8. stock valuation.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Stock Valuation FIN - 311 Chapter 8 Spring 2013 G. Kholjigitov
Stock Valuation FIN - 311 Chapter 8 Spring 2013 G. Kholjigitov
 1 -2 Lecture main topics: • Difference between equity & debts • Common stock • Preferred stock • Going public & IPO • Stock valuation • Zero growth stock. Constant growth stock. Irregular growth stock. Required return. Preferred stock. Shareholder voting. Stock market reporting
1 -2 Lecture main topics: • Difference between equity & debts • Common stock • Preferred stock • Going public & IPO • Stock valuation • Zero growth stock. Constant growth stock. Irregular growth stock. Required return. Preferred stock. Shareholder voting. Stock market reporting
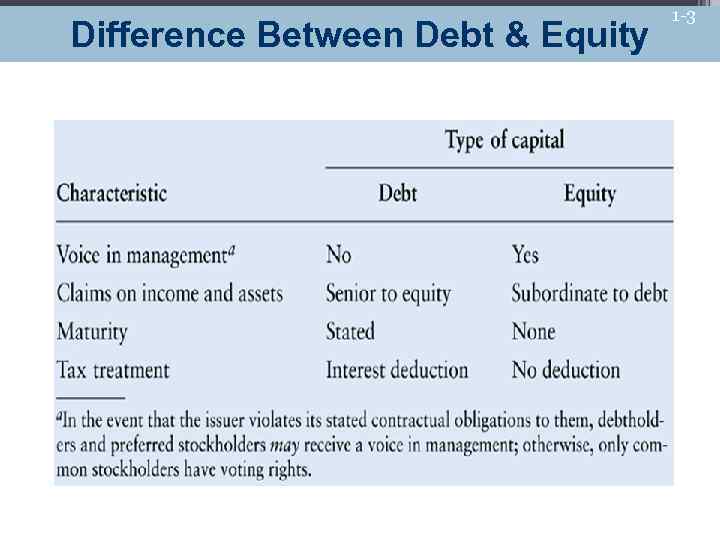 Difference Between Debt & Equity 1 -3
Difference Between Debt & Equity 1 -3
 1 -4 The Nature of Equity Capital Voice in Management • Unlike bondholders and other credit holders, holders of equity capital are owners of the firm • Common equity holders have voting rights that permit them to elect the firm’s board of directors and to vote on special issues • Bondholders and preferred stockholders receive no such privileges
1 -4 The Nature of Equity Capital Voice in Management • Unlike bondholders and other credit holders, holders of equity capital are owners of the firm • Common equity holders have voting rights that permit them to elect the firm’s board of directors and to vote on special issues • Bondholders and preferred stockholders receive no such privileges
 1 -5 The Nature of Equity Capital Claims on Income & Assets • Equity holders are have a residual claim on the firm’s income and assets • Their claims can not be paid until the claims of all creditors, including both interest and principle payments on debt have been satisfied • Because equity holders are the last to receive distributions, they expect greater returns to compensate them for the additional risk they bear
1 -5 The Nature of Equity Capital Claims on Income & Assets • Equity holders are have a residual claim on the firm’s income and assets • Their claims can not be paid until the claims of all creditors, including both interest and principle payments on debt have been satisfied • Because equity holders are the last to receive distributions, they expect greater returns to compensate them for the additional risk they bear
 1 -6 The Nature of Equity Capital Maturity • Unlike debt, equity capital is a permanent form of financing • Equity has no maturity date and never has to be repaid by the firm
1 -6 The Nature of Equity Capital Maturity • Unlike debt, equity capital is a permanent form of financing • Equity has no maturity date and never has to be repaid by the firm
 1 -7 The Nature of Equity Capital Tax Treatment • While interest paid to bondholders is tax-deductible to the issuing firm, dividends paid to preferred and common stock holders is not • In effect, this further lowers the cost of debt relative to the cost of equity as a source of financing to the firm
1 -7 The Nature of Equity Capital Tax Treatment • While interest paid to bondholders is tax-deductible to the issuing firm, dividends paid to preferred and common stock holders is not • In effect, this further lowers the cost of debt relative to the cost of equity as a source of financing to the firm
