7243d146478951bad5f8d111c07219bb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Stereotactic Gamma Knife Raiodusrgery For Vestibular Schwannoma Ming-Hsi Sun Hung-Chuan Pan Chiung-Chyi Shen Neurosurgery Taichung Veterans General Hospital Neuroscience combined conference

1968 - The first prototype of Leksell Gamma Knife® was installed in Stockholm, Sweden. The delivery of a single, high dose of irradiation to a small and critically located intracranial volume through the intact skull
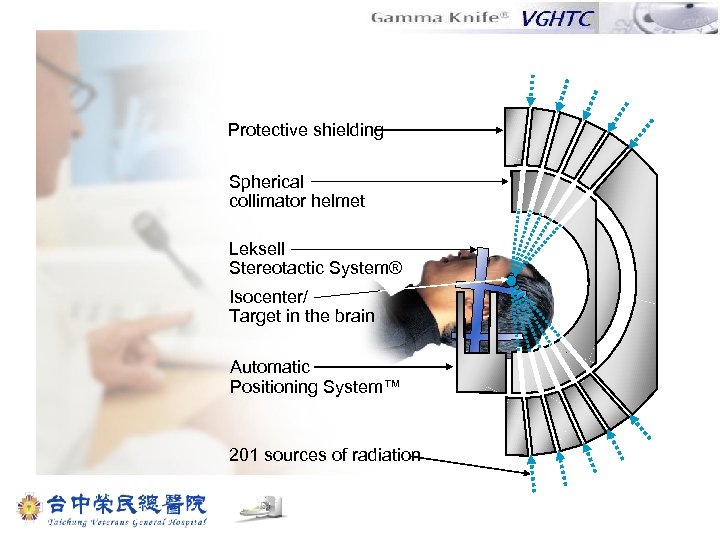
Protective shielding Spherical collimator helmet Leksell Stereotactic System® Isocenter/ Target in the brain Automatic Positioning System™ 201 sources of radiation
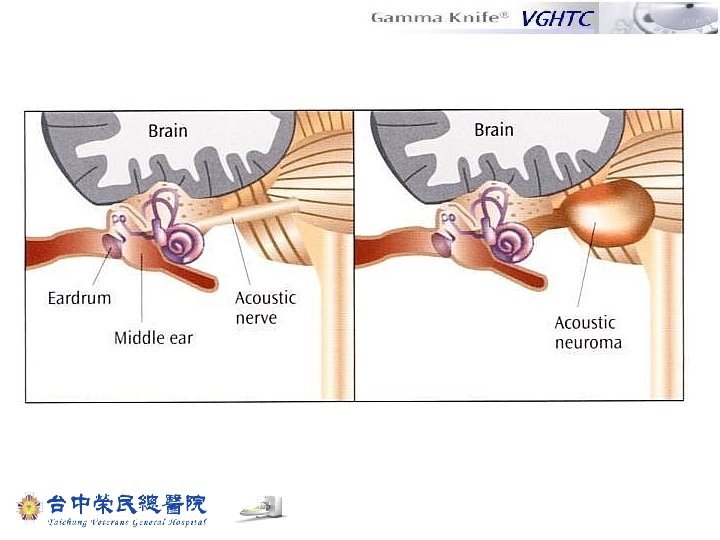
