections that may be distributed across multiple institutions, sites, and storage systems. • Digital libraries publish data, and provide services for discovery and display • Persistent archives preserve data, managing the migration to new technology


Generic Infrastructure • Can a single system provide all of the features needed to implement each type of data management system, while supporting access across administrative domains and managing data stored in multiple types of storage systems? • Answer is data grid technology

Shared Collections • Purpose of SRB data grid is to enable the creation of a collection that is shared between academic institutions • • Register digital entity into the shared collection Assign owner, access controls Assign descriptive, provenance metadata Manage state information • Audit trails, versions, replicas, backups, locks • Size, checksum, validation date, synchronization date, … • Manage interactions with storage systems • Unix file systems, Windows file systems, tape archives, … • Manage interactions with preferred access mechanisms • Web browser, Java, WSDL, C library, …
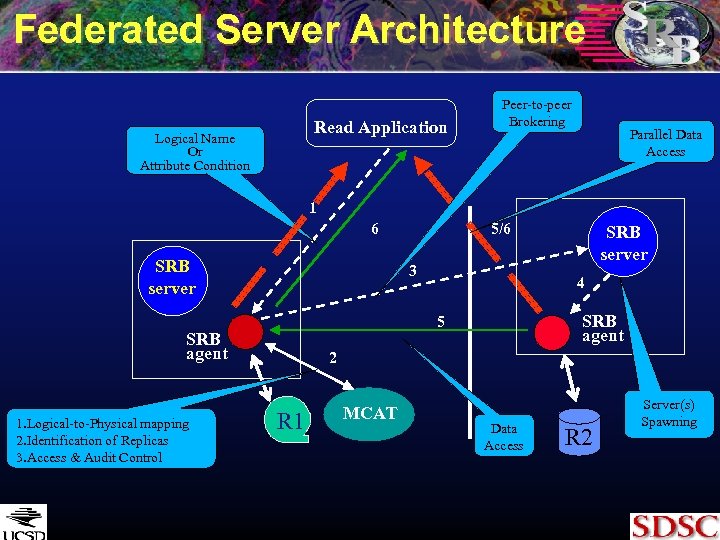
Federated Server Architecture Read Application Logical Name Or Attribute Condition Peer-to-peer Brokering Parallel Data Access 1 6 SRB server 3 SRB server 4 SRB agent 5 SRB agent 1. Logical-to-Physical mapping 2. Identification of Replicas 3. Access & Audit Control 5/6 2 R 1 MCAT Data Access R 2 Server(s) Spawning

Generic Infrastructure • Digital libraries now build upon data grids to manage distributed collections • DSpace digital library - MIT and Hewlitt Packard • Fedora digitial library - Cornell University and University of Virginia • Persistent archives build upon data grids to manage technology evolution • NARA research prototype persistent archive • California Digital Library - Digital Preservation Repository • NSF National Science Digital Library persistent archive

