L5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Stomach and Duodenum L 5 Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department: Surgery Rawand M. Haweizy Senior Lecturer M. B. Ch. B, MSc, MRCS e. mail: rawand_haweizy@yahoo. com
Stomach and Duodenum L 5 Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department: Surgery Rawand M. Haweizy Senior Lecturer M. B. Ch. B, MSc, MRCS e. mail: rawand_haweizy@yahoo. com
 Objectives l l To recognize and understand: Sequelae of peptic ulcer surgery and its management. Complications of peptic ulcer and how it manage. Causes of gastric outlet obstruction and its metabolic changes. Gastric polyps and its role in gastric cancer.
Objectives l l To recognize and understand: Sequelae of peptic ulcer surgery and its management. Complications of peptic ulcer and how it manage. Causes of gastric outlet obstruction and its metabolic changes. Gastric polyps and its role in gastric cancer.
 Contents • Sequelae of PU surgery. Complications of PU. Ø Perforations Ø Gastric outlet obstructions(GOO) • Gastric polyps •
Contents • Sequelae of PU surgery. Complications of PU. Ø Perforations Ø Gastric outlet obstructions(GOO) • Gastric polyps •
 Introduction l l Surgery for peptic ulcer nowadays rarely performed. Complications following surgery in PU frequent and challenging to treat. Complications still occur in PU despite wide use of PPI. Gastric polyp can be true or false polyp and may be precancerous.
Introduction l l Surgery for peptic ulcer nowadays rarely performed. Complications following surgery in PU frequent and challenging to treat. Complications still occur in PU despite wide use of PPI. Gastric polyp can be true or false polyp and may be precancerous.
 Sequelae of peptic ulcer surgery l l l l Recurrent ulceration Small stomach syndrome Bile vomiting Early and late dumping Post-vagotomy diarrhoea Malignant transformation Nutritional consequences Gallstones
Sequelae of peptic ulcer surgery l l l l Recurrent ulceration Small stomach syndrome Bile vomiting Early and late dumping Post-vagotomy diarrhoea Malignant transformation Nutritional consequences Gallstones
 The complications of peptic ulceration l Ø Ø Ø The common complications of peptic ulcer are: Perforation Bleeding Stenosis
The complications of peptic ulceration l Ø Ø Ø The common complications of peptic ulcer are: Perforation Bleeding Stenosis
 Perforated peptic ulcer Epidemiology l Despite widespread use of PPI and eradication therapy, l The incidence of perforated PU changed little. l Considerable change in epidemiology of perforated PU in WEST.
Perforated peptic ulcer Epidemiology l Despite widespread use of PPI and eradication therapy, l The incidence of perforated PU changed little. l Considerable change in epidemiology of perforated PU in WEST.
 Perforated peptic ulcer cont, d l l l Previously, most patients middle aged. Ratio of 2: 1 of men: women. Steady increase in age of patients suffering from this complication. Increase number of women affected. Perforations now occur commonly in elderly female. NSAIDs appear responsible for these perforations.
Perforated peptic ulcer cont, d l l l Previously, most patients middle aged. Ratio of 2: 1 of men: women. Steady increase in age of patients suffering from this complication. Increase number of women affected. Perforations now occur commonly in elderly female. NSAIDs appear responsible for these perforations.
 Perforated peptic ulcer cont, d Clinical features l l l History of peptic ulceration. Sudden-onset, severe, generalized abdominal pain. Bacterial peritonitis supervenes over few hours. Abdomen exhibits a board-like rigidity. Classic presentation of perforated PU observed less commonly than in past. Most common site of perforation , anterior aspect of duodenum.
Perforated peptic ulcer cont, d Clinical features l l l History of peptic ulceration. Sudden-onset, severe, generalized abdominal pain. Bacterial peritonitis supervenes over few hours. Abdomen exhibits a board-like rigidity. Classic presentation of perforated PU observed less commonly than in past. Most common site of perforation , anterior aspect of duodenum.
 Perforated peptic ulcer cont, d l Anterior or incisural GU may perforate. l Gastric ulcers may perforate into the lesser sac. l Can be particularly difficult to diagnose. l These patients not have obvious peritonitis.
Perforated peptic ulcer cont, d l Anterior or incisural GU may perforate. l Gastric ulcers may perforate into the lesser sac. l Can be particularly difficult to diagnose. l These patients not have obvious peritonitis.
 Perforated peptic ulcer cont, d Investigations l Ø l l Erect plain chest radiograph : Free gas under Right hemidiaphragm in> 50% of cases. CT imaging is more accurate. Serum amylase levels tested.