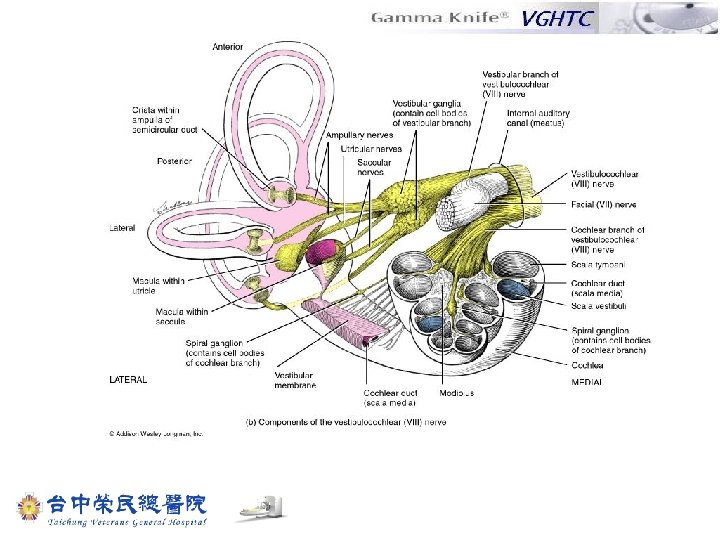
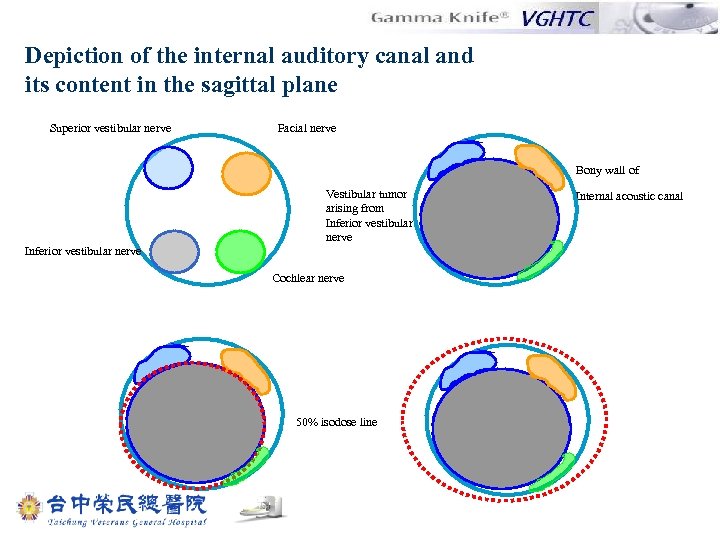
Depiction of the internal auditory canal and its content in the sagittal plane Superior vestibular nerve Facial nerve Bony wall of Vestibular tumor arising from Inferior vestibular nerve Cochlear nerve 50% isodose line Internal acoustic canal
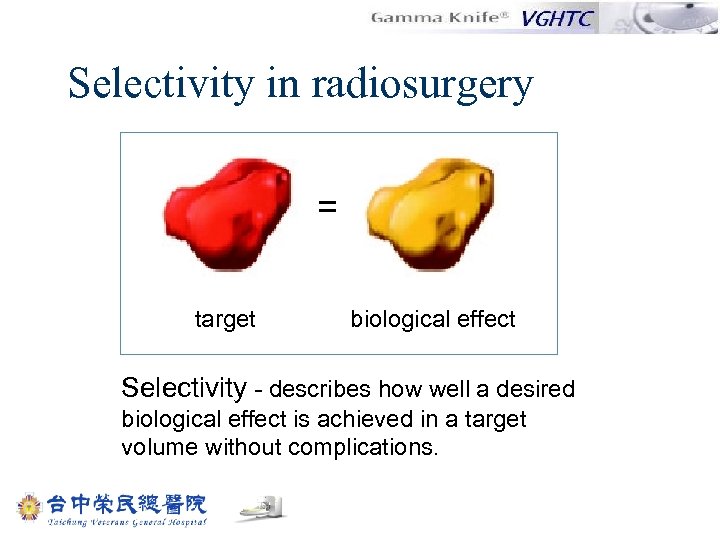
Selectivity in radiosurgery = target biological effect Selectivity - describes how well a desired biological effect is achieved in a target volume without complications.
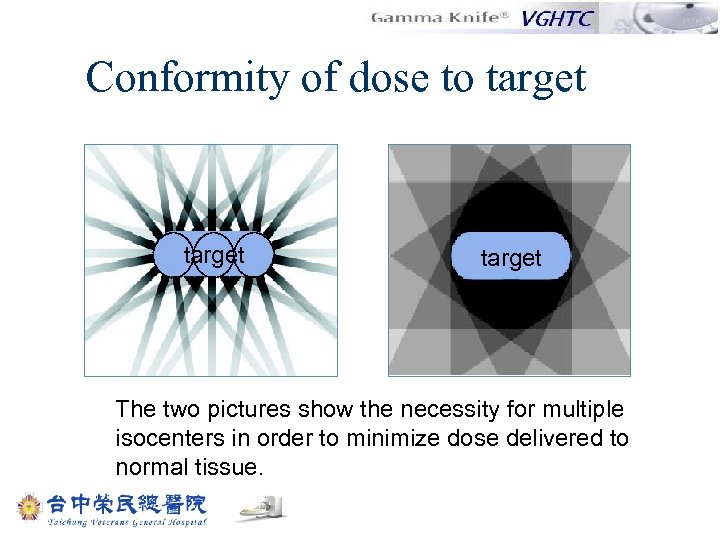
Conformity of dose to target The two pictures show the necessity for multiple isocenters in order to minimize dose delivered to normal tissue.
