32691dfb5535919ef00162aa5ad369b6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Stoichiometry for Strugglers by Daniel Haradem & Kathy Vondracek of Allen ISD for CAST 2016 in San Antonio, TX Workshop 1041 Website: allenisd. org/Page/49042

Tricks to Trade -- The scribble (It goes underneath the # that you are starting with) -- Green and Pink Highlighters (Go and Stop) -- The Tape (Conversation factors based off 1 base unit) -- Swish/Swish song (used for cancelling units) -- Showing your work(use parenthesis and multiply signs) -- Calculator (alternating multiply and divide)

Pressure Conversion with Pressure Tape 1 atm = 760 mm Hg = 760 torr =101. 33 KPa = 14. 7 psi Your car tires require 35. 0 psi to run optimally. How many atmosphere is this? 35. 0 psi x 1 atm 14. 7 psi = 2. 38 atm
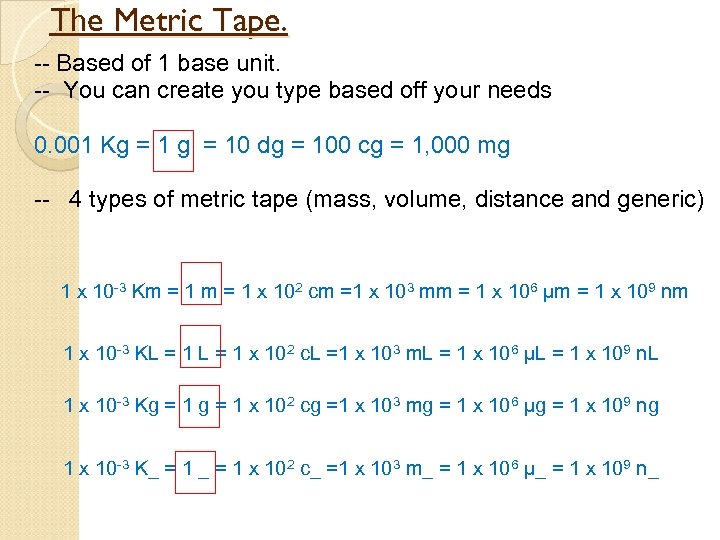
The Metric Tape. -- Based of 1 base unit. -- You can create you type based off your needs 0. 001 Kg = 10 dg = 100 cg = 1, 000 mg -- 4 types of metric tape (mass, volume, distance and generic) 1 x 10 -3 Km = 1 x 102 cm =1 x 103 mm = 1 x 106 µm = 1 x 109 nm 1 x 10 -3 KL = 1 x 102 c. L =1 x 103 m. L = 1 x 106 µL = 1 x 109 n. L 1 x 10 -3 Kg = 1 x 102 cg =1 x 103 mg = 1 x 106 µg = 1 x 109 ng 1 x 10 -3 K_ = 1 x 102 c_ =1 x 103 m_ = 1 x 106 µ_ = 1 x 109 n_
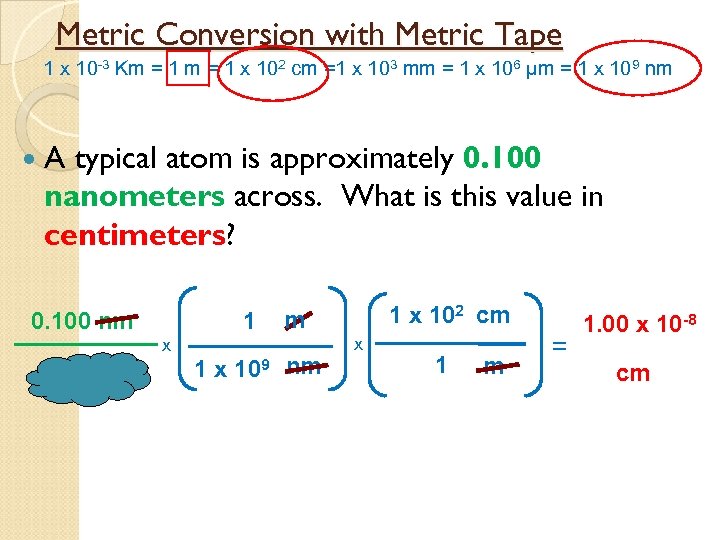
