 Stock Valuation Jeff Cahn & Tom Mrjenovich
Stock Valuation Jeff Cahn & Tom Mrjenovich
 Why Own Common Stock? n n Capital Gains – Increase in stocks price Dividends – Monthly, quarterly, or yearly payouts of a corporations earnings. q Not all corporations pay dividends
Why Own Common Stock? n n Capital Gains – Increase in stocks price Dividends – Monthly, quarterly, or yearly payouts of a corporations earnings. q Not all corporations pay dividends
 Valuation n The stocks price is the present value of the expected future dividends plus the present value of any capital gains.
Valuation n The stocks price is the present value of the expected future dividends plus the present value of any capital gains.
 Dividend Discount Models n Zero-Growth Model n Constant-Growth Model n Multiple-Growth Model
Dividend Discount Models n Zero-Growth Model n Constant-Growth Model n Multiple-Growth Model
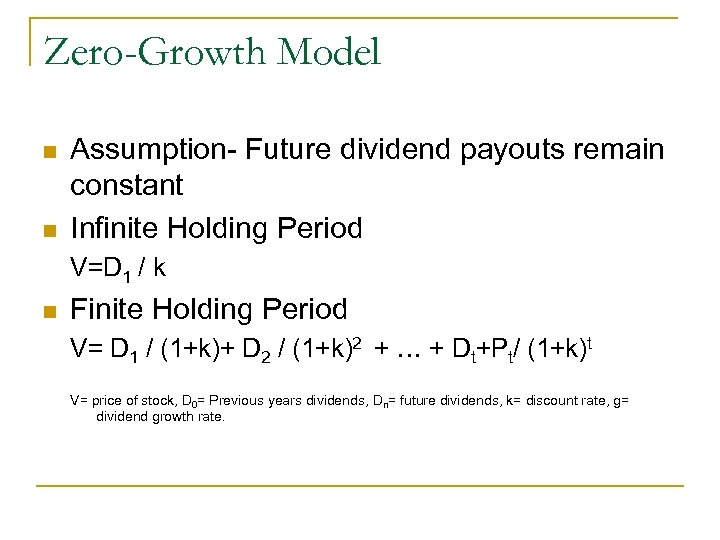 Zero-Growth Model n n Assumption- Future dividend payouts remain constant Infinite Holding Period V=D 1 / k n Finite Holding Period V= D 1 / (1+k)+ D 2 / (1+k)2 + … + Dt+Pt/ (1+k)t V= price of stock, D 0= Previous years dividends, Dn= future dividends, k= discount rate, g= dividend growth rate.
Zero-Growth Model n n Assumption- Future dividend payouts remain constant Infinite Holding Period V=D 1 / k n Finite Holding Period V= D 1 / (1+k)+ D 2 / (1+k)2 + … + Dt+Pt/ (1+k)t V= price of stock, D 0= Previous years dividends, Dn= future dividends, k= discount rate, g= dividend growth rate.
 Example 1 You want to buy xyz corporations stock today. You plan to sell it in 2 years. It will pay a dividend of $2. 00 per year over the next two years (at the end of each year). The stock price at the end of year 2 will be $15. 00. The discount rate is 8%, how much should you pay for the stock?
Example 1 You want to buy xyz corporations stock today. You plan to sell it in 2 years. It will pay a dividend of $2. 00 per year over the next two years (at the end of each year). The stock price at the end of year 2 will be $15. 00. The discount rate is 8%, how much should you pay for the stock?