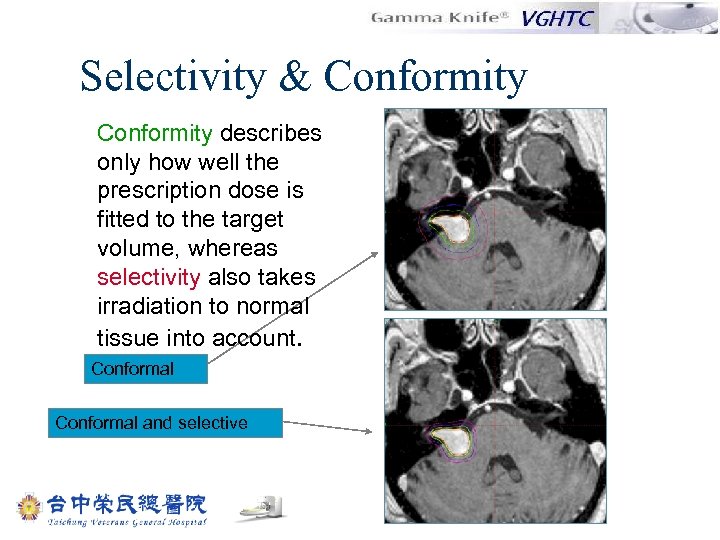
Selectivity & Conformity describes only how well the prescription dose is fitted to the target volume, whereas selectivity also takes irradiation to normal tissue into account. Conformal and selective
Gamma Knife® surgery
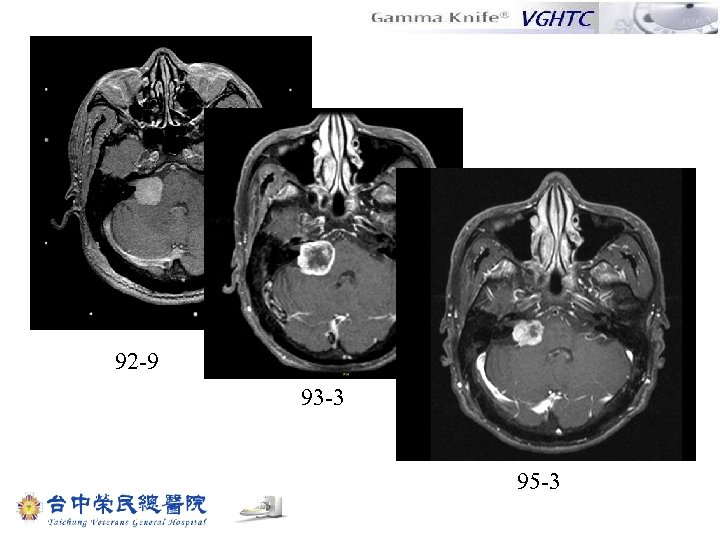
92 -9 93 -3 95 -3
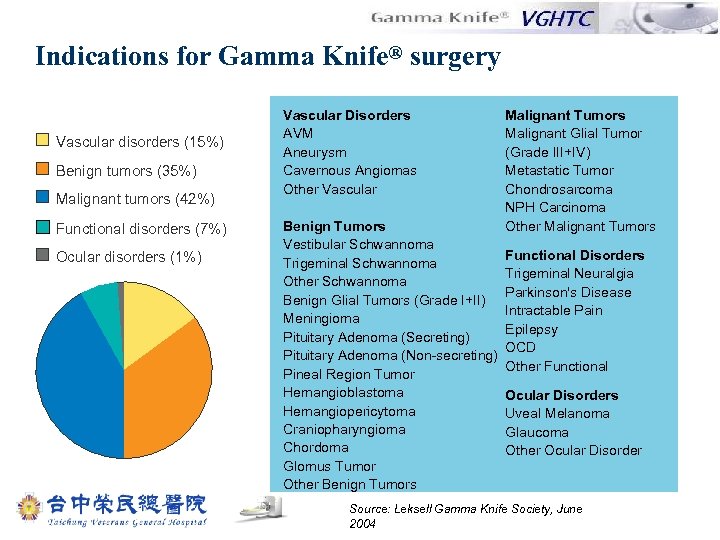
Indications for Gamma Knife® surgery Vascular disorders (15%) Benign tumors (35%) Malignant tumors (42%) Functional disorders (7%) Ocular disorders (1%) Vascular Disorders AVM Aneurysm Cavernous Angiomas Other Vascular Benign Tumors Vestibular Schwannoma Trigeminal Schwannoma Other Schwannoma Benign Glial Tumors (Grade I+II) Meningioma Pituitary Adenoma (Secreting) Pituitary Adenoma (Non-secreting) Pineal Region Tumor Hemangioblastoma Hemangiopericytoma Craniopharyngioma Chordoma Glomus Tumor Other Benign Tumors Malignant Glial Tumor (Grade