Metric Conversion with Metric Tape 1 x 10 -3 Km = 1 x 102 cm =1 x 103 mm = 1 x 106 µm = 1 x 109 nm A typical atom is approximately 0. 100 nanometers across. What is this value in centimeters? 0. 100 nm 1 x 102 cm m 1 x 109 nm x 1 m = 1. 00 x 10 -8 cm

Metric Conversion (Transitive Law) 1 x 10 -3 Km = 1 x 102 cm =1 x 103 mm = 1 x 106 µm = 1 x 109 nm A typical atom is approximately 0. 100 nanometers across. What is this value in centimeters? 0. 100 nm 1 x 102 cm x 109 nm = 1. 00 x 10 -8 cm

Metric Conversion (Proportions) 1 x 10 -3 Km = 1 x 102 cm =1 x 103 mm = 1 x 106 µm = 1 x 109 nm A typical atom is approximately 0. 100 nanometers across. What is this value in centimeters? 0. 100 nm ? ? ? cm = 1 x 109 nm 1 x 102 cm Ans: 1. 00 x 10 -8 cm Cross-multiply and divide Either Commit to Dimensional Analysis or Proportions…. . (NOT BOTH)
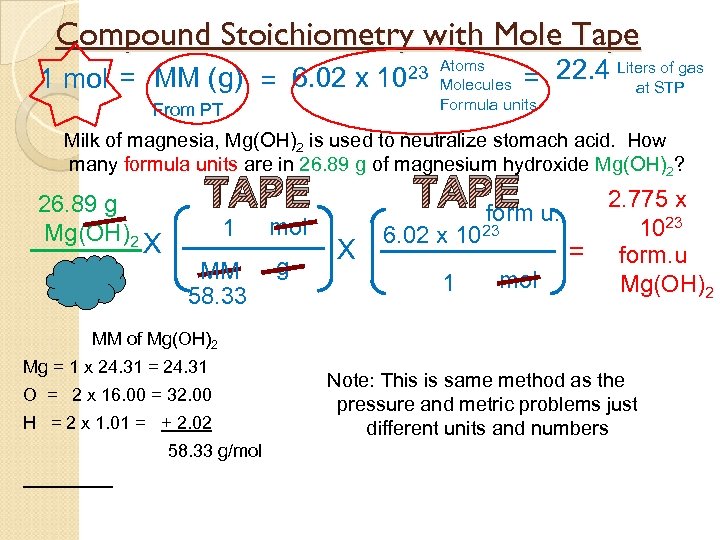
Compound Stoichiometry with Mole Tape 1 mol = MM (g) = 6. 02 x From PT of gas = 22. 4 Liters. STP at 23 Atoms 10 Molecules Formula units Milk of magnesia, Mg(OH)2 is used to neutralize stomach acid. How many formula units are in 26. 89 g of magnesium hydroxide Mg(OH)2? 26. 89 g Mg(OH)2 TAPE u. form TAPE X 1 MM 58. 33 mol g X 6. 02 x 1023 1 mol 2. 775 x 1023 = form. u Mg(OH)2 MM of Mg(OH)2 Mg = 1 x 24. 31 = 24. 31 O = 2 x 16. 00 = 32. 00 H = 2 x 1. 01 = + 2. 02 58. 33 g/mol Note: This is same method as the pressure and metric problems just different units and numbers