 1 -8 Common Stock Ownership • The common stock of a firm can be privately owned by an individual, by a closely owned small group of investors, or publicly owned by a broad group of investors • Typically, small corporations are privately or closely owned and if their shares are traded, this occurs infrequently and in small amounts • Large corporations are typically publicly owned and have shares that are actively traded on major securities exchanges
1 -8 Common Stock Ownership • The common stock of a firm can be privately owned by an individual, by a closely owned small group of investors, or publicly owned by a broad group of investors • Typically, small corporations are privately or closely owned and if their shares are traded, this occurs infrequently and in small amounts • Large corporations are typically publicly owned and have shares that are actively traded on major securities exchanges
 1 -9 Common Stock Par Value • Unlike bonds, common stock may be sold without par value • The par value of a common stock is generally low ($1) and is a relatively useless value established in the firm’s corporate charter • A low par value may be advantageous in states where certain corporate taxes are based on the par value of the stock
1 -9 Common Stock Par Value • Unlike bonds, common stock may be sold without par value • The par value of a common stock is generally low ($1) and is a relatively useless value established in the firm’s corporate charter • A low par value may be advantageous in states where certain corporate taxes are based on the par value of the stock
 1 -10 Common Stock Preemptive Rights • A preemptive right allows common stockholders to maintain their proportionate ownership in a corporation when new shares are issued • This allows existing shareholders to maintain voting control and protect against the dilution of their ownership • In a rights offering, the firm grants rights to its existing shareholders, which permits them to purchase additional shares at a price below the current price
1 -10 Common Stock Preemptive Rights • A preemptive right allows common stockholders to maintain their proportionate ownership in a corporation when new shares are issued • This allows existing shareholders to maintain voting control and protect against the dilution of their ownership • In a rights offering, the firm grants rights to its existing shareholders, which permits them to purchase additional shares at a price below the current price
 1 -11 Common Stock Authorized, Outstanding, and Issued Shares • Authorized shares are the number of shares of common stock that a firm’s corporate charter allows • Outstanding shares are the number of shares of common stock held by the public • Treasury stock is the number of outstanding shares that have been purchased by the firm • Issued shares are the number of shares that have been put into circulation and includes both outstanding shares and treasury stock
