5386f5d5f375a4d1a89617e2be846076.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50

Step-by-Step Guide on Risk Management For Metalworking Sector
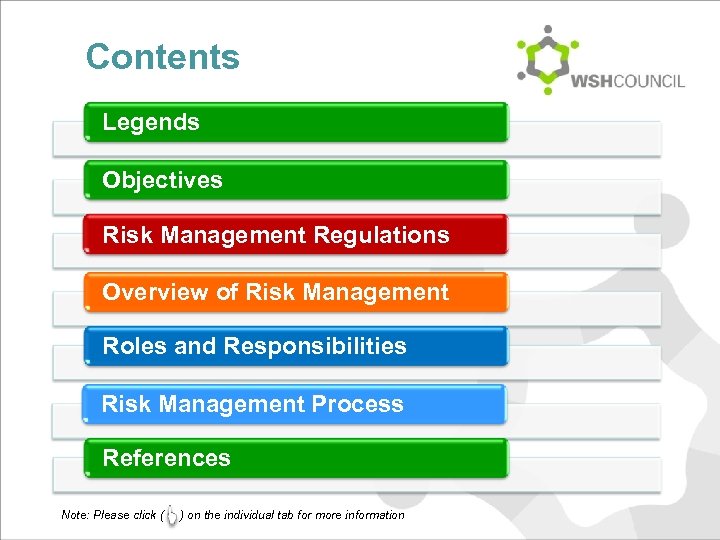
Contents Legends Objectives Risk Management Regulations Overview of Risk Management Roles and Responsibilities Risk Management Process References Note: Please click ( ) on the individual tab for more information
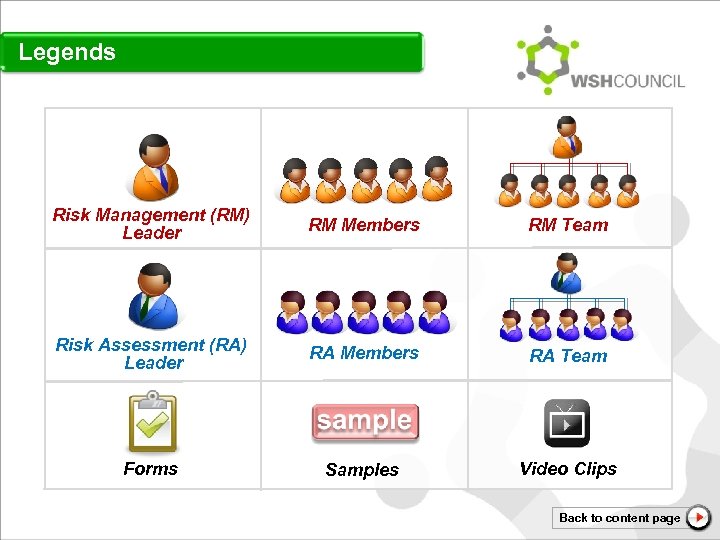
Legends Risk Management (RM) Leader RM Members RM Team Risk Assessment (RA) Leader RA Members RA Team Forms Samples Video Clips Back to content page

Objectives • This Guide aims to provide basic guidance in implementing risk management (RM) at workplaces. • Potential incidents can be prevented when hazards are identified and risks are managed. Back to content page

Risk Management Regulations • The WSH (Risk Management) Regulations is one of the key components of the Workplace Safety and Health (WSH) Act. • Under the Regulations, all workplaces are required to conduct risk assessments for routine and non-routine work. Back to content page

Overview of Risk Management involves • identifying and analysing safety and health hazards associated with work; • assessing the risks involved; • prioritising measures to control the hazards and reduce the risks; • controlling and monitoring the risks; and • communicating these risks to all affected persons. Back to content page

Roles and Responsibilities Employer Roles and Responsibilities of an Employer TASK DETAILS ! Risk Assessment (RA) § Ensure RA is conducted and available for all work activities § Require RA updates to be provided in regular meetings (eg: WSH Committee Meeting) § Ensure RA is reviewed / revised at least once every 3 years, or when there is - an incident, near miss or dangerous occurrence; - a significant change in work processes, facilities, work practices or work procedures, or change in workplace condition and layout; or - new information on WSH risks 7/50

Employer Roles and Responsibilities of an Employer TASK DETAILS ! Risk Control § Require all reasonably practicable steps to be taken to Measures (RCM) eliminate/minimize any foreseeable risk § Require RCM to be implemented according to the hierarchy of control § Support the implementation of RCM ! Risk Register § Require Risk Register to be updated and available at all time ! RA Records § Ensure RA records are kept for 3 years from the approval date ! Contractors / suppliers § Require contractors / suppliers to conduct RA and implement risk control measures for work carried out by them at the workplace 8/50