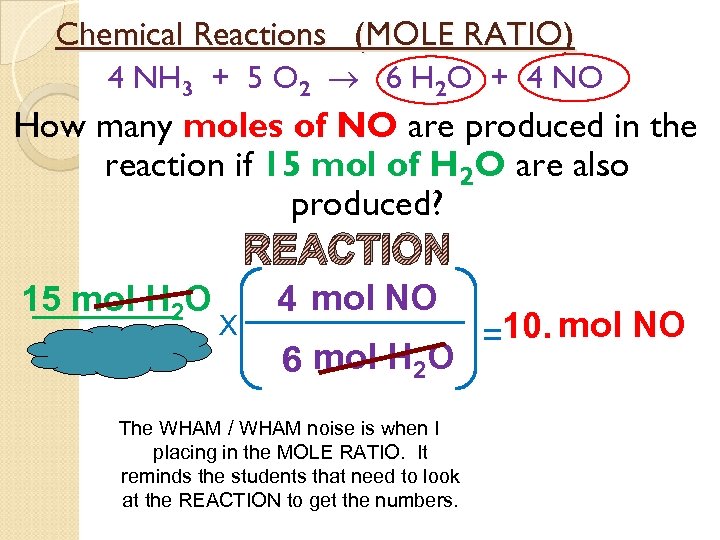
Chemical Reactions (MOLE RATIO) 4 NH 3 + 5 O 2 6 H 2 O + 4 NO How many moles of NO are produced in the reaction if 15 mol of H 2 O are also produced? REACTION 15 mol H 2 O X 4 mol NO 6 mol H 2 O The WHAM / WHAM noise is when I placing in the MOLE RATIO. It reminds the students that need to look at the REACTION to get the numbers. =10. mol NO

Plan Your Stoichiometry -- Always figure out where you are starting and where you are going. Checklist -- Go to moles (TAPE) -- Use mole ratio (REACTION) -- Go away from moles (TAPE) -- Steps may be deleted based on your start and finish Mole Map --Vertical Arrows are (TAPE) steps Horizontal Arrows are mole ratios (REACTION) steps --Arrows may be deleted based on your start and finish
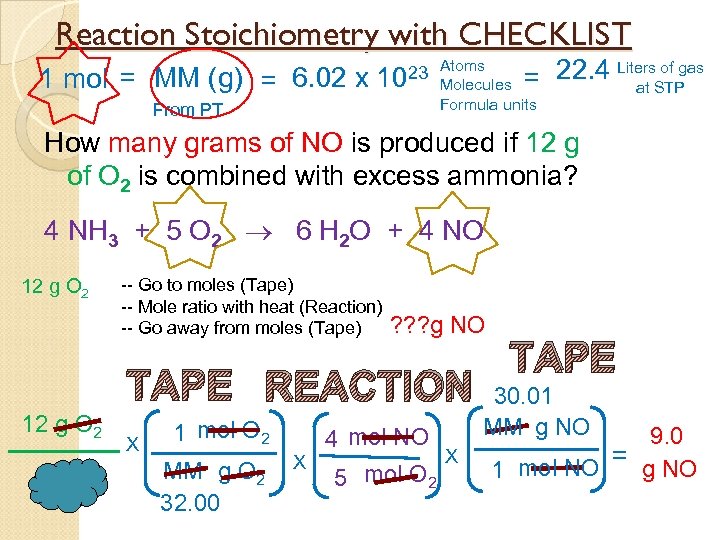
Reaction Stoichiometry with CHECKLIST 1 mol = MM (g) = 6. 02 x 23 Atoms 10 From PT of gas = 22. 4 Liters. STP at Molecules Formula units How many grams of NO is produced if 12 g of O 2 is combined with excess ammonia? 4 NH 3 + 5 O 2 6 H 2 O + 4 NO 12 g O 2 -- Go to moles (Tape) -- Mole ratio with heat (Reaction) -- Go away from moles (Tape) ? ? ? g NO TAPE REACTION 12 g O 2 X 1 mol O 2 MM g O 2 32. 00 4 mol NO X X 5 mol O 2 TAPE 30. 01 MM g NO 9. 0 = g NO 1 mol NO
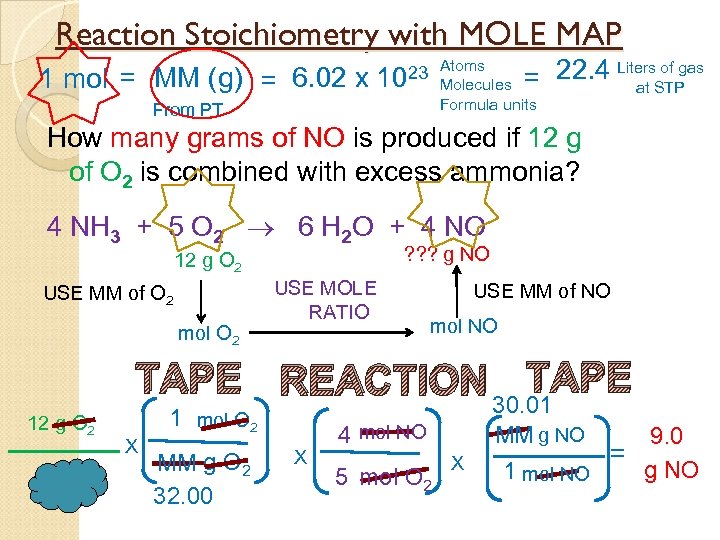
