474b3b393ea428d0ed9865c2e801d395.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Stochastic and Rule Based Tagger for Nepali Language Krishna Sapkota Shailesh Pandey Prajol Shrestha nec & MPP

POS Tagger for Nepali • What is a Tagger? • POS Tagger Disambiguate the Lexical Category of Words in a Language • Why we need it? • Basic Necessity for NLP Research • Nepal has moved into a position where it is feeling a need for it with the Recent development of Nepalinux

Our Approach • Build a Rule Based Tagger • Simultaneously Build a Statistical Tagger • Combine Both for a Flexible Tagger with Better Overall Accuracy

Stochastic Tagger Prerequisites • A Relatively Large/Diverse Annotated Corpus • Larger and More Diverse the Corpus, Better is the Tagger

Foundations of Stochastic Approach • Markov Assumption • Hidden Markov Model • Viterbi Search
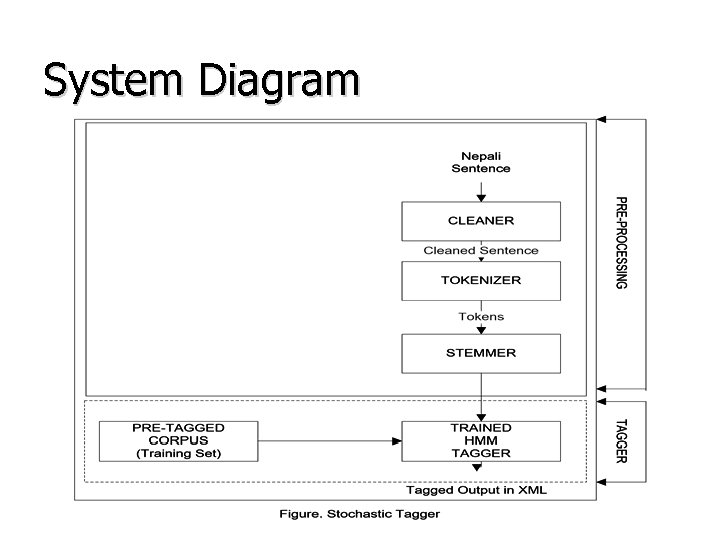
System Diagram
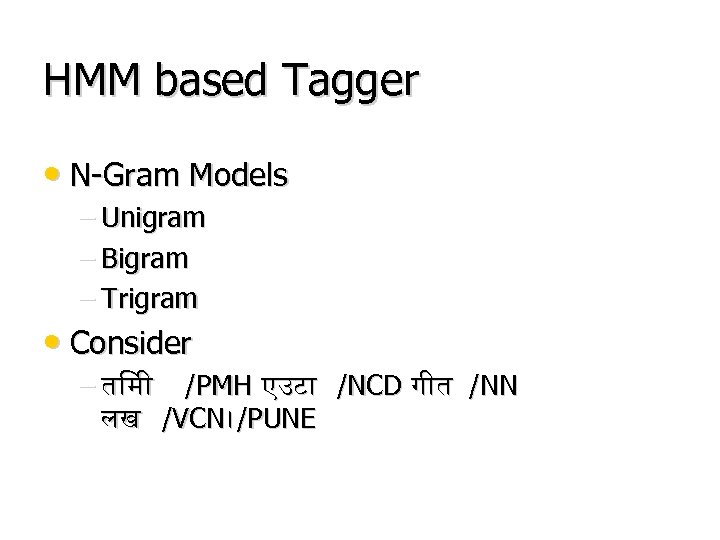
HMM based Tagger • N-Gram Models – Unigram – Bigram – Trigram • Consider – त म /PMH एउट /NCD ग त /NN लख /VCN। /PUNE

TAGGING PROCESS • Find the probability of occurrence of each category from corpus and store it – For example probability of noun occurring – No of probabilities = no of tagset • For bigram extract and store bigram probabilities – For example Noun following by determiner – No of bigram probabilities= (no of tagset)2 • Search the transitional probabilities path for best sequence of tags
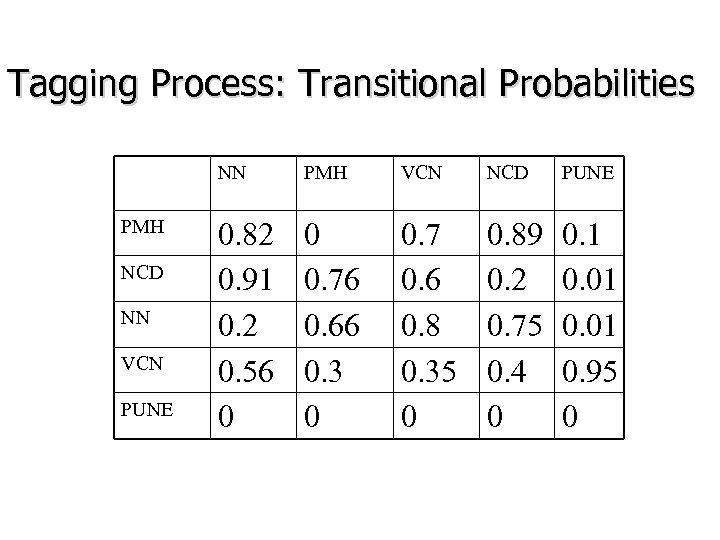
Tagging Process: Transitional Probabilities NN PMH NCD NN VCN PUNE PMH VCN NCD PUNE 0. 82 0. 91 0. 2 0. 56 0 0 0. 76 0. 66 0. 3 0 0. 7 0. 6 0. 8 0. 35 0 0. 89 0. 2 0. 75 0. 4 0 0. 1 0. 01 0. 95 0