Manager Roles and Responsibilities of a Manager TASK DETAILS ! Risk Assessment (RA) § Ensure RA is carried out and available for all work activities § Approve RA and ensure risk level is not rated ‘high risk’ § Review / Revise RA at least once every 3 years from the approval date, or when there is - an incident, near miss or dangerous occurrence; - a significant change in the work processes, facilities, work practices or work procedures, or change in workplace condition and layout; or - new information on WSH risk 9/50

Manager Roles and Responsibilities of a Manager TASK DETAILS ! Risk Control Measures (RCM) § Prepare an action plan to implement RCM § Ensure RCM are carried out and monitor their effectiveness § Ensure safe work procedures (SWP) are available for all operations and implemented § Review RA if the RCM are inadequate and ineffective ! Risk Register § Ensure risk register is updated and available at all time 10/50

Manager Roles and Responsibilities of a Manager TASK DETAILS ! RA Records § Maintain and update RA records § Keep RA records for 3 years from the approval date ! Contractors / suppliers § Ensure contractors / suppliers conduct RA and implement risk control measures for work carried out by them within the workplace ! Communication § Ensure all persons exposed to the risks are informed of : - the nature of the risks - risk control measures - safe work procedures 11/50

Employee Roles and Responsibilities of an Employee TASK DETAILS ! Risk Assessment (RA) § Understand the hazards and possible injury / ill-health for carrying out activities assigned to him ! Risk Control Measures (RCM) § Comply with all risk control measures ! Communication § Inform Manager of : § Adhere to safe work procedures established at the workplace - new hazards / risks and ways to reduce hazards / risks, or - any shortcomings in the safe work procedures or risk control measures § Report any unsafe behaviour of other workers Back to content page
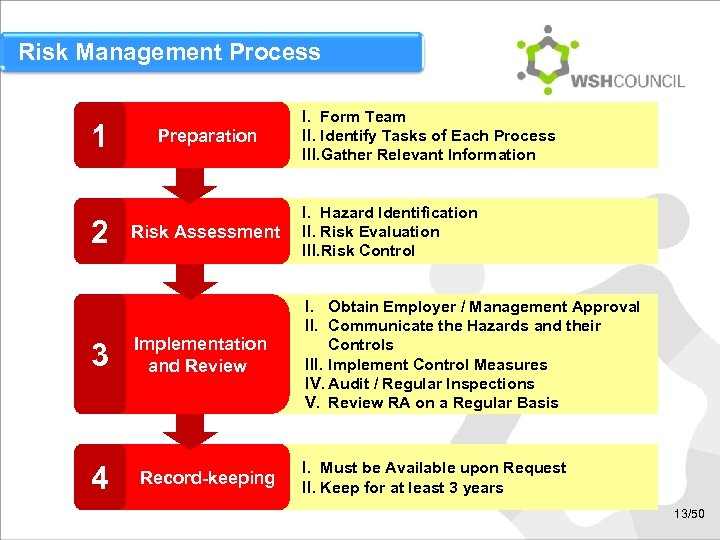
Risk Management Process 1 2 3 4 Preparation I. Form Team II. Identify Tasks of Each Process III. Gather Relevant Information Risk Assessment I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control Implementation and Review I. Obtain Employer / Management Approval II. Communicate the Hazards and their Controls III. Implement Control Measures IV. Audit / Regular Inspections V. Review RA on a Regular Basis Record-keeping I. Must be Available upon Request II. Keep for at least 3 years 13/50

1 Preparation I. Form Team II. Identify Tasks of Each Process III. Gather Relevant Information I. Form Team A. Appointment of RM Team A 1. Employer to: • Appoint a RM Leader • Appoint RM Members • Ensure RM Team is trained and competent in risk management • Engage RM Consultant to assist RM Team if further assistance is required 14/50
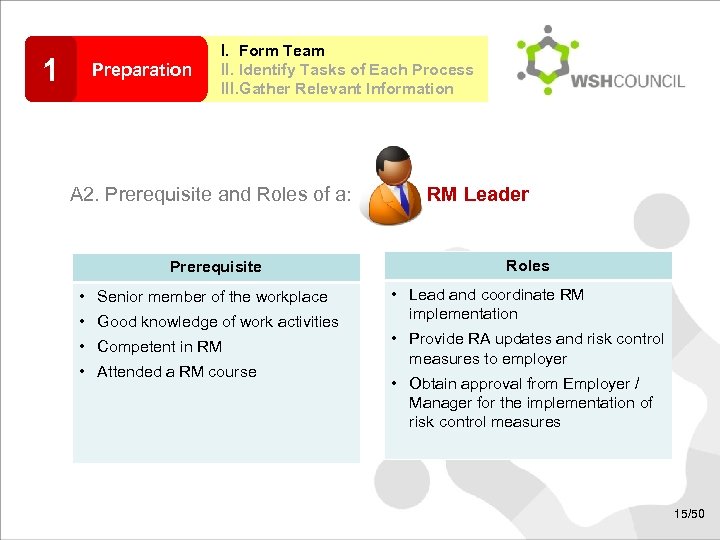
1 Preparation I. Form Team II. Identify Tasks of Each Process III. Gather Relevant Information A 2. Prerequisite and Roles of a: Prerequisite • Senior member of the workplace • Good knowledge of work activities • Competent in RM • Attended a RM course RM Leader Roles • Lead and coordinate RM implementation • Provide RA updates and risk control measures to employer • Obtain approval from Employer / Manager for the implementation of risk control measures 15/50
1 Preparation I. Form Team II. Identify Tasks of Each Process III. Gather Relevant Information A 3. Prerequisite and Composition of : RM Members Prerequisite • Good knowledge of work activities • Competent in RM • Attended a RM course Composition • Comprise staff/workers from different levels, discipline and work areas • E. g. : Management staff, area manager, engineers, RA Leaders, supervisors, production operators, etc 16/50
1 Preparation I. Form Team II. Identify Tasks of Each Process III. Gather Relevant Information A 4. Main Function of RM Team: RM Leader Function • Understand the workplace processes • Set RM objectives • Set RA boundaries, e. g. : by - department - function - work activity RM Members • Assign RA Teams to conduct RA for specific areas • Decide on hazards review period 17/50