1 -11 Common Stock Authorized, Outstanding, and Issued Shares • Authorized shares are the number of shares of common stock that a firm’s corporate charter allows • Outstanding shares are the number of shares of common stock held by the public • Treasury stock is the number of outstanding shares that have been purchased by the firm • Issued shares are the number of shares that have been put into circulation and includes both outstanding shares and treasury stock
 1 -12 Common Stock Voting Rights • Each share of common stock entitles its holder to one vote in the election of directors and on special issues • Votes are generally assignable and may be cast at the annual stockholders meeting • Many firms have issued two or more classes of stock differing mainly in having unequal voting rights • Usually, class A common stock is designated as nonvoting while class B is designated as voting
1 -12 Common Stock Voting Rights • Each share of common stock entitles its holder to one vote in the election of directors and on special issues • Votes are generally assignable and may be cast at the annual stockholders meeting • Many firms have issued two or more classes of stock differing mainly in having unequal voting rights • Usually, class A common stock is designated as nonvoting while class B is designated as voting
 1 -13 Common Stock Voting Rights • Because most shareholders do not attend the annual meeting to vote, they may sign a proxy statement giving their votes to another party • Occasionally, when the firm is widely owned, outsiders may wage a proxy battle to unseat existing management and gain control
1 -13 Common Stock Voting Rights • Because most shareholders do not attend the annual meeting to vote, they may sign a proxy statement giving their votes to another party • Occasionally, when the firm is widely owned, outsiders may wage a proxy battle to unseat existing management and gain control
 Common Stock 1 -14 Dividends • Payment of dividends is at the discretion of the board of directors • Dividends may be made in cash, additional shares of stock, and even merchandise • Because stockholders are residual claimants - they receive dividend payments only after all claims have been settled with the government, creditors, and preferred stockholders
Common Stock 1 -14 Dividends • Payment of dividends is at the discretion of the board of directors • Dividends may be made in cash, additional shares of stock, and even merchandise • Because stockholders are residual claimants - they receive dividend payments only after all claims have been settled with the government, creditors, and preferred stockholders
 1 -15 Preferred Stock • Preferred stock is an equity instrument that usually pays a fixed dividend and has a prior claim on the firm’s earnings and assets in case of liquidation • The dividend is expressed as either a dollar amount or as a percentage of its par value • Therefore, unlike common stock a preferred stock’s par value may have real significance • If a firm fails to pay a preferred stock dividend, the dividend is said to be in arrears
1 -15 Preferred Stock • Preferred stock is an equity instrument that usually pays a fixed dividend and has a prior claim on the firm’s earnings and assets in case of liquidation • The dividend is expressed as either a dollar amount or as a percentage of its par value • Therefore, unlike common stock a preferred stock’s par value may have real significance • If a firm fails to pay a preferred stock dividend, the dividend is said to be in arrears