National Science Digital Library • URLs for educational material for all grade levels registered into repository at Cornell • SDSC crawls the URLs, registers the web pages into a SRB data grid, builds a persistent archive • 750, 000 URLs • 13 million web pages • About 3 TBs of data
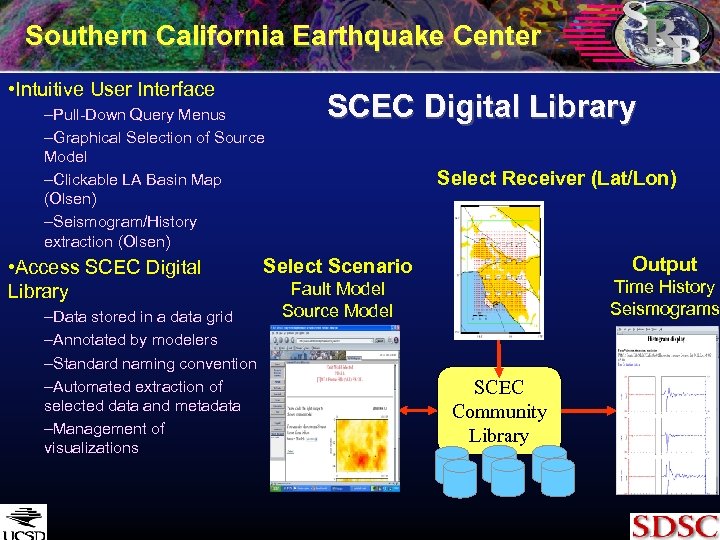
Southern California Earthquake Center • Intuitive User Interface –Pull-Down Query Menus –Graphical Selection of Source Model –Clickable LA Basin Map (Olsen) –Seismogram/History extraction (Olsen) • Access SCEC Digital Library –Data stored in a data grid –Annotated by modelers –Standard naming convention –Automated extraction of selected data and metadata –Management of visualizations SCEC Digital Library Select Receiver (Lat/Lon) Output Select Scenario Time History Seismograms Fault Model Source Model SCEC Community Library
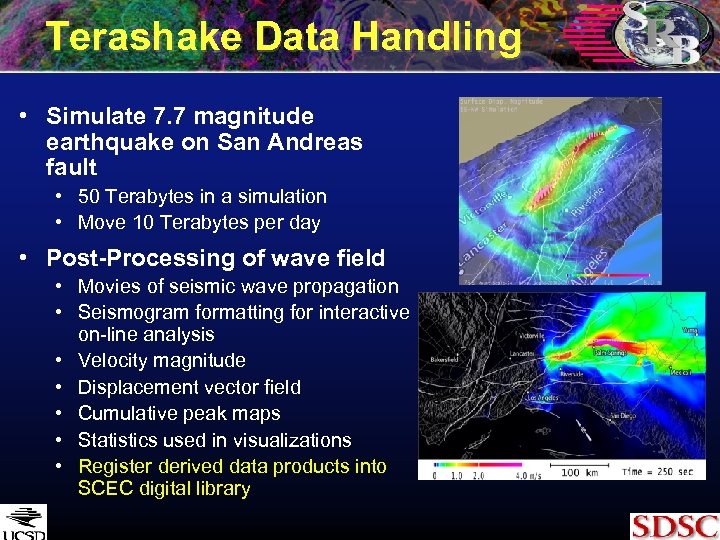
Terashake Data Handling • Simulate 7. 7 magnitude earthquake on San Andreas fault • 50 Terabytes in a simulation • Move 10 Terabytes per day • Post-Processing of wave field • Movies of seismic wave propagation • Seismogram formatting for interactive on-line analysis • Velocity magnitude • Displacement vector field • Cumulative peak maps • Statistics used in visualizations • Register derived data products into SCEC digital library