TAGGING PROCESS: AN EXAMPLE • The tags are hidden but we see words • Is tag sequence X likely with this word Find X that maximizes the probability product of possible sequence
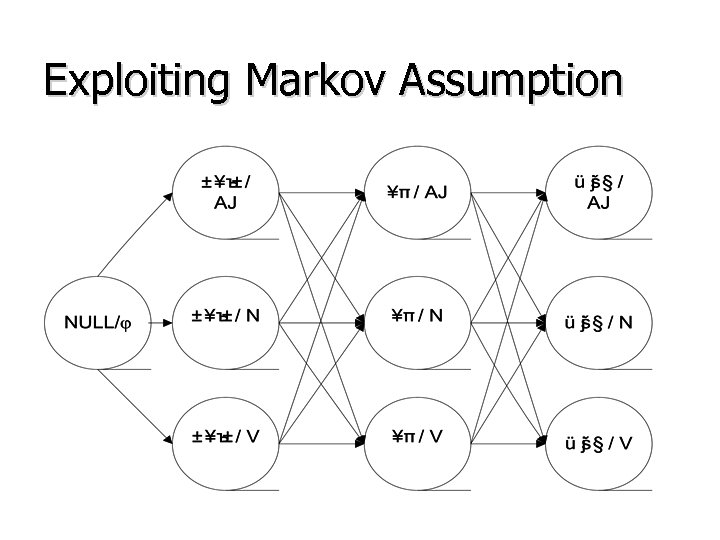
Exploiting Markov Assumption

Viterbi Search • Find the best sequence with the minimal steps – For T words and N lexical category the brute force method would require NT steps – Viterbi algorithm reduces the steps to k*T*N 2 with guarantee to find the solution

Rule Based Tagger • Rule Based POS tagging Methodology • A given word is given it's corresponding POS tag. We have a POS tagset of 91 tags generated by MPP for the general use of NLP. • Three Parts of tagging • 1 st root words tagging with lexicon look up. • 2 nd tag words based on it's morpheme. • 3 rd tag ambiguous or untagged words based on context.

• Root word tagging • A lexicon containing root words and it's corresponding POS tag will be present. Each word will be compared to the word present in the lexicon and tagged according to it. The words could be tagged with multiple POS tags. • • म न स /NN घर/NN अधय र /NC_ADQ अचमम /NC_ADQ

• Morpheme based tagging • Nepali being a very rich language in morphemes, so tagging the words with the help of morphemes. • गर +द /VDAI • गर +आउ +छ /VCHU

• Context based tagging • These context based rules are used when ambiguous words appear or if a word is not tagged. In this tagging process we consider the context in which it comes. We make rules based on the context for example : • गरन /VNE_ADR 2 POS tags • To disambiguate it we use rules such as : • If the word is followed by a NN it is ADR and if by Verb it is VNE.

• Context based tagging • Similarly if the word is untagged then: • झरझर • if झरझर प न परय । is not tagged then the word after words is a NN common noun and VYO so we could give it a ADQL adverb(qualitative).
Current Direction • Common Stemmer Design • Corpus Study • Format of Input/Output/Storage

References • J. Allen “Natural Language Understanding”, Pearson Edition • Scott M. Thede and Mary P. Harper. A second-order Hidden Markov Model for • part-of-speech tagging. In Proceedings of the 37 th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pages 175 --182. • • • http: //citeseer. ist. psu. edu/thede 99 secondorder. html Automated Part of Speech Tagging, Handout for LING 361, Fall 1995. Georgetown University. http: //www. georgetown. edu/faculty/ballc/ling 361/tagging_overview. html Hardie et al. Nelralec/Bhasha Sanchar Working Paper 2 Categorisation for automated morphosyntactic analysis of Nepali: introducing the Nelralec Tagset (NT-01) http: //www. bhashasanchar. org. /dfs/nelralec-wp-tagset. pdf D. Jurafsky and J. H. Martin, “Speech and Language Processing”, Pearson Edition. IITB India, Seminar report

• Questions • Thank You!
474b3b393ea428d0ed9865c2e801d395.ppt