65a4a13e4b34f7ab10e5c9de75ce0d7b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 134
 Stereotypes
Stereotypes
 Definition of Stereotype Fixed form or convention n Something lacking in originality or individuality n
Definition of Stereotype Fixed form or convention n Something lacking in originality or individuality n
 How we get information n Somatic n What we personal experience through our senses
How we get information n Somatic n What we personal experience through our senses
 How we get information n Extrasomatic n Sources of information external to your personal senses
How we get information n Extrasomatic n Sources of information external to your personal senses
 How we get information n Mechanical sources n Extend our senses n Microscopes and telescopes for sight n Amplifiers for sound
How we get information n Mechanical sources n Extend our senses n Microscopes and telescopes for sight n Amplifiers for sound
 How we get information n Association n Depends on who we associate with n Also known as socialization n Leads to how we behave through a series of steps n Emotion n Belief n Attitude n Finally, behavior
How we get information n Association n Depends on who we associate with n Also known as socialization n Leads to how we behave through a series of steps n Emotion n Belief n Attitude n Finally, behavior
 How we get information n Vicariously Through imagination n Through the media n
How we get information n Vicariously Through imagination n Through the media n
 What do we do with all that information? Sort it into categories n The categories are stereotypes n Why categorize? n So we can think n It’s the way the human mind works n
What do we do with all that information? Sort it into categories n The categories are stereotypes n Why categorize? n So we can think n It’s the way the human mind works n
 Pigeonholing Put any and all information we gather about anything, regardless of source, into a box, the stereotype n Most stereotypes are very complex n
Pigeonholing Put any and all information we gather about anything, regardless of source, into a box, the stereotype n Most stereotypes are very complex n
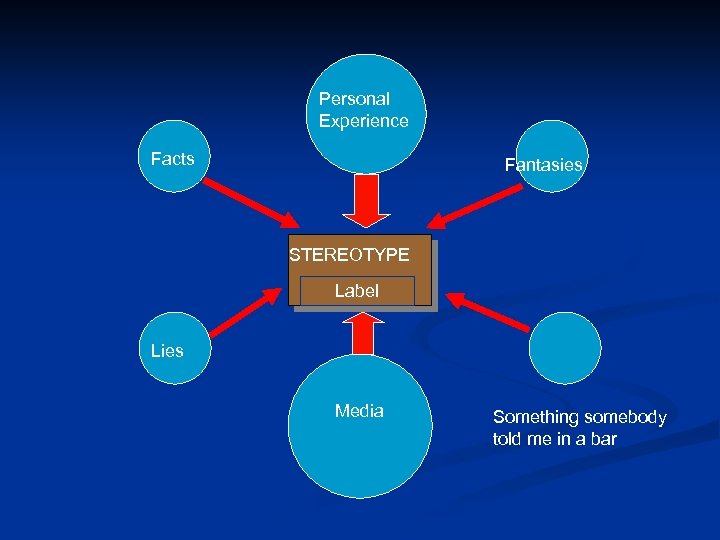 Personal Experience Facts Fantasies STEREOTYPE Label Lies Media Something somebody told me in a bar
Personal Experience Facts Fantasies STEREOTYPE Label Lies Media Something somebody told me in a bar
 Stereotypes are shortcuts to thinking Called a “heuristic” device n Identify superficial characteristics n n See, hear, smell something What you perceive triggers a stereotype box n Everything in the box comes out as a single, solid block of information, whether the information is true or not n
Stereotypes are shortcuts to thinking Called a “heuristic” device n Identify superficial characteristics n n See, hear, smell something What you perceive triggers a stereotype box n Everything in the box comes out as a single, solid block of information, whether the information is true or not n
 Back to Stereotypes What’s important is the contents of that box n Recap n Primary sources are what you put in personally n Secondary are from other sources n n A rank is assigned to what’s in the box
Back to Stereotypes What’s important is the contents of that box n Recap n Primary sources are what you put in personally n Secondary are from other sources n n A rank is assigned to what’s in the box
 Stereotypes are neither positive nor negative n Depends on if others’ stereotypes match your own n You perceive a stereotype as negative if it doesn’t match your own n Stereotypes that do match your own you consider to be facts n
Stereotypes are neither positive nor negative n Depends on if others’ stereotypes match your own n You perceive a stereotype as negative if it doesn’t match your own n Stereotypes that do match your own you consider to be facts n
 reality n People create their own n Varies from person to person
reality n People create their own n Varies from person to person
 Why Are There Stereotypes in the media? Reflects the reality of the audience n Economic factors n
Why Are There Stereotypes in the media? Reflects the reality of the audience n Economic factors n
 Occupations Police Officers – greatly overrepresented n Lawyers & Courtroom Trials – real or fictional, it’s sensationalized… n Farmers – where is media produced? n College Students – One Bourbon, One Shot, and One Beer n
Occupations Police Officers – greatly overrepresented n Lawyers & Courtroom Trials – real or fictional, it’s sensationalized… n Farmers – where is media produced? n College Students – One Bourbon, One Shot, and One Beer n
 TV and Stereotypes n Uses stereotypes the audience already holds n Don’t want to challenge beliefs: that might turn the audience away
TV and Stereotypes n Uses stereotypes the audience already holds n Don’t want to challenge beliefs: that might turn the audience away
 TV and Stereotypes n 1950 s n Leave It to Beaver, Father Knows Best stereotypes n Good vs. evil stereotypes
TV and Stereotypes n 1950 s n Leave It to Beaver, Father Knows Best stereotypes n Good vs. evil stereotypes
 Leave It to Beaver
Leave It to Beaver
 The Donna Reed Show
The Donna Reed Show
 Father Knows Best
Father Knows Best
 Martin Kane – Private Eye
Martin Kane – Private Eye
 The Untouchables
The Untouchables
 TV and Stereotypes n n 1950 s n Leave It to Beaver, Father Knows Best stereotypes Late 1960 s to today n Rise of anti-war and women’s and civil rights n Challenged old stereotypes and reinforced new ones
TV and Stereotypes n n 1950 s n Leave It to Beaver, Father Knows Best stereotypes Late 1960 s to today n Rise of anti-war and women’s and civil rights n Challenged old stereotypes and reinforced new ones
 Bewitched
Bewitched
 I Dream of Jeannie
I Dream of Jeannie
 The Dick van Dyke Show
The Dick van Dyke Show