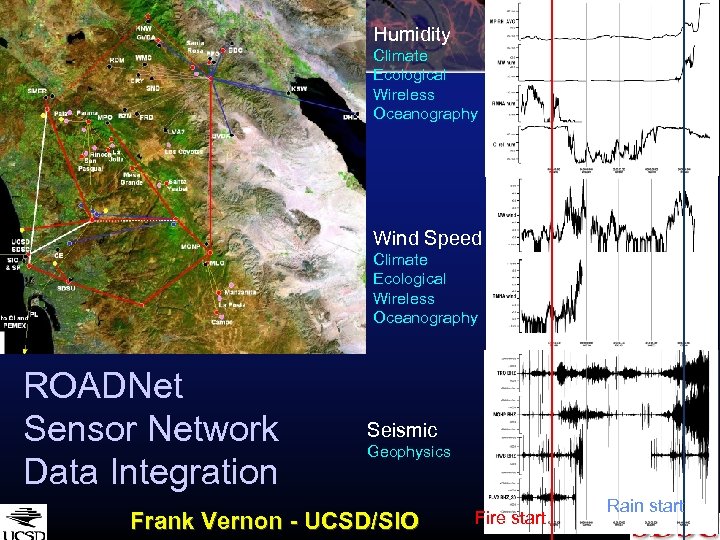
Humidity Climate Ecological Wireless Oceanography Wind Speed Climate Ecological Wireless Oceanography ROADNet Sensor Network Data Integration Seismic Geophysics Frank Vernon - UCSD/SIO Fire start Rain start
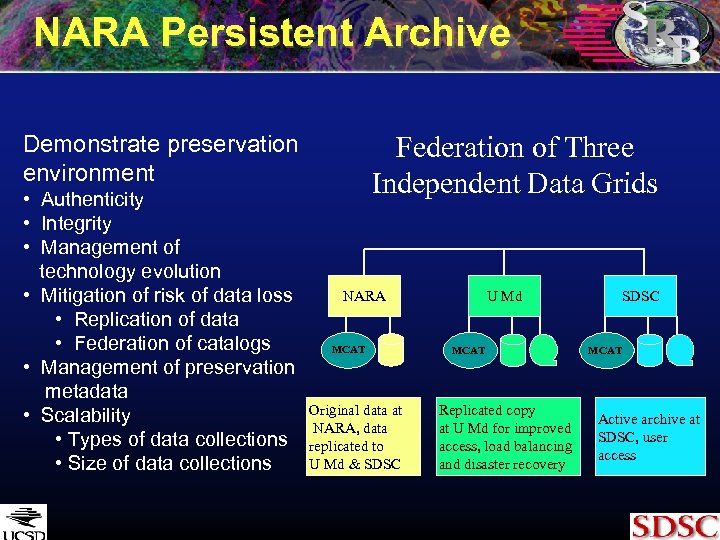
NARA Persistent Archive Demonstrate preservation environment • Authenticity • Integrity • Management of technology evolution • Mitigation of risk of data loss • Replication of data • Federation of catalogs • Management of preservation metadata • Scalability • Types of data collections • Size of data collections Federation of Three Independent Data Grids NARA MCAT Original data at NARA, data replicated to U Md & SDSC U Md MCAT Replicated copy at U Md for improved access, load balancing and disaster recovery SDSC MCAT Active archive at SDSC, user access
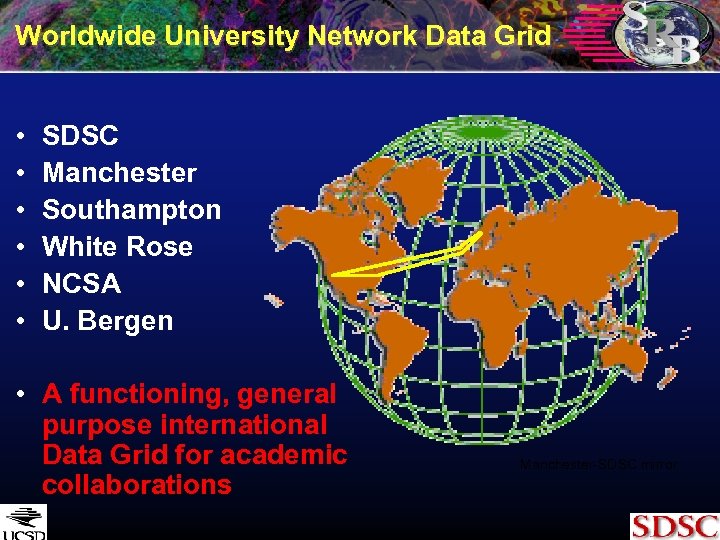
Worldwide University Network Data Grid • • • SDSC Manchester Southampton White Rose NCSA U. Bergen • A functioning, general purpose international Data Grid for academic collaborations Manchester-SDSC mirror