Reaction Stoichiometry with MOLE MAP 1 mol = MM (g) = 6. 02 x of gas = 22. 4 Liters. STP at 23 Atoms 10 Molecules Formula units From PT How many grams of NO is produced if 12 g of O 2 is combined with excess ammonia? 4 NH 3 + 5 O 2 6 H 2 O + 4 NO ? ? ? g NO 12 g O 2 USE MM of O 2 mol O 2 USE MOLE RATIO USE MM of NO mol NO TAPE REACTION TAPE 12 g O 2 1 mol O 2 X MM g O 2 32. 00 X 30. 01 MM g NO 4 mol NO 5 mol O 2 X 9. 0 = g NO 1 mol NO
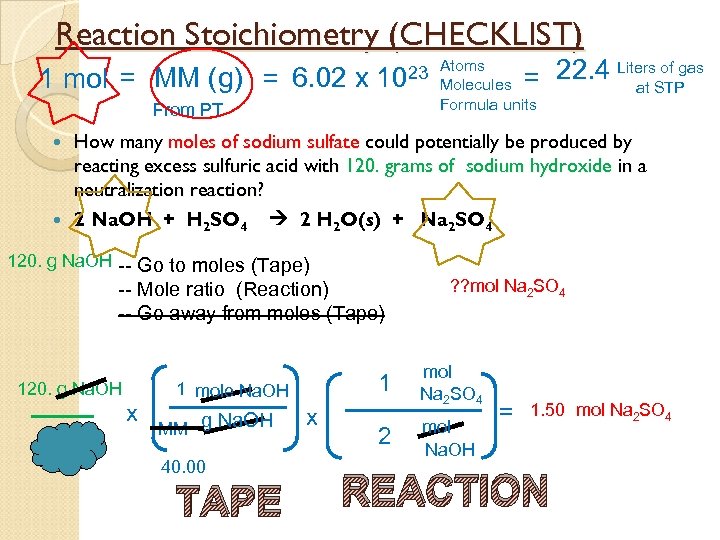
Reaction Stoichiometry (CHECKLIST) 1 mol = MM (g) = 6. 02 x of gas = 22. 4 Liters. STP at 23 Atoms 10 Molecules Formula units From PT How many moles of sodium sulfate could potentially be produced by reacting excess sulfuric acid with 120. grams of sodium hydroxide in a neutralization reaction? 2 Na. OH + H 2 SO 4 2 H 2 O(s) + Na 2 SO 4 120. g Na. OH -- Go to moles (Tape) -- Mole ratio (Reaction) -- Go away from moles (Tape) 120. g Na. OH x 1 1 mole Na. OH MM g Na. OH 40. 00 TAPE x 2 ? ? mol Na 2 SO 4 mol Na. OH = 1. 50 mol Na 2 SO 4 REACTION
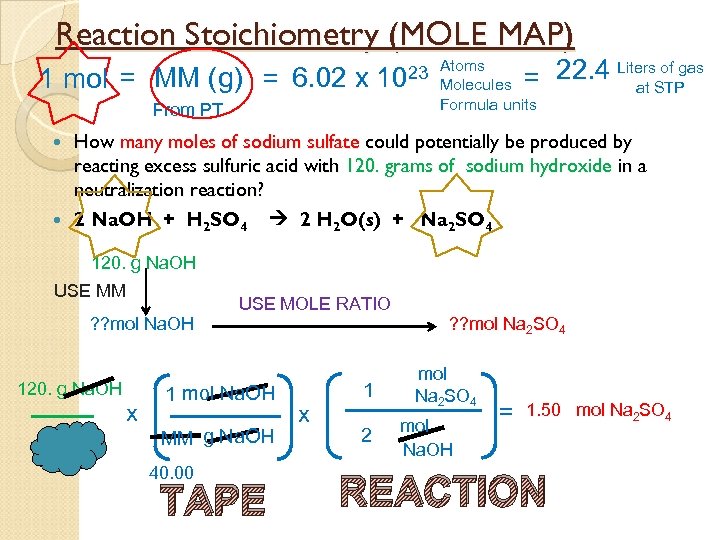
Reaction Stoichiometry (MOLE MAP) 1 mol = MM (g) = 6. 02 x of gas = 22. 4 Liters. STP at 23 Atoms 10 From PT Molecules Formula units How many moles of sodium sulfate could potentially be produced by reacting excess sulfuric acid with 120. grams of sodium hydroxide in a neutralization reaction? 2 Na. OH + H 2 SO 4 2 H 2 O(s) + Na 2 SO 4 120. g Na. OH USE MM ? ? mol Na. OH 120. g Na. OH x USE MOLE RATIO 1 mol Na. OH MM g Na. OH 40. 00 TAPE x 1 2 ? ? mol Na 2 SO 4 mol Na. OH = 1. 50 mol Na 2 SO 4 REACTION

