10-step-6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Step-6 Select the Proper Interaction Devices
Step-6 Select the Proper Interaction Devices
 Why is it important? n n n Selecting the proper device-based control to do the required job is critical to system success. A good fit b/w user & control will lead to fast, accurate performance. A poor fit will result in lower productivity, produce more errors, & increase user fatigue.
Why is it important? n n n Selecting the proper device-based control to do the required job is critical to system success. A good fit b/w user & control will lead to fast, accurate performance. A poor fit will result in lower productivity, produce more errors, & increase user fatigue.
 Characteristics of Input Devices n Direct & Indirect pointing devices - Light pen, the finger, voice Mouse, trackball, keyboard n Discreet & Continuous - - letters, numbers, commands Dragging, drawing n Direction, Distance, & Speed - Mouse vs. Trackball -
Characteristics of Input Devices n Direct & Indirect pointing devices - Light pen, the finger, voice Mouse, trackball, keyboard n Discreet & Continuous - - letters, numbers, commands Dragging, drawing n Direction, Distance, & Speed - Mouse vs. Trackball -
 Characteristics of Input Devices (cont. ) n n n n Trackball Joystick Graphic tablet or Trackpad Touch Screen Light Pen Voice Mouse Keyboard
Characteristics of Input Devices (cont. ) n n n n Trackball Joystick Graphic tablet or Trackpad Touch Screen Light Pen Voice Mouse Keyboard
 Design Guidelines n Touch Screen - Screen objects >= 1. 9 x 1. 9 cm Object separation >= 0. 3 cm Visual, auditory feedback Instructional invitation n Mouse - - “hot zone” for small items Double-clicks as only means
Design Guidelines n Touch Screen - Screen objects >= 1. 9 x 1. 9 cm Object separation >= 0. 3 cm Visual, auditory feedback Instructional invitation n Mouse - - “hot zone” for small items Double-clicks as only means
 Design Guidelines (cont. ) n - Keyboard ? Standard typewriter keyboard 1870 Sholes QWERTY layout
Design Guidelines (cont. ) n - Keyboard ? Standard typewriter keyboard 1870 Sholes QWERTY layout
 Design Guidelines (cont. ) n Provide keyboard accelerators (p. 337) - Single keys Standard platform Shift + key Ctrl + key n Provide keyboard equivalents - - n Standard platform First letter Provide window navigation through use of keyboard keys
Design Guidelines (cont. ) n Provide keyboard accelerators (p. 337) - Single keys Standard platform Shift + key Ctrl + key n Provide keyboard equivalents - - n Standard platform First letter Provide window navigation through use of keyboard keys
 MAXIM n The greater the effort to accomplish a task, the less likely that the task will be accomplished successfully.
MAXIM n The greater the effort to accomplish a task, the less likely that the task will be accomplished successfully.
 Other Input Devices n n n Gesture Facial expression Eye tracking Iris & fingerprint recognition Handwriting
Other Input Devices n n n Gesture Facial expression Eye tracking Iris & fingerprint recognition Handwriting
 Selecting the Proper Input Device n - - Keyboard vs. Mouse Time to move one’s hand from the keyboard, grasp the mouse, & point at a screen object ~ 1. 5 – 2 sec Skilled typist can type 13 -15 chars Average typist: 4 -6 chars
Selecting the Proper Input Device n - - Keyboard vs. Mouse Time to move one’s hand from the keyboard, grasp the mouse, & point at a screen object ~ 1. 5 – 2 sec Skilled typist can type 13 -15 chars Average typist: 4 -6 chars
 Selecting the Proper Input Device (cont. ) Control Research (p. 436) n n Direct pointing devices fastest for pointing at stationary targets Mouse, trackball, graphic tablet – same in positioning speed & accuracy. Joystick – slowest. Tracking small, slowly moving targets? Pointing & dragging: mouse, graphic tablet, trackball?
Selecting the Proper Input Device (cont. ) Control Research (p. 436) n n Direct pointing devices fastest for pointing at stationary targets Mouse, trackball, graphic tablet – same in positioning speed & accuracy. Joystick – slowest. Tracking small, slowly moving targets? Pointing & dragging: mouse, graphic tablet, trackball?
 Guidelines for Selecting the Proper Input Device n - Consider the characteristics of the task Provide keyboard for tasks involving - heavy text entry & manipulation - movement through structured arrays - Provide an alternative pointing device for graphical or drawing tasks.
