8924066c17fb13331af8c5089b81595d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Stochastic optimization in high dimension Stéphane Vialle Stephane. Vialle@supelec. fr Xavier Warin Xavier. Warin@edf. fr Sophia 21/10/08
Stochastic optimization in high dimension Stéphane Vialle Stephane. Vialle@supelec. fr Xavier Warin Xavier. Warin@edf. fr Sophia 21/10/08
 EDF and its customers The assets 58 nuclear power plants on 19 areas (86. 6%) 14 thermal power plants (4. 6%) 440 hydro plants and 220 dams (8. 8%) Solar energy, wind power (< 0. 5%) Customers Different kind of customers A lot of style of contracts (for example swing where the producer can suspend delivery) 2 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
EDF and its customers The assets 58 nuclear power plants on 19 areas (86. 6%) 14 thermal power plants (4. 6%) 440 hydro plants and 220 dams (8. 8%) Solar energy, wind power (< 0. 5%) Customers Different kind of customers A lot of style of contracts (for example swing where the producer can suspend delivery) 2 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
 Assets management at EDF Manage water stocks, fuel , customers contracts. Goal : maximize the expected cash flow minimize risk Under constraints Satisfy the customer load Respect pollution constraints 3 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
Assets management at EDF Manage water stocks, fuel , customers contracts. Goal : maximize the expected cash flow minimize risk Under constraints Satisfy the customer load Respect pollution constraints 3 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
 Asset management at EDF Hazards : Demand Hydraulicity (inflows) Weather patterns (cold means high demand) Market prices Assets outages. Stochastic control problem in high dimension : Number of state variable linked to : Number of hazards Number of stock to be dealt with 4 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
Asset management at EDF Hazards : Demand Hydraulicity (inflows) Weather patterns (cold means high demand) Market prices Assets outages. Stochastic control problem in high dimension : Number of state variable linked to : Number of hazards Number of stock to be dealt with 4 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
 Numerical methods associated Decomposition methods (Lemaréchal) Very effective for time resolution Duality gap (non convexity) Dynamic programming (Bellman 1957) Very general (non convex, binary …) Face curse of dimensionnality, global risk constraints difficult to implement Stochastic Dual Dynamic programming (Pereira) Approximate convex Bellman values for stocks (needs convexity) Bender cuts leads to Linear Programming problem Global risk constraints difficult to implement 5 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