1 Preparation I. Form Team II. Identify Tasks of Each Process III. Gather Relevant Information B. Appointment of RA Team B 1. RM Team to: • Appoint RA Leaders among the RM Members • Assist RA Leaders if further assistance is needed 18/50
1 Preparation I. Form Team II. Identify Tasks of Each Process III. Gather Relevant Information B 2. Prerequisite and Roles of a : Prerequisite • A member of RM Team RA Leader Roles • Form RA Team • Lead and co-ordinate RA implementation • Provide update to RM Team on RA implementation and risk control measures 19/50
1 Preparation I. Form Team II. Identify Tasks of Each Process III. Gather Relevant Information B 3. Prerequisite and Composition of : RA Members Prerequisite • Good knowledge of the work activities Composition • Comprise staff/workers involved in the work, as well as contractors, suppliers and other persons who are familiar with the work 20/50
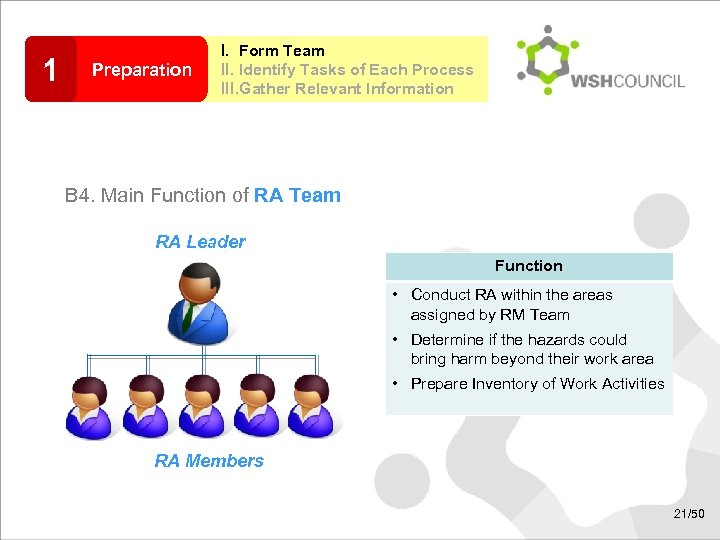
1 Preparation I. Form Team II. Identify Tasks of Each Process III. Gather Relevant Information B 4. Main Function of RA Team RA Leader Function • Conduct RA within the areas assigned by RM Team • Determine if the hazards could bring harm beyond their work area • Prepare Inventory of Work Activities RA Members 21/50
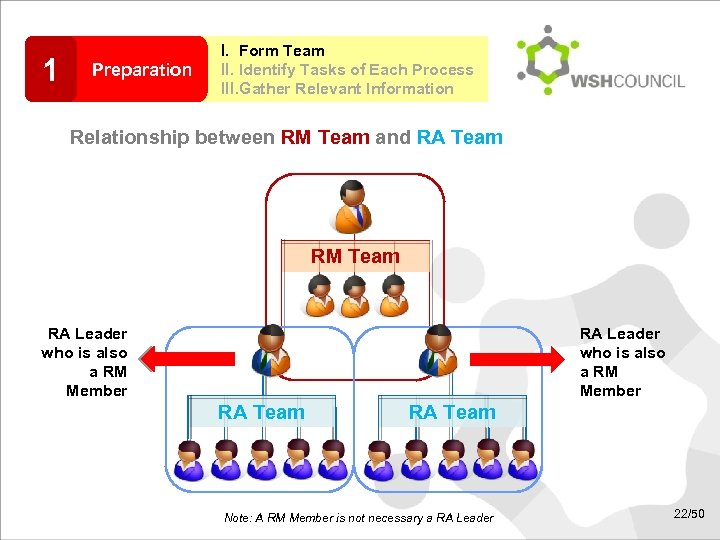
1 Preparation I. Form Team II. Identify Tasks of Each Process III. Gather Relevant Information Relationship between RM Team and RA Team RM Team RA Leader who is also a RM Member RA Team Note: A RM Member is not necessary a RA Leader 22/50
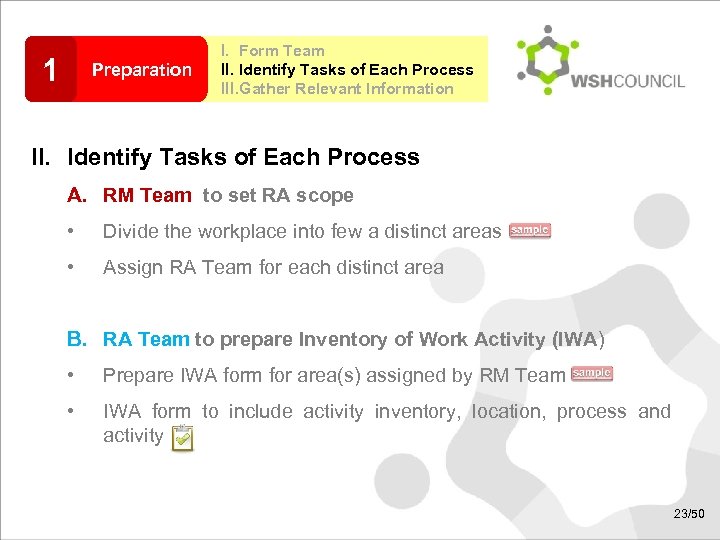
1 Preparation I. Form Team II. Identify Tasks of Each Process III. Gather Relevant Information II. Identify Tasks of Each Process A. RM Team to set RA scope • Divide the workplace into few a distinct areas • Assign RA Team for each distinct area B. RA Team to prepare Inventory of Work Activity (IWA) • Prepare IWA form for area(s) assigned by RM Team • IWA form to include activity inventory, location, process and activity 23/50