WUNGrid Collections • Bio. Sim. Grid • Molecular structure collaborations • White Rose Grid • Distributed Aircraft Maintenance Environment • Medieval Studies • Music Grid • e-Print collections • DSpace • Astronomy

Bio. Sim. Grid • Kaihsu Tai, Stuart Murdock, Bing Wu, Muan Hong Ng, Steven Johnston, Hans Fangohr, Simon J. Cox, Paul Jeffreys, Jonathan W. Essex, Mark S. P. Sansom (2004) Bio. Sim. Grid: towards a worldwide repository for biomolecular simulations. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2: 3219– 3221 DOI: 10. 1039/b 411352 g • University of Oxford • • • Mark Sansom, Biochemistry Paul Jeffreys, e-Science Kaihsu Tai, Biochemistry Bing Wu, Biochemistry / e-Science University of Southampton • • • Jonathan Essex, Chemistry Simon Cox, e-Science Stuart Murdock, Chemistry / e-Science Muan Hong Ng, e-Science Hans Fangohr, e-Science Steven Johnston, e-Science • Elsewhere • David Moss, Birkbeck, London • Adrian Mulholland, Bristol • Charles Laughton, Nottingham • Leo Caves, York

KEK Data Grid • • • Japan Taiwan South Korea Australia Poland US • A functioning, general purpose international Data Grid for highenergy physics Manchester-SDSC mirror
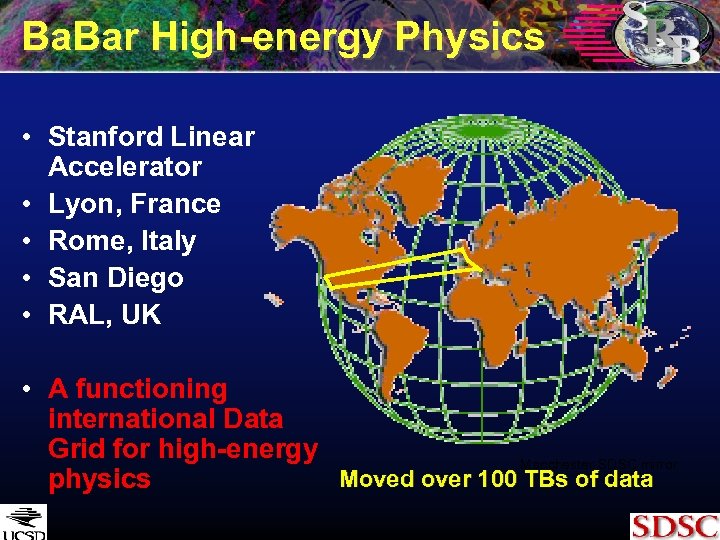
Ba. Bar High-energy Physics • Stanford Linear Accelerator • Lyon, France • Rome, Italy • San Diego • RAL, UK • A functioning international Data Grid for high-energy Manchester-SDSC mirror Moved over 100 TBs of data physics
Astronomy Data Grid • Chile • Tucson, Arizona • NCSA, Illinois • A functioning international Data Grid for Astronomy Manchester-SDSC mirror Moved over 400, 000 images

International Institutions (2005)
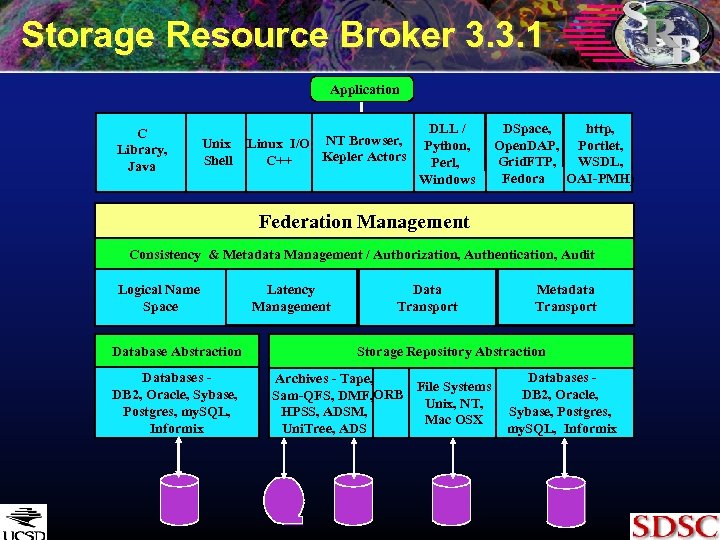
Storage Resource Broker 3. 3. 1 Application C Library, Java Unix Shell Linux I/O NT Browser, Kepler Actors C++ DLL / Python, Perl, Windows DSpace, http, Open. DAP, Portlet, Grid. FTP, WSDL, Fedora OAI-PMH) Federation Management Consistency & Metadata Management / Authorization, Authentication, Audit Logical Name Space Database Abstraction Databases DB 2, Oracle, Sybase, Postgres, my. SQL, Informix Latency Management Data Transport Metadata Transport Storage Repository Abstraction Archives - Tape, File Systems Sam-QFS, DMF, ORB Unix, NT, HPSS, ADSM, Mac OSX Uni. Tree, ADS Databases DB 2, Oracle, Sybase, Postgres, my. SQL, Informix