 1 -16 Preferred Stock • In general, arrearage must be paid before common stockholders receive a dividend • Preferred stocks which possess this characteristic are called cumulative preferred stocks • Preferred stocks are also often referred to as hybrid securities because they possess the characteristics of both common stocks and bonds • Preferred stocks are like common stock because they are perpetual securities with no maturity date
1 -16 Preferred Stock • In general, arrearage must be paid before common stockholders receive a dividend • Preferred stocks which possess this characteristic are called cumulative preferred stocks • Preferred stocks are also often referred to as hybrid securities because they possess the characteristics of both common stocks and bonds • Preferred stocks are like common stock because they are perpetual securities with no maturity date
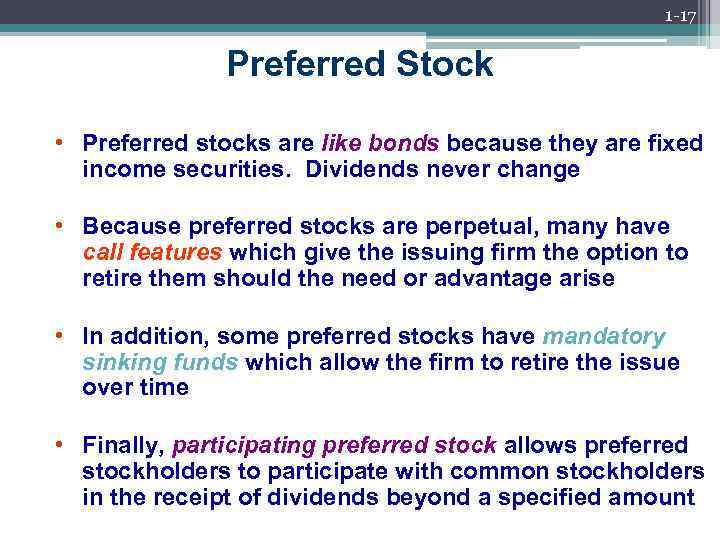 1 -17 Preferred Stock • Preferred stocks are like bonds because they are fixed income securities. Dividends never change • Because preferred stocks are perpetual, many have call features which give the issuing firm the option to retire them should the need or advantage arise • In addition, some preferred stocks have mandatory sinking funds which allow the firm to retire the issue over time • Finally, participating preferred stock allows preferred stockholders to participate with common stockholders in the receipt of dividends beyond a specified amount
1 -17 Preferred Stock • Preferred stocks are like bonds because they are fixed income securities. Dividends never change • Because preferred stocks are perpetual, many have call features which give the issuing firm the option to retire them should the need or advantage arise • In addition, some preferred stocks have mandatory sinking funds which allow the firm to retire the issue over time • Finally, participating preferred stock allows preferred stockholders to participate with common stockholders in the receipt of dividends beyond a specified amount
 1 -18 Issuing Common Stock • Initial financing for most firms typically comes from a firm’s original founders in the form of a common stock investment • Early stage debt or equity investors are unlikely to make an investment in a firm unless the founders also have a personal stake in the business • Initial non-founder financing usually comes first from private equity investors • After establishing itself, a firm will often “go public” by issuing shares of stock to a much broader group
1 -18 Issuing Common Stock • Initial financing for most firms typically comes from a firm’s original founders in the form of a common stock investment • Early stage debt or equity investors are unlikely to make an investment in a firm unless the founders also have a personal stake in the business • Initial non-founder financing usually comes first from private equity investors • After establishing itself, a firm will often “go public” by issuing shares of stock to a much broader group