Perforated peptic ulcer cont, d Investigations l Ø l l Erect plain chest radiograph : Free gas under Right hemidiaphragm in> 50% of cases. CT imaging is more accurate. Serum amylase levels tested.
 Perforated peptic ulcer cont, d Treatment l l l Initial priorities: resuscitation and analgesia. Following resuscitation, treatment principally surgical. Laparotomy is performed. Laparoscopy may be used. Massive duodenal or gastric perforation ( simple closure impossible), Billroth II gastrectomy. Conservative management
Perforated peptic ulcer cont, d Treatment l l l Initial priorities: resuscitation and analgesia. Following resuscitation, treatment principally surgical. Laparotomy is performed. Laparoscopy may be used. Massive duodenal or gastric perforation ( simple closure impossible), Billroth II gastrectomy. Conservative management
 Perforated peptic ulcer cont, d Treatment cont, d l l l Patients with Helicobacter associated ulcers, eradication therapy appropriate. Lifelong treatment with proton pump inhibitors reasonable option, Especially those to continue with NSAID treatment.
Perforated peptic ulcer cont, d Treatment cont, d l l l Patients with Helicobacter associated ulcers, eradication therapy appropriate. Lifelong treatment with proton pump inhibitors reasonable option, Especially those to continue with NSAID treatment.
 Gastric Outlet Obstruction(GOO) • Ø Ø • • The two common causes are: Gastric cancer Pyloric stenosis due to PU. GOO regarded malignant until proved otherwise. In PU, the stenosis lies in first part of duodenum( duodenal cap).
Gastric Outlet Obstruction(GOO) • Ø Ø • • The two common causes are: Gastric cancer Pyloric stenosis due to PU. GOO regarded malignant until proved otherwise. In PU, the stenosis lies in first part of duodenum( duodenal cap).
 Gastric Outlet Obstruction (GOO) cont, d l The common causes: Ø Chronic duodenal ulceration/fibrosis Antral gastric carcinoma Carcinoma of the head of pancreas Ø Ø
Gastric Outlet Obstruction (GOO) cont, d l The common causes: Ø Chronic duodenal ulceration/fibrosis Antral gastric carcinoma Carcinoma of the head of pancreas Ø Ø
 Gastric Outlet Obstruction cont, d l Rare causes: Ø Variety of benign tumours Lymphoma Crohn, s disease Duodenal haematoma Adult pyloric hypertrophy Annular pancreas Mucosal diaphragm Willkie's disease(Arterio-Mesenteric compression) Ø Ø Ø Ø
Gastric Outlet Obstruction cont, d l Rare causes: Ø Variety of benign tumours Lymphoma Crohn, s disease Duodenal haematoma Adult pyloric hypertrophy Annular pancreas Mucosal diaphragm Willkie's disease(Arterio-Mesenteric compression) Ø Ø Ø Ø
 Gastric Outlet Obstruction cont, d Clinical Features: l l In benign obstruction history of PU. Non-bilious vomiting (contain food stuffs taken many days before). looks unwell, dehydrated and losing weight. On exam: stomach distended , succution splash audible (shaking abdomen of the patient)
Gastric Outlet Obstruction cont, d Clinical Features: l l In benign obstruction history of PU. Non-bilious vomiting (contain food stuffs taken many days before). looks unwell, dehydrated and losing weight. On exam: stomach distended , succution splash audible (shaking abdomen of the patient)
 Gastric Outlet Obstruction cont, d Metabolic Effects: l l l Initially hypochloremic alkalosis. Patient dehydrated and renal dysfunction follows. hyponatremia , renal sodium retention takes place. Potassium lost in kidneys causing hypokalemia. Alkalosis causes lowering of ionized Calcium causing tetany.
Gastric Outlet Obstruction cont, d Metabolic Effects: l l l Initially hypochloremic alkalosis. Patient dehydrated and renal dysfunction follows. hyponatremia , renal sodium retention takes place. Potassium lost in kidneys causing hypokalemia. Alkalosis causes lowering of ionized Calcium causing tetany.
 Gastric Outlet Obstruction cont, d Management: l l Correcting dehydration: giving normal saline with potassium inside. Stomach emptied using NG tube and lavage. Endoscopy done and biopsy taken to exclude malignancy. Contrast radiology also used to diagnose.
Gastric Outlet Obstruction cont, d Management: l l Correcting dehydration: giving normal saline with potassium inside. Stomach emptied using NG tube and lavage. Endoscopy done and biopsy taken to exclude malignancy. Contrast radiology also used to diagnose.