Guidelines for Selecting the Proper Input Device n - Consider the characteristics of the task Provide keyboard for tasks involving - heavy text entry & manipulation - movement through structured arrays - Provide an alternative pointing device for graphical or drawing tasks.
 Guidelines for Selecting the Proper Input Device (cont. ) n - Some suggested best uses (pt – pointing, se – selecting, dw – drawing, dg – dragging, tr - tracking): Mouse – pt, se, dw, dg Joystick – se, tr Trackball – pt, se, tr Touch screen – pt, se Graphic tablet – pt, se, dw, dg.
Guidelines for Selecting the Proper Input Device (cont. ) n - Some suggested best uses (pt – pointing, se – selecting, dw – drawing, dg – dragging, tr - tracking): Mouse – pt, se, dw, dg Joystick – se, tr Trackball – pt, se, tr Touch screen – pt, se Graphic tablet – pt, se, dw, dg.
 Guidelines for Selecting the Proper Input Device (cont. ) n - Provide touch screens under the following conditions: The opportunity for training is minimal Targets are large, discreet, & spread out Frequency of use is low Desk space is at a premium Little or no text input requirement exists
Guidelines for Selecting the Proper Input Device (cont. ) n - Provide touch screens under the following conditions: The opportunity for training is minimal Targets are large, discreet, & spread out Frequency of use is low Desk space is at a premium Little or no text input requirement exists
 Guidelines for Selecting the Proper Input Device (cont. ) Consider the characteristics of the: n Users & their preferences - n n n Provide keyboards for touch typists Environment Hardware Device in relation to the application Provide flexibility Minimize eye & hand movements bw devices
Guidelines for Selecting the Proper Input Device (cont. ) Consider the characteristics of the: n Users & their preferences - n n n Provide keyboards for touch typists Environment Hardware Device in relation to the application Provide flexibility Minimize eye & hand movements bw devices
 Window pointer
Window pointer
 Pointer Guidelines n - - The pointer Should be visible at all times Should contrast well with its background Should maintain its size across all screen locations & during movement The hotspot should be easy to locate & see Location should not warp (change position)
Pointer Guidelines n - - The pointer Should be visible at all times Should contrast well with its background Should maintain its size across all screen locations & during movement The hotspot should be easy to locate & see Location should not warp (change position)
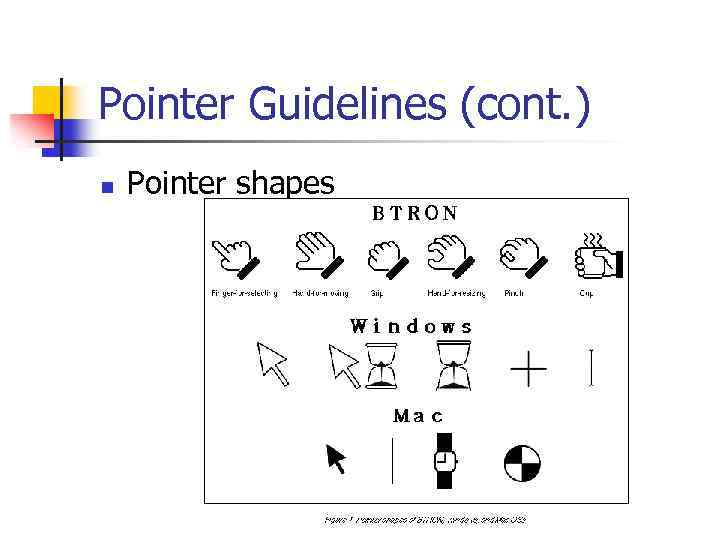 Pointer Guidelines (cont. ) n Pointer shapes
Pointer Guidelines (cont. ) n Pointer shapes
 Pointer Guidelines (cont. ) n - - The shape of a pointer Should clearly indicate its purpose & meaning Should be constructed of already defined shapes Should not be used for any purpose other than its already defined meaning Do not create new shapes for already defined standard functions
Pointer Guidelines (cont. ) n - - The shape of a pointer Should clearly indicate its purpose & meaning Should be constructed of already defined shapes Should not be used for any purpose other than its already defined meaning Do not create new shapes for already defined standard functions
 Output Devices Screens - image, colors, size, portability, usage n Speakers n
Output Devices Screens - image, colors, size, portability, usage n Speakers n