 Solution 1 n V= D 1 / (1+k)+ D 2+P 2 / (1+k)2 n V=
Solution 1 n V= D 1 / (1+k)+ D 2+P 2 / (1+k)2 n V=
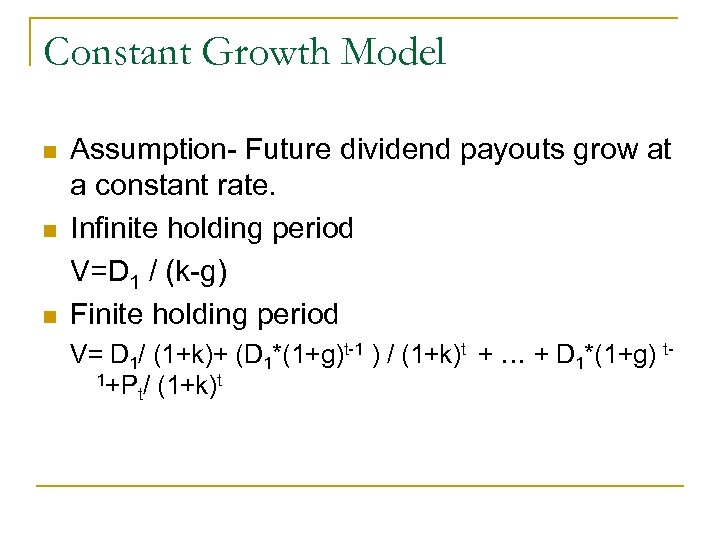 Constant Growth Model n n n Assumption- Future dividend payouts grow at a constant rate. Infinite holding period V=D 1 / (k-g) Finite holding period V= D 1/ (1+k)+ (D 1*(1+g)t-1 ) / (1+k)t + … + D 1*(1+g) t 1+P / (1+k)t t
Constant Growth Model n n n Assumption- Future dividend payouts grow at a constant rate. Infinite holding period V=D 1 / (k-g) Finite holding period V= D 1/ (1+k)+ (D 1*(1+g)t-1 ) / (1+k)t + … + D 1*(1+g) t 1+P / (1+k)t t
 Example 2 You want to buy xyz corporation today. XYZ corporation paid a dividend of $2. 00 yesterday. Assuming their dividend will grow 2% per year forever and a discount rate 8%, what is a fair price?
Example 2 You want to buy xyz corporation today. XYZ corporation paid a dividend of $2. 00 yesterday. Assuming their dividend will grow 2% per year forever and a discount rate 8%, what is a fair price?
 Solution 2 n V=D 1 / (k-g) D 1= D 0*(1+g) n V= V=
Solution 2 n V=D 1 / (k-g) D 1= D 0*(1+g) n V= V=
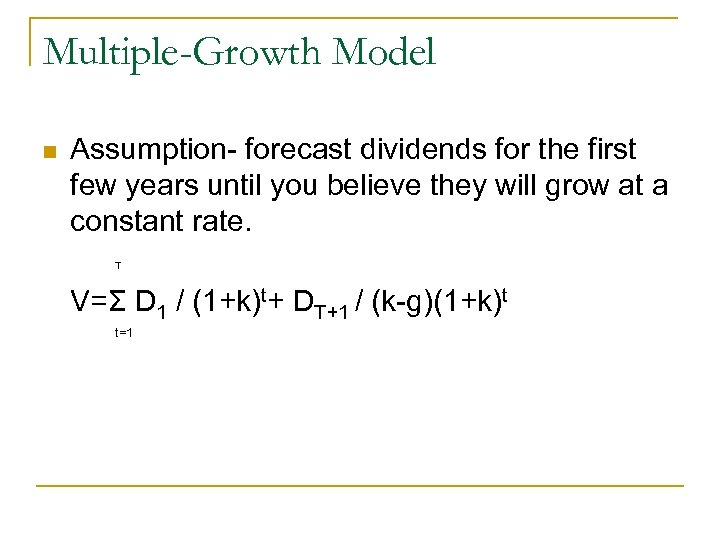 Multiple-Growth Model n Assumption- forecast dividends for the first few years until you believe they will grow at a constant rate. T V=Σ D 1 / (1+k)t+ DT+1 / (k-g)(1+k)t t=1
Multiple-Growth Model n Assumption- forecast dividends for the first few years until you believe they will grow at a constant rate. T V=Σ D 1 / (1+k)t+ DT+1 / (k-g)(1+k)t t=1
 Example 3 You want to buy xyz corporation stock today. You forecast they will pay a dividend of $2. 00 in year 1, $1. 50 in year 2, and $3. 00 in year 3. From year 3 onwards they will have a growth rate of 2% and a discount rate of 8%. What would you be willing to pay?
Example 3 You want to buy xyz corporation stock today. You forecast they will pay a dividend of $2. 00 in year 1, $1. 50 in year 2, and $3. 00 in year 3. From year 3 onwards they will have a growth rate of 2% and a discount rate of 8%. What would you be willing to pay?
 Solution 3 T V=Σ D 1 / (1+k)t+ DT+1 / (k-g)(1+k)t t=1 V= V=
Solution 3 T V=Σ D 1 / (1+k)t+ DT+1 / (k-g)(1+k)t t=1 V= V=
 Questions?
Questions?