 Julia
Julia


 TV and Stereotypes n Introduction of cable Hundreds of channels n Can find a channel that reflects whatever your stereotypes are n
TV and Stereotypes n Introduction of cable Hundreds of channels n Can find a channel that reflects whatever your stereotypes are n
 Movies and Stereotypes n Use the stereotypes held by the makers Makes their beliefs part of their audience’s stereotypes n D. W. Griffith’s “Birth of a Nation” (1915) n
Movies and Stereotypes n Use the stereotypes held by the makers Makes their beliefs part of their audience’s stereotypes n D. W. Griffith’s “Birth of a Nation” (1915) n
 Society was local and parochial
Society was local and parochial
 Society became more homogenous
Society became more homogenous
 Movies reflect the makers’ society
Movies reflect the makers’ society
 Birth of a Nation - 1915 D. W. Griffith’s epic about the Civil War n He was a racist, segregationist and supporter of the Confederacy n Extolled the Ku Klux Klan as heroes n Portrayed freed black slaves as rampaging animals and rapists of white women n
Birth of a Nation - 1915 D. W. Griffith’s epic about the Civil War n He was a racist, segregationist and supporter of the Confederacy n Extolled the Ku Klux Klan as heroes n Portrayed freed black slaves as rampaging animals and rapists of white women n

