 Step-12 Choose the Proper Colors
Step-12 Choose the Proper Colors
 Color Uses n n n Relating or tying elements into groupings Breaking apart separate groupings of information Highlighting or calling attention to important information Identifying the logical structure of ideas, processes, or sequences Identifying status of information Increasing screen appeal
Color Uses n n n Relating or tying elements into groupings Breaking apart separate groupings of information Highlighting or calling attention to important information Identifying the logical structure of ideas, processes, or sequences Identifying status of information Increasing screen appeal
 Possible Problems with Color n n n High attention-getting capacity Interference with use of other screens Varying sensitivity of the eye to different colors Color-viewing deficiencies Color connotations Cross-disciplinary & cross cultural differences
Possible Problems with Color n n n High attention-getting capacity Interference with use of other screens Varying sensitivity of the eye to different colors Color-viewing deficiencies Color connotations Cross-disciplinary & cross cultural differences
 MAXIM n Poor use of color is worse than not using it at all. MYTH n If we can’t do it right, do it big. If we can’t do it big, do it in color.
MAXIM n Poor use of color is worse than not using it at all. MYTH n If we can’t do it right, do it big. If we can’t do it big, do it in color.
 Usage n n - Design for monochrome first Use colors conservatively. Do not use color where other identification techniques, such as location, are available (Ex: menu bar) More colors increase Response times Chance of errors due to color confusion The chance of the Christmas tree effect
Usage n n - Design for monochrome first Use colors conservatively. Do not use color where other identification techniques, such as location, are available (Ex: menu bar) More colors increase Response times Chance of errors due to color confusion The chance of the Christmas tree effect
 MAXIM n Content is always more important than color.
MAXIM n Content is always more important than color.
 Step-13 Organize and Layout Windows and Pages
Step-13 Organize and Layout Windows and Pages
 General Guidelines n n n Present the proper amount of information Divide information into logical units Organize by the degree of interrelationship Provide an ordering that is logical & sequential, & eases visual/motor work Place controls properly Aesthetics
General Guidelines n n n Present the proper amount of information Divide information into logical units Organize by the degree of interrelationship Provide an ordering that is logical & sequential, & eases visual/motor work Place controls properly Aesthetics
 Creating Groupings n See p. 730
Creating Groupings n See p. 730
 MAXIM n Designers work hard so users don’t have to. MYTH n This way of doing it must be right because (fill in the blank) does it that way.
MAXIM n Designers work hard so users don’t have to. MYTH n This way of doing it must be right because (fill in the blank) does it that way.
 Web Page Guidelines n n Page layout (p. 750) Navigation elements Homepage Page elements
Web Page Guidelines n n Page layout (p. 750) Navigation elements Homepage Page elements
 Screen Examples n See p. 761
Screen Examples n See p. 761
 Step-14 Test, and Retest
Step-14 Test, and Retest
 Usability n n n Effective Efficient Engaging Error tolerant Easy to learn
Usability n n n Effective Efficient Engaging Error tolerant Easy to learn
 The Importance of Usability Testing n n n n Developers & users possess different models Developer’s intuitions are not always correct There is no average user & developer It’s impossible to predict usability from appearance Design standards & guidelines are not sufficient Informal feedback is inadequate Problems found late are more difficult & expensive to fix Advantages over a competitive product can be achieved
The Importance of Usability Testing n n n n Developers & users possess different models Developer’s intuitions are not always correct There is no average user & developer It’s impossible to predict usability from appearance Design standards & guidelines are not sufficient Informal feedback is inadequate Problems found late are more difficult & expensive to fix Advantages over a competitive product can be achieved
 MAXIM n Test early, test often. MYTH n The design is finished.
MAXIM n Test early, test often. MYTH n The design is finished.
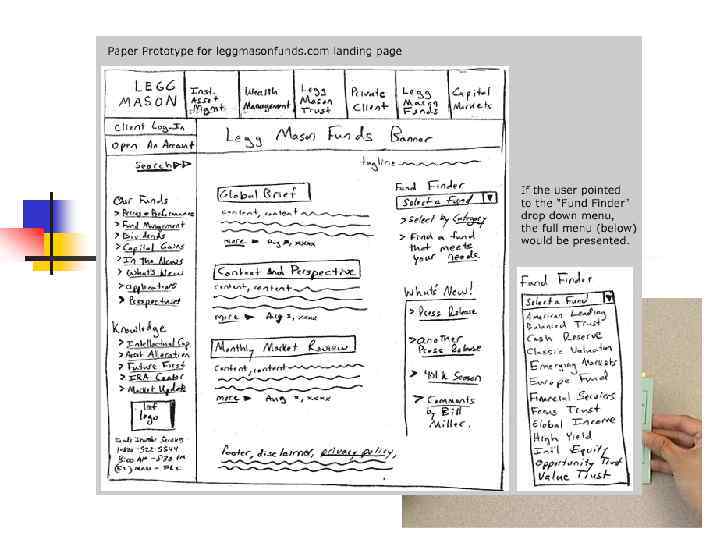 Prototypes n n n Hand sketches & scenarios Interactive paper prototypes (video) Programmed facades
Prototypes n n n Hand sketches & scenarios Interactive paper prototypes (video) Programmed facades
 Testing Elements & Tools n See p. 778
Testing Elements & Tools n See p. 778
 The LAST maxim! n Not even the most brilliantly conceived & ingenious computer system can do all that it was designed to do – or even a small part of what it was designed to do – unless the brilliance of its operation & purpose is matched by the cunning simplicity of its user interface (Hicks & Essinger, 1991)
The LAST maxim! n Not even the most brilliantly conceived & ingenious computer system can do all that it was designed to do – or even a small part of what it was designed to do – unless the brilliance of its operation & purpose is matched by the cunning simplicity of its user interface (Hicks & Essinger, 1991)