Numerical methods associated Decomposition methods (Lemaréchal) Very effective for time resolution Duality gap (non convexity) Dynamic programming (Bellman 1957) Very general (non convex, binary …) Face curse of dimensionnality, global risk constraints difficult to implement Stochastic Dual Dynamic programming (Pereira) Approximate convex Bellman values for stocks (needs convexity) Bender cuts leads to Linear Programming problem Global risk constraints difficult to implement 5 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
 EDF process Optimize the cost function J with approximation and keep all the optimal commands at each step (no asset constraints as ramp constraint, minimum time before restarting etc…) Use a Monte Carlo simulator with all the assets and constraints to calcule accurate average earnings, risk measure Goal Incorporate more stocks in the optimizer to be more accurate A way to do it : Use parallelism fo Stochastic Programming optimization See influence of optimisation parallelisation on simulation 6 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
EDF process Optimize the cost function J with approximation and keep all the optimal commands at each step (no asset constraints as ramp constraint, minimum time before restarting etc…) Use a Monte Carlo simulator with all the assets and constraints to calcule accurate average earnings, risk measure Goal Incorporate more stocks in the optimizer to be more accurate A way to do it : Use parallelism fo Stochastic Programming optimization See influence of optimisation parallelisation on simulation 6 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
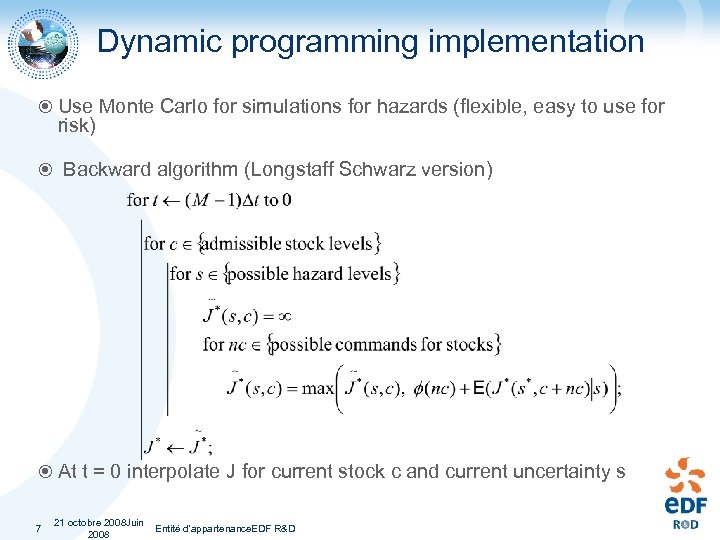 Dynamic programming implementation Use Monte Carlo for simulations for hazards (flexible, easy to use for risk) Backward algorithm (Longstaff Schwarz version) At t = 0 interpolate J for current stock c and current uncertainty s 7 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
Dynamic programming implementation Use Monte Carlo for simulations for hazards (flexible, easy to use for risk) Backward algorithm (Longstaff Schwarz version) At t = 0 interpolate J for current stock c and current uncertainty s 7 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