 KKK in Wash. , DC – 1925
KKK in Wash. , DC – 1925
 Joseph Goebbels
Joseph Goebbels
 Der Ewvige Jude
Der Ewvige Jude
 Der Ewige Jude n Wherever rats appear they bring ruin, by destroying mankind's goods and foodstuffs.
Der Ewige Jude n Wherever rats appear they bring ruin, by destroying mankind's goods and foodstuffs.
 n They are cunning, cowardly, and cruel, and are found mostly in large packs. Among the animals, they represent the rudiment of an insidious and underground destruction -
n They are cunning, cowardly, and cruel, and are found mostly in large packs. Among the animals, they represent the rudiment of an insidious and underground destruction -
 n - just like the Jews among human beings.
n - just like the Jews among human beings.
 Wake Island
Wake Island
 Destination: Tokyo
Destination: Tokyo
 Wake Island
Wake Island
 Mrs. Miniver
Mrs. Miniver
 Since You Went Away
Since You Went Away
 The Wild One
The Wild One

 Rebel Without a Cause
Rebel Without a Cause
 12 Angry Men
12 Angry Men


 Giant
Giant
 Easy Rider
Easy Rider
 Easy Rider
Easy Rider
 To Kill a Mockingbird
To Kill a Mockingbird
 In the Heat of the Night
In the Heat of the Night




 Little Big Man
Little Big Man
 Dances With Wolves
Dances With Wolves
 Jaws
Jaws


 Inside Out
Inside Out
 Gender & Stereotyping Common gender roles n Common gender shapes n Objectification common n
Gender & Stereotyping Common gender roles n Common gender shapes n Objectification common n
 Roles of women n Disproportionately seen in domestic roles Laundry, cleaning, cooking n Child care n
Roles of women n Disproportionately seen in domestic roles Laundry, cleaning, cooking n Child care n


 Roles of women n Business, professional, community roles Range of occupational roles has increased n The Superwoman
Roles of women n Business, professional, community roles Range of occupational roles has increased n The Superwoman
 3 Common Stereotyped Portrayals n Women as Objects
3 Common Stereotyped Portrayals n Women as Objects
 3 Common Stereotyped Portrayals n Women as submissive
3 Common Stereotyped Portrayals n Women as submissive
 3 Common Stereotyped Portrayals n Women as inferior
3 Common Stereotyped Portrayals n Women as inferior

 Sex Appeal n Gender linked because of different goals: n For men it’s sex with ease and no complications n In other words, attract more women that want to have sex with you n For women it’s attract more men from which to choose n Select the best among the possible choices, and the greater the selection, the better the choice
Sex Appeal n Gender linked because of different goals: n For men it’s sex with ease and no complications n In other words, attract more women that want to have sex with you n For women it’s attract more men from which to choose n Select the best among the possible choices, and the greater the selection, the better the choice
 Sex Appeal n Male and female animals have different sexual strategies based on the cost of sex n Males are promiscuous because the cost is very low n A little time, a little energy, then move on n Criteria are simple – she has to be there, breathing, and impregnable n Females are picky because the cost is so high n Lots of time, lots of energy n Must select the best possible male, not the nearest n Criteria can be complex
Sex Appeal n Male and female animals have different sexual strategies based on the cost of sex n Males are promiscuous because the cost is very low n A little time, a little energy, then move on n Criteria are simple – she has to be there, breathing, and impregnable n Females are picky because the cost is so high n Lots of time, lots of energy n Must select the best possible male, not the nearest n Criteria can be complex
 n Non-humans are concerned with genetics Males want, on an instinctive level, to have as many offspring as possible to ensure genetic success n Females, because of the cost of reproduction, on an instinctive level want the best genes in their male n Males compete with other males, usually physically, to demonstrate they’re the best choice n Females select the winner because he’s shown he’s better than the other males n
n Non-humans are concerned with genetics Males want, on an instinctive level, to have as many offspring as possible to ensure genetic success n Females, because of the cost of reproduction, on an instinctive level want the best genes in their male n Males compete with other males, usually physically, to demonstrate they’re the best choice n Females select the winner because he’s shown he’s better than the other males n
 Sex appeal in humans Humans have the most complex social life on Earth n Instinctive criteria for men are the same as for any other male animal – she’s there n Criteria for women is far more complex: n n Not just genetically, but socially: n Be a good father – help with raising children n be a good provider – have money, social connections, etc.
Sex appeal in humans Humans have the most complex social life on Earth n Instinctive criteria for men are the same as for any other male animal – she’s there n Criteria for women is far more complex: n n Not just genetically, but socially: n Be a good father – help with raising children n be a good provider – have money, social connections, etc.
 Sex appeal for men n n Buy the product, get the woman Think of all those Axe commercials
Sex appeal for men n n Buy the product, get the woman Think of all those Axe commercials