Using States to Determine How to go to Moles -- Solids (Use the Molar Mass) -- Liquids (Use Density and then Molar Mass) -- Gases at STP (Use 22. 4 L) -- Gases at non-STP conditions (Use Ideal Gas Law) -- Aqueous (Use Molarity X Volume in Liters)
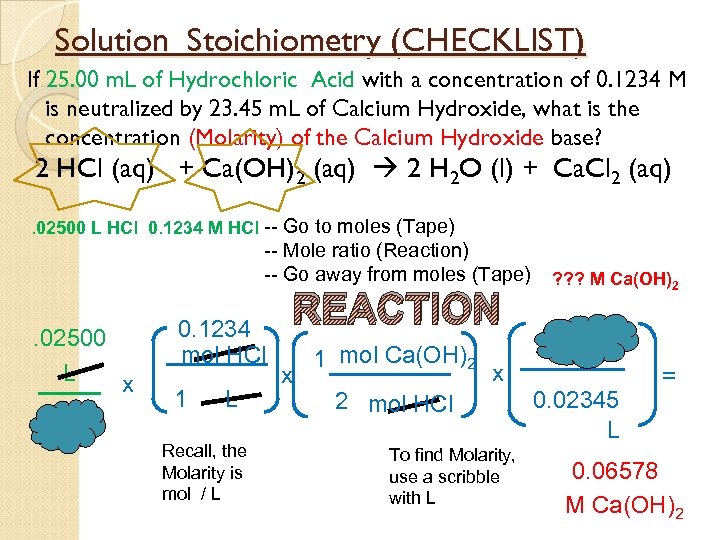
Solution Stoichiometry (CHECKLIST) If 25. 00 m. L of Hydrochloric Acid with a concentration of 0. 1234 M is neutralized by 23. 45 m. L of Calcium Hydroxide, what is the concentration (Molarity) of the Calcium Hydroxide base? 2 HCl (aq) + Ca(OH)2 (aq) 2 H 2 O (l) + Ca. Cl 2 (aq). 02500 L HCl 0. 1234 M HCl -- Go to moles (Tape) -- Mole ratio (Reaction) -- Go away from moles (Tape) . 02500 L x 0. 1234 mol HCl 1 L Recall, the Molarity is mol / L REACTION x 1 mol Ca(OH)2 ? ? ? M Ca(OH)2 x 2 mol HCl To find Molarity, use a scribble with L 0. 02345 L = 0. 06578 M Ca(OH)2
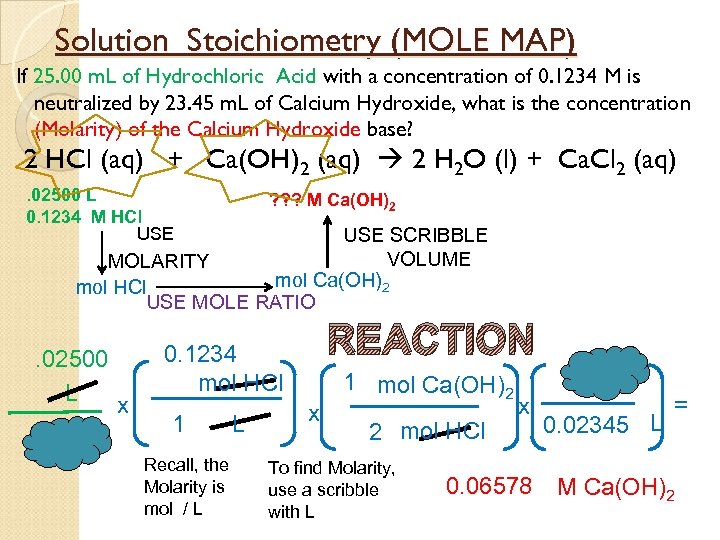
Solution Stoichiometry (MOLE MAP) If 25. 00 m. L of Hydrochloric Acid with a concentration of 0. 1234 M is neutralized by 23. 45 m. L of Calcium Hydroxide, what is the concentration (Molarity) of the Calcium Hydroxide base? 2 HCl (aq) + Ca(OH)2 (aq) 2 H 2 O (l) + Ca. Cl 2 (aq). 