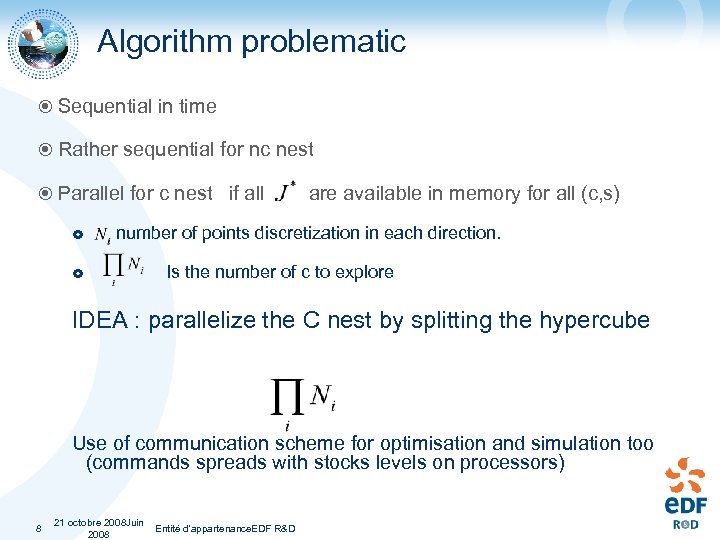 Algorithm problematic Sequential in time Rather sequential for nc nest Parallel for c nest if all are available in memory for all (c, s) number of points discretization in each direction. Is the number of c to explore IDEA : parallelize the C nest by splitting the hypercube Use of communication scheme for optimisation and simulation too (commands spreads with stocks levels on processors) 8 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
Algorithm problematic Sequential in time Rather sequential for nc nest Parallel for c nest if all are available in memory for all (c, s) number of points discretization in each direction. Is the number of c to explore IDEA : parallelize the C nest by splitting the hypercube Use of communication scheme for optimisation and simulation too (commands spreads with stocks levels on processors) 8 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
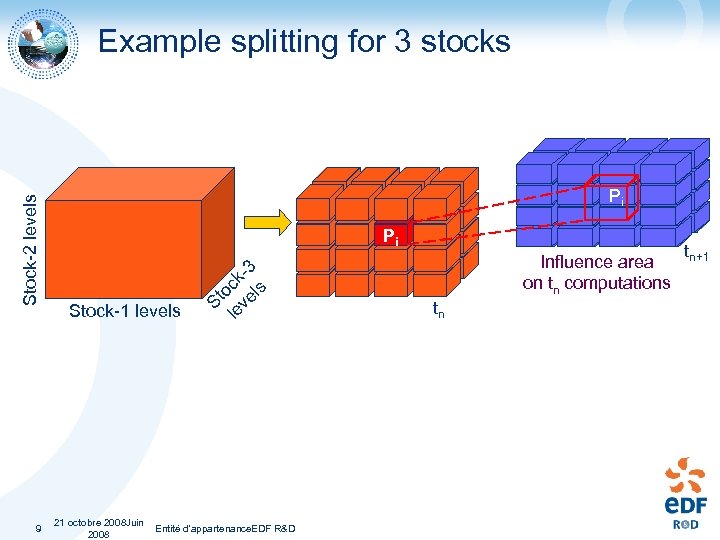 Example splitting for 3 stocks 9 Pi Stock-1 levels le ock ve -3 ls Pi St Stock-2 levels 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008 Influence area on tn computations tn tn+1
Example splitting for 3 stocks 9 Pi Stock-1 levels le ock ve -3 ls Pi St Stock-2 levels 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008 Influence area on tn computations tn tn+1
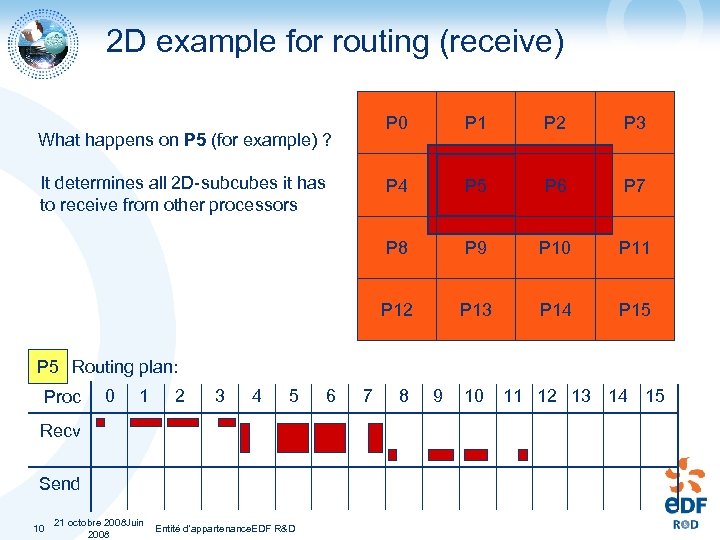 2 D example for routing (receive) P 0 P 3 P 5 P 6 P 7 P 8 P 9 P 10 P 11 P 12 It determines all 2 D-subcubes it has to receive from other processors P 2 P 4 What happens on P 5 (for example) ? P 13 P 14 P 15 P 5 Routing plan: Proc 0 1 2 3 4 5 Recv Send 10 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
2 D example for routing (receive) P 0 P 3 P 5 P 6 P 7 P 8 P 9 P 10 P 11 P 12 It determines all 2 D-subcubes it has to receive from other processors P 2 P 4 What happens on P 5 (for example) ? P 13 P 14 P 15 P 5 Routing plan: Proc 0 1 2 3 4 5 Recv Send 10 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
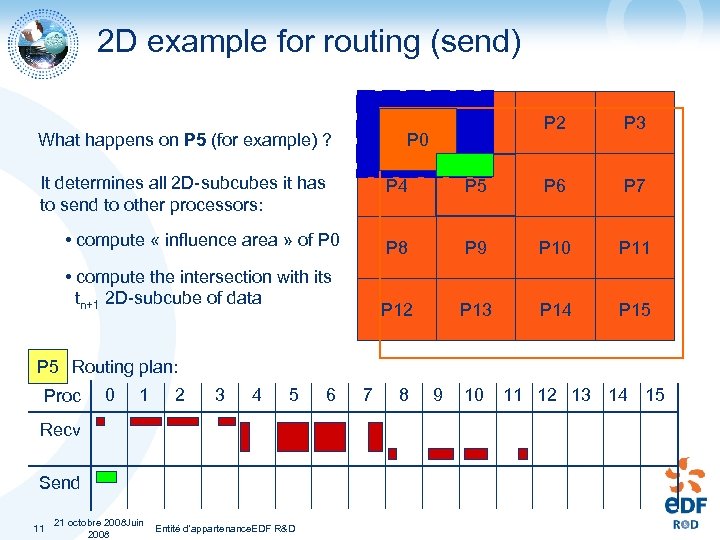 2 D example for routing (send) What happens on P 5 (for example) ? P 0 P 1 P 2 P 3 It determines all 2 D-subcubes it has to send to other processors: P 4 P 5 P 6 P 7 • compute « influence area » of P 0 P 8 P 9 P 10 P 11 • compute the intersection with its tn+1 2 D-subcube of data P 12 P 13 P 14 P 15 P 5 Routing plan: Proc 0 1 2 3 4 5 Recv Send 11 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
2 D example for routing (send) What happens on P 5 (for example) ? P 0 P 1 P 2 P 3 It determines all 2 D-subcubes it has to send to other processors: P 4 P 5 P 6 P 7 • compute « influence area » of P 0 P 8 P 9 P 10 P 11 • compute the intersection with its tn+1 2 D-subcube of data P 12 P 13 P 14 P 15 P 5 Routing plan: Proc 0 1 2 3 4 5 Recv Send 11 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