 1 -19 Going Public • When a firm wishes to sell its stock in the primary market, it has three alternatives • A public offering or IPO, in which it offers its shares for sale to the general public (our focus • A rights offering, in which new shares are sold to existing shareholder • A private placement, in which the firm sells new securities directly to an investor or a group of investors
1 -19 Going Public • When a firm wishes to sell its stock in the primary market, it has three alternatives • A public offering or IPO, in which it offers its shares for sale to the general public (our focus • A rights offering, in which new shares are sold to existing shareholder • A private placement, in which the firm sells new securities directly to an investor or a group of investors
 1 -20 IPOs • IPOs are typically made by small, fast-growing companies that either: • require additional capital to continue expanding, or • have met a milestone for going public that was established in a contract to obtain VC funding • The firm must obtain approval of current shareholders, and hire an investment bank to underwrite the offering • The investment banker is responsible for promoting the stock and selling its shares
1 -20 IPOs • IPOs are typically made by small, fast-growing companies that either: • require additional capital to continue expanding, or • have met a milestone for going public that was established in a contract to obtain VC funding • The firm must obtain approval of current shareholders, and hire an investment bank to underwrite the offering • The investment banker is responsible for promoting the stock and selling its shares
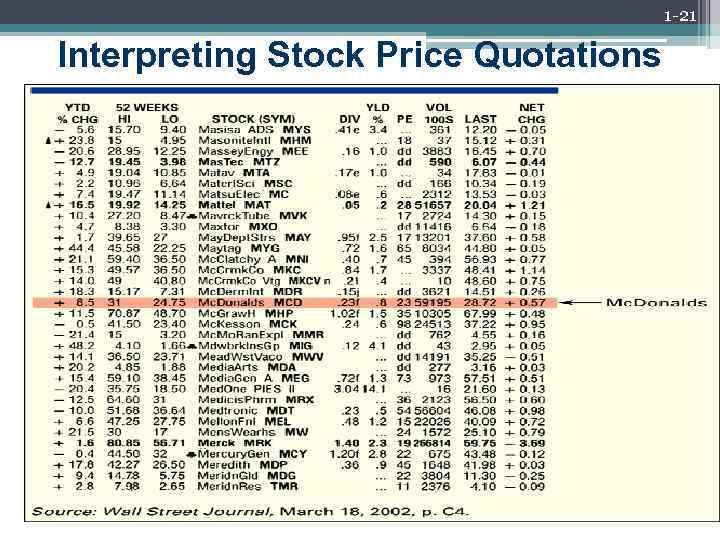 1 -21 Interpreting Stock Price Quotations
1 -21 Interpreting Stock Price Quotations
 1 -22 Common Stock Valuation • Stockholders expect to be compensated for their investment in a firm’s shares through periodic dividends and capital gains • Investors purchase shares when they feel they are undervalued and sell them when they believe they are overvalued
1 -22 Common Stock Valuation • Stockholders expect to be compensated for their investment in a firm’s shares through periodic dividends and capital gains • Investors purchase shares when they feel they are undervalued and sell them when they believe they are overvalued
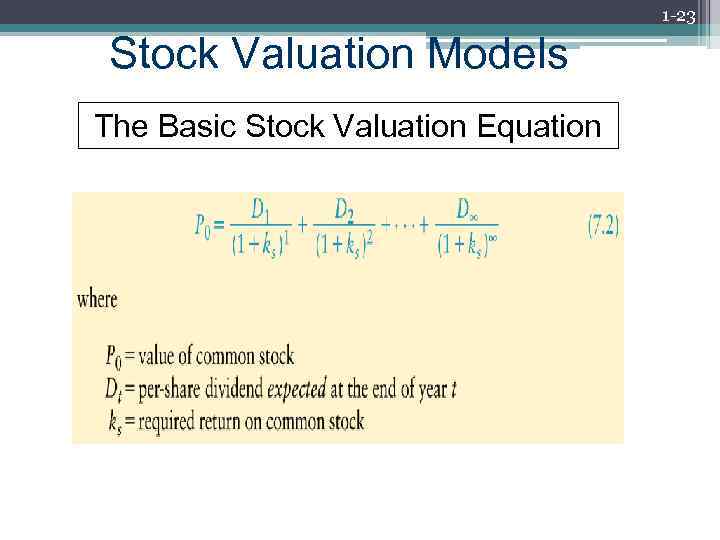 1 -23 Stock Valuation Models The Basic Stock Valuation Equation
1 -23 Stock Valuation Models The Basic Stock Valuation Equation
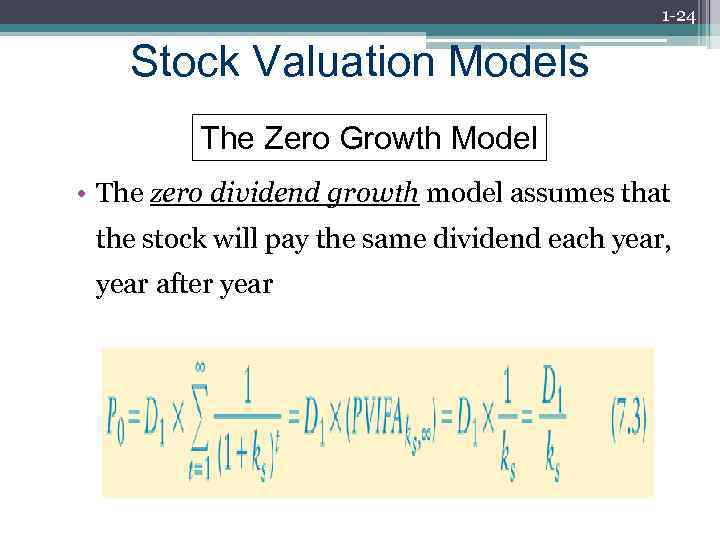 1 -24 Stock Valuation Models The Zero Growth Model • The zero dividend growth model assumes that the stock will pay the same dividend each year, year after year
1 -24 Stock Valuation Models The Zero Growth Model • The zero dividend growth model assumes that the stock will pay the same dividend each year, year after year
 1 -25 Zero growth stock Rainbow Rentals pays a constant annual dividend of $1. 00 per share on their common stock. How much are you willing to pay for one share of this stock if you want to earn a 9% rate of return?
1 -25 Zero growth stock Rainbow Rentals pays a constant annual dividend of $1. 00 per share on their common stock. How much are you willing to pay for one share of this stock if you want to earn a 9% rate of return?