02500 L 0. 1234 M HCl USE ? ? ? M Ca(OH)2 USE SCRIBBLE VOLUME MOLARITY mol Ca(OH)2 mol HCl USE MOLE RATIO . 02500 L x REACTION 0. 1234 mol HCl 1 Recall, the Molarity is mol / L L x 1 mol Ca(OH)2 2 mol HCl To find Molarity, use a scribble with L x 0. 06578 0. 02345 L = M Ca(OH)2
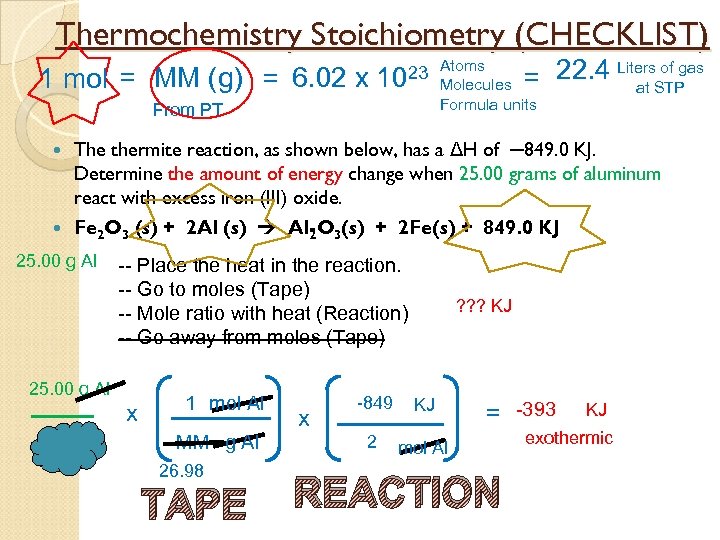
Thermochemistry Stoichiometry (CHECKLIST) 1 mol = MM (g) = 6. 02 x of gas = 22. 4 Liters. STP at 23 Atoms 10 Molecules Formula units From PT The thermite reaction, as shown below, has a ΔH of ─849. 0 KJ. Determine the amount of energy change when 25. 00 grams of aluminum react with excess iron (III) oxide. Fe 2 O 3 (s) + 2 Al (s) Al O 3(s) + 2 Fe(s) + 849. 0 KJ 2 25. 00 g Al -- Place the heat in the reaction. -- Go to moles (Tape) -- Mole ratio with heat (Reaction) -- Go away from moles (Tape) 25. 00 g Al x 1 mol Al MM g Al 26. 98 TAPE ? ? ? KJ KJ 2 x -849 mol Al = -393 REACTION KJ exothermic
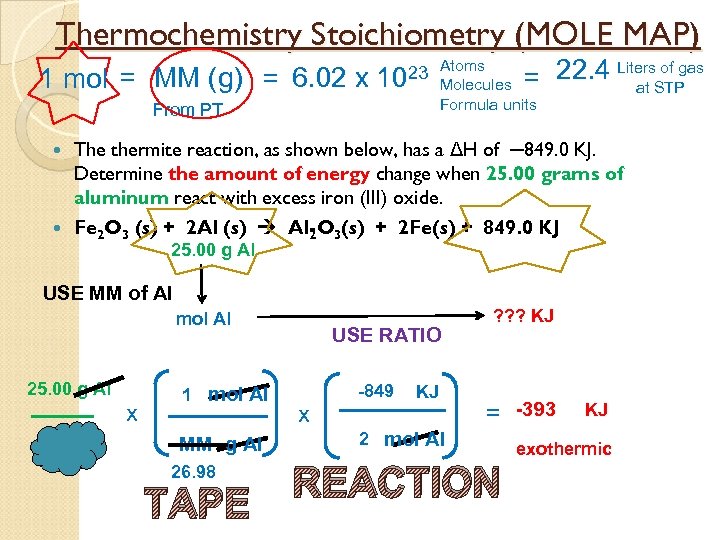
Thermochemistry Stoichiometry (MOLE MAP) 1 mol = MM (g) = 6. 02 x of gas = 22. 4 Liters. STP at 23 Atoms 10 Molecules Formula units From PT The thermite reaction, as shown below, has a ΔH of ─849. 0 KJ. Determine the amount of energy change when 25. 00 grams of aluminum react with excess iron (III) oxide. Fe 2 O 3 (s) + 2 Al (s) Al O 3(s) + 2 Fe(s) + 849. 0 KJ 2 25. 00 g Al USE MM of Al mol Al 25. 00 g Al x 1 mol Al MM g Al 26. 98 TAPE USE RATIO x -849 KJ ? ? ? KJ = -393 2 mol Al REACTION KJ exothermic