III+IV) Metastatic Tumor Chondrosarcoma NPH Carcinoma Other Malignant Tumors Functional Disorders Trigeminal Neuralgia Parkinson's Disease Intractable Pain Epilepsy OCD Other Functional Ocular Disorders Uveal Melanoma Glaucoma Other Ocular Disorder Source: Leksell Gamma Knife Society, June 2004
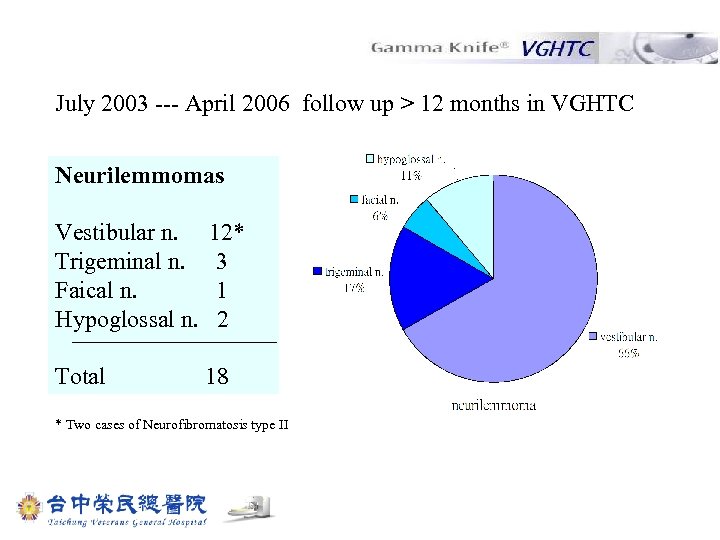
July 2003 --- April 2006 follow up > 12 months in VGHTC Neurilemmomas Vestibular n. Trigeminal n. Faical n. Hypoglossal n. 12* 3 1 2 Total 18 * Two cases of Neurofibromatosis type II
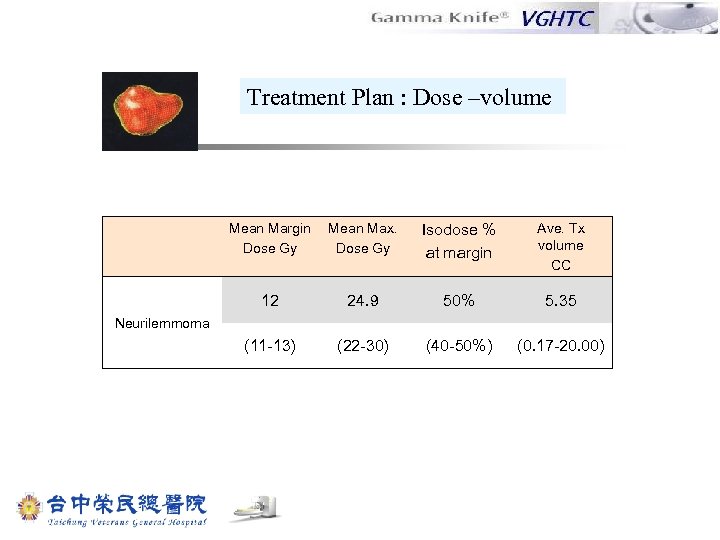
Treatment Plan : Dose –volume Mean Margin Dose Gy Mean Max. Dose Gy Isodose % at margin Ave. Tx volume CC 12 24. 9 50% 5. 35 (11 -13) (22 -30) (40 -50%) (0. 17 -20. 00) Neurilemmoma
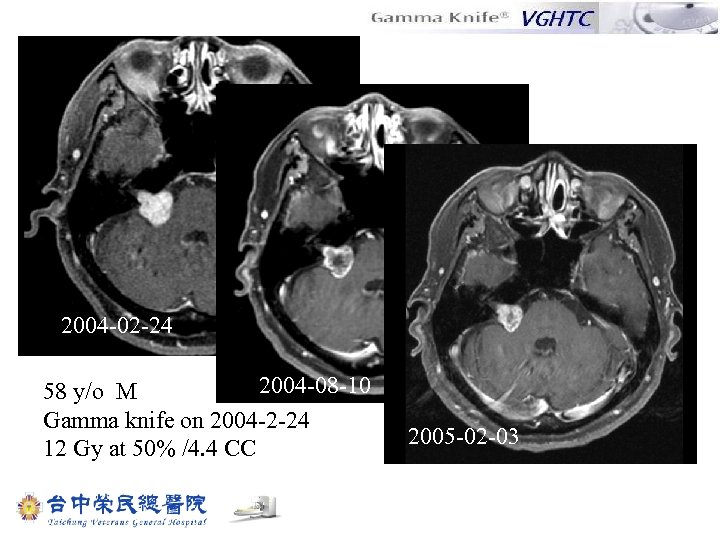
2004 -02 -24 2004 -08 -10 58 y/o M Gamma knife on 2004 -2 -24 12 Gy at 50% /4. 4 CC 2005 -02 -03