1 Preparation I. Form Team II. Identify Tasks of Each Process III. Gather Relevant Information A. RM Team to gather information related to RM scoping : • Workplace layout plan • Process or work flowchart • List of work activities in the process 24/50

1 Preparation I. Form Team II. Identify Tasks of Each Process III. Gather Relevant Information B. RA Teams to gather information on RA process : • • • List of tools, machinery and chemicals used Records of past incidents & accidents Observations, interviews and feedback on WSH related matters WSH inspection records and audit reports Manufacturer’s instruction manual including safety data sheets Relevant legislation, Codes of Practice and specifications Details of existing risk control measures Safe work procedures Copies of previous RA Medical records of workers Note: The above information ONLY serve as a guide 25/50

2 Risk Assessment I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control Risk Assessment is a process of : • Identifying and analysing safety and health hazards associated with work; • Assessing the risks involved; and • Prioritising measures to control the hazards and reduce the risks Risk Assessment must be available for all work activities 26/50
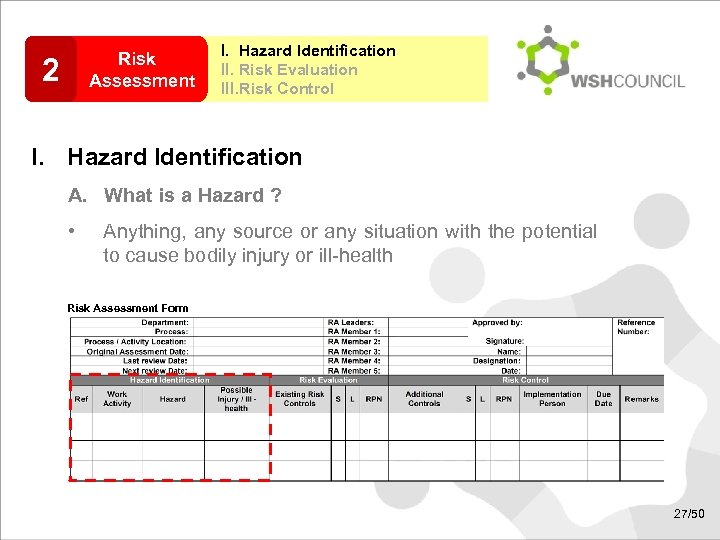
Risk Assessment 2 I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control I. Hazard Identification A. What is a Hazard ? • Anything, any source or any situation with the potential to cause bodily injury or ill-health Risk Assessment Form 27/50