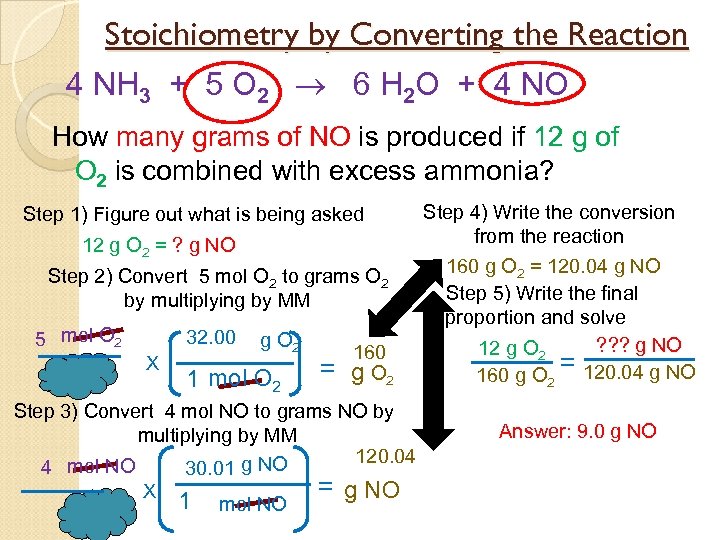
Stoichiometry by Converting the Reaction 4 NH 3 + 5 O 2 6 H 2 O + 4 NO How many grams of NO is produced if 12 g of O 2 is combined with excess ammonia? Step 1) Figure out what is being asked 12 g O 2 = ? g NO Step 2) Convert 5 mol O 2 to grams O 2 by multiplying by MM 5 mol O 2 32. 00 X g O 2 1 mol O 2 = 160 g O 2 Step 3) Convert 4 mol NO to grams NO by multiplying by MM 120. 04 4 mol NO 30. 01 g NO = g NO X 1 mol NO Step 4) Write the conversion from the reaction 160 g O 2 = 120. 04 g NO Step 5) Write the final proportion and solve ? ? ? g NO 12 g O 2 = 160 g O 2 120. 04 g NO Answer: 9. 0 g NO
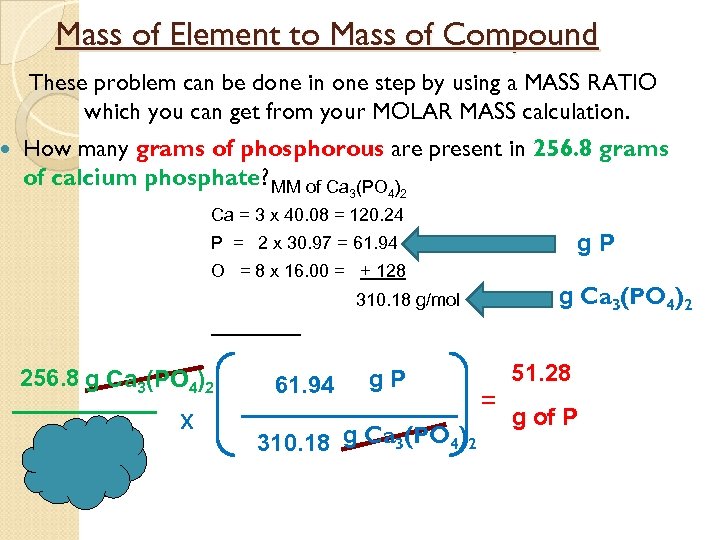
Mass of Element to Mass of Compound These problem can be done in one step by using a MASS RATIO which you can get from your MOLAR MASS calculation. How many grams of phosphorous are present in 256. 8 grams of calcium phosphate? MM of Ca (PO ) 3 4 2 Ca = 3 x 40. 08 = 120. 24 g. P P = 2 x 30. 97 = 61. 94 O = 8 x 16. 00 = + 128 g Ca 3(PO 4)2 310. 18 g/mol 256. 8 g Ca 3(PO 4)2 x 61. 94 g. P 310. 18 g Ca 3(PO 4)2 = 51. 28 g of P
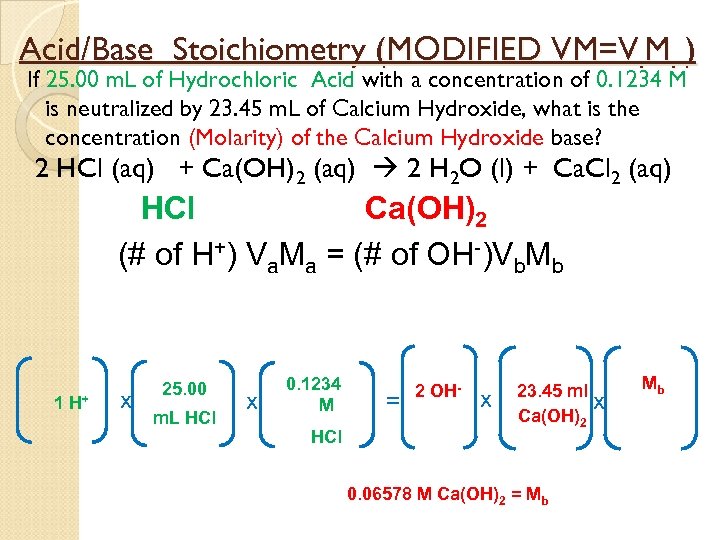