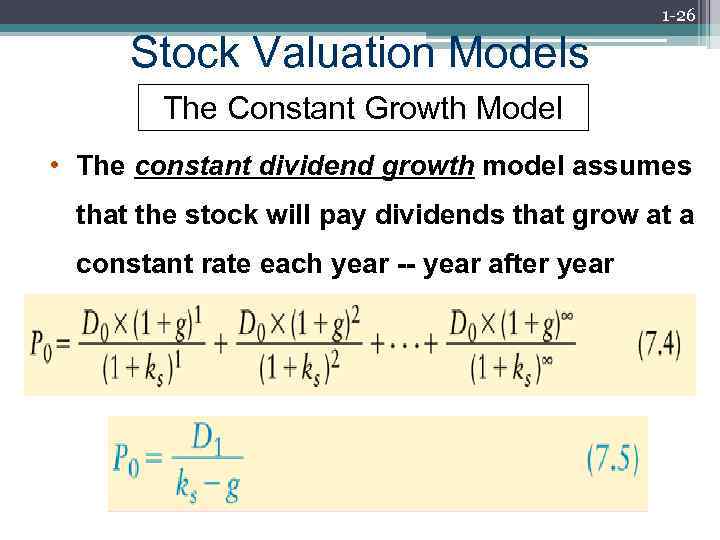 1 -26 Stock Valuation Models The Constant Growth Model • The constant dividend growth model assumes that the stock will pay dividends that grow at a constant rate each year -- year after year
1 -26 Stock Valuation Models The Constant Growth Model • The constant dividend growth model assumes that the stock will pay dividends that grow at a constant rate each year -- year after year
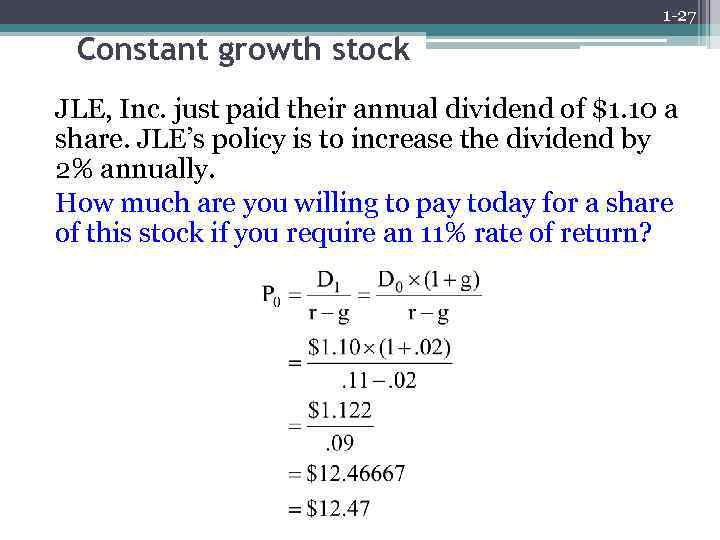 1 -27 Constant growth stock JLE, Inc. just paid their annual dividend of $1. 10 a share. JLE’s policy is to increase the dividend by 2% annually. How much are you willing to pay today for a share of this stock if you require an 11% rate of return?
1 -27 Constant growth stock JLE, Inc. just paid their annual dividend of $1. 10 a share. JLE’s policy is to increase the dividend by 2% annually. How much are you willing to pay today for a share of this stock if you require an 11% rate of return?
 1 -28 Constant growth stock SLG, Inc. announced today that they will be increasing their annual dividend to $1. 60 per share next year. After that, they expect to increase the dividend by 3% annually. You want to buy shares of stock in this company but can not afford to do so for another two years. At that time, you will buy shares if you can earn a 12% rate of return. How much will you be willing to pay for one share of this stock two years from today?
1 -28 Constant growth stock SLG, Inc. announced today that they will be increasing their annual dividend to $1. 60 per share next year. After that, they expect to increase the dividend by 3% annually. You want to buy shares of stock in this company but can not afford to do so for another two years. At that time, you will buy shares if you can earn a 12% rate of return. How much will you be willing to pay for one share of this stock two years from today?
 1 -29 Constant growth stock Alex’s Ventures, Inc. stock has a 13% rate of return and a current market price of $16. 18. The company pays annual dividends. The last dividend paid was $1. 40 per share. What is the growth rate of this stock?