 Gastric Outlet Obstruction cont, d Management cont, d l l Antisecretory agent (iv H 2 -receptor blocker or PPI). Early cases resolve on conservative treatment (edema subside). If surgery required : Gastro -Enterostomy+ Vagotomy. Endoscopic treatment( balloon dilatation) in early cases?
Gastric Outlet Obstruction cont, d Management cont, d l l Antisecretory agent (iv H 2 -receptor blocker or PPI). Early cases resolve on conservative treatment (edema subside). If surgery required : Gastro -Enterostomy+ Vagotomy. Endoscopic treatment( balloon dilatation) in early cases?
 Gastric Outlet Obstruction cont, d Adult pyloric stenosis l l Rare condition. Relationship to childhood condition unclear. Some patients have long history( problems with gastric emptying). Commonly treated by pyloroplasty not pyloromyotomy
Gastric Outlet Obstruction cont, d Adult pyloric stenosis l l Rare condition. Relationship to childhood condition unclear. Some patients have long history( problems with gastric emptying). Commonly treated by pyloroplasty not pyloromyotomy
 Gastric Outlet Obstruction cont, d Pyloric mucosal diaphragm l l l Origin of this rare condition unknown. Usually not become apparent until middle life. When found: simple excision of mucosal diaphragm.
Gastric Outlet Obstruction cont, d Pyloric mucosal diaphragm l l l Origin of this rare condition unknown. Usually not become apparent until middle life. When found: simple excision of mucosal diaphragm.
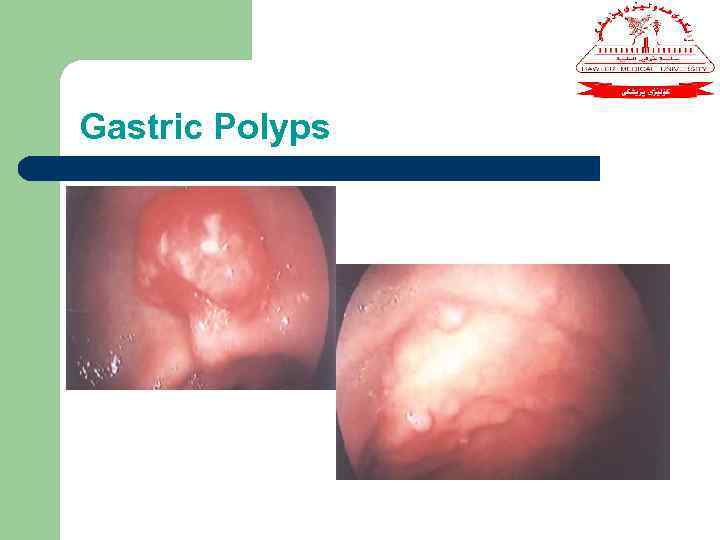 Gastric Polyps
Gastric Polyps
 Gastric Polyps cont, d l l Ø Ø Number of conditions manifest as gastric polyps. Main importance represent early gastric cancer. Biopsy is essential. Most common type: Metaplastic (associated with H. pylori infection). Inflammatory polyps also common.
Gastric Polyps cont, d l l Ø Ø Number of conditions manifest as gastric polyps. Main importance represent early gastric cancer. Biopsy is essential. Most common type: Metaplastic (associated with H. pylori infection). Inflammatory polyps also common.
 Gastric Polyps cont, d Ø l l Ø Ø Ø l Ø Ø Fundic gland polyps: (associated with use of PPI and familial polyposis). None proven malignant potential. True adenomas have : Malignant potential Should be removed Account 10% of polypoid lesions. Gastric carcinoids: arising from ECL cells seen in pernicious anaemia.
Gastric Polyps cont, d Ø l l Ø Ø Ø l Ø Ø Fundic gland polyps: (associated with use of PPI and familial polyposis). None proven malignant potential. True adenomas have : Malignant potential Should be removed Account 10% of polypoid lesions. Gastric carcinoids: arising from ECL cells seen in pernicious anaemia.
 Summary Ø Ø Ø Surgury for uncomplicated PU rarely done. There a lot of complications following surgery for PU and difficult to treat. Main coplications of PU: perforation. bleeding and pyloric obstruction. Most of complications need invasive and semiinvasive procedure Main importance of gastric polyps are its precancerous Next lecture: Gastric cancer and its management.
Summary Ø Ø Ø Surgury for uncomplicated PU rarely done. There a lot of complications following surgery for PU and difficult to treat. Main coplications of PU: perforation. bleeding and pyloric obstruction. Most of complications need invasive and semiinvasive procedure Main importance of gastric polyps are its precancerous Next lecture: Gastric cancer and its management.