 Portrayals of women n Physical Appearance n Youth = beauty n Primary goal: stay young and attractive n Age n Women over 30, and especially those 50+ are underrepresented n 70% of women in TV ads are under 35 n 40% of men
Portrayals of women n Physical Appearance n Youth = beauty n Primary goal: stay young and attractive n Age n Women over 30, and especially those 50+ are underrepresented n 70% of women in TV ads are under 35 n 40% of men
 Nothing New
Nothing New
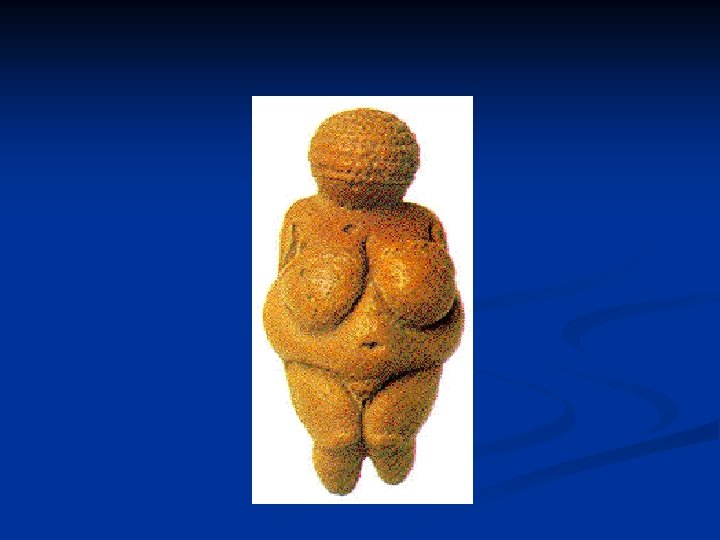




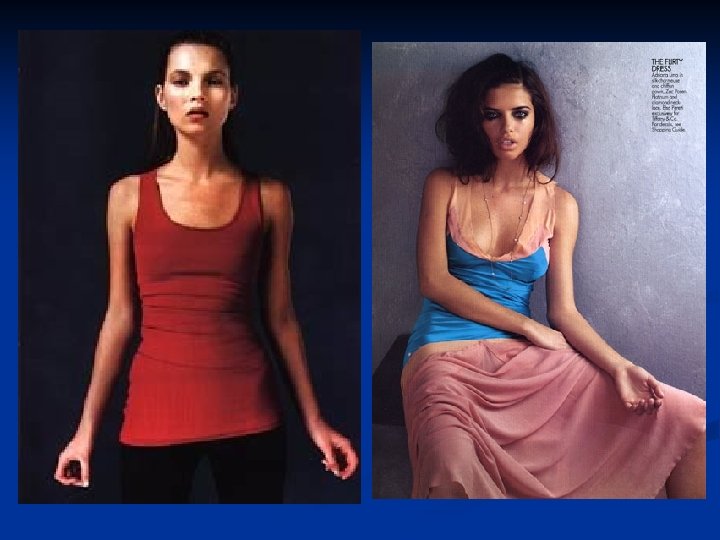
 Portrayals of women n Thin ideal n Average U. S. woman: 5’ 4” and 140 lbs. Average U. S. model: 5’ 11” and 117 lbs. Gap widening between models and real women n 1975: 8% less than the average woman Now: 23% less Even young girls are body conscious Many 6 to 12 -ys olds have been on a diet (35%) 53% of 13 -yr olds report being unhappy with their bodies Most normal weight girls believe they are overweight (50 -70%)
Portrayals of women n Thin ideal n Average U. S. woman: 5’ 4” and 140 lbs. Average U. S. model: 5’ 11” and 117 lbs. Gap widening between models and real women n 1975: 8% less than the average woman Now: 23% less Even young girls are body conscious Many 6 to 12 -ys olds have been on a diet (35%) 53% of 13 -yr olds report being unhappy with their bodies Most normal weight girls believe they are overweight (50 -70%)