1 -29 Constant growth stock Alex’s Ventures, Inc. stock has a 13% rate of return and a current market price of $16. 18. The company pays annual dividends. The last dividend paid was $1. 40 per share. What is the growth rate of this stock?
 Irregular growth stock 1 -30 Isaac’s Shoes just announced that they will commence paying annual dividends next year. The plan is to pay $. 50, $. 75 and $1. 00 per share over the next three years, respectively. After that the company plans on increasing the dividend by 2. 5% annually. The market rate of return on this stock is 12. 5%. What should the market price of this stock be?
Irregular growth stock 1 -30 Isaac’s Shoes just announced that they will commence paying annual dividends next year. The plan is to pay $. 50, $. 75 and $1. 00 per share over the next three years, respectively. After that the company plans on increasing the dividend by 2. 5% annually. The market rate of return on this stock is 12. 5%. What should the market price of this stock be?
 Irregular growth stock Nu-Tek, Inc. just paid their annual dividend of $1. 20 per share. The company has stated that dividends will increase by 20% a year for the next two years. After that, the dividends will increase by 4% annually. What is one share of this stock worth today if the required return is 14%?
Irregular growth stock Nu-Tek, Inc. just paid their annual dividend of $1. 20 per share. The company has stated that dividends will increase by 20% a year for the next two years. After that, the dividends will increase by 4% annually. What is one share of this stock worth today if the required return is 14%?
 Required return The common stock of Flo’s Home Furnishings has a 3. 5% dividend yield. You expect the company to grow by 6% annually. What is the required return on this stock?
Required return The common stock of Flo’s Home Furnishings has a 3. 5% dividend yield. You expect the company to grow by 6% annually. What is the required return on this stock?
 Required return The common stock of Roy’s Outdoor Sports Store has a market rate of return of 17. 5% and a market price of $15. 00 per share. Roy’s will pay their annual dividend next week in the amount of $2. 10 per share. What is the capital gains yield on this stock?
Required return The common stock of Roy’s Outdoor Sports Store has a market rate of return of 17. 5% and a market price of $15. 00 per share. Roy’s will pay their annual dividend next week in the amount of $2. 10 per share. What is the capital gains yield on this stock?
 Preferred stock The 7% preferred stock of Lamey, Inc. is priced to yield a 12. 5% rate of return. What is the market price of this stock?
Preferred stock The 7% preferred stock of Lamey, Inc. is priced to yield a 12. 5% rate of return. What is the market price of this stock?
 Preferred stock The Oil Town Co. pays dividends on their 6% cumulative preferred stock on an annual basis. The company has not paid this dividend for the last two years. This year the company is doing better financially and wants to pay dividends on both their preferred and their common stock. What is the minimum amount they must pay per share to their preferred stockholders before distributing any dividends to their common stockholders? Would your answer differ if the preferred stock was noncumulative? Annual dividend =. 06 $100 = $6. 00 Minimum due per share to the preferred stockholders: Cumulative: $6 + $6 = $18 Non-cumulative: $6
Preferred stock The Oil Town Co. pays dividends on their 6% cumulative preferred stock on an annual basis. The company has not paid this dividend for the last two years. This year the company is doing better financially and wants to pay dividends on both their preferred and their common stock. What is the minimum amount they must pay per share to their preferred stockholders before distributing any dividends to their common stockholders? Would your answer differ if the preferred stock was noncumulative? Annual dividend =. 06 $100 = $6. 00 Minimum due per share to the preferred stockholders: Cumulative: $6 + $6 = $18 Non-cumulative: $6
 Shareholder voting WV & BK, Inc. has 125, 000 shares of common stock outstanding. The company currently has 2 open seats on their board of directors and uses cumulative voting. How many shares of stock must you own to ensure your election to one of the open positions if you doubt that anyone else will vote for you?
Shareholder voting WV & BK, Inc. has 125, 000 shares of common stock outstanding. The company currently has 2 open seats on their board of directors and uses cumulative voting. How many shares of stock must you own to ensure your election to one of the open positions if you doubt that anyone else will vote for you?