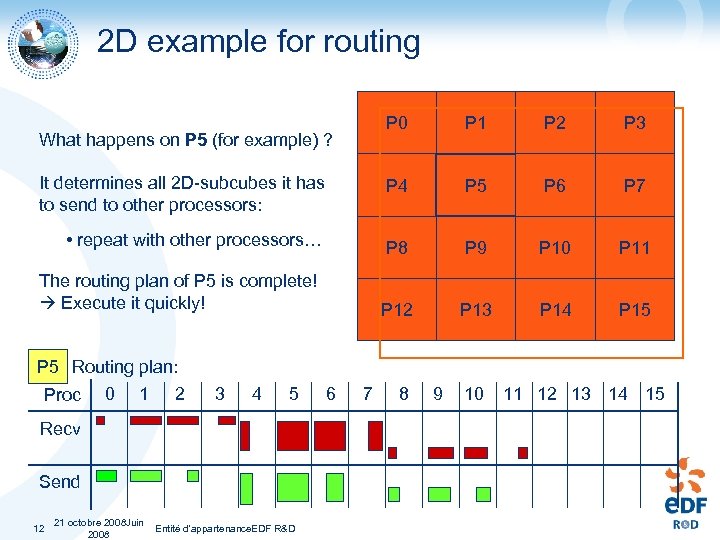 2 D example for routing P 0 P 1 P 2 P 3 It determines all 2 D-subcubes it has to send to other processors: P 4 P 5 P 6 P 7 • repeat with other processors… P 8 P 9 P 10 P 11 P 12 P 13 P 14 P 15 What happens on P 5 (for example) ? The routing plan of P 5 is complete! Execute it quickly! P 5 Routing plan: Proc 0 1 2 3 4 5 Recv Send 12 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
2 D example for routing P 0 P 1 P 2 P 3 It determines all 2 D-subcubes it has to send to other processors: P 4 P 5 P 6 P 7 • repeat with other processors… P 8 P 9 P 10 P 11 P 12 P 13 P 14 P 15 What happens on P 5 (for example) ? The routing plan of P 5 is complete! Execute it quickly! P 5 Routing plan: Proc 0 1 2 3 4 5 Recv Send 12 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
 C+ implementation Parallelization: • MPI: Mpich-1, Open. MPI, IBM MPI communication routines: MPI_Issend, MPI_Irecv, MPI_Wait overlap all communications when executing a routing plan (to speedup) do not use “extra communication buffers” (to size up) • + multithreading: Intel TBB or Open. MP to speedup and to size up more (than using only message passing) Scientific computing libraries: Blitz++, Boost, Clapack, Sprng. Total: • 57000 lines of C++ code • 10% for parallelization management • Parallelization can be withdrawn by preprocessing for small cas debug • Same source code on PC-cluster and Blue Gene/L and Blue Gene/P 13 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
C+ implementation Parallelization: • MPI: Mpich-1, Open. MPI, IBM MPI communication routines: MPI_Issend, MPI_Irecv, MPI_Wait overlap all communications when executing a routing plan (to speedup) do not use “extra communication buffers” (to size up) • + multithreading: Intel TBB or Open. MP to speedup and to size up more (than using only message passing) Scientific computing libraries: Blitz++, Boost, Clapack, Sprng. Total: • 57000 lines of C++ code • 10% for parallelization management • Parallelization can be withdrawn by preprocessing for small cas debug • Same source code on PC-cluster and Blue Gene/L and Blue Gene/P 13 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
 Test case presentation Optimization and simulation on 518 days with time step of one day One stock of water : 225 points discretizations (c) 5 commands (0 to 5000 MW each day for nc ) 6 stocks of month future products with delivery of energy (peak and off peak hours) 5 points discretization for each one 5 commandes ( -2000 MW (sell) to 2000 Mw (buy) tested every 2 weeks Aggregated view of thermal assets. Up to 225*5^6 points discretizations and 5^7 commands to tests 14 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