 Representations of men n Some very stable stereotypes Sturdy oak: Hard working, good provider n Big wheel: trappings of social and financial success n Tough, emotionless beings n
Representations of men n Some very stable stereotypes Sturdy oak: Hard working, good provider n Big wheel: trappings of social and financial success n Tough, emotionless beings n




 Representations of men n Physical appearance Attractive & strong Upper body muscles, six pack Less emphasis on slight aging Gray hair But emphasis on young and strong Balding weakness
Representations of men n Physical appearance Attractive & strong Upper body muscles, six pack Less emphasis on slight aging Gray hair But emphasis on young and strong Balding weakness

 Representations of men n Roles: Primarily outside the home n Uncomfortable/out of place in domestic roles n Unable to function with regard to housework, child care n Need to be bailed out by wife n
Representations of men n Roles: Primarily outside the home n Uncomfortable/out of place in domestic roles n Unable to function with regard to housework, child care n Need to be bailed out by wife n



 Stereotypes on TV n Two types of data: n How TV portrays certain groups n How stereotyped TV affects viewers
Stereotypes on TV n Two types of data: n How TV portrays certain groups n How stereotyped TV affects viewers
 How TV Portrays Gender Men are more prevalent (60%/40%) n When women are portrayed, they tend to be: n Younger than men (18 -34 yrs vs. 18 -56 yrs) n Romantically involved n Dressed provocatively n Employed in lower paying jobs n
How TV Portrays Gender Men are more prevalent (60%/40%) n When women are portrayed, they tend to be: n Younger than men (18 -34 yrs vs. 18 -56 yrs) n Romantically involved n Dressed provocatively n Employed in lower paying jobs n
 Gender in Children’s Saturday AM Programs by Network (Calvert et al. , 1997)
Gender in Children’s Saturday AM Programs by Network (Calvert et al. , 1997)
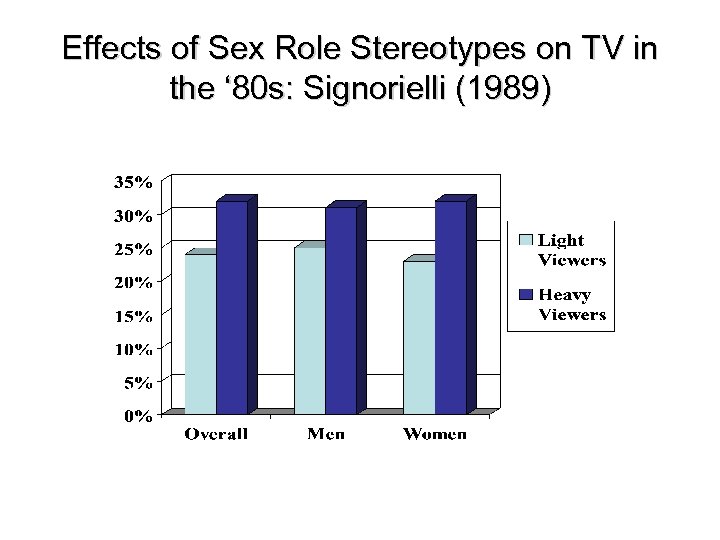 Effects of Sex Role Stereotypes on TV in the ‘ 80 s: Signorielli (1989)
Effects of Sex Role Stereotypes on TV in the ‘ 80 s: Signorielli (1989)
