ffd9593758448e8ffdc83222096a6911.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10

Stonehenge is a symbol of ancient knowledge
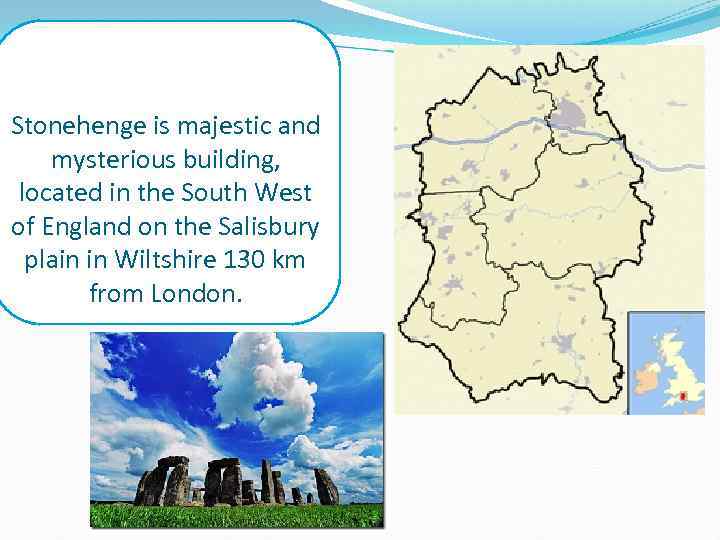
Stonehenge is majestic and mysterious building, located in the South West of England on the Salisbury plain in Wiltshire 130 km from London.

Stonehenge is a bit younger than the famous Egyptian pyramids. Stonehenge from the ancient British word "Stan Henguas" – "Hanging Stones". These stones were erected more for the 8000 years before Christ .

The Dating Of Stonehenge. The first researchers linked the construction of Stonehenge with the druids. Excavations, however, have pushed back the time of creation of Stonehenge to the bronze age.

According to the legends of the ancient Celts, Stonehenge made himself Merlin. According to another legend, its construction was attributed lived before the Flood, giants. However, besides these very vague myths, no other evidence about the builders of Stonehenge left.

It is well known that Stonehenge was a sacred place of the druids, representatives of the priestly caste of the ancient Celts. According to many scientists, they knew his secrets. But the druids their secrets are not divulged. They are very well versed in astronomy (in the structure and motion of stars, the size of the Earth and planets and various astronomical phenomena).

Some scientists believe that Stonehenge – the ancient Observatory of the stone age, which allows high accuracy to conduct astronomical observations. In Midsummer it attracts crowds of people to watch the sunrise.

Stonehenge is the burial place of the local elite. It is also often argued that Stonehenge was used for burials. After the excavations the scientists came to the conclusion that the only Stonehenge it was buried about 240 people, which before burial was cremated. Archaeologists believe that most likely there were buried the representatives of the local elite or the ruling dynasty.
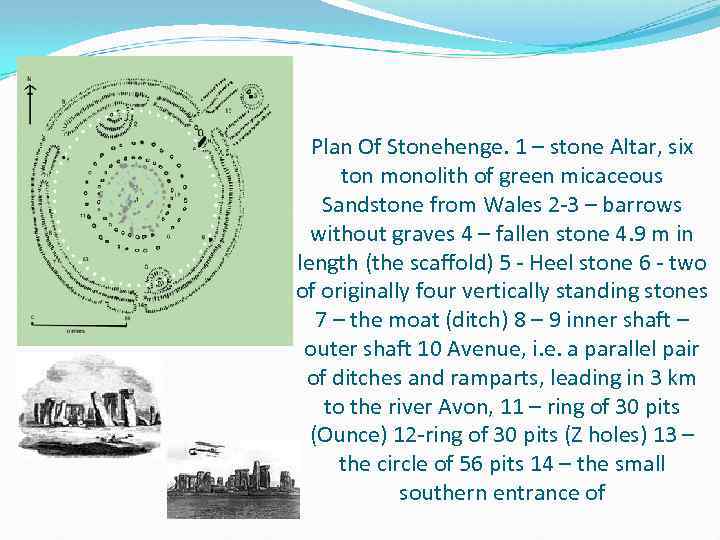
Plan Of Stonehenge. 1 – stone Altar, six ton monolith of green micaceous Sandstone from Wales 2 -3 – barrows without graves 4 – fallen stone 4. 9 m in length (the scaffold) 5 - Heel stone 6 - two of originally four vertically standing stones 7 – the moat (ditch) 8 – 9 inner shaft – outer shaft 10 Avenue, i. e. a parallel pair of ditches and ramparts, leading in 3 km to the river Avon, 11 – ring of 30 pits (Ounce) 12 -ring of 30 pits (Z holes) 13 – the circle of 56 pits 14 – the small southern entrance of

The location of the stones. 30 stones form a circle with a diameter of 33 m. These stones have a 4. 1 m height, 2. 1 m in width and weigh about 25 tons. On top of them put the stones – jumper length of about 3. 2 m and a width of 1 m and a thickness of 0. 8 m so that the tops of the lintels are 4. 9 m above ground level. The stones were fixed by means of a system of "groove and tongue". The arc of the outer ring of stones is preserved along with the ceilings.
ffd9593758448e8ffdc83222096a6911.ppt