Radiographic follow-up Tumor volume Stable 4 Acoustic Neurilemmoma (12) decrease 6 Enlarge Failure 1 1* § 5 Control rate 91. 6% cases in hearing function (audiometry : 1 improvement, 1 worsening , 3 stable ) §Facial nerve function preservation : all *One large acoustic neuroma underwent surgical resection 6 months after GKS due to persistent dizziness and imbalance
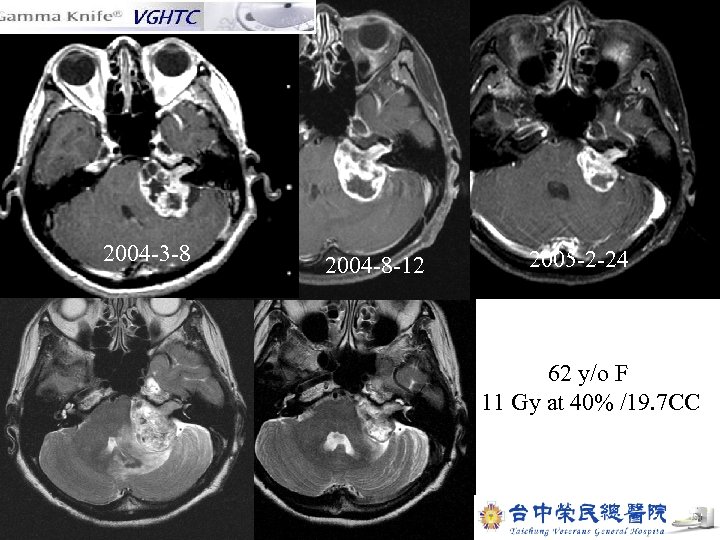
2004 -3 -8 2004 -8 -12 2005 -2 -24 62 y/o F 11 Gy at 40% /19. 7 CC
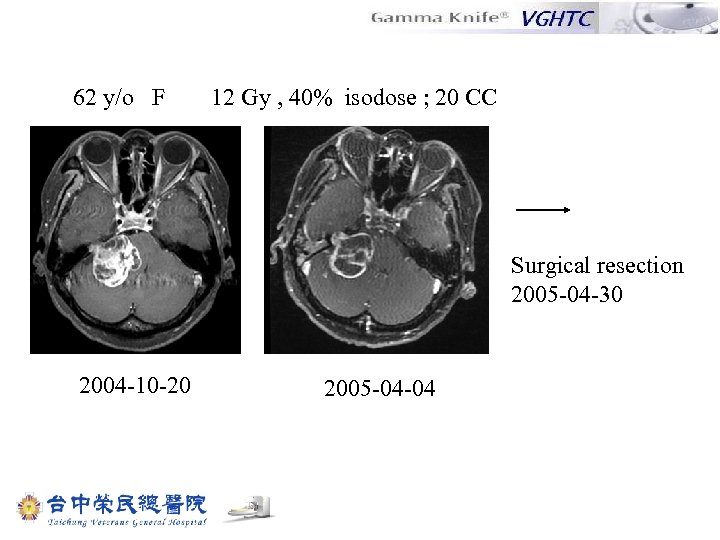
62 y/o F 12 Gy , 40% isodose ; 20 CC Surgical resection 2005 -04 -30 2004 -10 -20 2005 -04 -04

Microsurgery • Retrosigmoid ( Suboccipital ) Approach • Transslabyrinthine Approach • Middle Cranial Fossa Approach
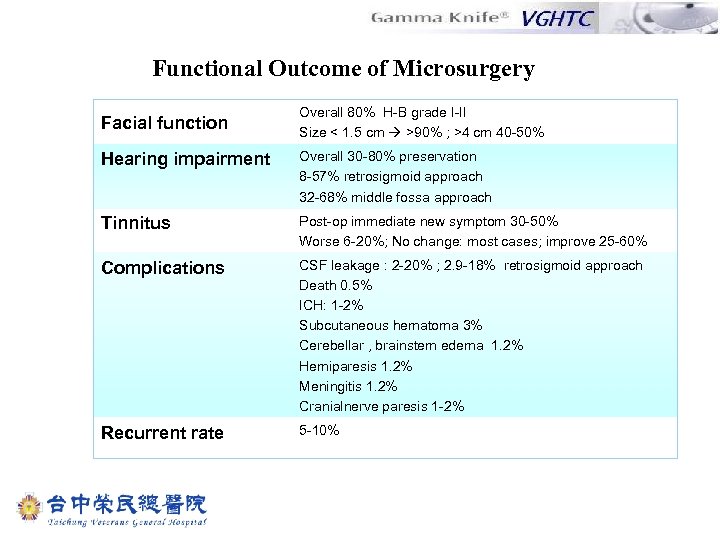
Functional Outcome of Microsurgery Facial function Overall 80% H-B grade I-II Size < 1. 