Test case presentation Optimization and simulation on 518 days with time step of one day One stock of water : 225 points discretizations (c) 5 commands (0 to 5000 MW each day for nc ) 6 stocks of month future products with delivery of energy (peak and off peak hours) 5 points discretization for each one 5 commandes ( -2000 MW (sell) to 2000 Mw (buy) tested every 2 weeks Aggregated view of thermal assets. Up to 225*5^6 points discretizations and 5^7 commands to tests 14 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
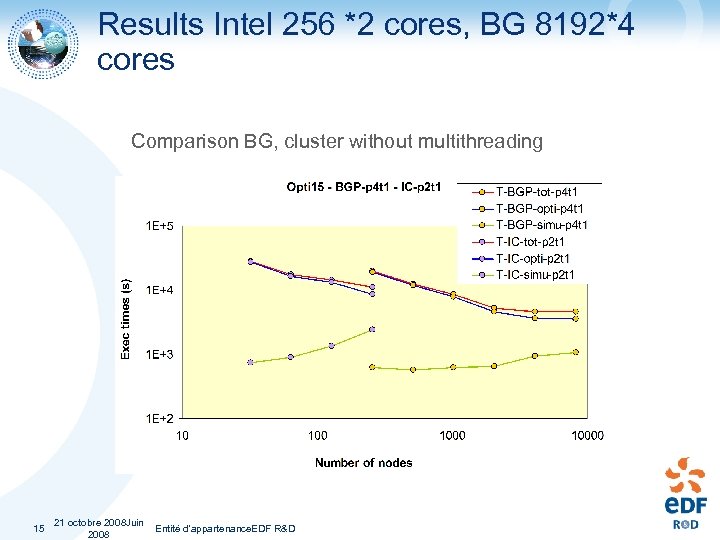 Results Intel 256 *2 cores, BG 8192*4 cores Comparison BG, cluster without multithreading 15 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
Results Intel 256 *2 cores, BG 8192*4 cores Comparison BG, cluster without multithreading 15 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
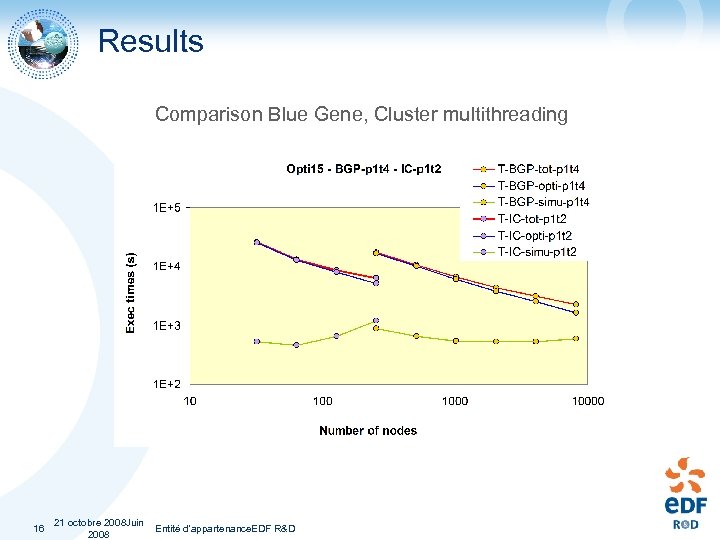 Results Comparison Blue Gene, Cluster multithreading 16 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
Results Comparison Blue Gene, Cluster multithreading 16 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
 Results • Some optimizations carried out for Blue Gene • Should improve the results in intel. • ICC should be used instead of ICC on intel • Some more optimizations on Blue Gene should bring the optimization part around 1000 s on 8192 mpi sessions with 4 threads 17 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
Results • Some optimizations carried out for Blue Gene • Should improve the results in intel. • ICC should be used instead of ICC on intel • Some more optimizations on Blue Gene should bring the optimization part around 1000 s on 8192 mpi sessions with 4 threads 17 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
 Conclusion • Tool developped for stochastic optimization with a limited number of stocks (< 10) • Will bring some reference calculation for some other methods (supposing convexity for example) giving some results on how far of optimality we are. • To be tested on EDF data without approximation for asset • Will be a candidate for GPU cluster optimization 18 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008
Conclusion • Tool developped for stochastic optimization with a limited number of stocks (< 10) • Will bring some reference calculation for some other methods (supposing convexity for example) giving some results on how far of optimality we are. • To be tested on EDF data without approximation for asset • Will be a candidate for GPU cluster optimization 18 21 octobre 2008 Juin Entité d'appartenance. EDF R&D 2008