Risk Assessment 2 I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control B. How to Identify Hazard? B 1. RA Leader to determine ways to identify hazards • brainstorming • process hazard analysis • process review • job safety analysis B 2. RA Team to determine sources of hazards • physical • chemical • mechanical • biological • electrical • others B 3. RA Team to consider if the hazards could cause harm beyond their immediate area of work 28/50
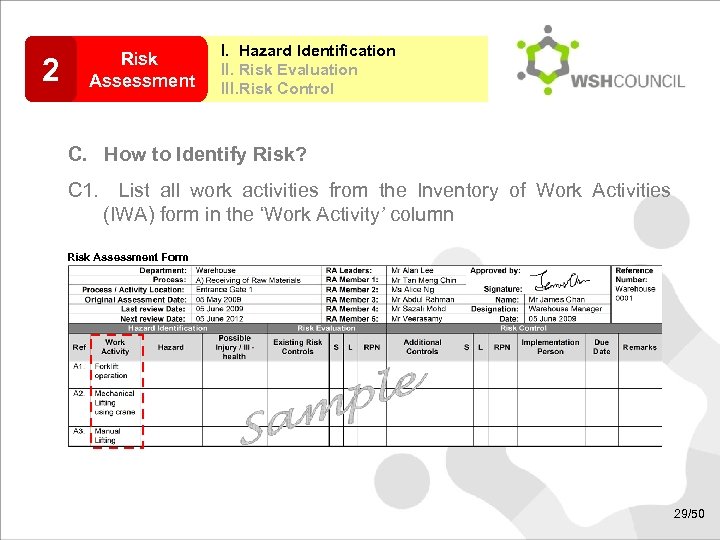
2 Risk Assessment I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control C. How to Identify Risk? C 1. List all work activities from the Inventory of Work Activities (IWA) form in the ‘Work Activity’ column Risk Assessment Form 29/50
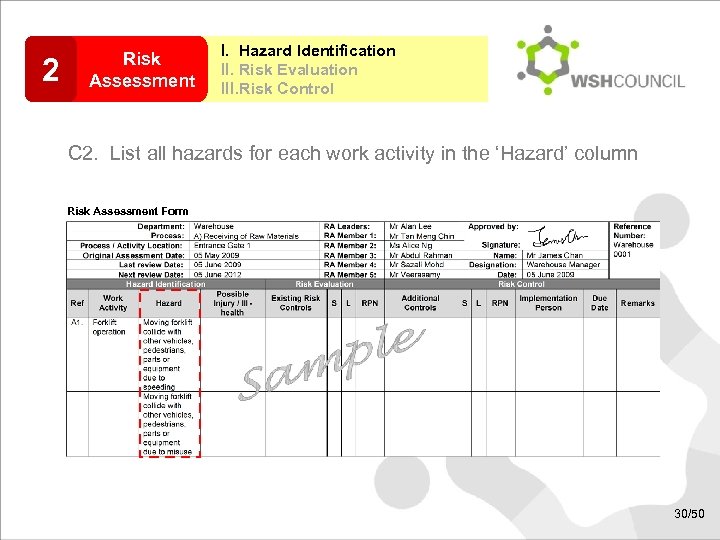
2 Risk Assessment I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control C 2. List all hazards for each work activity in the ‘Hazard’ column Risk Assessment Form 30/50
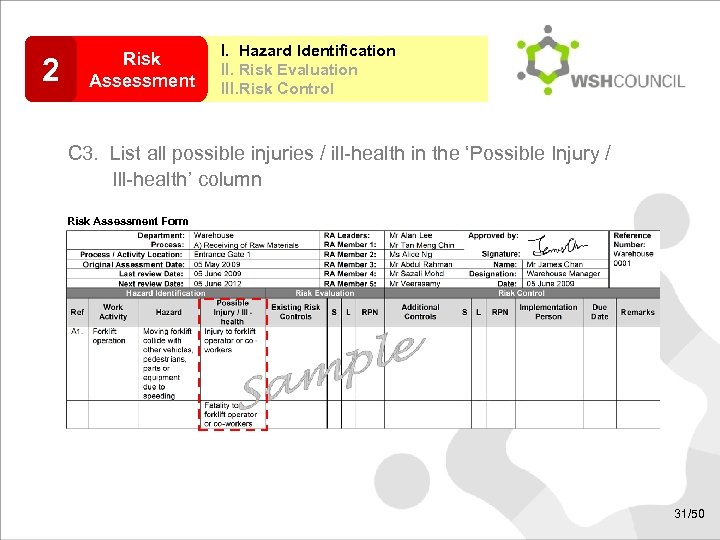