 Effects of Gender Stereotypes on Viewers n Positive correlation between TV viewing and sexist attitudes
Effects of Gender Stereotypes on Viewers n Positive correlation between TV viewing and sexist attitudes
 Effects of Gender Stereotypes on Viewers (Jennings et al) Women viewed traditional or role-reversed ads n Role reversed ads: n Independence of judgment n Self-confidence in public speaking n n Traditional ads: n Women who viewed traditional ads were less independent and less self-confident
Effects of Gender Stereotypes on Viewers (Jennings et al) Women viewed traditional or role-reversed ads n Role reversed ads: n Independence of judgment n Self-confidence in public speaking n n Traditional ads: n Women who viewed traditional ads were less independent and less self-confident
 TV and Kid’s Beliefs About Chores: Signorielli & Lears (1992) n n Study of 4 th and 5 th grade boys and girls Chores included washing dishes, mow lawn, help cook, help clean, make bed, household repairs Kids indicated which were boys only, girls only, or either boys or girls TV viewing positively correlated with sexstereotyped attitudes toward chores (. 25 overall, . 25 for boys, . 22 for girls)
TV and Kid’s Beliefs About Chores: Signorielli & Lears (1992) n n Study of 4 th and 5 th grade boys and girls Chores included washing dishes, mow lawn, help cook, help clean, make bed, household repairs Kids indicated which were boys only, girls only, or either boys or girls TV viewing positively correlated with sexstereotyped attitudes toward chores (. 25 overall, . 25 for boys, . 22 for girls)
 Minorities on Prime-Time TV n Blacks n n Latinos n n Currently around 3%, significant under-representation and little change over time Asian Americans n n Currently around 18% of recurring characters, represents a large increase over time Currently around 2%, little change over time Native Americans n Few if any on TV
Minorities on Prime-Time TV n Blacks n n Latinos n n Currently around 3%, significant under-representation and little change over time Asian Americans n n Currently around 18% of recurring characters, represents a large increase over time Currently around 2%, little change over time Native Americans n Few if any on TV