5 cm >90% ; >4 cm 40 -50% Hearing impairment Overall 30 -80% preservation 8 -57% retrosigmoid approach 32 -68% middle fossa approach Tinnitus Post-op immediate new symptom 30 -50% Worse 6 -20%; No change: most cases; improve 25 -60% Complications CSF leakage : 2 -20% ; 2. 9 -18% retrosigmoid approach Death 0. 5% ICH: 1 -2% Subcutaneous hematoma 3% Cerebellar , brainstem edema 1. 2% Hemiparesis 1. 2% Meningitis 1. 2% Cranialnerve paresis 1 -2% Recurrent rate 5 -10%
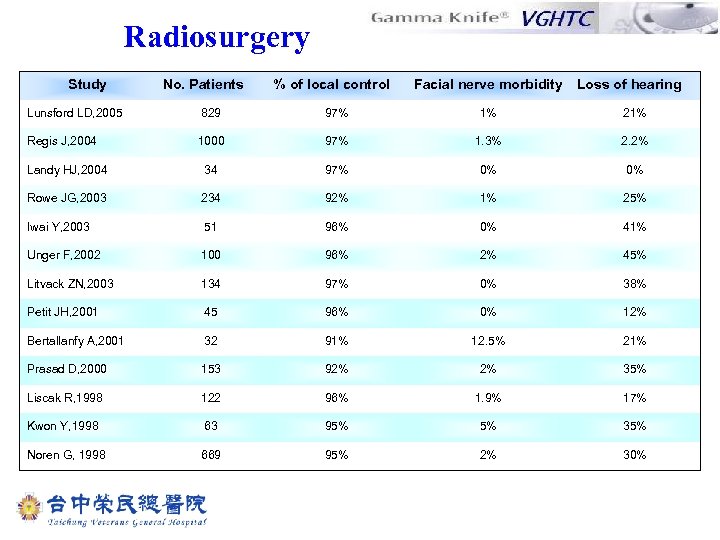
Radiosurgery Study No. Patients % of local control Facial nerve morbidity Loss of hearing Lunsford LD, 2005 829 97% 1% 21% Regis J, 2004 1000 97% 1. 3% 2. 2% Landy HJ, 2004 34 97% 0% 0% Rowe JG, 2003 234 92% 1% 25% Iwai Y, 2003 51 96% 0% 41% Unger F, 2002 100 96% 2% 45% Litvack ZN, 2003 134 97% 0% 38% Petit JH, 2001 45 96% 0% 12% Bertallanfy A, 2001 32 91% 12. 5% 21% Prasad D, 2000 153 92% 2% 35% Liscak R, 1998 122 96% 1. 9% 17% Kwon Y, 1998 63 95% 5% 35% Noren G, 1998 669 95% 2% 30%