SRB Objectives • Automate all aspects of data discovery, access, management, analysis, preservation • Security paramount • Distributed data • Provide distributed data support for • • Data sharing - data grids Data publication - digital libraries Data preservation - persistent archives Data collections - Real time sensor data

SRB Developers Reagan Moore Michael Wan Arcot Rajasekar Wayne Schroeder Charlie Cowart Lucas Gilbert Bing Zhu Antoine de Torcy Sheau-Yen Chen George Kremenek Arun Jagatheesan Marcio Faerman Sifang Lu Richard Marciano - PI - SRB Architect - SRB Manager - SRB Productization - in. Q - Jargon - Perl, Python, Windows - my. SRB web browser - SRB Administration - SRB Collections - Matrix workflow - SCEC Application - ROADnet Application - SALT persistent archives Contributors from UK e-Science, Academia Sinica, Ohio State University, Aerospace Corporation, … 75 FTE-years of support About 300, 000 lines of C

History • 1995 - DARPA Massive Data Analysis Systems • 1997 - DARPA/USPTO Distributed Object Computation Testbed • 1998 - NSF National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure • 1998 - DOE Accelerated Strategic Computing Initiative data grid • 1999 - NARA persistent archive • 2000 - NASA Information Power Grid • 2001 - NLM Digital Embryo digital library • 2001 - DOE Particle Physics data grid • 2001 - NSF Grid Physics Network data grid • 2001 - NSF National Virtual Observatory data grid • 2002 - NSF National Science Digital Library persistent archive • 2003 - NSF Southern California Earthquake Center digital library • 2003 - NIH Biomedical Informatics Research Network data grid • 2003 - NSF Real-time Observatories, Applications, and Data management Network • 2004 - NSF ITR, Constraint based data systems • 2005 - LC Digital Preservation Lifecycle Management • 2005 - LC National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation program