 Content of Ethnic Stereotypes on TV News: Dixon & Linz (2000) Examined local news programs in LA area n Intergroup comparisons n Interrole comparisons n Interreality comparison n
Content of Ethnic Stereotypes on TV News: Dixon & Linz (2000) Examined local news programs in LA area n Intergroup comparisons n Interrole comparisons n Interreality comparison n
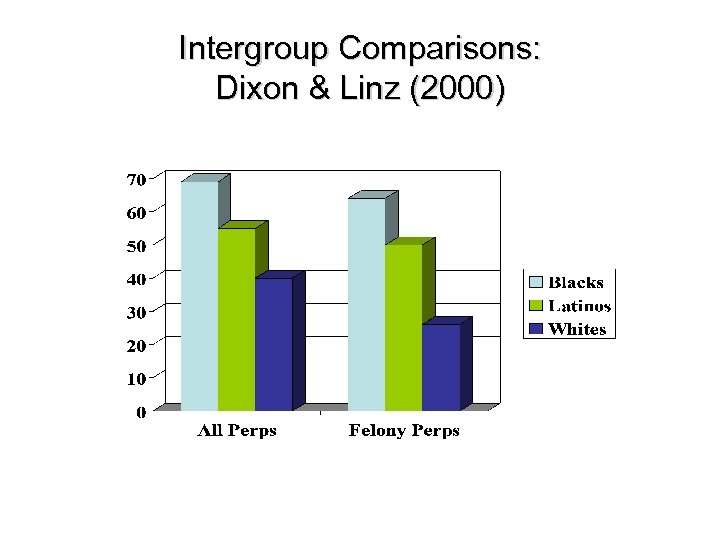 Intergroup Comparisons: Dixon & Linz (2000)
Intergroup Comparisons: Dixon & Linz (2000)
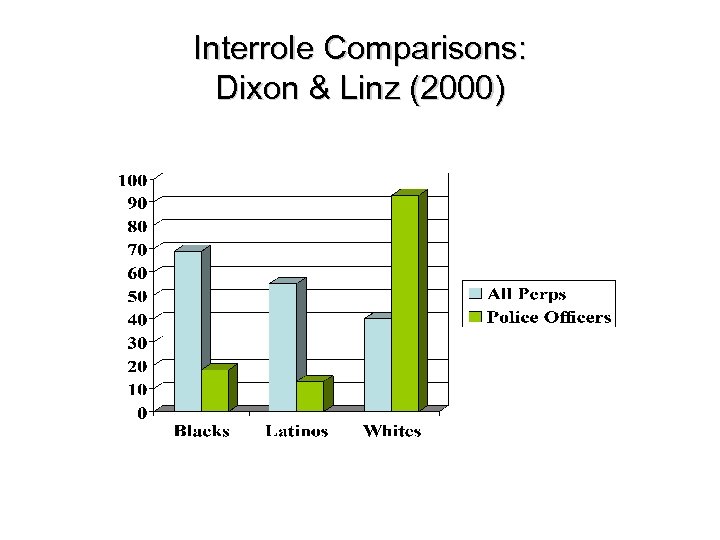 Interrole Comparisons: Dixon & Linz (2000)
Interrole Comparisons: Dixon & Linz (2000)
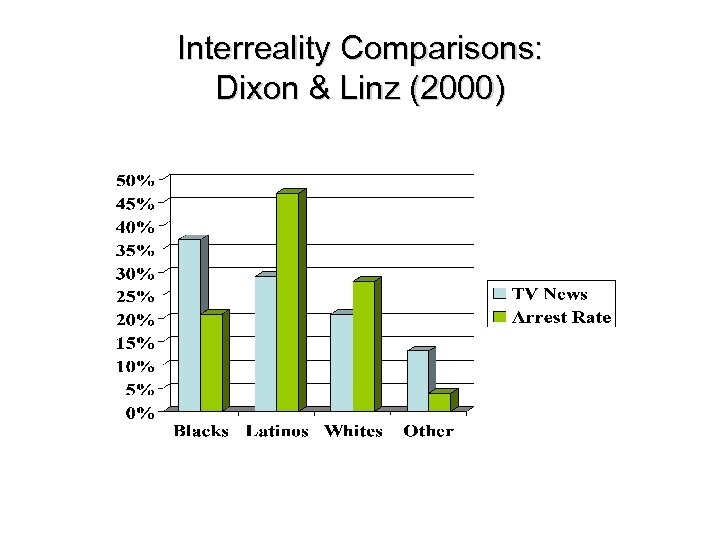 Interreality Comparisons: Dixon & Linz (2000)
Interreality Comparisons: Dixon & Linz (2000)
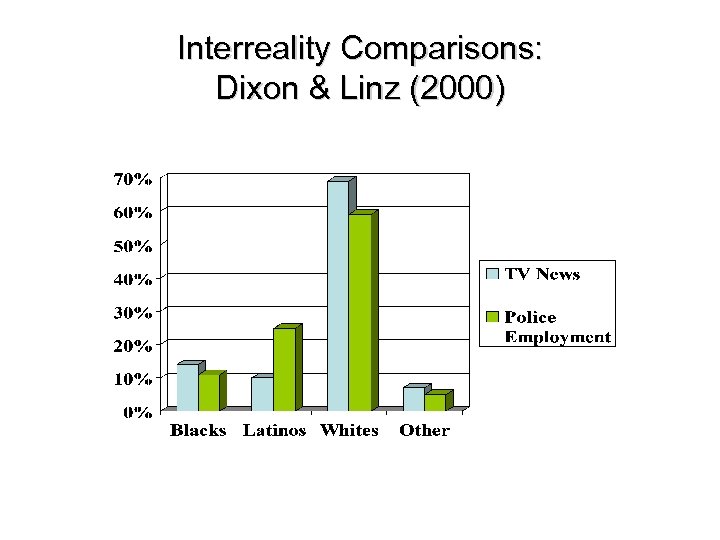 Interreality Comparisons: Dixon & Linz (2000)
Interreality Comparisons: Dixon & Linz (2000)
 Portrayals of African Americans in media: Two Important Factors Recognition n Respect n
Portrayals of African Americans in media: Two Important Factors Recognition n Respect n
 Minority Portrayals The Four stages of Minority Portrayals 1. ) Non-Recognition – exclusion from media n 2. ) Ridicule – the dominant group bolster itself by putting down & stereotyping the minority
Minority Portrayals The Four stages of Minority Portrayals 1. ) Non-Recognition – exclusion from media n 2. ) Ridicule – the dominant group bolster itself by putting down & stereotyping the minority
 Stepin Fetchit
Stepin Fetchit
 Bill “Bojangles” Robinson
Bill “Bojangles” Robinson
 Eddie Cantor
Eddie Cantor
 Beulah / Amos ‘n’ Andy
Beulah / Amos ‘n’ Andy
 Minority Portrayals The Four stages of Minority Portrayals 1. ) Non-Recognition – exclusion from media n 2. ) Ridicule – the dominant group bolster itself by putting down & stereotyping the minority 3. ) Regulation – minority group members appear as protectors of the existing order
Minority Portrayals The Four stages of Minority Portrayals 1. ) Non-Recognition – exclusion from media n 2. ) Ridicule – the dominant group bolster itself by putting down & stereotyping the minority 3. ) Regulation – minority group members appear as protectors of the existing order