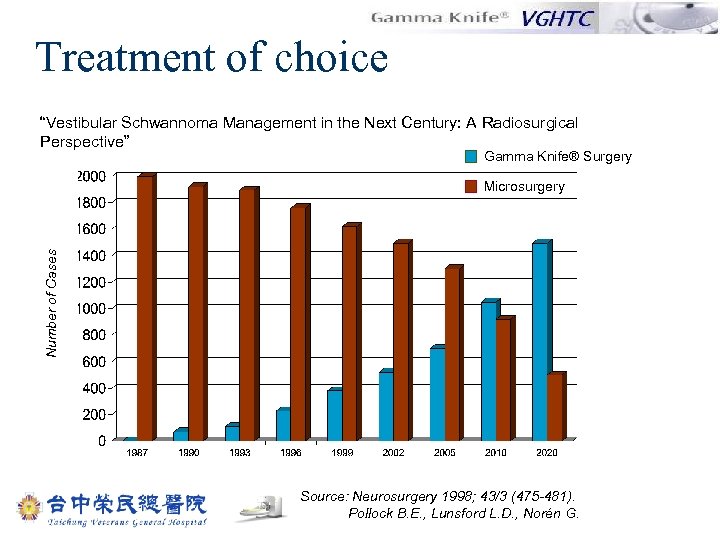
Treatment of choice “Vestibular Schwannoma Management in the Next Century: A Radiosurgical Perspective” Gamma Knife® Surgery Number of Cases Microsurgery Source: Neurosurgery 1998; 43/3 (475 -481). Pollock B. E. , Lunsford L. D. , Norén G.
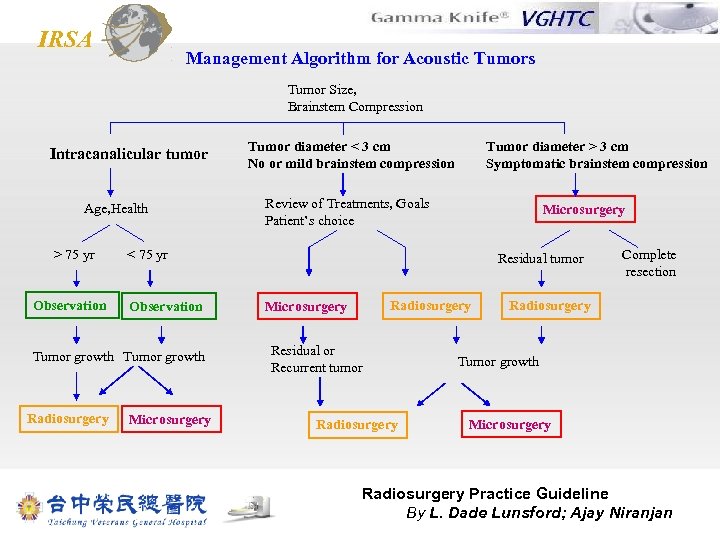
IRSA Management Algorithm for Acoustic Tumors Tumor Size, Brainstem Compression Intracanalicular tumor Age, Health > 75 yr Observation Tumor diameter > 3 cm Symptomatic brainstem compression Review of Treatments, Goals Patient’s choice Microsurgery < 75 yr Observation Tumor growth Radiosurgery Tumor diameter < 3 cm No or mild brainstem compression Microsurgery Residual tumor Radiosurgery Microsurgery Residual or Recurrent tumor Radiosurgery Complete resection Radiosurgery Tumor growth Microsurgery Radiosurgery Practice Guideline By L. Dade Lunsford; Ajay Niranjan
7243d146478951bad5f8d111c07219bb.ppt