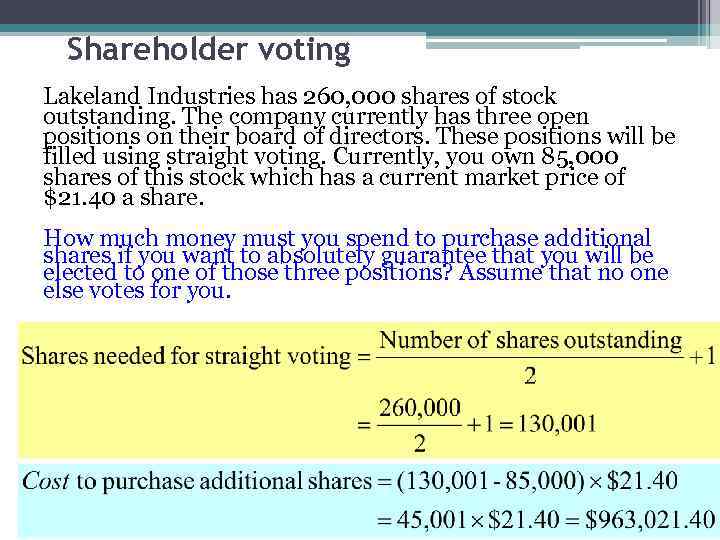 Shareholder voting Lakeland Industries has 260, 000 shares of stock outstanding. The company currently has three open positions on their board of directors. These positions will be filled using straight voting. Currently, you own 85, 000 shares of this stock which has a current market price of $21. 40 a share. How much money must you spend to purchase additional shares if you want to absolutely guarantee that you will be elected to one of those three positions? Assume that no one else votes for you.
Shareholder voting Lakeland Industries has 260, 000 shares of stock outstanding. The company currently has three open positions on their board of directors. These positions will be filled using straight voting. Currently, you own 85, 000 shares of this stock which has a current market price of $21. 40 a share. How much money must you spend to purchase additional shares if you want to absolutely guarantee that you will be elected to one of those three positions? Assume that no one else votes for you.
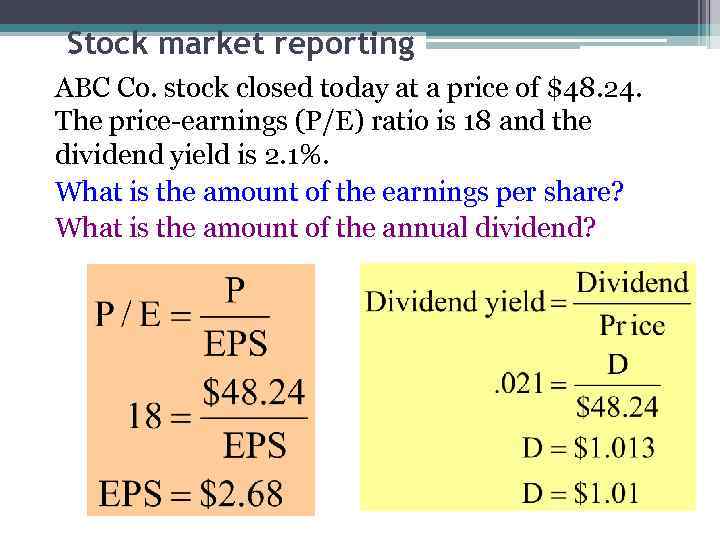 Stock market reporting ABC Co. stock closed today at a price of $48. 24. The price-earnings (P/E) ratio is 18 and the dividend yield is 2. 1%. What is the amount of the earnings per share? What is the amount of the annual dividend?
Stock market reporting ABC Co. stock closed today at a price of $48. 24. The price-earnings (P/E) ratio is 18 and the dividend yield is 2. 1%. What is the amount of the earnings per share? What is the amount of the annual dividend?