2 Risk Assessment I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control C 3. List all possible injuries / ill-health in the ‘Possible Injury / Ill-health’ column Risk Assessment Form 31/50
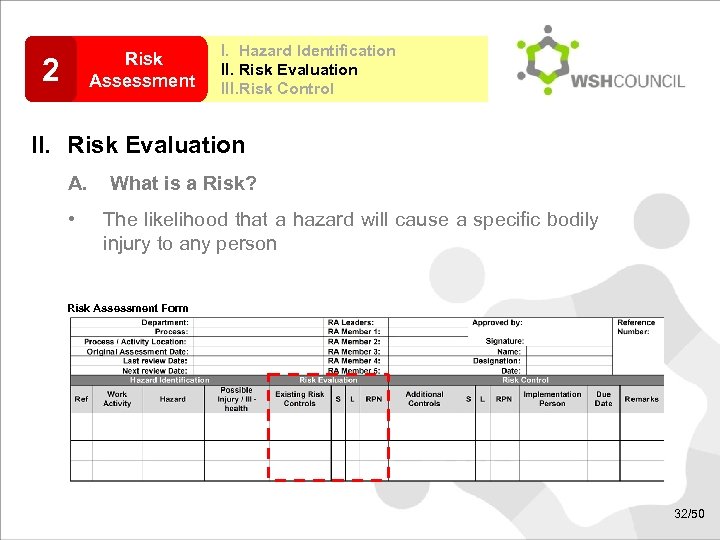
Risk Assessment 2 I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control II. Risk Evaluation A. • What is a Risk? The likelihood that a hazard will cause a specific bodily injury to any person Risk Assessment Form 32/50
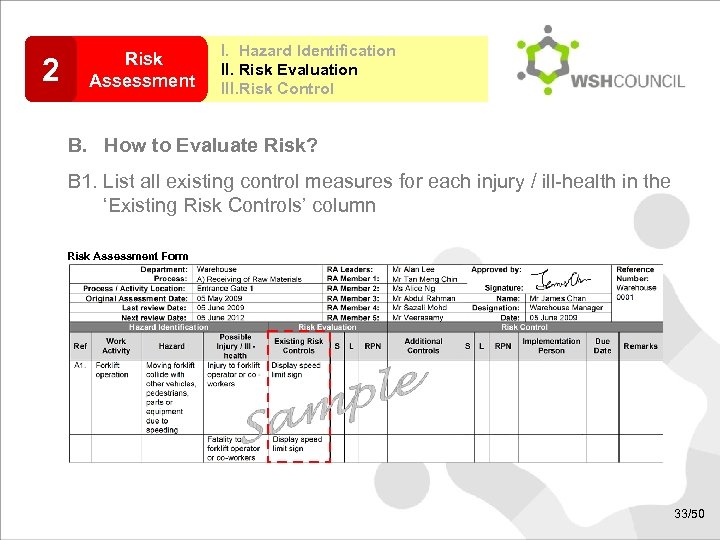
2 Risk Assessment I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control B. How to Evaluate Risk? B 1. List all existing control measures for each injury / ill-health in the ‘Existing Risk Controls’ column Risk Assessment Form 33/50
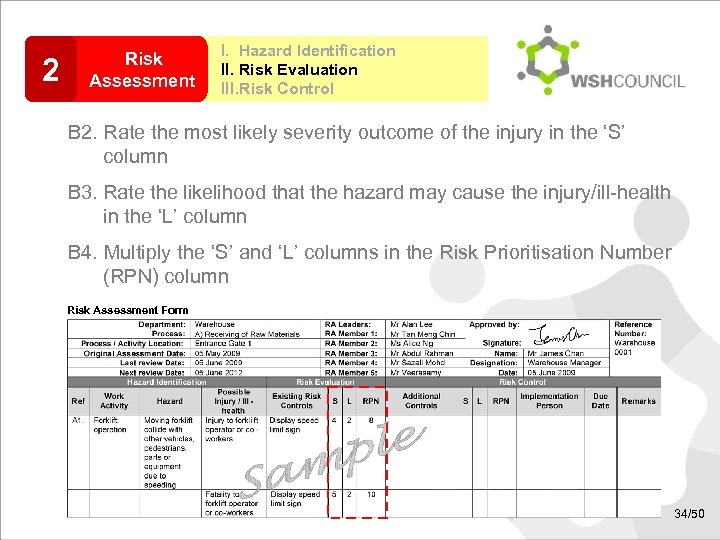
2 Risk Assessment I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control B 2. Rate the most likely severity outcome of the injury in the ‘S’ column B 3. Rate the likelihood that the hazard may cause the injury/ill-health in the ‘L’ column B 4. Multiply the ‘S’ and ‘L’ columns in the Risk Prioritisation Number (RPN) column Risk Assessment Form 34/50