 Minority Portrayals The Four stages of Minority Portrayals 1. ) Non-Recognition – exclusion from media n 2. ) Ridicule – the dominant group bolster itself by putting down & stereotyping the minority 3. ) Regulation – minority group members appear as protectors of the existing order 4. ) Respect – appearance in full range of roles
Minority Portrayals The Four stages of Minority Portrayals 1. ) Non-Recognition – exclusion from media n 2. ) Ridicule – the dominant group bolster itself by putting down & stereotyping the minority 3. ) Regulation – minority group members appear as protectors of the existing order 4. ) Respect – appearance in full range of roles
 Samuel L. Jackson
Samuel L. Jackson
 Morgan Freeman
Morgan Freeman
 Effects of Viewing Stereotyped Portrayals of African Americans (Armstrong et al. ) n n Effects of TV entertainment and news viewing 2 surveys, measured n n n Viewing of entertainment and news Perception of African Americans’ economic condition Findings n n TV news viewing related to believing that African Americans had lower economic standing TV entertainment viewing related to believing that African Americans had higher economic standing
Effects of Viewing Stereotyped Portrayals of African Americans (Armstrong et al. ) n n Effects of TV entertainment and news viewing 2 surveys, measured n n n Viewing of entertainment and news Perception of African Americans’ economic condition Findings n n TV news viewing related to believing that African Americans had lower economic standing TV entertainment viewing related to believing that African Americans had higher economic standing
 What Theories Could Explain Effects of Media on Stereotypes? n Cultivation n n Social Learning Theory n n n Influences perceptions about the behaviors of members of other groups with whom we have little contact Imitation of behaviors of models on TV Lack of models, or punishment, reduces modeling of behavior among certain groups Priming n Influence how we interpret behaviors of specific group members
What Theories Could Explain Effects of Media on Stereotypes? n Cultivation n n Social Learning Theory n n n Influences perceptions about the behaviors of members of other groups with whom we have little contact Imitation of behaviors of models on TV Lack of models, or punishment, reduces modeling of behavior among certain groups Priming n Influence how we interpret behaviors of specific group members