Development • SRB 1. 1. 8 - December 15, 2000 • Basic distributed data management system • Metadata Catalog • SRB 2. 0 - February 18, 2003 • Parallel I/O support • Bulk operations • SRB 3. 0 - August 30, 2003 • Federation of data grids • SRB 3. 4 - October 31, 2005 • Feature requests (extensible schema)
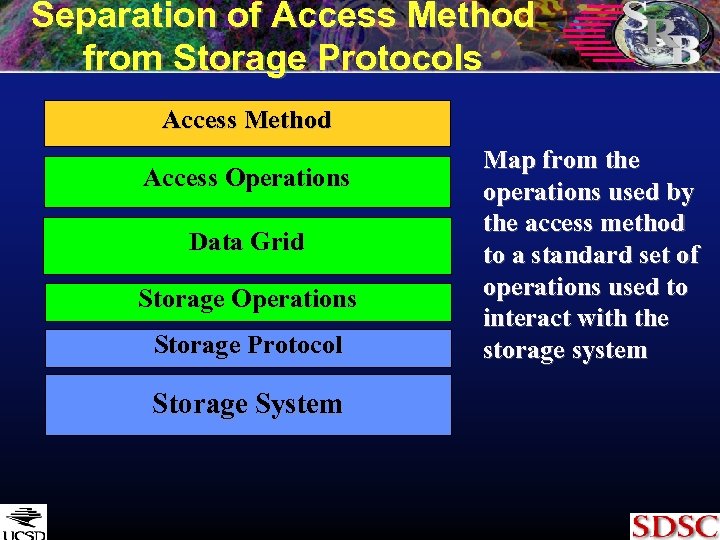
Separation of Access Method from Storage Protocols Access Method Access Operations Data Grid Storage Operations Storage Protocol Storage System Map from the operations used by the access method to a standard set of operations used to interact with the storage system
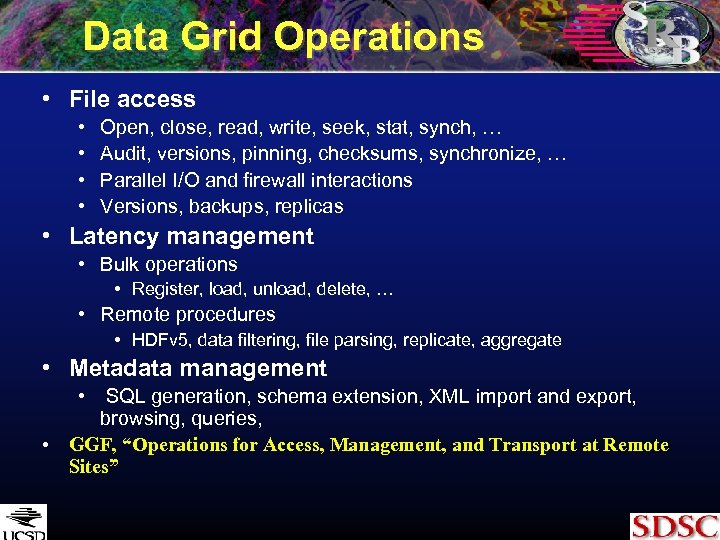
Data Grid Operations • File access • • Open, close, read, write, seek, stat, synch, … Audit, versions, pinning, checksums, synchronize, … Parallel I/O and firewall interactions Versions, backups, replicas • Latency management • Bulk operations • Register, load, unload, delete, … • Remote procedures • HDFv 5, data filtering, file parsing, replicate, aggregate • Metadata management • SQL generation, schema extension, XML import and export, browsing, queries, • GGF, “Operations for Access, Management, and Transport at Remote Sites”
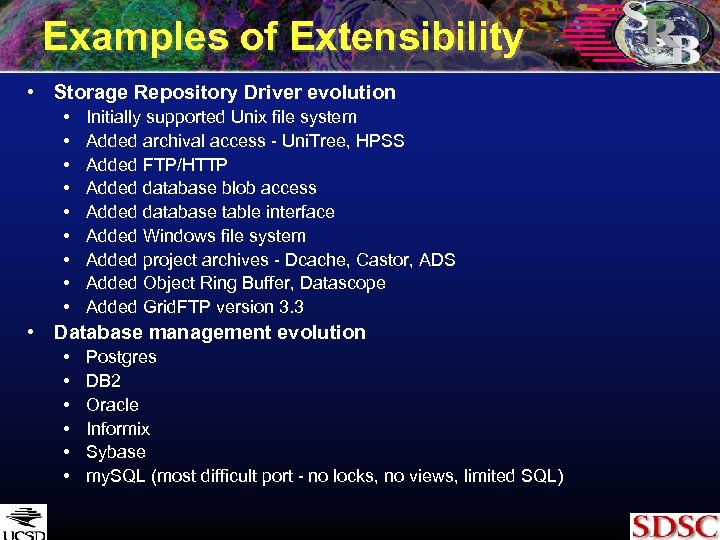
Examples of Extensibility • Storage Repository Driver evolution • • • Initially supported Unix file system Added archival access - Uni. Tree, HPSS Added FTP/HTTP Added database blob access Added database table interface Added Windows file system Added project archives - Dcache, Castor, ADS Added Object Ring Buffer, Datascope Added Grid. FTP version 3. 3 • Database management evolution • • • Postgres DB 2 Oracle Informix Sybase my. SQL (most difficult port - no locks, no views, limited SQL)