Acid/Base Stoichiometry (MODIFIED VM=V. M. ) If 25. 00 m. L of Hydrochloric Acid with a concentration of 0. 1234 M is neutralized by 23. 45 m. L of Calcium Hydroxide, what is the concentration (Molarity) of the Calcium Hydroxide base? 2 HCl (aq) + Ca(OH)2 (aq) 2 H 2 O (l) + Ca. Cl 2 (aq) HCl Ca(OH)2 (# of H+) Va. Ma = (# of OH-)Vb. Mb 1 H+ x 25. 00 m. L HCl x 0. 1234 M HCl = 2 OH- x 23. 45 ml x Ca(OH)2 0. 06578 M Ca(OH)2 = Mb Mb

Video Resources -- Pressure Tape https: //vimeo. com/166356342 But It Works https: //vimeo. com/167114263 -- Metric Conversions Metric Tape https: //vimeo. com/168331657 Transitive Law https: //vimeo. com/168333510 Proportions https: //vimeo. com/167111081 --Compound Stoichiometry (Mole Tape) https: //vimeo. com/167110420 Chemical Reactions (Mole Ratio) https: //vimeo. com/167110048

Video Resources -- Reaction Stoichiometry Checklist 1 https: //vimeo. com/167107604 Mole Map 1 https: //vimeo. com/167107216 Checklist 2 https: //vimeo. com/167106728 Mole Map 2 https: //vimeo. com/167106309 -- Solution Stoichiometry Checklist https: //vimeo. com/168332177 Mole Map https: //vimeo. com/168332576 -- Thermochemistry Stoichiometry Checklist https: //vimeo. com/166991562 Mole Map https: //vimeo. com/166988720 -- Stoichiometry by Converting the Reaction https: //vimeo. com/166953338 -- Mass of Element to Mass of Compound https: //vimeo. com/166950996 -- Acid/Base Stoichiometry Modified VM= VM https: //vimeo. com/166946639
32691dfb5535919ef00162aa5ad369b6.ppt