2 Risk Assessment I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control B 5. Compare the ‘RPN’ against the Risk Matrix B 6. RA Team to take action according to the recommended actions based on the current risk level Risk Assessment Form 35/50

2 Risk Assessment I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control Risk Evaluation based on Code of Practice on Risk Management (1 of 2) Severity Scoring (‘S’ column) Likelihood Scoring (‘L’ column) Classification of Risk (Risk Matrix) (‘RPN’ column) 36/50

2 Risk Assessment I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control Risk Evaluation based on Code of Practice on Risk Management (2 of 2) Risk Matrix 37/50
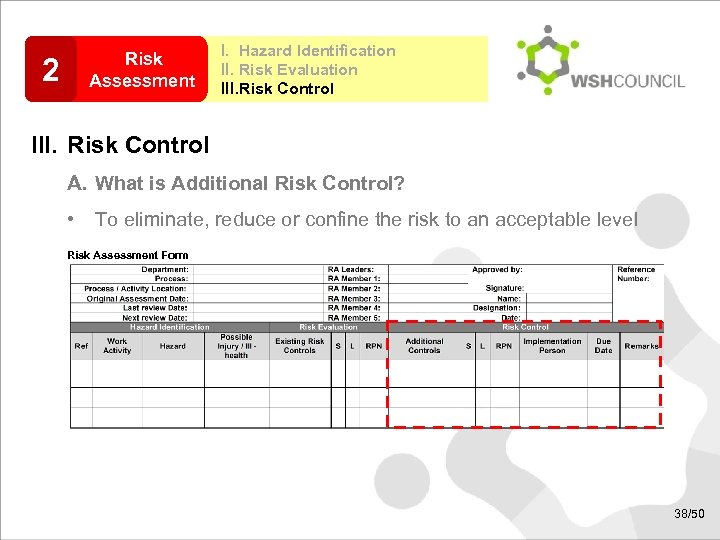
2 Risk Assessment I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control A. What is Additional Risk Control? • To eliminate, reduce or confine the risk to an acceptable level Risk Assessment Form 38/50
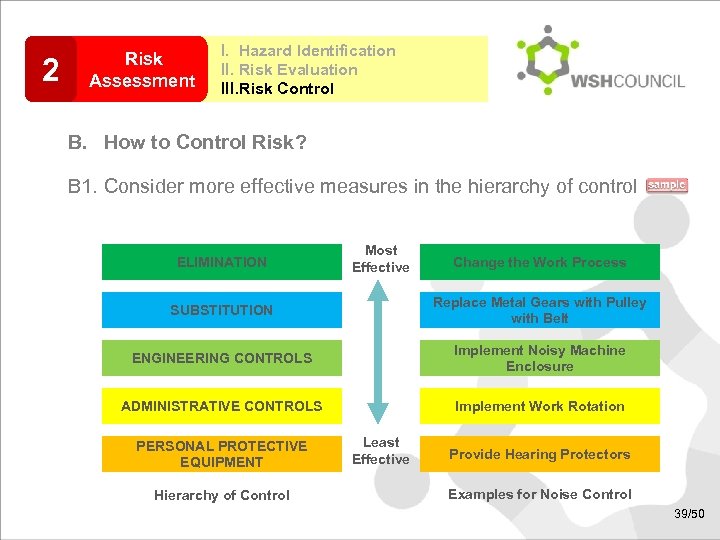
2 Risk Assessment I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control B. How to Control Risk? B 1. Consider more effective measures in the hierarchy of control ELIMINATION Most Effective Change the Work Process SUBSTITUTION Replace Metal Gears with Pulley with Belt ENGINEERING CONTROLS Implement Noisy Machine Enclosure ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROLS Implement Work Rotation PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT Hierarchy of Control Least Effective Provide Hearing Protectors Examples for Noise Control 39/50
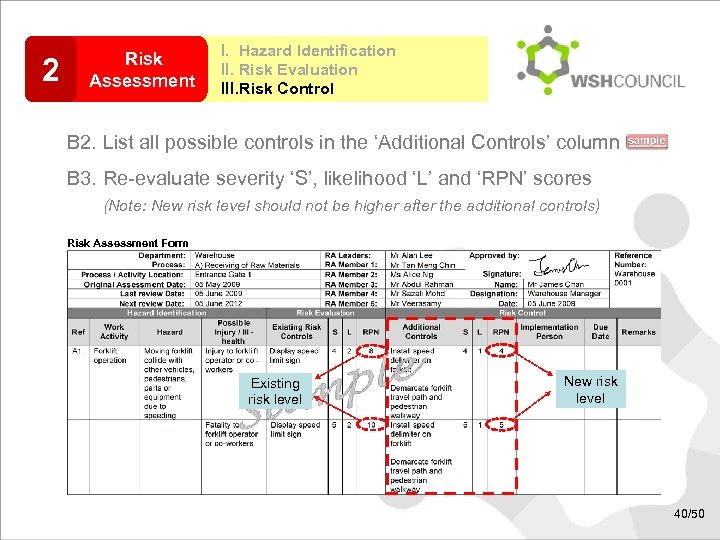
2 Risk Assessment I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control B 2. List all possible controls in the ‘Additional Controls’ column B 3. Re-evaluate severity ‘S’, likelihood ‘L’ and ‘RPN’ scores (Note: New risk level should not be higher after the additional controls) Risk Assessment Form Existing risk level New risk level 40/50
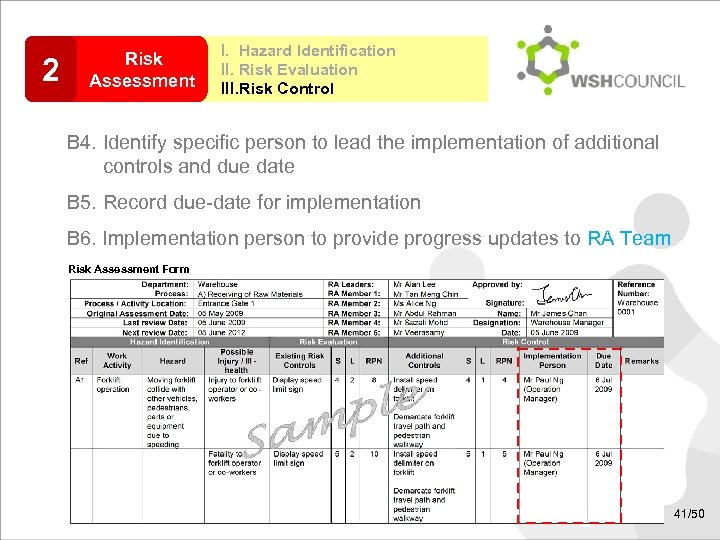
2 Risk Assessment I. Hazard Identification II. Risk Evaluation III. Risk Control B 4. Identify specific person to lead the implementation of additional controls and due date B 5. Record due-date for implementation B 6. Implementation person to provide progress updates to RA Team Risk Assessment Form 41/50