Examples of Extensibility • The 3 fundamental APIs are C library, shell commands, Java • Other access mechanisms are ported on top of these interfaces • API evolution • • • Initial access through C library, Unix shell command Added i. NQ Windows browser (C++ library) Added my. SRB Web browser (C library and shell commands) Added Java (Jargon) Added Perl/Python load libraries (shell command) Added WSDL (Java) Added OAI-PMH, Open. DAP, DSpace digital library (Java) Added Kepler actors for dataflow access (Java) Added Grid. FTP version 3. 3 (C library) Added Fedora
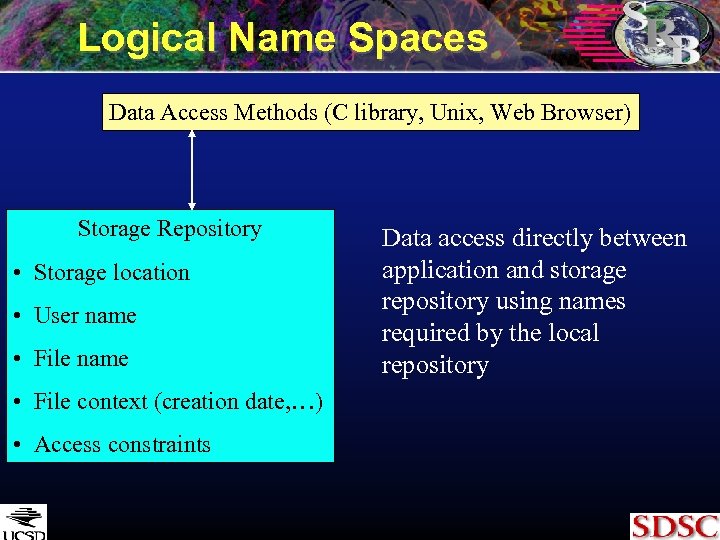
Logical Name Spaces Data Access Methods (C library, Unix, Web Browser) Storage Repository • Storage location • User name • File context (creation date, …) • Access constraints Data access directly between application and storage repository using names required by the local repository
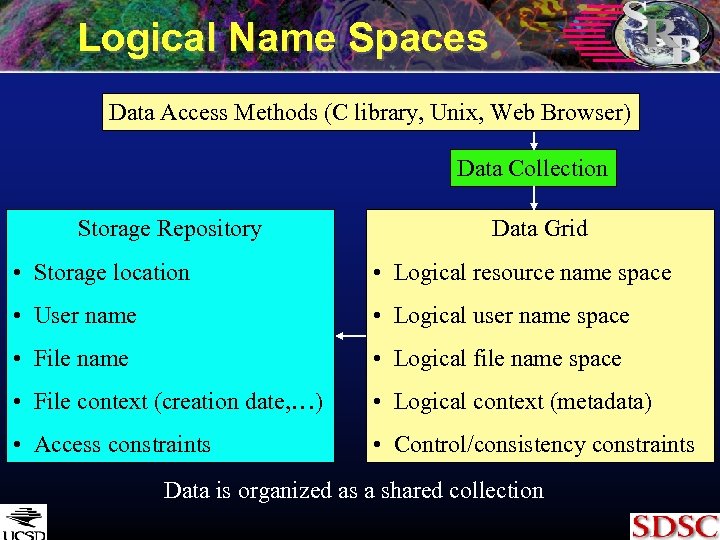
Logical Name Spaces Data Access Methods (C library, Unix, Web Browser) Data Collection Storage Repository Data Grid • Storage location • Logical resource name space • User name • Logical user name space • File name • Logical file name space • File context (creation date, …) • Logical context (metadata) • Access constraints • Control/consistency constraints Data is organized as a shared collection
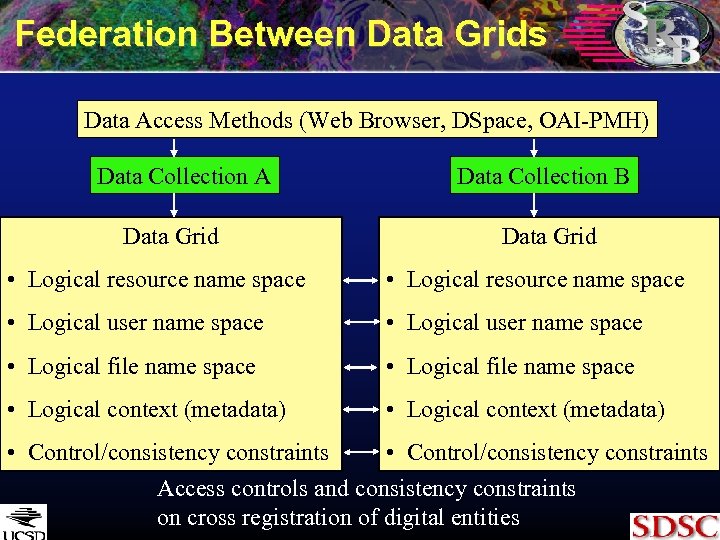
Federation Between Data Grids Data Access Methods (Web Browser, DSpace, OAI-PMH) Data Collection A Data Grid Data Collection B Data Grid • Logical resource name space • Logical user name space • Logical file name space • Logical context (metadata) • Control/consistency constraints Access controls and consistency constraints on cross registration of digital entities