I. 3 I. Implementation and Review II. IV. V. Obtain Employer / Management Approval Communicate the Hazards and their Controls Implement Control Measures Audit / Regular Inspections Review RA on a Regular Basis Obtain Employer / Management Approval Manager to : • Approve RA form • Prepare an action plan to implement the measures • Implement the recommended risk control measures • Monitor the action plan 42/50

I. Implementation and Review 3 II. IV. V. Obtain Employer / Management Approval Communicate the Hazards and their Controls Implement Control Measures Audit / Regular Inspections Review RA on a Regular Basis II. Communicate the Hazards and their Controls Manager to Inform All Persons Exposed to the Risk about : • The nature of risks • Any measures / safe work procedures implemented • Means to minimise / eliminate the risks 43/50

I. Implementation and Review 3 II. IV. V. Obtain Employer / Management Approval Communicate the Hazards and their Controls Implement Control Measures Audit / Regular Inspections Review RA on a Regular Basis Examples of Communication Channel : • Toolbox meeting / briefing before the start of any work • Video tools ü Mechanical Lifting ü Machine Operation Maintenance ü Working in Noisy Environment 44/50

I. Implementation and Review 3 II. IV. V. Obtain Employer / Management Approval Communicate the Hazards and their Controls Implement Control Measures Audit / Regular Inspections Review RA on a Regular Basis III. Implement Control Measures Manager to : • Implement risk control measures • Ensure an action plan is available, monitored and implemented (including timeline and person in charge) • Ensure risk control measures are implemented and effective 45/50

I. Implementation and Review 3 II. IV. V. Obtain Employer / Management Approval Communicate the Hazards and their Controls Implement Control Measures Audit / Regular Inspections Review RA on a Regular Basis IV. Audit / Regular Inspections Manager to : • Ensure regular inspection and audits are carried out so that the risk control measures are implemented and effective 46/50

I. Implementation and Review 3 II. IV. V. Obtain Employer / Management Approval Communicate the Hazards and their Controls Implement Control Measures Audit / Regular Inspections Review RA on a Regular Basis V. Review RA on a Regular Basis Manager to : • Review / Revise RA at least once every 3 years, or ü after an incident, near miss or dangerous occurrence; ü a significant change in the work processes, facilities, work practices or work procedures, or change in workplace condition and layout (e. g. : introduction of new machinery, or chemicals or raw materials); or ü new information on WSH risk 47/50
Recordkeeping 4 I. Must be Available upon Request II. Keep for at least 3 years RA Records Must be Available upon Request Manager to : • Ensure RA records to be readily available upon request • RA records include: ü RA forms ü RA Register ü Risk control measures records ü Safe work procedures ü Training records 48/50
Recordkeeping 4 I. Must be Available upon Request II. Keep for at least 3 years II. Keep RA Records for at least 3 years Manager to : • Keep all RA records for at least 3 years Back to content page

References • Workplace Safety and Health Act • Workplace Safety and Health (Risk Management) Regulations • Code of Practice on Workplace Safety and Health (WSH) Risk Management • Workplace Safety and Health Council http: //www. wshc. sg • Ministry of Manpower http: //www. mom. gov. sg Back to content page
5386f5d5f375a4d1a89617e2be846076.ppt