Types of Risk • Media failure • Replicate data onto multiple media • Vendor specific systemic errors • Replicate data onto multiple vendor products • Operational error • Replicate data onto a second administrative domain • Natural disaster • Replicate data to a geographically remote site • Malicious user • Replicate data to a deep archive

How Many Replicas • Three sites minimize risk • Primary site • Supports interactive user access to data • Secondary site • Supports interactive user access when first site is down • Provides 2 nd media copy, located at a remote site, uses different vendor product, independent administrative procedures • Deep archive • Provides 3 rd media copy, staging environment for data ingestion, no user access
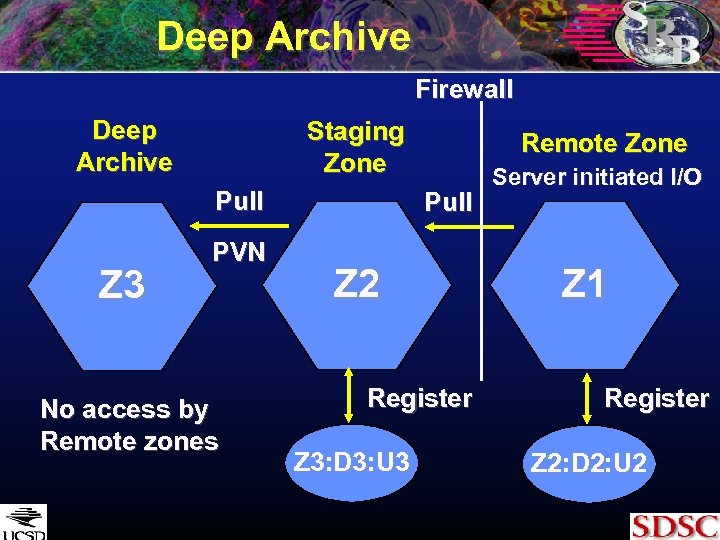
Deep Archive Firewall Deep Archive Staging Zone Pull Z 3 PVN No access by Remote zones Remote Zone Pull Z 2 Register Z 3: D 3: U 3 Server initiated I/O Z 1 Register Z 2: D 2: U 2

For More Information Reagan W. Moore San Diego Supercomputer Center moore@sdsc. edu http: //www. sdsc. edu/srb/
fd3875ca96d59dab9578cd353bbb1aa6.ppt